ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Панникулиты (Пн) представляют гетерогенную группу воспалительных заболеваний, которые характеризуются поражением подкожной жировой клетчатки (ПЖК), опорно-двигательного аппарата и внутренних органов.
Единая концепция этиологии и патогенеза Пн в настоящее время отсутствует. Определенная роль отводится инфекционным факторам (вирусам, бактериям), травмам, приему лекарственных препаратов, иммуноопосредованным/аутоиммунным и аутовоспалительным заболеваниям [1–4].
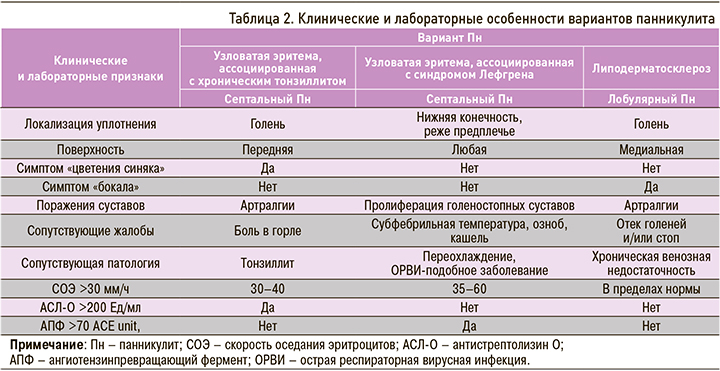
Следует отметить, что классификация Пн до сих пор остается предметом обсуждений. Ряд авторов предложил группировать Пн в зависимости от этиологии и гистоморфологической картины. В соответствии с преимущественным преобладанием воспалительных изменений в соединительнотканных перегородках (септах) или жировых дольках выделяют преимущественно септальный (СПн) и лобулярный (ЛПн) виды заболевания. Оба вида Пн могут протекать с признаками васкулита и без такового, что находит отражение в клинической картине болезни (табл. 1) [4–7].

Клиническая характеристика Пн отличается вариабельной интенсивностью болезненности уплотнений, которые имеют различную окраску (от телесной до багрово-синюшной), локализуются преимущественно на нижних конечностях, реже на верхних конечностях, туловище и лице. Для СПн типичен симптом «цветения синяка», уплотнения регрессируют без образования язв и рубцов. При ЛПн узлы чаще множественные, иногда они сливаются с формированием неровных конгломератов, которые разрешаются в течение нескольких недель, оставляя «блюдцеобразные» западения кожи вследствие атрофии ПЖК. Иногда узел вскрывается с выделением маслянисто-пенистой массы и формированием плохо заживающих изъязвлений и атрофичных рубцов. Часто развитию Пн предшествуют лихорадка (до 41 °С), общая слабость, тошнота, рвота, снижение аппетита, полиартралгии, по поводу которых пациент обращается к разным специалистам (к терапевту, ревматологу, дерматологу, хирургу, онкологу и др.) [1, 2, 4, 6–8].
Успех диагностики Пн зависит от тщательно собранного анамнеза с указанием сведений о предшествующих заболеваниях, принимаемых лекарственных средствах, фоновой патологии, а также от адекватной оценки клинической симптоматики, лабораторных показателей и выявления типичных морфологических изменений.
Изменения лабораторных показателей при Пн носят неспецифический характер, отражая наличие и выраженность воспалительного процесса. Поэтому они (за исключением α1-антитрипсина, амилазы/липазы, мочевой кислоты, креатининфосфокиназы и антинуклеарного фактора с антителами к двуспиральной ДНК) позволяют судить только об активности болезни, а не о нозологической принадлежности. Большую роль в верификации Пн играет гистоморфологическая картина, которая является «золотым стандартом» диагностики заболевания, особенно лобулярной его формы [5, 9, 10].
Возможно атипичное течение болезни со слабо выраженной кожной симптоматикой и отсутствием характерных морфологических признаков. В подобных случаях определенный диагноз устанавливают через несколько месяцев и даже лет после дебюта Пн.
Дифференциальная диагностика узловатых поражений подкожной клетчатки, особенно на нижних конечностях, нередко сопряжена с серьезными трудностями. В связи с этим правильная оценка клинических и лабораторных проявлений у таких больных, поиск диагностических маркеров приобретают огромное значение для верификации варианта Пн и адекватной тактики терапии. Приводим клинические наблюдения трех вариантов Пн у пациентов разного возраста и пола.
