Инфаркт миокарда (ИМ), несмотря на значительные достижения в диагностике и лечении, остается одной из ведущих причин инвалидизации и смертности населения экономически развитых стран. Согласно данным Росстата, в 2016 г. в России было зарегистрировано 159 тыс. случаев ИМ, а число умерших от него составило 62,9 тыс. человек [1]. Раннее выявление и своевременное начало лечения ИМ позволяет снизить частоту осложнений и уровень летальности. Диагностика ИМ затруднена в случаях атипичного течения заболевания, отсутствии четких, однозначно интерпретируемых изменений ЭКГ или наличии факторов, затрудняющих выявление признаков ишемии и некроза миокарда (блокада левой ножки пучка Гиса (ЛНПГ), искусственные водители ритма, хроническая аневризма ЛЖ, рубцовые изменения).
Ключевым методом верификации диагноза ИМ в настоящее время является ферментодиагностика, при этом наиболее распространенными и общепризнанными маркерами некроза миокарда считаются сердечные тропонины (сТн), а в случае их недоступности – МВ-фракция креатинфосфокиназы (МВ-КФК) [2]. Несмотря на высокую кардиоспецифичность, данные маркеры вследствие медленного высвобождения недостаточно информативны в первые часы заболевания, в то время как более ранний маркер повреждения миокарда – миоглобин обладает низкой специфичностью. Появление и внедрение в практику высокочувствительных методов определения тропонинов (вчТн) позволило повысить выявляемость ИМ, особенно без стойкого подъема сегмента ST ЭКГ (ИМбпST), в ранние сроки, но оказалось сопряжено со снижением специфичности. Следует отметить, что тесты на вчТн содержат различные комплексы моноклональных антител, связывающихся с разными эпитопами, поэтому имеют различную чувствительность и специфичность, разные значения 99-й процентили, диагностические уровни, а также алгоритмы измерения и интерпретации результатов. Таким образом, сравнение абсолютных концентраций вчТн, полученных с помощью тестов различных производителей, не представляется возможным. Необходимость серийного определения вчТн и отсутствие так называемых прикроватных экспресс-тестов их оценки усложняет выполнение методики и в ряде случаев может приводить к задержке в выборе тактики ведения больного.
В последние годы был предложен целый ряд новых маркеров некроза миокарда, таких как легкие цепи миозина I (MLC-1), Ca2+-АТФаза саркоплазматического ретикулума (СР), дезоксирибонуклеаза I типа (DNAse1), гликогенфосфорилаза (GP-BB), карбоангидаза III типа, ишемически модифицированный альбумин (ИМА), сердечный белок, связывающий миозин типа С (cMyC). Среди них особое внимание привлекает сердечная форма белка, связывающего жирные кислоты (сБСЖК), который является цитозольным белком кардиомиоцитов и отвечает за транспорт жирных кислот и других липофильных соединений внутри клетки. Небольшая масса (15 кДа) и высокое содержание в цитоплазме приводят к быстрому высвобождению сБСЖК в кровоток при повреждении миокарда. сБСЖК имеет при ИМ сходную с миоглобином кинетику, повышаясь в крови до диагностических значений уже через 1–2 ч после начала клинических проявлений, максимальные концентрации маркера определяются через 6 ч после повреждения миокарда, а возвращение к нормальным значениям происходит спустя приблизительно 24 ч [3]. Особенности высвобождения и кинетики позволяют рассматривать сБСЖК в качестве раннего маркера повреждения миокарда, а также использовать его для диагностики рецидивирующих нарушений коронарного кровотока. Среди состояний, при которых описано повышение уровня сБСЖК в отсутствии патологии сердца, необходимо отметить тяжелую почечную или печеночно-клеточную недостаточность, острые нарушения мозгового кровообращения, массивные ожоги, ранения и травмы, тяжелую анемию и выраженную гипертриглицеридемию.
