ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Под хронической болезнью почек (ХБП) понимают персистирующее в течение 3 мес или более поражение органа вследствие действия различных этиологических факторов, анатомической основой которого является процесс замещения нормальных анатомических структур фиброзом, приводящим к его дисфункции [1, 2].
Фиброз – необратимое состояние, возникающее в ответ на различные по своей этиологии повреждающие воздействия. Именно его выраженность и скорость прогрессирования определяют степень нарушения почечной функции. Временной критерий в 3 мес выбран для ХБП потому, что в эти сроки острые варианты развития дисфункции почек, как правило, завершаются выздоровлением или приводят к очевидным клинико-морфологическим признакам хронизации процесса. Под маркерами повреждения почек понимают любые выявляемые при клинико-лабораторном обследовании изменения, отражающие наличие патологического процесса в почечной ткани. Таким образом, если в процессе клинического обследования повторно, на протяжении 3 мес, обнаруживаются маркеры повреждения почек, то постановка диагноза ХБП правомочна и необходима [1–3].
АКТУАЛЬНОСТЬ ПРОБЛЕМЫ
В многочисленных международных исследованиях установлено, что ХБП распространена так же широко, как и наиболее социально значимые сердечно-сосудистые заболевания, сахарный диабет (СД), ожирение [2–6]. В общей популяции признаки повреждения почек и/или снижение скорости клубочковой фильтрации (СКФ) выявляются у каждого десятого представителя и встречаются в среднем у 13,4% населения как индустриально развитых, так и развивающихся стран [2, 7]. Весьма значительно и количество смертей, ассоциированных с ХБП. Кроме того, во всех странах возрастает число пациентов с терминальной почечной недостаточностью, а следовательно, и потребность в диализных койках и трансплантации почек. Считается, что ХБП в скором времени может занять 5-е место в рейтинге причин смерти населения земного шара [3]. До заместительной почечной терапии (ЗПТ) доживает лишь 1 из 30 больных ХБП, остальные умирают от сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний [7].
Для России проблема ХБП не менее актуальна. По данным эпидемиологических исследований, ее симптомы наблюдаются у 36% населения в возрасте старше 60 лет, а у лиц трудоспособного возраста нарушение почечной функции имеет место в 16% случаев [3]. У пациентов с сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями частота выявления ХБП увеличивается до 26%. В наблюдательной программе ХРОНОГРАФ (2016) было установлено, что 48% лиц со значительно сниженной СКФ и 96% с незначительным снижением этого показателя не знают о том, что у них есть ХБП [8]. По информации Регистра Российского диализного общества (2016), ЗПТ в нашей стране получали около 35 000 человек, а ежегодный прирост таких пациентов составляет 10,8% [7].
В свою очередь, согласно данным главного специалиста Департамента здравоохранения Москвы по нефрологии О.М. Котенко (2019), 10% жителей Москвы имеют факторы риска развития ХБП, при этом большая часть пациентов с этим заболеванием лечится у терапевтов, эндокринологов, кардиологов. Принципиально то, что ХБП можно предупредить и лечить. Все вышеприведенные данные подтверждают важность и актуальность профилактики, раннего выявления и рационального ведения пациентов с ХБП.
ФАКТОРЫ РИСКА, ЭТИОЛОГИЯ И ПАТОГЕНЕЗ ХРОНИЧЕСКОЙ БОЛЕЗНИ ПОЧЕК
Быстрый рост в популяции количества больных со сниженной функцией почек – не узкоспециальная, а общемедицинская междисциплинарная проблема, имеющая серьезные социально-экономические последствия. ХБП – это наднозологическое, групповое понятие, объединяющее чрезвычайно разнородные и разнообразные первичные и чаще вторичные (проявления и осложнения других заболеваний) поражения почек. При этом имеет место единство основных патогенетических механизмов, общих факторов риска развития и прогрессирования заболевания и, следовательно, общих методов первичной, вторичной профилактики и лечения [2, 9].
В концепции ХБП важное значение придается определению факторов риска развития и прогрессирования хронического патологического процесса в почечной ткани. Только при учете этих факторов, оценке их значимости и модифицируемости можно эффективно осуществлять меры первичной и вторичной профилактики хронических заболеваний почек [6, 8, 9].
