Вопросы диагностики и прогнозирования развития нарушений ритма сердца (НРС) остаются достаточно актуальной проблемой современной медицины. Повышенный интерес обусловлен, с одной стороны, связью НРС с риском внезапной смерти, а с другой – высокой частотой выявления НРС у лиц без органических заболеваний сердечно-сосудистой системы [1]. Выделение предикторов, свидетельствующих о высоком риске развития аритмий, – актуальная задача практической кардиологии. На сегодняшнее время к факторам, которые характеризуют так называемую электрическую нестабильность миокарда (ЭНМ), относят около двух десятков различных показателей, однако особое внимание уделяется тем параметрам, которые могут быть оценены без использования инвазивных методов исследования. К таким показателям относят снижение показателей вариабельности и патологические значения турбулентности (ТРС) ритма сердца, увеличение продолжительности и дисперсии интервала QT. Основным методом оценки названных параметров является холтеровское мониторирование (ХМ) электрокардиограммы (ЭКГ). В настоящее время разработаны алгоритмы оценки этих параметров, определение их включено в международные рекомендации для стратификации риска у лиц с органическими заболеваниями сердца [2].
В качестве одной из возможных причин НРС называют наследственные нарушения (дисплазии) соединительной ткани (ННСТ), которые, согласно рекомендациям Российского кардиологического общества (РКО), принято делить на классифицируемые; к ним относятся достаточно редкие генетически детерминированные заболевания [синдромы Марфана (СМ), Элерса–Данло, пролапса митрального клапана (ПМК) и др.] и неклассифицируемые (в русскоязычной литературе часто называемые дисплазиями соединительной ткани). Диагностика классифицируемых ННСТ опирается на международные согласованные критерии, которые регулярно пересматриваются [3–6].
Характер НРС при классифицируемых ННСТ изучен достаточно хорошо. Так, для пациентов с СМ и ПМК характерна повышенная частота наджелудочковых (НЖЭ) и желудочковых (ЖЭ) экстрасистол, нередко у таких пациентов выявляются пробежки желудочковой тахикардии [7, 8]. Высокая частота сердечных аритмий при этих ННСТ сопровождается признаками ЭНМ – удлинением интервала QT, патологическими значениями ТРС [9, 10].
Критерии выявления неклассифицированных ННСТ до сих пор являются несогласованными. Наиболее разумным, с нашей точки зрения, является подход, изложенный в рекомендациях РКО [11, 12], авторы которых предлагают выделять диспластические фенотипы (ДФ) на основе схожести фенотипических признаков. Наиболее распространенным и изученным на сегодняшний день ДФ является марфаноидная внешность (МВ) [13]. Алгоритм диагностики МВ, изложенный в Рекомендациях [11, 12], основан на выявлении не менее четырех любых костных признаков (КП) дизэмбриогенеза. В 2017 г. нами были уточнены диагностические критерии МВ с учетом специфичности отдельных признаков [14]. К наиболее специфичным КП мы отнесли килевидную и воронкообразную деформации грудной клетки, высокое арковидное нёбо, арахнодактилию (включающую симптомы запястья и большого пальца), долихостеномелию (ДСМ), оцениваемую при выполнении хотя бы одного коэффициента: размах рук/рост >1,03 и соотношение верхнего сегмента тела к нижнему <0,89 [15]. Ранее нами было показано, что при таком подходе, учитывающем специфичность отдельных КП, МВ выявляется у 16% юношей и 9% девушек [14].
Выделение МВ как ДФ показало свою перспективность. Так, нами установлено, что для лиц с МВ, так же как и для пациентов с СМ [16] и первичным ПМК [17], характерно развитие кардиомиопатии, которая проявляется значительным снижением величины циркулярной деформации миокарда левого желудочка [18, 19]. Есть данные о более частом выявлении у пациентов с МВ признаков вегетативной дисфункции [20]. Однако характер сердечных аритмий у пациентов с МВ различных возрастных групп ранее не изучался. Не изучалась ранее и информативность маркеров ЭНМ для стратификации риска развития НРС у лиц с МВ.