В 2007 г. специалисты Национальной академии клинической биохимии США включили сБСЖК в перечень рекомендованных биомаркеров некроза миокарда, а в 2011 г. эксперты Европейского общества кардиологов в рекомендациях по ведению пациентов с ОКС без подъема сегмента ST указали, что определение сБСЖК может улучшить диагностику в ранние сроки заболевания [4]. Однако вплоть до настоящего времени в среде экспертов нет единого мнения в отношении целесообразности применения теста на сБСЖК.
Исследования диагностической эффективности сБСЖК у больных ОКС отличаются большой разнородностью по срокам от начала заболевания, контингенту выбранных больных, сравниваемым биомаркерам, методам определения уровня сБСЖК и изучаемым характеристикам. Имеющиеся работы можно разделить на те, в которых изучались возможности самостоятельного определения сБСЖК для диагностики различных форм ОКС, и те, в которых оценивались возможности определения сБСЖК совместно с другими маркерами повреждения и некроза миокарда (мультимаркерный подход).
ЭФФЕКТИВНОСТЬ сБСЖК В ДИАГНОСТИКЕ ОКС ПО СРАВНЕНИЮ С ДРУГИМИ БИОМАРКЕРАМИ
Уже первые работы, посвященные изучению диагностических характеристик сБСЖК у больных ОКС, появившиеся в самом конце ХХ столетия, показали его основные достоинства и очевидные преимущества перед использовавшимися в то время маркерами некроза миокарда. Так, Ishii и соавт. (1997) выявили преимущества сБСЖК в чувствительности, специфичности, диагностической точности и эффективности перед миоглобином в первые 6 ч с момента появления болей в грудной клетке, а Okamoto и соавт. (2000) показали большую чувствительность определения сБСЖК (92,9%) по сравнению с миоглобином (88,6%) и МВ-КФК (18,6%) во все промежутки времени до 12 ч от момента возникновения симптоматики. Специфичность сБСЖК (67%) превосходила таковую для миоглобина (57,1%), но уступала МВ-КФК (98%), что не повлияло на преимущество в диагностической эффективности биомаркера, определяемой по площади AUC, которая составила 0,921 для сБСЖК, 0,843 для миоглобина и 0,654 для МВ-КФК соответственно [5, 6].
Chan и соавт. (2004) было показано, что сБСЖК обладает наилучшими диагностическими характеристиками по сравнению с сТн I и КФК в первые 8 ч ОКС у больных с предполагаемым ИМ. Площадь AUC для сБСЖК была достоверно больше, чем у сТн I и КФК, как при поступлении, так и спустя 1 ч. Чувствительность и отрицательная прогностическая значимость (ОПЗ) теста на сБСЖК уже через 1 ч после поступления повышались до 100%, а остальные маркеры достигали таких же показателей только спустя 7 ч, что позволило сделать вывод о том, что сБСЖК является наиболее ранним маркером ИМ [7]. Аналогичный результат был получен McCann с соавт. (2008), показавшими, что определение сБСЖК превосходит сTн T в выявлении ИМ в первые 4 ч заболевания (73 против 55%; p=0,043). Специфичность сБСЖК составляла 71%. Было также отмечено, что совместное определение обоих маркеров увеличивает чувствительность до 85% [8].
Серия последующих работ подтвердила данные о большей диагностической эффективности определения сБСЖК у больных с подозрением на ОКС по сравнению с миоглобином, MB-КФК, сТн I и рядом других биомаркеров, особенно в первые 6 ч с момента возникновения болевого синдрома [9–13]. Даже, несмотря на то что сБСЖК уступал в специфичности сердечным тропонинам и МВ-КФК благодаря значительно более высокой чувствительности, именно сБСЖК стал рассматриваться некоторыми авторами в качестве предпочтительного раннего маркера верификации диагноза [14].
