Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания (ССЗ) занимают лидирующие позиции среди причин смертности среди городского и сельского населения в нашей стране и во всем мире уже более 40 лет [1, 2]. По данным ВОЗ, в последние годы отмечается некоторое снижение смертности от ССЗ. В 2014 г. ССЗ были причиной 33% всех смертей, в России же на долю умерших от болезней системы кровообращения пришлось 60% [3]. ССЗ становятся причиной смерти пациентов с сахарным диабетом (СД) в 65% случаев. Не случайно Американская кардиологическая ассоциация ставит знак равенства между этими заболеваниями.
Негативное влияние СД на сердце реализуется преимущественно через 3 основных патогенетических механизма:
- повреждение коронарных артерий;
- развитие диабетической кардиомиопатии;
- развитие автономной нейропатии миокарда.
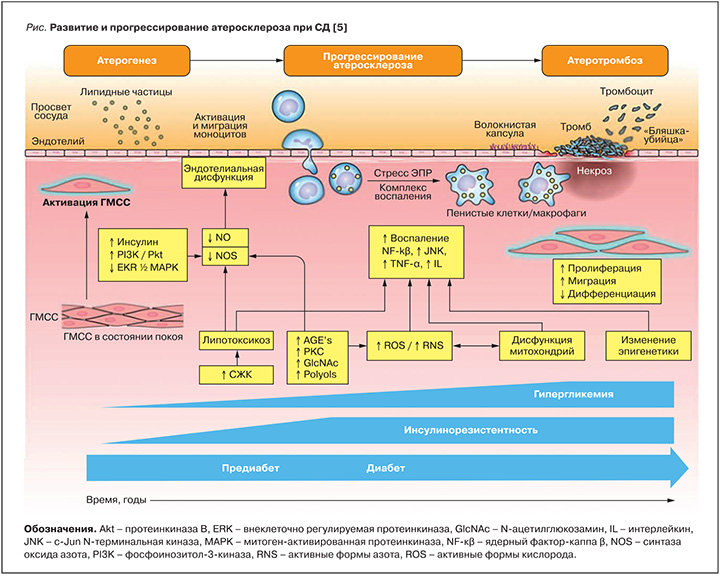
Для пациентов с СД 2 типа характерно раннее развитие и быстрое прогрессирование атеросклероза, симметричность и мультисегментарность поражения артерий среднего и малого калибра, больший объем самих атером и меньший диаметр просвета коронарной артерии, по сравнению с лицами без СД [4]. На рисунке в обобщенном виде представлены процессы атерогенеза, прогрессирования атеросклероза и атеротромбоза при сахарном диабете. Гипергликемия и увеличение концентрации свободных жирных кислот в крови приводят к накоплению липидов вне жирового депо, в том числе в сердечной мышце [6]. Кардиомиоциты не способны хранить большие запасы липидов, содержащих ацилглицеролы и церамиды, в результате чего реализуется механизм липотоксичности: недоокисленные липидные фрагменты приводят к активации воспалительных сигнальных путей, включая протеинкиназу С и ядерный фактор К, которые препятствуют передаче сигналов инсулина [7]. Развивающаяся инсулинорезистентность ограничивает поступление глюкозы в кардиомиоциты и создает предпосылки для перехода к преимущественному окислению жирных кислот как основного источника энергии, что является отличительной чертой диабетического сердца [8]. Изменения энергетического метаболизма миокарда являются центральными для сердечной дисфункции при СД и приводят к снижению сократительной способности в ответ на электрические раздражители [9].