Многие факторы, ассоциирующиеся с развитием дисфункции почек, одновременно являются и «традиционными» сердечно-сосудистыми факторами риска: среди них артериальная гипертензия (АГ), СД, дислипидемия, ожирение, метаболический синдром, табакокурение (табл. 1) [2, 9–13].

Существует несколько основных механизмов патогенеза ХБП.
1. Функционально-адаптивные механизмы:
- гиперперфузия и гиперфильтрация в клубочках;
- внутриклубочковая гипертензия;
- гипоперфузия почек;
- гипоксия интерстиция;
- нарушения почечного транспорта белка (протеинурия);
- структурно-клеточные адаптивные механизмы;
- увеличение диаметра капилляров клубочка;
- гипертрофия структур почек;
- дисбаланс между синтезом и деградацией матрикса соединительной ткани почек;
- гломерулосклероз;
- тубулоинтерстициальный склероз.
2. Изменения экспрессии медиаторов клеточного и структурного повреждения: цитокинов, факторов роста, пептидов (макромолекул).
3. Метаболические и эндокринные механизмы:
- высокое потребление белка;
- дислипопротеидемия;
- нарушения минерального обмена;
- гиперпаратиреоидизм;
- гиперурекимия;
- анемия.
4. Влияние врожденных и генетических факторов:
- врожденное уменьшение количества нефронов;
- полиморфизм генов, контролирующих экспрессию нефротропных биологически активных веществ.
Условно выделяют три уровня повреждения почек:
- «надпочечный, преренальный», связанный с нарушением кровоснабжения почек (при гипертонической болезни, СД, хронической сердечной недостаточности), когда первично страдают сосуды разного калибра, что приводит к нарушению кровоснабжения нефрона;
- «почечный, ренальный», когда происходит прямое повреждение кортикального слоя, например, при нефритах, системных заболеваниях. В этих случаях первично страдают клубочки: их фильтр начинает пропускать слишком большие количества белков, с обратным всасыванием (реабсорбцией) которых канальцы не справляются и перестают пропускать первичную мочу. Как следствие, клубочек запустевает, и весь нефрон выходит из строя. При других заболеваниях первично страдают канальцы (интерстиций): они повреждаются первыми, а уже затем нарушается работа клубочка, которому некуда фильтровать первичную мочу. Это интерстициальные заболевания (интерстициальные нефриты, пиелонефриты, обменные нефропатии);
- «подпочечный, инфраренальный», при котором нарушается пассаж мочи из-за затруднения ее оттока, например, при урологических заболеваниях. Это сопровождается присоединением инфекции и прямым либо опосредованным повреждением канальцев и клубочков.
Необходимо отметить, что это весьма схематичное и упрощенное деление, не отражающее все разнообразие патологических процессов, однако оно помогает представить основные пути повреждения почек и возможные направления профилактики и лечения [1–3, 14].
КЛАССИФИКАЦИЯ ХРОНИЧЕСКОЙ БОЛЕЗНИ ПОЧЕК
Риски общей и сердечно-сосудистой смертности, развития терминальной почечной недостаточности, острого повреждения почек, скорости прогрессирования ХБП прямо коррелируют с уровнем СКФ и выраженностью протеинурии. Причем оба эти фактора имеют собственную, независимую друг от друга прогностическую значимость, поэтому должны оба учитываться в классификации ХБП и при прогнозировании ее осложнений и исходов (табл. 2).
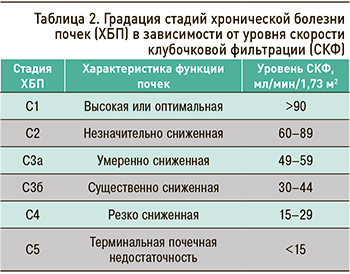
СКФ 60–89 мл/мин/1,73 м2 расценивается как начальное или незначительное снижение этого показателя. Для установления ХБП в этом случае необходимо также наличие также маркеров почечного повреждения. При их отсутствии ХБП не диагностируется. Для лиц 65 лет и старше указанный диапазон значений СКФ интерпретируется как вариант возрастной нормы: таких пациентов относят в группу высокого риска развития ХБП, рекомендуют им контроль состояния почек не реже 1 раза в год, проводят активную профилактику ХБП [1].