Особую диагностическую сложность среди пациентов с ОКС представляют случаи ИМбпST. Ряд исследователей изучали эффективность определения сБСЖК селективно в этой группе больных, однако полученные результаты оказались противоречивыми. По данным Charpentier и соавт. (2011), определение сБСЖК как количественным, так и качественным методом было недостаточно эффективным в диагностике ОКСбпST в сроки до 12 ч из-за низкой специфичности, в то время как Chandran и соавт. (2014) выявили, что количественное определение сБСЖК превосходит по диагностической значимости определение сТн I и T у больных ИМбпST в первые 6–8 ч с момента возникновения клинических проявлений [15, 16].
С появлением в клинической практике высокочувствительных методик определения сердечных тропонинов дискуссия о выборе идеального маркера повреждения миокарда получила свое продолжение. Inoue и соавт. (2011) показали, что определение сБСЖК не уступало по своим диагностическим характеристикам вчТн Т, а совместное определение сБСЖК и миелопероксидазы может улучшить диагностику ОКС, в особенности в первые 2 ч заболевания [17]. Схожие результаты были отмечены Cappellini и соавт. (2013), выявивших высокую ОПЗ теста сБСЖК (100%); при этом по площади AUC сБСЖК не уступал вчТн Т, что, по мнению авторов, позволяет использовать этот маркер для исключения ИМ у больных с болями в грудной клетке [18]. Uitterdijk и соавт. (2013) показали, что концентрация сБСЖК в крови быстрее повышается и лучше коррелирует с размерами зоны ИМ и наличием феномена no-reflow у пациентов с ИМпST, подвергшихся ЧКВ, чем вчТн I [19]. В ряде других работ выявлена приблизительно равная эффективность сБСЖК и вчТн, а, по данным Kellens и соавт. (2016), определение сБСЖК хоть и уступало в целом в диагностической точности вчТн Т у пациентов с высоким риском наличия ОКС, но может являться более полезным в ранние сроки после возникновения болей в грудной клетке [20–22].
Неоднозначные результаты получены при изучении корреляции уровня сБСЖК и тяжести поражения коронарного русла. Zeren и соавт. (2013) не выявили такой связи у пациентов с ОКС без подъема сегмента ST, в то время как Kitamura и соавт. (2016) показали, что концентрация сБСЖК коррелирует с количеством пораженных венечных артерий и наличием их тромботического поражения [23, 24].
В последние годы были опубликованы результаты нескольких крупных метаанализов исследований, посвященных эффективности сБСЖК в диагностике ОКС, которые показали более скромные возможности данного биомаркера по сравнению с вчТн. Согласно данным Carroll и соавт. (2013), обобщившим результаты 17 исследований, чувствительность и специфичность сБСЖК составили в среднем 81% (95% ДИ 50–95%) и 80% (26–98%) соответственно для количественного и 68% (11–97%) и 92% (20–100%) для качественного определения биомаркера. Добавление сБСЖК к тропонину повышало чувствительность с 42–75% до 76–97%, но снижало специфичность с 94–100 до 65–93% [25]. Аналогичные результаты отмечены в метаанализе Lippi (2013), включившем 2735 больных. Авторы не рекомендовали самостоятельное определение сБСЖК при ОКС, однако предположили целесообразность его использования совместно с тропониновым тестом [26]. Метаанализ, проведенный Xu и соавт. (2017), объединивший данные 22 исследований с участием 6602 пациентов, также показал, что самостоятельное определение сБСЖК обладает недостаточной диагностической точностью для подтверждения или исключения ИМ в первые 6 ч, в то время как совместное определение с вчТн незначительно повышает чувствительность [27].