Инсулинорезистентность предшествует развитию предиабета и СД и прогрессирует со временем, тогда как гипергликемия возникает при предиабете и постепенно нарастает с развитием СД. Инсулинорезистентность, гиперинсулинемия и гипергликемия способствуют запуску и развитию множества патологических процессов, включая увеличение концентрации свободных жирных кислот (СЖК), увеличение образования конечных продуктов гликирования (AGE), активацию протеинкиназы C (PKC), окислительный стресс, дисфункцию митохондрий и эпигенетические модификации. Все вместе эти факторы способствуют эндотелиальной дисфункции и воспалению, приводящему к активации гладкомышечных клеток сосудистой стенки (ГМСС) и моноцитов и повреждению эндотелия. Для СД характерно повышение концентрации модифицированных (окисленных) липопротеинов низкой плотности (ЛПНП) и их накопление в субэндотелиальном слое уязвимых участков сосудистой стенки. Лейкоциты, циркулирующие в кровотоке, прикрепляются к эндотелию сосуда и затем мигрируют в структуры ГМСС. Эти моноциты захватывают липопротеины и превращаются в пенистые клетки/макрофаги, продуцирующие протеиназы и воспалительные медиаторы, включая фактор некроза опухоли-α (TNF-α) и интерлейкины. Образование воспалительного комплекса и стресс эндоплазматического ретикулума (ЭПР) приводят к пролиферации макрофагов и активации воспалительного процесса, что в свою очередь, вызывает фенотипическую перестройку ГМСС (пролиферация, миграция и дедифференцировка). В ответ на повреждение сосудов ГМСС выделяет коллаген с образованием фиброзной капсулы, которая способствует стабильности атеросклеротической бляшки. Атерома постепенно увеличивается в объеме, что приводит к стенозированию артерии. По мере прогрессирования атеросклероза фиброзная капсула атеросклеротической бляшки истончается, что делает ее уязвимой. Параллельно с этим нарушается эффероцитоз (фагоцитарный клиренс) макрофагов, насыщенных липидами, что приводит к образованию некротического ядра, ускоряющего сосудистое воспаление, некроз, тромбоз. Согласно последним исследованиям по визуализации миокарда (МРТ с контрастным усилением), у пациентов с СД 2 типа без артериальной гипертензии имеет место специфическое концентрическое ремоделирование левого желудочка, что, в свою очередь, ведет к нарушению энергетического обмена в миокарде и снижению систолической функции [10, 11]. Гипертрофия диабетического сердца является следствием накопления триглицеридов в структурах кардиомиоцитов и/или увеличения внеклеточного объема соединительной ткани как ключевого индикатора фиброза [12, 16]. Кроме того, считается, что сама по себе гиперинсулинемия напрямую способствует гипертрофии миокарда [17], что связано, прежде всего, с изменениями процессов транскрипции. Различные эпигенетические и генетические изменения, возникающие в результате гиперинсулинемии, активируют множественные транскрипционные факторы, которые регулируют экспрессию внеклеточного и клеточного белка. Активация таких факторов, в свою очередь, вызывает накопление белков во внеклеточном матриксе и приводит к гипертрофии кардиомиоцитов и фокальному фиброзу миокарда при сахарном диабете. Обнаружена прямая связь между перфузией сердечной мышцы, доступностью энергетического субстрата и функцией миокарда у пациентов с сахарным диабетом, что позволяет выделить микроциркуляторную недостаточность как причину развития диабетической кардиомиопатии [18]. Дефекты микроциркуляции миокарда обусловлены снижением уровня биодоступного оксида азота [13]. В клетках гладкой мускулатуры коронарных сосудов оксид азота активирует как протеинкиназу, так и гуанилилциклазу, что необходимо для коронарной релаксации [14]. В условиях пониженной чувствительности к инсулину происходит как увеличение деградации оксида азота, так и уменьшение производства оксида азота. Для пациентов с сахарным диабетом характерны снижение плотности капиллярного русла и гиалиноз артериол [15]. Периваскулярный фиброз и интерстициальные изменения, образование микроаневризм в артериолах малого калибра и утолщение стенок капилляров приводят к ишемии кардиомиоцитов при сахарном диабете. Ишемия, в свою очередь, способствует дальнейшему ускоренному прогрессированию фиброза миокарда, повышению жесткости кардиомиоцитов и их дисфункции.
Диабетическая кардиоваскулярная автономная нейропатия является хроническим осложнением СД и приводит к нарушениям в сосудистой гемодинамике и сердечном ритме. Распространенность данного осложнения может достигать 60% среди людей с длительным стажем сахарного диабета [19]. Аномальный симпатический тонус вызывает повышенное периферическое сосудистое сопротивление и уменьшает эластичность сосудов [20], снижает резервы перфузии миокарда [21]. По данным исследования P Iyngkaran и соавт., существует прямая связь между развитием диабетической кардиомиопатии и активацией нервной системы [22]. Активация симпатической нервной системы увеличивает β1-адренергическую сигнализацию и экспрессию, что облегчает интерстициальный фиброз, гипертрофию кардиомиоцитов, нарушает сократительную функцию миокарда и сопровождается увеличением апоптоза кардиомиоцитов [23]. Активность парасимпатической нервной системы снижается, изменяется активность и плотность мускариновых рецепторов. Прямое или опосредованное стимулирование блуждающего нерва может иметь положительное влияние как на ремоделирование сердца, так и на клинические исходы [24].