 Настоящее исследование предпринято с целью изучения НРС и оценки возможности применения критериев ЭНМ для стратификации риска у лиц с МВ.
Настоящее исследование предпринято с целью изучения НРС и оценки возможности применения критериев ЭНМ для стратификации риска у лиц с МВ.
МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДЫ
В исследование включены 119 лиц молодого возраста из числа студентов СПбГПМУ в возрасте от 18 до 25 лет (средний возраст 19,9±1,6 года), из них 53 юноши, 66 девушек и 111 пациентов старших возрастных групп (средний возраст 61,2±8,7 года), из них 49 мужчин и 62 женщины со стабильным течением ИБС, стенокардией напряжения 1–2 функционального класса. Диагноз ИБС устанавливали на основании комплексного клинического и инструментального обследования, включавшего сбор жалоб, регистрацию электрокардиограммы покоя, нагрузочные тесты (велоэргометрию). Пациенты с вазоспастической стенокардией, постинфарктным кардиосклерозом, патологией щитовидной железы, алкогольной кардиомиопатией, пороками сердца и сахарным диабетом из исследования были исключены. Всем обследованным выполнено фенотипическое и антропометрическое обследование для выявления КП и коэффициентов ДСМ. Диагностику МВ у лиц молодого возраста проводили согласно Российским рекомендациям [11, 12] и уточненным критериям [14]. У лиц старших возрастных групп МВ выявляли с учетом изменения информативности ряда признаков с возрастом. К наиболее надежным КП относили деформации грудной клетки, симптомы арахнодактилии и высокое арковидное нёбо. В то же время известно, что специфичность таких признаков, как сколиотическая деформация позвоночника и плоскостопие у лиц старшего возраста, крайне низка, а снижение высоты межпозвонковых дисков и связанное с этим уменьшение роста может приводить к неверному расчету коэффициентов ДСМ [21].
 Всем обследованным выполнено ХМ ЭКГ в течение суток (Кардиотехника, ЗАО «Инкарт», Санкт-Петербург). Оценивались НРС, продолжительность корригированного интервала QT (QTc) и дисперсия QT (QTd) оценивались программно при регистрации ЭКГ с помощью комплекса KtResult 3. Патологическими значениями продолжительности QTc считали удлинение более 480 мс, QTd – более 50 мс. При выявлении не менее двух ЖЭ оценивали параметры ТРС: к патологическим значениям ТРС относили значения начала (TO) более 0%, а наклона (TS) менее 2,5 мс/RR [22].
Всем обследованным выполнено ХМ ЭКГ в течение суток (Кардиотехника, ЗАО «Инкарт», Санкт-Петербург). Оценивались НРС, продолжительность корригированного интервала QT (QTc) и дисперсия QT (QTd) оценивались программно при регистрации ЭКГ с помощью комплекса KtResult 3. Патологическими значениями продолжительности QTc считали удлинение более 480 мс, QTd – более 50 мс. При выявлении не менее двух ЖЭ оценивали параметры ТРС: к патологическим значениям ТРС относили значения начала (TO) более 0%, а наклона (TS) менее 2,5 мс/RR [22].
Статистика: количественные данные представлены как среднее ± стандартное отклонение. Значимость различий между количественными признаками определялась при помощи t-критерия Стьюдента, между качественными признаками – при помощи непараметрических методов (критерий Манна–Уитни; р <0,05). Статистическая обработка данных была выполнена при помощи программы Statistica 8 (StatSoft, Inc.).
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
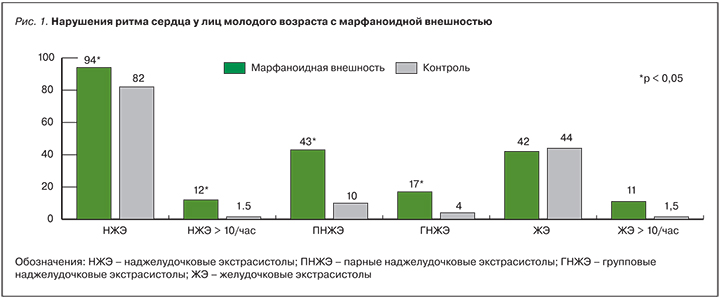
Для оценки распространенности НРС среди лиц молодого возраста с МВ были выделены 2 группы: в основную вошли 47 человек, контрольную группу составили 72 человека с единичными (до трех) низкоспецифичными КП (рис. 1).