Большинство работ, посвященных изучению сБСЖК для верификации инфаркта миокарда, было выполнено с использованием иммуноферментного анализа (ИФА). Несмотря на то что данный метод позволяет количественно оценить уровень сБСЖК, дает более точные результаты и обладает более высоким прогностическим значением, его проведение в ранние сроки ОКС оказывается менее приемлемым, поскольку требует специального оборудования, обученного персонала, значительных временных и финансовых затрат. В связи с этим для практического применения большую значимость имеют экспресс-методы определения данного маркера. Такие тесты основаны на иммунохроматографическом методе и позволяют провести качественную или полуколичественную оценку уровня сБСЖК, а их несомненным достоинством является возможность применения не только в стационарах, но и в амбулаторных и даже домашних условиях. Исследования диагностической эффективности экспресс-тестов не столь многочисленны и обычно выполнялись на небольших выборках больных, а полученные результаты отличаются значительным разбросом. В большинстве случаев в таких работах использовался качественный иммунохроматографический экспресс-тест CardioDetect (Rennesens GmbH, Германия), имеющий порог чувствительности к сБСЖК 7 нг/мл.
Как и в случае с количественным определением, большинством исследователей было выявлено преимущество качественной оценки содержания сБСЖК при ОКС по сравнению с определением МВ-КФК и сТн I и T в первые 6 ч с момента возникновения клинических проявлений вне зависимости от типа ЭКГ изменений [28–32].
Особый интерес представляли работы, в которых изучили возможность применения качественного определения сБСЖК в амбулаторных условиях врачами терапевтами и общей практики. Bruins Slot с соавт. (2013) показали, что данный тест более оправдан с целью подтверждения диагноза ОКС, нежели его исключения, а предварительное обучение врачей методике постановки теста позволяет повысить ее эффективность [33]. Willemsen и соавт. (2015) предположили, что применение экспресс-тестов для качественного определения сБСЖК врачами общей практики и приемных отделений позволяет снизить частоту неоправданных госпитализаций [34].
РОССИЙСКИЙ ОПЫТ КАЧЕСТВЕННОГО ОПРЕДЕЛЕНИЯ сБСЖК
В 2008 г. НПО «БиоТест» (Новосибирск) разработан первый отечественный экспресс-тест для качественного определения сБСЖК в цельной венозной крови «КардиоБСЖК» с аналитической чувствительностью 15 нг/мл. В последующие несколько лет был проведен целый ряд исследований эффективности данного экспресс-теста в диагностике различных форм ОКС [35]. Кратко их результаты представлены в таблице.
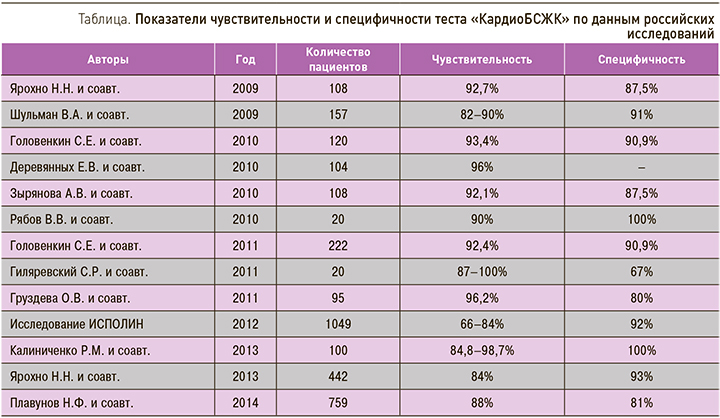
Крупнейшим российским многоцентровым исследованием по изучению данного маркера является ИСследование ПО изучению кЛИНической эффективности ранней диагностики острого инфаркта миокарда с помощью белка, связывающего жирные кислоты (ИСПОЛИН), в котором в 24 центрах из 17 городов РФ были включены 1049 пациентов. Всем больным с типичным приступом ангинозных болей (или его эквивалентами) длительностью более 20 мин и давностью возникновения в пределах 1–12 ч при поступлении в стационар одномоментно проводилось определение содержания сБСЖК (с помощью экспресс-теста «КардиоБСЖК») и сердечного тропонина I (с помощью качественного экспресс-теста Troponin I WB-Check-1 (VEDALAB, Франция), с чувствительностью теста 1 нг/мл) в цельной венозной крови. В 200 случаях уровень тропонина I измерялся количественно иммунохемилюминесцентным методом. Окончательный диагноз устанавливался на основании совокупности клинических, ЭКГ и лабораторных данных, согласно действовавшим рекомендациям ESC и ВНОК. Чувствительность теста на сБСЖК у 724 больных с подтвержденным диагнозом ИМ составила 73,8 против 46,7% у тропонина I. Специфичность тестов была оценена по 325 больным без ОИМ и составила 92% для