КЛИНИЧЕСКОЕ НАБЛЮДЕНИЕ № 1
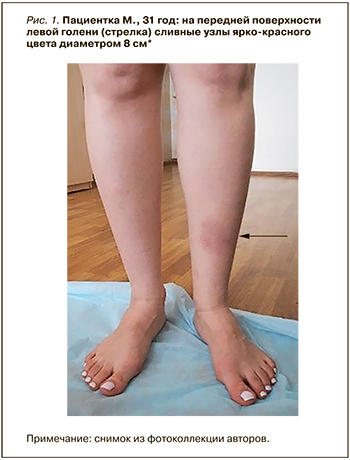
Пациентка М., 31 год, 13.10.2021 обратилась в Научно-исследовательский институт ревматологии им В.А. Насоновой с жалобами на появление болезненных красных уплотнений голеней, повышение температуры тела до 37,3 °С, боль в левом коленном суставе.
Данные анамнеза: пациентка считает себя больной с сентября 2021 г., когда на фоне болей в горле, повышения температуры до 37,6 °С впервые отметила артралгии левого коленного сустава и узловое образование на передней поверхности правой голени. Диагностирована фолликулярная ангина и узловатая эритема, на фоне проводимой терапии азитромицином (250 мг/сут в течение 6 дней) признаки тонзиллита были купированы, однако после окончания курса лечения появились новые узлы на левой голени.
Данные осмотра: состояние относительно удовлетворительное. Нормостеническое телосложение, рост 167 см, вес 51кг. Слизистые оболочки нормальной окраски. Единичные болезненные (50 мм по визуальной аналоговой шкале, ВАШ) эритематозные уплотнения на передней поверхности голеней с диаметром 8 и 3 см, с площадью поражения 1,5 ладони (рис. 1). Мышечная система без патологии. Движения в суставах в полном объеме. Боль (30 мм по ВАШ) при пальпации левого коленного сустава. Периферические лимфоузлы не увеличены. В легких дыхание везикулярное, хрипов нет. Область сердца не изменена. Верхушечный толчок пальпируется в 5 м/р по срединно-ключичной линии. Частота сердечных сокращений (ЧСС) 60/мин, артериальное давление (АД) 115/60 мм рт.ст. Язык чистый влажный. Живот мягкий, при пальпации безболезненный. Перкуторно печень и селезенка не увеличены. Симптом «поколачивания» отрицательный с обеих сторон. Стул регулярный, диурез не изменен. Щитовидная железа при пальпации не увеличена.
Клинический анализ крови: гемоглобин – 117 г/л, лейкоциты – 8,56×109/л, эозинофилы – 6%, лимфоциты – 19%, моноциты – 4%, тромбоциты – 324×109/л, скорость оседания эритроцитов (СОЭ) – 37 мм/ч (по Вестергрену).
Биохимический анализ крови: глюкоза – 4,84 ммоль/л, холестерин – 4,48 ммоль/л, аспартатаминотрансфераза (АСТ) – 15,8 Ед/л, аланинаминотрансфераза (АЛТ) – 22,6 Ед/л, креатинин – 70 мкмоль/л, ферритин – 86,5, общий белок – 70 г/л, антистрептолизин О (АСЛ-О) – 800 Ед/мл.
Иммунологический анализ крови: С-реактиный белок (СРБ) – 4,9 (норма 0–3,0) мг/л, ревматоидный фактор (РФ) <9,5 (норма 0–15) МЕ/мл, анти-дсДНК – 7,2 (0–20) Ед/мл, криоглобулины отрицательны, центральный компонент системы комплемента (С3с) – 1,14 (0,5–0,9) г/л, компонент системы комплемента (С4с) – 0,29 (0,1–0,4) г/л, ангиотензинпревращающий фермент (АПФ) – 42 ACE unit, полимеразная цепная реакция (ПЦР) к SARS-CoV-2 – негативная.
Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки (КТ ОГК): данных в пользу наличия патологических изменений в паренхиме легких, средостении и увеличение внутригрудных лимфатических узлов не получено.
Ультразвуковая допплерография (УЗДГ) вен и артерий нижних конечностей: без патологии.
Диагноз: узловатая эритема острого течения, хронический тонзиллит.
Рекомендации пациенту: внутрь – нестероидные противовоспалительные препараты (НПВП), амоксициллин + клавулановая кислота 875 мг + 125 мг 2 раза/сут в течение 7 дней, дипиридамол 75 мг/сут, наружно диклофенак в форме геля 2% 3 раза/сут 14 дней.