Основные признаки, позволяющие предполагать наличие у больного ХБП, нюансы ее клинической картины в зависимости от уровня (стадии) снижения СКФ и рекомендуемый минимальный объем лабораторной диагностики системных осложнений этой патологии, представлены в таблицах 3–5.

ИНСТРУМЕНТАЛЬНЫЕ МЕТОДИКИ ОБСЛЕДОВАНИЯ
Выполнение ультразвукового исследования (УЗИ) почек показано пациентам с подозрением на ХБП и всем больным с известной ХБП С1–С5 для выявления и оценки макроскопических изменений органа и их динамики [1, 3]. Основные УЗИ-признаки необратимых изменений почек включают уменьшение размера, толщины коры и/или паренхимы с увеличением эхогенности, кисты (при этом обнаружение только кисты почек не является признаком ХБП). При исследовании также выявляют обструктивные нарушения, опухоли и изменения интерстиция почек.
Пациентам с ХБП и подозрением на нарушение проходимости почечных артерий для первичной диагностики рекомендуется проведение дуплексного сканирования артерий почек, которое при сомнительных результатах или явных ограничениях метода следует дополнить магнитно-резонансной томографией (МРТ) с контрастированием или компьютерной томографией (КТ).
Российские эксперты не рекомендуют при подозрении на ХБП выполнение с целью ее первичной диагностики рентгенографии почек и мочевыводящих путей, обзорной урографии, внутривенной урографии, КТ почек и надпочечников, МРТ почек, так как рентгенография почек обладает низкой информативностью в обнаружении изменений паренхимы органа [1, 2].
Пациентов с ХБП и АГ рекомендуется суточное мониторирование артериального давления (АД) для уточнения диагноза, контроля эффективности, безопасности антигипертензивной терапии и оценки прогноза. Для АГ при ХБП характерно повышение и отсутствие снижения систолического АД во время сна, более низкие значения диастолического АД днем и, как следствие, повышенное пульсовое АД с увеличением распространенности этих изменений по мере снижения СКФ. Эти параметры имеют отчетливую прямую корреляцию с почечными и сердечно-сосудистыми исходами у больных с ХБП.
ПОДХОДЫ К ЛЕЧЕНИЮ ХРОНИЧЕСКОЙ БОЛЕЗНИ ПОЧЕК
Для успешной профилактики и лечения ХБП важно выделить ключевые «мишени», на которые должно быть направлено терапевтическое вмешательство. На некоторые факторы риска, такие как возраст или генетическая предрасположенность, подействовать невозможно, однако коррекция модифицируемых факторов (СД, АД, сердечно-сосудистые заболевания, болезни почек) позволяет предотвратить или существенно замедлить развитие ХБП [5, 15–17]. Другой целью лечения является замедление и стабилизация на целевых значениях факторов прогрессирования и осложнений ХБП.
Общие подходы к терапии ХБП включают немедикаментозные методы: коррекцию массы тела, содержания белка и других ингредиентов в диете, физическую активность, прекращение курения.
Лекарственная терапия описывается в терминах специфической ренопротекции с использованием ингибиторов АПФ и блокаторов рецепторов к ангиотензину II, оказывающих воздействие на многие механизмы кардиоренального континуума [14]. Неспецифическая кардиоренопротекция подразумевает нормализацию АД, липидного спектра, использование антиангинальной и антитромбоцитарной терапии с учетом коморбидных и фоновых заболеваний, а также коррекцию минеральных и костных нарушений [14, 16, 17].