сБСЖК и 97,2% для тропонина. Точность теста на сБСЖК равнялась 79,3%, тропонинового теста – 62,2%. Положительная прогностическая ценность теста на сБСЖК составила 0,95, тропонинового теста – 0,97, а отрицательная – 0,61 и 0,45 соответственно. Во временном промежутке 1–3 ч с момента возникновения клинических проявлений чувствительность теста на сБСЖК составила 65,8%, на тропонин I – 37,9%, а специфичность – 87 и 95,9% соответственно. В сроки 3–6 ч с момента развития ОКС чувствительность сБСЖК соответствовала 84%, тропонина I – 52,2%, а специфичность – 95,9 и 96,9%. Наконец, во временном интервале 6–12 ч показатели чувствительности и специфичности составляли 70,6 и 94,3% для сБСЖК и 52 и 99% для тропонина I. Таким образом, чувствительность теста на сБСЖК достигала максимума во временном интервале от 3 до 6 ч с момента развития ИМ. Во все изученные сроки чувствительность теста на сБСЖК превосходила тропониновый тест на 18–32%, немного уступая ему в специфичности. В любом интервале времени площади под соответствующими ROC-кривыми для сБСЖК неизменно превосходили аналогичные площади для тропонина I, что подтвердило большую прогностическую ценность метода. При оценке результатов тестов в зависимости от имевшихся ЭКГ- изменений более высокие показатели чувствительности теста на сБСЖК отмечались при элевации сегмента ST (74,9%, n=574) и блокаде ЛНПГ (100%, n=13) по сравнению с депрессией сегмента ST или отсутствием/неспецифическими изменениями. При всех типах ЭКГ изменений чувствительность теста на сБСЖК была выше тропонинового теста на 19–73%. Специфичность теста на сБСЖК немного уступала тесту на тропонин I, но при этом была более 90% при любом типе изменений ЭКГ [36].
Опыт применения экспресс-теста «КардиоБСЖК» на догоспитальном этапе был изучен в 2 крупных работах. Ярохно Н.Н. и соавт. (2013) оценили возможность определения сБСЖК для ранней стратификации риска на этапе скорой медицинской помощи. В исследование были включены 933 больных с подозрением на ОКСбпST и длительностью клинических проявлений 1–12 ч, разделенных на 2 группы. Пациентам первой группы (n=442) проводилась стратификация риска по шкале TIMI с дополнительным определением сБСЖК вместо стандартного тропонинового теста. Пациентам второй группы (n=491) стратификация риска не выполнялась. Применение протокола стратификации риска у больных с подозрением на ОКСбпST привело к госпитализации 83,7% больных, что на 23,8% выше, чем в контрольной группе. Показатели чувствительности и специфичности теста составили 84 и 93%. Таким образом, применение протокола стратификации риска, включающего определение сБСЖК, позволяет дифференцировать степень риска раннего некроза миокарда у пациентов с ОКСбпST [37]. В еще одном исследовании участвовали 88 бригад 57 подстанций скорой и неотложной медицинской помощи им. А.С. Пучкова г. Москвы. Тест на определение уровня сБСЖК выполнялся врачами СМП, а данные об окончательном диагнозе были получены из стационаров. В исследование было включено 759 пациентов. В 642 случаях (84,6%) был подтвержден диагноз ИМ, в 117 (15,4%) – других сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний. Чувствительность теста составила 88%, специфичность – 81%. При сравнении результатов тестов у больных ОКС с подъемом и без подъема сегмента ST выявлена сопоставимая чувствительность метода (89 и 86% соответственно), при более высоком показателе специфичности у больных ОКСбпST (82% против 65), что, по-видимому, было обусловлено малым количеством больных без ИМ в этой группе. Показатели чувствительности и специфичности теста в интервале 1–4 ч. с момента начала болевого синдрома составили 85 и 84%, 4–6 ч – 95 и 78% и 6–12 ч – по 91% соответственно. Было отмечено, что предварительное обучение медицинского персонала методике тестирования позволяет улучшить результаты применения теста [38].