Через 5 дней терапии уплотнения приобрели желтоватый или зеленоватый оттенок, что сделало их похожими на синяки (симптом «синяка»), боль по ВАШ уменьшилась до 35 мм. Регресс узловатой эритемы отмечен через 2 нед.
КЛИНИЧЕСКОЕ НАБЛЮДЕНИЕ № 2
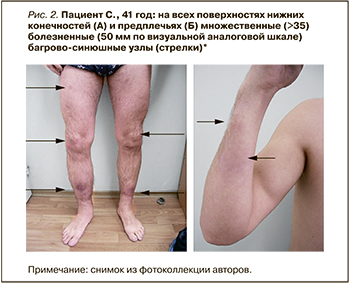
Пациент С., 41 год, предъявлял жалобы на множественные распространенные узлы нижних конечностей, субфебрильную температуру, артралгии голеностопных суставов, плотный отек голеней.
Данные анамнеза: в марте 2020 г. после переохлаждения пациент отметил кашель, повышенную потливость и озноб к вечеру, три красных болезненных уплотнения на правой голени. В течение недели воспалительный процесс на голенях приобрел распространенный и множественный характер. Консультирован терапевтом, заподозрена узловатая эритема. При обследовании: гемоглобин – 133г/л, лейкоциты – 9,62×109/л, тромбоциты – 266×109/л, СОЭ – 42 мм/ч (В), РФ – 7,8 (норма 0–15) МЕ/ мл, СРБ – 48,5 мг/л, АСЛ-О – 316,9 Ед/мл, ПЦР к SARS- CoV-2 – негативная, антитела SARS-CoV-2 к IgG – 59 Ед/мл и IgM – 0,2 Ед/мл. По данным гистологического исследования узла – фрагмент кожи с подкожной клетчаткой. Эпидермис без патологических изменений. Отмечается отек периваскулярных пространств и скудные лимфогистиоцитарные элементы в верхней трети дермы. На фоне проводимой терапии НПВП (целекоксиб 600 мг/сут) и ципрофлоксацином (500 мг/сут в течение 7 дней) уменьшилась интенсивность окраски узлов, но возникали новые элементы. В связи с прогрессированием заболевания и недостаточной эффективностью терапии пациент был направлен на консультацию в Научно-исследовательский институт ревматологии им. В.А. Насоновой с целью исключения аутоиммунного заболевания.
Данные объективного осмотра: состояние относительно удовлетворительное. Нормостеническое телосложение, рост 171 см, вес 83 кг. Слизистые оболочки нормальной окраски. На всех поверхностях нижних конечностей и предплечьях множественные (>35) болезненные (60 мм по ВАШ) багрово-синюшные узлы диаметром 3–6 см с площадью поражения 6 ладоней (рис. 2). Мышечная система без патологии. Сглаженность контуров и боль (50 мм по ВАШ) голеностопных суставов. Периферические лимфоузлы не увеличены. В легких дыхание везикулярное, хрипов нет. Тоны сердца ясные, ритмичные. АД 125/70 мм рт.ст. Живот мягкий, при пальпации безболезненный. Стул, диурез в норме.
Данные лабораторных обследований: гемоглобин – 126 г/л, лейкоциты – 8,2×109/л, лейкоциты палочкоядерные – 5%, лейкоциты сегментоядерные – 62%, эозинофилы – 3%, лимфоциты – 25%, моноциты – 5%, тромбоциты – 265×109/л, СОЭ – 39 мм/ч (В), СРБ – 44,3 Мг/л, АСЛ-О – 100 Ед/мл, АПФ – 84 ACE unit, ПЦР к SARS-CoV-2 – негативная, другие показатели в пределах нормы.
Результаты КТ ОГК: увеличение внутригрудных лимфоузлов до 15 мм, формирующиеся фиброзно-интерстициальные изменения в задненижних отделах легких.
Диагноз: саркоидоз острый (синдром Лефгрена) с поражением легких и внутригрудных лимфатических узлов, голеностопных суставов, вторичная узловатая эритема. Пациент консультирован пульмонологом, диагноз подтвержден.
Рекомендации пациенту: внутрь гидроксихлорохин 600 мг/сут, НПВП (нимесулид 200 мг/ сут), этилметилгидроксипиридина сукцинат 750 мг/ сут, токоферол 800 мг/сут, наружно диклофенак в форме геля 2% 3 раза/сут 14 дней.