АНЕМИЯ ПРИ ХРОНИЧЕСКОЙ БОЛЕЗНИ ПОЧЕК
Анемия при ХБП имеет важное значение в силу значимого воздействия на течение патологии почек и сопутствующих заболеваний. Наличие анемии у больных ХБП ассоциировано с повышенным риском серьезных сердечно-сосудистых событий, госпитализаций, развития когнитивных нарушений и снижения качества жизни; помимо этого, тяжесть анемии служит независимым предиктором смертности [18, 19]. Анемия при ХБП усугубляет клиническое течение основного заболевания за счет увеличения риска как смерти от всех причин [20], так и от сердечно-сосудистых нарушений [21] и связана с прогрессированием ХБП [22].
Анемия диагностируется у взрослых и детей старше 15 лет с ХБП, если концентрация гемоглобина составляет меньше 130 г/л у мужчин и меньше 120 г/л у женщин [2, 18–23]. Как правило, это нормоцитарная, нормохромная анемия, но у пациентов на гемодиализе, при язвенно-эрозивном поражении слизистой желудочно-кишечного тракта, дефиците железа она может быть микроцитарной и гипохромной [23, 24]. Для выявления анемии у пациентов с ХБП рекомендуется измерять концентрацию гемоглобина при наличии клинических показаний или:
- по меньшей мере ежегодно у пациентов с ХБП 3;
- по меньшей мере дважды в год у пациентов с ХБП 4–5 до диализа;
- по меньшей мере каждые 3 мес у пациентов с ХБП 5 на гемодиализе и на перитонеальном диализе.
У пациентов с анемией, не получающих лечения эритропоэтинами, измерять концентрацию гемоглобина необходимо при наличии клинических показаний или:
- каждые 3 мес у пациентов с ХБП 3–5 до диализа и на перитонеальном диализе;
- ежемесячно у пациентов с ХБП 5 на гемодиализе.
При исследовании образцов крови определяют гемоглобин, гематокрит, характеристику эритроцита, ретикулоциты. Также оцениваются показатели содержания железа: железо сыворотки, ферритин, трансферрин, насыщение трансферрина сыворотки. У больных на диализе образцы крови берутся непосредственно перед проведением этой процедуры.
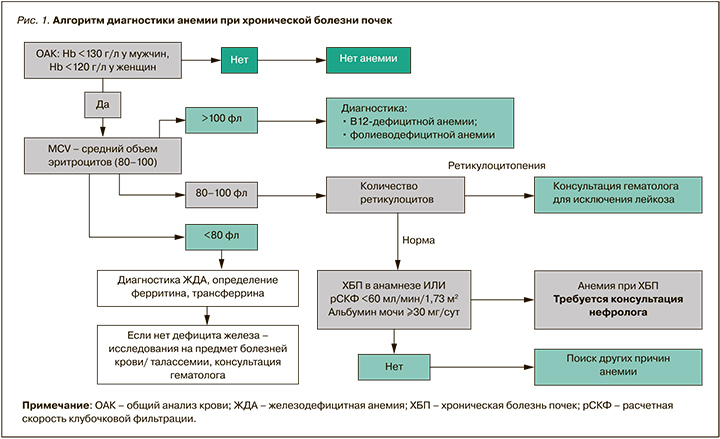
Алгоритм диагностики анемии при ХБП приведен на рисунке 1.
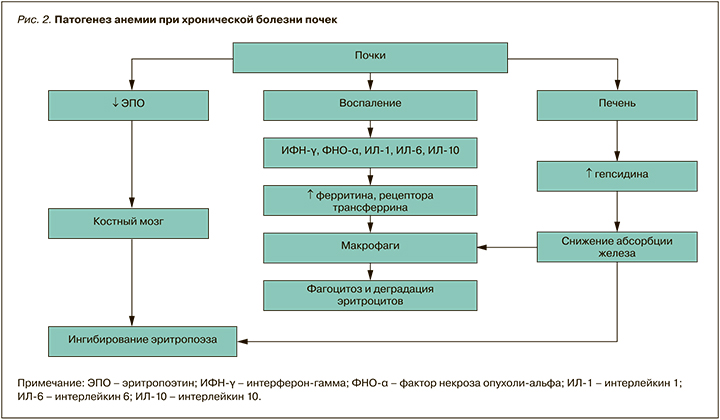
Этиология анемии при ХБП отражена в таблице 6, а ее сложный и многофакторный патогенез – на рисунке 2.