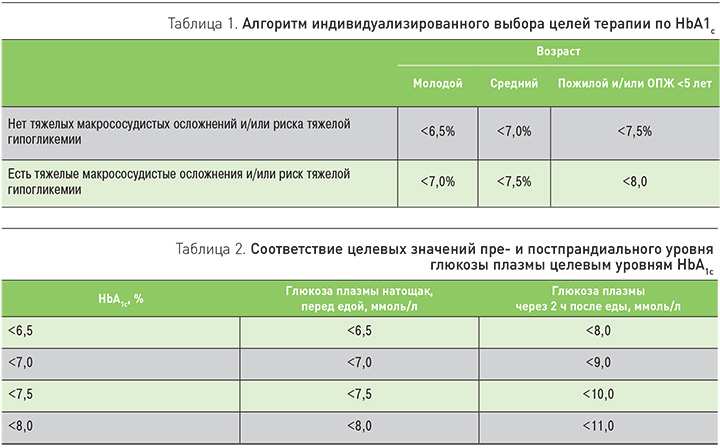
Могут ли терапевтические стратегии управления СД 2 типа предотвратить развитие сердечно-сосудистых осложнений или улучшить их прогноз – вопрос, не теряющий своей актуальности и сегодня. Модификация образа жизни (изменение характера питания, расширение объема физической активности) – основа лечения СД 2 типа, однако пациенты не всегда комплаентны и зачастую быстро утрачивают мотивацию, в связи с чем у врача возникает стремление как можно раньше начать медикаментозное лечение. В «Алгоритмах специализированной медицинской помощи больным сахарным диабетом» последние годы большое внимание уделяется индивидуализированному выбору целей сахароснижающей терапии (табл. 1, 2).
Индивидуальные целевые значения гликемии и гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c) определяются с учетом возраста пациента, ожидаемой продолжительности жизни (ОПЖ), наличия тяжелых сопутствующих состояний и риска гипогликемий. Основными критериями риска развития гипогликемии являются склонность к гипогликемиям в анамнезе, большая продолжительность СД, пожилой возраст, ХБП С3 и выше, деменция, инсулинотерапия (особенной интенсифицированные режимы).
Самый сложный вопрос, стоящий перед врачом: какой же препарат или комбинацию выбрать? Следует подчеркнуть, что этот выбор зависит от большого количества факторов:
- исходного уровеня и целевых значений гликемии и HbA1c;
- наличия клинических симптомов декомпенсации СД;
- доминирующих клинических проблем (сопутствующих заболеваний);
- подтвержденных сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний;
- ИБС (инфаркта миокарда в анамнезе, шунтирования/стентирования коронарных артерий, ИБС с поражением одного или нескольких коронарных сосудов);
- ишемического или геморрагического инсульта в анамнезе;
- заболевания периферических артерий (с симптоматикой или без);
- хронической сердечной недостаточности;
- ХБП С 1-3а (СКФ ≥45 мл/мин/1,73 м2);
- ХБП С 3б-5 (СКФ <45 мл/мин/1,73 м2);
- ожирение.
Показания, противопоказания и ограничения к использованию различных сахароснижающих препаратов.
Оценка эффективности проводимого лечения должна выполняться 1 раз в 3 мес, при этом интенсификация терапии осуществляется не позднее чем через 6 мес. Определяющий постулат в стратегии гликемического контроля: «Лечение до цели, а не до неудачи».