Суммируя полученные в российских исследованиях данные, можно констатировать, что во всех работах отмечена высокая чувствительность теста, колебавшаяся в зависимости от сроков с начала заболевания и контингента выбранных больных, в пределах 66–100%. По всей видимости, отличия в точности могут быть связаны с различным количеством больных с большим по объему ИМ, практически всегда дающих положительный результат теста. Специфичность метода также являлась весьма высокой, варьируя в пределах 87,5–100%. В первые 3 ч с момента возникновения клинических проявлений качественный тест на сБСЖК имел наибольшую чувствительность по сравнению с другими маркерами некроза миокарда. В сроки от 3 до 6 ч сБСЖК и миоглобин показали сопоставимые цифры чувствительности, но сБСЖК имел в два раза большую специфичность, а при проведении теста через 6–12 ч от начала болевого синдрома максимальная чувствительность отмечалась у сердечных тропонинов и МВ-КФК при сопоставимых значениях специфичности.
ОПРЕДЕЛЕНИЕ сБСЖК В СОЧЕТАНИИ С ДРУГИМИ МАРКЕРАМИ НЕКРОЗА МИОКАРДА
Учитывая особенности кинетики различных маркеров, одновременное определение сразу нескольких биомаркеров повреждения и некроза миокарда представляется оправданным для увеличения диагностической эффективности. Актуальным также является поиск наиболее эффективных комбинаций различных маркеров.
Body с соавт. (2011) выявили, что одномоментная оценка уровней сБСЖК и сТн I позволяет более достоверно исключать диагноз ИМ по сравнению с совместным определением миоглобина, сТн I и MB-КФК [9]. McMahon и соавт. (2012) показали, что совместное определение сБСЖК и сТн I с наибольшей достоверностью как подтверждает, так и исключает диагноз ИМ в ранние сроки по сравнению с комбинациями других биомаркеров [10]. Jacobs и соавт. (2015) предложили сочетанное определение копептина, сБСЖК и сТн I для улучшения точности диагностики у пациентов с болями в грудной клетке, особенно в первые 3 ч [39].
При изучении эффективности сочетанного определения сБСЖК с вчТн большая часть исследований показала, что комбинация биомаркеров с большей достоверностью подтверждает или опровергает диагноз ИМ, особенно в ранние сроки заболевания [40–44], хотя не все работы подтвердили эту концепцию [45–46].
Среди преимуществ мультимаркерного подхода отмечается возможность в ряде случаев исключать диагноз ИМ без необходимости серийного определения сердечных тропонинов, увеличить количество выявляемых пациентов без ОКС, что позволит выписывать их в ранние сроки из стационара, снизить частоту госпитализаций и уменьшить экономические затраты [47–49].
ВОЗМОЖНОСТИ сБСЖК В ПРОГНОЗИРОВАНИИ ТЕЧЕНИЯ ОКС
Отдельный практический интерес вызывает определение содержания сБСЖК для прогнозирования течения ОКС. O’Donoghue и соавт. (2006) продемонстрировали, что повышенный уровень сБСЖК у пациентов с ОКС ассоциирован с повышением риска смерти (отношение рисков (ОР) 4,1; 95% ДИ 2,6–6,5), развития повторного ИМ (ОР 1,6; 95% ДИ 1,0–2,5) и ХСН (ОР 4,5; 95% ДИ 2,6–7,8). Проведенный анализ показал, что сБСЖК является независимым от клинических показателей и других биомаркеров предиктором развития осложнений ОКС [50].