В последние годы показана роль в развитии гематологических нарушений индуцируемого гипоксией фактора (HIF), который является основным регулятором продукции эритропоэтинов и доступности железа. В условиях нормального уровня кислорода ингибитор фактора HIF – гидроксилаза HIF-PH – находится в избытке и вызывает непрерывное разрушение одной из его субъединиц, HIF-α, предотвращая развитие ответа на гипоксию. При понижении уровня кислорода HIF-PH становится неактивным, поскольку для ферментативных реакций требуется кислород; в результате происходит накопление HIF-α2. HIF-α димеризуются с HIF-β и поступают в ядро, стимулируя транскрипцию гена эритропоэтина, отвечающего за индукцию эритропоэза [25, 26].
За исследования реакций клеток на кислород, описание механизма клеточного ответа на гипоксию и роли HIF Уильяму Келину, Греггу Семенцу и сэру Питеру Рэтклиффу в 2019 г. была присуждена Нобелевская премия. Многочисленные исследования показали обоснованность применения антианемического средства роксадустата (Эврензо, «Астеллас») – ингибитора фактора HIF-PH (гидроксилазы HIF): имитируя реакцию организма на гипоксию, он запускает скоординированный эритропоэтический ответ при всей многофакторности анемии [27–29].
Активация пути HIF этим препаратом запускает скоординированный эритропоэтический ответ. Через активацию пути HIF препарат Эврензо повышает доступность железа и стимулирует эритропоэз, нивелируя эффекты анемии при ХБП [25–29].
В исследованиях APLS, OLYMPUS, ANDES роксадустат продемонстрировал эффективность в плане достижения и поддержания целевого уровня гемоглобина у недиализных пациентов в дозе, которая оставалась стабильной в течение 2 лет [30–32]. В отличие от пациентов из группы плацебо, у недиализных пациентов с ХБП, получавших препарат Эврензо, наблюдалось повышение среднего уровня гемоглобина, сохранявшееся с течением времени [30–32].
В исследовании DOLOMITES Эврензо показал сопоставимую эффективность в достижении и поддержании целевого уровня гемоглобина по сравнению с дарбэпоэтином альфа у недиализных пациентов [33], а также равную эффективность с эритропоэз-стимулирующими средствами (ЭСС) у пациентов на диализе [34]. Также препарат снижал частоту (различие достоверно, p=0,0246) переливаний эритроцитарной массы по сравнению с ЭСС у пациентов на стабильном диализе (объединенная выборка исследований ROCKIES, PYRENEES, SIERRAS) [35–37].
Добавим, что в приведенных исследованиях у пациентов на инцидентном диализе и без диализа роксадустат снижал уровень гепсидина, что вызывало повышение доступности железа при меньшем использовании внутривенных препаратов железа по сравнению с ЭСС, а также относительно плацебо (рис. 3, 4) [30–32, 35–38].

В исследовании DOLOMITES роксадустат поддерживал уровень железа при значимо меньшем использовании внутривенных препаратов железа по сравнению с дарбэпоэтином-альфа у пациентов не на диализе с ХБП: доля больных, получавших внутривенных препаратов железа в течение 36 нед, при применении Эврензо составила 6,2 против 12,7% в группе ЭСС [33]. Сходные результаты наблюдались и у пациентов на инцидентном диализе: роксадустат обеспечивал меньшую потребность во внутривенных препаратах железа по сравнению с эпоэтином альфа – 53,57 против 70,22 мг [38]. У пациентов на стабильном диализе Эврензо уменьшал среднее использование внутривенных препаратов железа по сравнению с ЭСС почти в 1,5 раза [30–32]. В объединенной выборке пациентов со стабильным и инцидентным диализом почти 64% пациентов, применявших роксадустат, не нуждались в препаратах железа, в отличие от 48,2% больных на терапии ЭСС [30–32, 38].