Влияние сахароснижающей терапии на течение и прогноз сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний уже многие годы приковывает внимание ученых и клиницистов во всем мире. Стоит отметить ряд исследований, посвященных данной проблеме. Еще в 1998 г. по результатам UKPDS продемонстрировано положительное влияние метформина на сердечно-сосудистые конечные точки у лиц, страдающих СД. Это исследование доказало преимущество метформина над другими сахароснижающими препаратами в снижении макрососудистых осложнений (частота развития инфаркта миокарда была снижена на 39%) при сопоставимом гликемическом контроле [25]. Также не подтвердились опасения в отношении повышения риска ССЗ на фоне терапии препаратами сульфонилмочевины [26]. В трех крупных исследованиях DREAM, ADOPT и RECORD [27] зафиксирован повышенный риск развития сердечной недостаточности на фоне приема росиглитазона, что существенно ограничило его использование. Другой представитель класса тиазолидиндинов – пиоглитазон – был полностью оправдан в исследованиях PROactive, CHICAGO, PERISCOPE, более того, были установлены его положительные влияния на ССЗ [28]. По результатам исследований SAVOR и EXAMINE сомнению подвергалась сердечно-сосудистая безопасности ингибиторов дипептидилпептидазы-4 (иДПП-4). Исследование TECOS продемонстрировало отсутствие риска развития сердечно-сосудистых событий на фоне приема ситаглиптина и повышенного риска госпитализации по поводу сердечной недостаточности.
На сегодняшний день у пациентов с СД 2 типа и ишемической болезнью сердца без признаков сердечной недостаточности приоритетными сахароснижающими препаратами являются ингибитор натрий-глюкозного котранспортера-2 (иНГЛТ 2) – эмпаглифлозин и агонист глюкагоноподобного пептида-1 (аГПП-1) – лираглутид. Все прочие многочисленные варианты пероральных сахароснижающих препаратов (ПССП) можно отнести к безопасным (нейтральным).
Особое внимание хотелось бы уделить ингибиторам НГЛТ-2 как относительно новому классу ПССП с уже хорошо доказанной эффективностью. В клинической практике представлено три препарата данного класса: дапаглифлозин, канаглифлозин и эмпаглифлозин. Основной механизм действия ингибиторов НГЛТ-2 заключается в ингибировании НГЛТ-2, что приводит к увеличению транспорта глюкозы к дистальной части нефрона, уменьшению почечной гиперфильтрации [29] и снижению порога почечной реабсорбции для глюкозы, в результате чего с мочой выводится от 80 до 100 г глюкозы в день [30]. Эти препараты снижают уровень HbA1c на 0,5–2,2% и не вызывают гипогликемии, кроме случаев, когда они используются в комбинации с препаратами сульфонилмочевины или инсулином [31]. Ингибиторы НГЛТ-2 снижают уровень АД без увеличения частоты сердечных сокращений, повышают уровень холестерина ЛПВП и ЛПНП и вызывают умеренное снижение массы тела. В исследовании, посвященном изучению влияния эмпаглифлозина на сердечно-сосудистые исходы у пациентов с СД 2 типа (EMPA-REG OUTCOME), было зарегистрировано 7020 пациентов с СД 2 типа с высоким риском сердечно-сосудистых событий, которые были рандомизированы в группу вмешательства и получали эмпаглифлозин по 10 и 25 мг/сут и в группу плацебо [32]. Первичная конечная точка в исследовании – смертность от сердечно-сосудистых причин, нефатальный инфаркт миокарда или нефатальный инсульт, а ключевой вторичной точкой была госпитализация в связи с сердечной недостаточностью. Исследование было прекращено досрочно, средний период наблюдения составил 3,1 года. Эмпаглифлозин приводил к снижению риска развития первичной конечной точки (HR, 0,86, 95%, ДИ 0,74–0,99, р=0,04), снижению риска сердечно-сосудистой смерти и смерти от всех причин. Потенциальные механизмы снижения сердечно-сосудистого риска на фоне терапии эмпаглифлозином включают снижение артериального давления и массы тела (включая висцеральное ожирение), снижение гипергликемии, альбуминурии, жесткости сосудистой стенки, подавление активности симпатической нервной системы, окислительного стресса, гиперурикемии, увеличение диуреза и повышение сократительной способности миокарда [33]. Другие потенциальные механизмы заслуживают дальнейшего обсуждения, в том числе потенциальные влияния на НГЛТ-2 [34] и метаболизм минералокортикоидов [35].