Через 10 дней комбинированная терапия способствовала уменьшению интенсивности боли как в суставах (30 мм по ВАШ), так и пораженных участках кожи с ПЖК (45 мм по ВАШ). Через 6 мес лечения отмечалась выраженная положительная динамика со стороны кожных покровов, суставов и данных КТ ОГК.
КЛИНИЧЕСКОЕ НАБЛЮДЕНИЕ № 3
Пациентка А., 52 года, консультирована в мае 2021 г. в Научно-исследовательском институте ревматологии им. В.А. Насоновой с целью уточнения диагноза. Жалобы при обращении – болезненное покраснение и плотный отек голеней, артралгии в коленных и левом голеностопном суставах.
Данные анамнеза: пациентка около 7 лет страдает периодическим отеком голеней. С 2018 г. наблюдается у флеболога с диагнозом хроническая венозная недостаточность, проводит курсовое лечение венотониками. С 2019 г. эпизодически наблюдаются артралгии коленных суставов. В июле 2020 г. впервые отметила уплотнение красного цвета на медиальной поверхности левой голени, которое постепенно увеличивалось в размере. Консультирована терапевтом и дерматологом, исключены рожистое воспаление и узловатая эритема. При обследовании: гемоглобин – 120 г/л, лейкоциты – 7,32×109/л, СОЭ – 11 мм/ч, СРБ – отрицательный, КТ ОГК – без патологии. Принимала НПВП (диклофенак 150 мг/cут), антибиотики – без эффекта.
Данные объективного осмотра: общее состояние удовлетворительное, гиперстеническое телосложение. Видимые слизистые чистые. На коже в средней трети голеней на передней и медиальной поверхностях диффузное болезненное (30 мм по ВАШ) уплотнение красного цвета с площадью поражения 7 ладоней (рис. 3). Плотный отек голеней, больше слева. Выраженный венозный рисунок нижних конечностей. Дыхание везикулярное, хрипов нет. Частота дыхательных движений (ЧДД) 16/мин. Тоны сердца ясные, ритмичные. АД 130/80 мм рт.ст. Живот мягкий, при пальпации безболезненный. Стул, диурез в норме.

Результаты лабораторного обследования: гемоглобин – 138 г/л, лейкоциты – 5,0×109/л, лейкоциты палочкоядерные – 2%, лейкоциты сегментоядерные – 62%, эозинофилы – 2%, лимфоциты – 27%, моноциты – 7%, тромбоциты – 206×109/л, СОЭ – 15 мм/ч, СРБ – 1,3 (норма 0–5,0) мг/л, АСЛ-О – 100 Ед/мл, АПФ – 61 ACE unit, Д-димер – 253 нг/ мл, другие результаты в рамках референтных значений.
Данные цветового дуплексного сканирования сосудов вен нижних конечностей: проходимость вен сохранена, визуализируется неравномерное утолщение и уплотнение стенок с постфлебитическими изменениями задних большеберцовых вен, больше слева, перфорантных и поверхностных вен голеней.
При проведении дыхательных и компрессионных проб: признаки недостаточности клапанов.
Данные патогистологического исследования уплотнения левой голени: в области гиподермы – склероз пограничной зоны клетчатки и склероз артерий мелкого калибра.
Пациентка консультирована флебологом: на основании данных анамнеза, клинико-лабораторной картины диагностировано хроническое варикозное расширение вен нижних конечностей, класс IV. Постфлебитический синдром.
Диагноз: лобулярный панникулит хронического течения: липодерматосклероз. Хроническое варикозное расширение вен нижних конечностей, класс IV. Постфлебитический синдром.
Рекомендации пациенту: внутрь НПВП (эторикоксиб 90 мг/сут), гидроксихлорохин 400 мг/ сут, венотоники (очищенная микронизированная флавоноидная фракция 1000 мг/сут), ацетилсалициловая кислота 75 мг + магния гидроксид 15,2 мг – 1 таб./сут, этилметилгидроксипиридина сукцинат 750 мг/ сут, местно (на уплотнения) диклофенак в форме геля 2% 3 раза/ сут в течение 14 дней, гепарин натрия в форме геля 1000 МЕ/г 2 раза/ сут в течение 3 нед, лечебная физкультура.