Сердечно-сосудистая безопасность (частота смерти, инфаркта миокарда, инсульта, госпитализаций по поводу нестабильной стенокардии и/или хронической сердечной недостаточности, смерти от любой причины) препарата Эврензо была сопоставима с дарбэпоэтином альфа у недиализных пациентов в исследовании DOLOMITES [33], с ЭСС у пациентов на инцидентном диализе в исследовании HIMALAYAS [38], а также в объединенной выборке исследований DOLOMITES, HIMALAYAS, ROCKIES и SIERRAS [33, 35, 37–39].
РЕЖИМ ДОЗИРОВАНИЯ РОКСАДУСТАТА
Эврензо следует принимать 3 раза в неделю, но дни приема при этом не должны идти подряд друг за другом. Доза рассчитывается исходя из веса пациента, самой распространенной дозировкой является 70 мг. В России доступны дозировки препарата 20, 50, 70, 100 и 150 мг. Для пациентов, начинающих лечение анемии, которые в настоящее время не получают ЭСС, рекомендуемая начальная доза Эврензо зависит от массы тела: <100 кг – 70 мг 3 раза в неделю, ≥ 100 кг – 100 мг 3 раза в неделю.
Таблетки Эврензо применяют внутрь независимо от приема пищи, проглатывая целиком, не разжевывая, не разламывая и не измельчая. Другой важный момент: их следует использовать как минимум за 1 ч до или через 1 ч после приема фосфатсвязывающих веществ (кроме лантана) или других лекарственных препаратов, содержащих поливалентные катионы (кальций, железо, магний или алюминий).
Суммируя вышесказанное, можно выделить следующие ключевые особенности этого оригинального препарата:
- роксадустат – первый пероральный ингибитор HIF-PH, зарегистрированный в России для лечения взрослых пациентов с анемией при ХБП;
- Эврензо сопоставим по эффективности с текущим стандартом терапии ЭСС, что было подтверждено средним изменением уровня гемоглобина в течение 104 нед у недиализных пациентов с ХБП и в течение 52 нед у пациентов на диализе;
- у пациентов, получавших Эврензо, наблюдалось снижение уровня гепсидина, частоты введения внутривенных препаратов железа и проведения резервной терапии по сравнению с пациентами групп плацебо и ЭСС;
- Эврензо не повышал риск сердечно-сосудистых событий и смертности по сравнению с ЭСС у недиализных пациентов и больных на инцидентном диализе;
- общий профиль безопасности Эврензо сопоставим с ЭСС по большинству оцененных критериев безопасности в исследуемой популяции пациентов с ХБП.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Проблема ХБП – одна из наиболее серьезных и важных в современной клинической практике. Существующая нефропротективная стратегия позволяет не только стабилизировать почечную функцию при нефропатиях различной этиологии, но и, возможно (а это главное), предупредить их развитие. Следовательно, необходимо как можно раньше выделять пациентов групп риска и проводить профилактические или лечебные мероприятия. Эта задача и ответственность ложатся на плечи врачей амбулаторного звена. Именно они осуществляют раннее выявление, этиологическую диагностику, динамическое наблюдение пациентов и нефропротекцию на ранних стадиях ХБП. Кроме того, совместно с нефрологом они наблюдают этих пациентов на поздних стадиях ХБП и при выполнении ЗПТ.
Исходя из результатов исследований и сформулированных рекомендаций, текущая цель лечения анемии при ХБП состоит не в достижении физиологически нормального диапазона гемоглобина у здоровых людей, а, скорее, в достижении его целевого уровня <12 г/дл [40–42]. Превышение уровня гемоглобина выше рекомендуемых целевых значений ассоциировалось с дополнительными тромботическими нежелательными явлениями, а также с развитием системной гипертензии и повышенным риском сердечно-сосудистых нарушений. В свою очередь, более высокие уровни гематокрита сопряжены с повышенной вероятностью тромбообразования из-за развивающегося синдрома сгущения крови [41, 43].
Коррекция анемии при ХБП имеет большое значение в том числе для лечения сопутствующих заболеваний. Перспективным препаратом при анемии, ассоциированной с ХБП, является пероральный ингибитор HIF-PH роксадустат (Эврензо), сочетающий благоприятный профиль безопасности и высокую эффективность у больных с различной степенью тяжести ХБП.