На 77 сессии ADA в этом году обнародованы результаты исследований CANVAS (4330 пациентов) и CANVAS–R (5812 пациентов) [36], где на фоне приема канаглифлозина продемонстрировано снижение риска развития первичной конечной точки на 14% и количества госпитализаций по поводу сердечной недостаточно на 33%. Отмечено значимое снижение альбуминурии, что, безусловно, свидетельствует о нефропротекции и возможном замедлении прогрессирования хронической болезни почек (по оценке СКФ до 40%), что подтверждает результаты исследования CREDENCE. Среди нежелательных явлений, ранее не характерных для этого класса препаратов, выделено повышение риска ампутаций нижних конечностей. Увеличение количества ампутаций было существенным (6,3 против 3,4/1000 пациенто-лет) и преимущественно наблюдалось у пациентов с указаниями на ранее перенесенные ампутации в анамнезе или наличием клинически значимых заболеваний периферических сосудов. Это указание позволяет нам выделить группу пациентов, у которой не желательно использование канаглифлозина во избежание развития вышеуказанной проблемы.
При сравнивнении между собой дизайна и результатов исследований EMPA-REG OUTCOME и CANVAS обращает на себя внимание тот факт, что при значимом снижении сердечно-сосудистых рисков в обоих исследованиях имеет место ряд существенных различий. В первом случае изучалась популяция пациентов с сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями, в исследовании CANVAS лишь 65% пациентов имели установленный диагноз сердечно-сосудистого заболевания, в исследовании EMPA-REG OUTCOME не зафиксировано значимого снижения частоты инсультов, в то время как в исследовании CANVAS этот показатель снизился на 10%. Однако в исследовании EMPA-REG OUTCOME отмечено очень быстрое расхождение по числу развивающихся сердечно-сосудистых событий, тогда как в исследовании CANVAS наблюдается более постепенное расхождение по этому параметру. Не исключено, что данные различия обусловлены непосредственно выборкой пациентов, которая во втором случае больше соответствует условиям реальной клинической практики.
По данным исследования CVD-REAL, при участии более 300 000 пациентов терапия дапаглифлозином у пациентов с СД 2 типа в условиях реальной клинической практики приводила к снижению госпитализаций по поводу почечной патологии на 62%, по причине сердечной недостаточности на 37% и общей смертности на 27% по сравнению с иДПП-4. У 100 000 пациентов с СД 2 типа, которым ингибиторы НГЛТ-2
были назначены впервые, отмечено значимое снижение сердечно-сосудистой смертности на 47% и частоты госпитализаций на 30% по сравнению с пациентами, получавшими другие ПССП. В обновленном анализе данных 30 клинических исследований IIb/III фазы не было выявлено новых нежелательных эффектов на фоне приема дапаглифлозина, при этом важно отметить отсутствие роста числа ампутаций нижних конечностей. В 2018 г. должны быть представлены результаты клинического исследования DECLARE по дапаглифлозину, после чего можно будет делать более обоснованные выводы о том, является ли снижение риска сердечно-сосудистых осложнений характерным для всего класса ингибиторов НГЛТ-2 или присуще лишь отдельным его представителям. Кроме того, будут более четко обозначены группы пациентов с клинически значимым изменением сердечно-сосудистого прогноза на фоне приема ингибиторов НГЛТ-2, что позволит определить преимущества их более раннего назначения.
Из-за положительного влияния на многочисленные факторы, играющие роль в развитии сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, ингибиторы НГЛТ-2 в настоящее время приобретают ряд преимуществ перед другими классами сахароснижающих препаратов, особенно у лиц с длительным СД и значимыми сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями. Однако не стоит забывать, что любая медикаментозная терапия должна проводиться с учетом индивидуальных целей конкретного пациента, которые должны быть приняты во внимание до начала лечения. Потенциальные побочные эффекты терапии ингибиторами НГЛТ-2 включают инфекции мочевыделительной системы, гиповолемию, «эугликемический» диабетический кетоацидоз и развитие остеопороза. Среди вновь выявленных нежелательных эффектов, не характерных ранее для этого класса препаратов, стоит выделить повышение риска ампутаций нижних конечностей на фоне приема канаглифлозина.
В заключение хочется подчеркнуть, что на сегодняшний день в арсенале диабетолога присутствует большое количество препаратов с высокой эффективностью и безопасностью, что облегчает многофакторное управление столь гетерогенным заболеванием, как СД 2 типа. Ингибиторы НГЛТ-2 во многом расширяют наши возможности и значимо меняют прогноз сердечно-сосудистых осложнений. Безусловно, присутствуют и минусы такого лечения, что, несомненно, следует учитывать по мере интенсификации терапии. Однако по результатам последних исследований, польза достоверно превышает риск, что является первостепенным и определяющим при выборе препарата.