Через 10 дней терапии отмечено уменьшение боли (10 мм по ВАШ) и интенсивности окраски уплотнения. Через 3 мес на фоне проводимого лечения установлен регресс кожных воспалительных элементов и плотности отека нижних конечностей.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
В современной клинической практике диагностика Пн сопряжена со значительными трудностями в связи с многообразием этиологических факторов. Общность клинической и лабораторной симптоматики, отсутствие специфических для Пн тестов часто служат причиной как гипо-, так и гипердиагностики заболевания. Поражение жировой ткани нередко представляет собой одну из наиболее сложных диагностических задач, особенно в дебюте основного заболевания, как для интернистов, так и ревматологов. Безусловно, важное значение в верификации основного диагноза имеют объективные данные.
При анализе клинических, лабораторных и инструментальных показателей представленных наблюдений обращает на себя внимание локализация поражения кожи и ПЖК – голень; в сочетании с определенным симптомокомплексом (табл. 2) такая картина нередко имитирует узловатую эритему. В настоящее время узловатая эритема расценивается как неспецифический иммуновоспалительный синдром, развивающийся в результате различных причин (инфекции, саркоидоз, аутоиммунные заболевания, прием некоторых лекарственных препаратов, воспалительные заболевания кишечника, беременность, злокачественные новообразования и др.) [1, 4, 6, 11, 12]. Несмотря на то что узловатая эритема не является редким заболеванием и характеризуется достаточно выразительной клинической симптоматикой, до настоящего времени не существует цельной и единой концепции ее этиопатогенеза, клинико-морфологического субстрата и терапии. Первый клинический случай, рассмотренный нами, демонстрирует классическое течение узловатой эритемы, развившейся после перенесенной А-стрептококковой инфекции глотки с типичной локализацией процесса на переднелатеральных поверхностях голеней и полным быстрым обратным развитием в результате комплексной антибактериальной и противовоспалительной терапии (см. табл. 2). Особое внимание при этом варианте Пн отводится локальному применению НПВП, особенно диклофенаку в форме геля 2%, который, благодаря своим оптимальным физико-химическим и структурным характеристикам, способен проникать и накапливаться в очагах воспаления [13].
Следует отметить, что, несмотря на достаточно типичную клиническую симптоматику узловатой эритемы в терапевтической практике, редко удается выявить ее этиологический фактор. Основная задача врача – определить заболевание на ранней стадии, что позволит приостановить или замедлить его развитие. Однако начальные проявления болезни нередко остаются незамеченными, и это затрудняет диагностику. К числу таких проявлений относится острый саркоидоз, или синдром Лефгрена – гранулематозное заболевание неизвестной этиологии, которое характеризуется клинической тетрадой в виде артралгии, лихорадки, внутригрудной лимфаденопатии и узловатой эритемы. Поражение кожи может быть начальным симптомом или развиться позже, в ходе заболевания. Для синдрома Лефгрена типичны симметричные безболезненные или умеренно болезненные четко очерченные возвышающиеся участки уплотнения кожи багрово-синюшной окраски на туловище, нижних конечностях и лице [14]. Узлы регрессируют без атрофии, рубцевания и изъязвления. В первые дни развития узловатой эритемы может сопровождаться повышением температуры тела до 38–39 °С, ознобом, потерей аппетита, бессонницей, ускоренным СОЭ. В 90% случаев острого саркоидоза отмечается вовлечение в воспалительный процесс суставов (голеностопных, коленных, локтевых) в виде периартикулярных изменений, развития теносиновитов, дактилитов, поражения костей и миопатий [15–17]. Выраженная клиническая симптоматика синдрома Лефгрена ассоциируется с системной воспалительной активностью и зачастую с повышением АПФ. Поскольку эпителиоидные клетки саркоидных гранулем синтезируют значительное количество АПФ, его уровень в сыворотке крови и жидкости бронхоальвеолярного лаважа зависит от общего объема гранулематозной ткани [18]. Тем не менее в многочисленных работах было показано, что в сравнении с растворимыми рецепторами к интерлейкину 2 (sIL2R) уровень АПФ выступает менее надежным критерием активности болезни. Это объясняется выраженным полиморфизмом гена, кодирующего АПФ, что существенно влияет на экспрессию фермента. Установлено также, что активность АПФ не может использоваться для прогноза течения заболевания в случае развития органной дисфункции [19]. При прогрессирующем течении саркоидоза в жидкости бронхоальвеолярного лаважа выявляются высокие уровни хемокинов (MIP-1, MCP-1, RANTES) и интерлейкина 8 (ИЛ-8), ответственных за рекрутирование эффекторных клеток воспаления в легочную ткань [20]. Другие исследователи определили повышенные уровни экспрессии ИЛ-2, ИЛ-12R, интерферона гамма и ИЛ-18R СD4+-лимфоцитами в жидкости бронхоальвеолярного лаважа [21, 22]. Однако наибольшей прогностической ценностью обладает уровень синтеза фактора некроза опухоли альфа альвеолярными макрофагами [21]. Таким образом, наличие типичных критериев синдрома Лефгрена у нашего пациента в дебюте заболевания вызвало значительные затруднения в верификации диагноза, что привело к неадекватной тактике терапии.