Onda и соавт. (2016) по результатам 12 мес наблюдения выявили, что сБСЖК является предиктором развития отдаленных тяжелых сердечно-сосудистых осложнений (MACE) у больных ОКС, которым были имплантированы стенты с лекарственным покрытием. Повышение уровня сБСЖК >6,2 нг/мл увеличивало риск развития MACE в 3,26 раза, а добавление к шкале GRACE показателей NT-proBNP и сБСЖК достоверно улучшало точность прогнозирования [51].
Британские исследователи показали, что включение определения сБСЖК в шкалу MACS у пациентов с ангинозными приступами позволяет эффективно прогнозировать развитие серьезных сердечно-сосудистых осложнений в течение 1 мес, что помогает выявлять больных с низким риском их развития, которые могут быть выписаны из стационара в ранние сроки [52, 53].
Метаанализ 7 исследований, проведенный Jones и соавт. (2017), включивший данные 6935 пациентов, показал, что повышенный уровень сБСЖК ассоциирован с более высоким риском летального исхода (отношение шансов (ОШ) варьировало в пределах от 1,2 до 15,2), однако отмечалась выраженная неоднородность в прогностическом значении сБСЖК при ОКС, связанная с различиями во времени определения маркера и выбранной популяции больных [54]. Учитывая то, что лишь в одном из проанализированных исследований определялась оценка уровня вчТн, авторы признают необходимость дальнейших проспективных исследований для уточнения прогностического значения сБСЖК у больных с подозрением на ОКС.
Результаты метаанализа, выполненного Hai-Long и соавт. (2018) и включившие данные 1994 больных ОКС со сроками наблюдения от 1 мес до 5 лет, продемонстрировали, что повышенный уровень сБСЖК значимо коррелировал с риском развития сердечно-сосудистых событий (ОШ 3,94; p <0,001) и летального исхода (ОШ 6,39; p <0,00001) [55].
Таким образом, есть предпосылки полагать, что определение уровня сБСЖК у больных с подозрением на ОКС, позволяет проводить более точную стратификацию риска и облегчать планирование индивидуальных схем лечения, что может способствовать оптимизации лечения, улучшению качества жизни пациентов, снижению частоты повторных госпитализаций и расходов на оказание медицинской помощи. Данные ряда работ указывают, что включение сБСЖК в применяемые в настоящее время шкалы стратификации риска, такие как TIMI и GRACE, может повысить их прогностическую точность.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Имеющиеся данные позволяют рассматривать сБСЖК в качестве надежного маркера повреждения и некроза миокарда, превосходящего в первые 1–12 ч с момента появления симптомов такие биомаркеры, как миоглобин, МВ-КФК и сердечные тропонины низкой и умеренной чувствительности. Данные по сравнению эффективности сБСЖК и высокочувствительных тропонинов крайне противоречивы. Качественные экспресс-тесты оценки уровня сБСЖК имеют большее практическое значение при ОКС, чем количественные методики, а их применение может быть оправданным в случаях, когда определение вчТн не представляется возможным. Учитывая высокие показатели чувствительности определения сБСЖК и менее высокую специфичность, можно предполагать большую значимость теста для исключения диагноза ИМ, нежели его подтверждения. Совместное определение сБСЖК и сердечных тропонинов может позволить более достоверно подтверждать или исключать наличие ИМ и расширить по срокам диагностическое окно. Такие комбинированные тесты могут найти свое применение, в том числе на амбулаторном этапе с целью решения вопроса о необходимости госпитализации, а также в условиях стационаров для выбора тактики ведения.