В третьем наблюдении была представлена пациентка с липодерматосклерозом (или склерозирующим Пн) – одним из вариантов лобулярного Пн, который характеризуется дегенеративно-дистрофическими изменениями ПЖК, возникающими у женщин среднего возраста на фоне хронической венозной недостаточности [23]. Заболевание проявляется уплотнениями на коже нижней трети голени(-ей), чаще в области медиальной поверхности, с последующей индурацией, гиперпигментацией и атрофией ПЖК (симптом «бокала»). В дальнейшем при отсутствии лечения возможно формирование на коже трофических язв [4, 7 ,24]. Часто липодерматосклероз расценивают как узловатую эритемы, что ведет к назначению неэффективного лечения и хронизации основного процесса.
Клинические наблюдения продемонстрировали очевидные дифференциальные различия (см. табл. 2), прежде всего в манифестный период болезни, что усложняло диагностику вариантов Пн.
Пациенты с Пн в 90% случаев предъявляют жалобы на болевой синдром мягких тканей и суставов, который может быть одним из основных клинических симптомов, ухудшающих качество жизни. В связи с этим первоочередная задача противоревматической терапии – максимально полное и быстрое купирование боли. НПВП занимают одно из центральных мест в фармакотерапии данной когорты больных. Однако высокая частота развития неблагоприятных реакций, отсутствие контроля за их пероральным приемом и настороженности пациентов в отношении возможных осложнений существенно ограничивают прием НПВП для лечения болевого синдрома.
В связи с этим перспективным представляется использование данной группы средств в виде мазей, кремов и гелей, что позволяет воздействовать непосредственно на очаг поражения при минимальном отрицательном влиянии на другие органы и ткани. Мягкая лекарственная форма, нанесенная на поверхность кожи, играет роль депо, из которого активное соединение в нижележащие структуры проникает постепенно, обеспечивая поддержание терапевтической концентрации в очаге поражения. Эффективность локальной терапии определяется способностью лекарственного средства преодолевать кожный барьер и суточной дозой препарата. При выборе средства локальной терапии врач обязательно должен учитывать, какое действующее вещество входит в состав препарата для наружного применения, и назначать средства, имеющие преимущества перед другими НПВП. Прохождение кожного барьера во многом зависит от основы противовоспалительной мази, крема или геля. Гелевая форма, безусловно, удобна для применения и более гигиенична. Считается, что средства локальной терапии в виде геля легче и быстрее проникают через кожу. В настоящее время «золотым стандартом» среди неселективных НПВП считается диклофенак натрия, с которым сравниваются все вводимые в клиническую практику селективные препараты [13, 25, 26]. Особенностью диклофенака является его равновесное влияние на обе изоформы циклооксигеназы, а также возможное воздействие на липооксигеназный путь: этим обусловлена его высокая анальгетическая и противовоспалительная активность [25–27]. После нанесения диклофенака в форме геля на кожу активное соединение накапливается в региональных мягких тканях, синовиальной оболочке и синовиальной жидкости суставов [25– 27]. При этом концентрация диклофенака в плазме крови примерно в 100 раз ниже, чем после приема этого лекарственного средства в форме таблеток [25, 26].
Таким образом, несмотря на обилие различных форм лекарственных препаратов для купирования болевого синдрома, средства локальной терапии не утратили своего значения. Они более безопасны для применения у лиц, имеющих потенциальный риск развития нежелательных явлений, и могут быть рекомендованы для использования в качестве симптоматической терапии у пациентов с различными заболеваниями, в том числе при Пн.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Необходимо подчеркнуть, что Пн представляют собой мультидисциплинарную проблему и могут встречаться в практике клиницистов разных специальностей – терапевтов, дерматологов, хирургов, гинекологов, инфекционистов и др. Многообразие форм и вариантов течения Пн требует проведения тщательного опроса и всестороннего клинико-лабораторного и инструментального обследования больных с целью верификации диагноза и своевременного назначения адекватной терапии.