Как видно из рис. 1, одиночные НЖЭ встречаются у подавляющего большинства пациентов обеих групп. Однако большое их число (более 10 в час) выявляется практически только среди пациентов с МВ (12 vs 1,5%; р=0,009). Также среди лиц основной группы достоверно чаще выявляются эпизоды парной (42,6 vs 9,7%, р=0,0001) и групповой (17,0 vs 4,2%; р=0,01) НЖЭ. Одиночная ЖЭ встречалась с одинаковой частотой в обеих группах, однако патологическое число ЖЭ (более 10 в час) выявлено практически только среди пациентов с МВ.
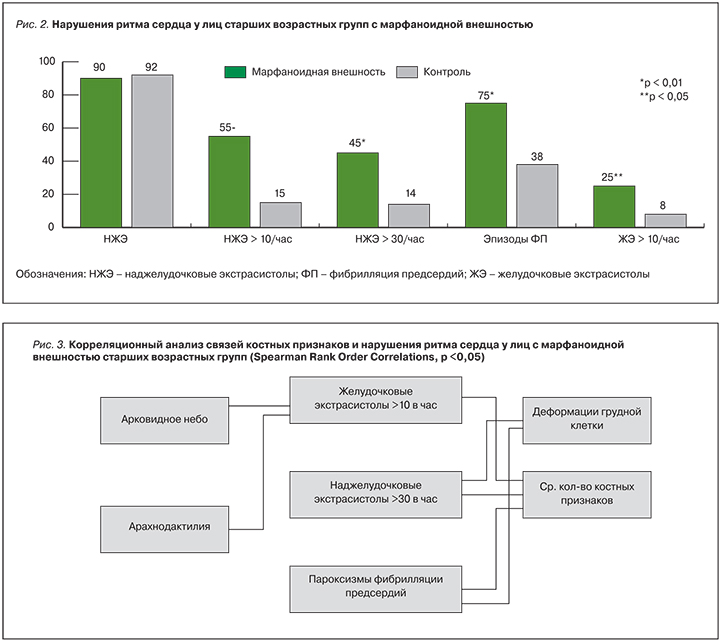
 Далее аналогичный анализ был проведен среди лиц старших возрастных групп с МВ, страдающих ишемической болезнью сердца. В основную вошли 46 пациентов с МВ, в контрольную – 65 человек с единичными КП, группы достоверно не различались по полу и возрасту, а также течением ИБС и средними значениями артериального давления. Результаты представлены на рис. 2.
Далее аналогичный анализ был проведен среди лиц старших возрастных групп с МВ, страдающих ишемической болезнью сердца. В основную вошли 46 пациентов с МВ, в контрольную – 65 человек с единичными КП, группы достоверно не различались по полу и возрасту, а также течением ИБС и средними значениями артериального давления. Результаты представлены на рис. 2.
Как следует из рис. 2, при анализе характера НРС у лиц старшей возрастной группы получены данные, аналогичные описанным в группе лиц молодого возраста. Для пациентов старшего возраста с МВ характерно более частое выявление патологического числа НЖЭ и ЖЭ. Кроме того, для пациентов с МВ в старшем возрасте характерно более частое выявление пароксизмов фибрилляции предсердий (ФП).
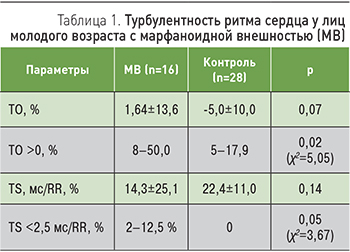
Для уточнения связи между КП, участвующими в алгоритме выявления МВ, был проведен корреляционный анализ, показавший наличие достоверных положительных связей ЖЭ в патологическим количестве с арковидным нёбом и симптомами арахнодактилии и НЖЭ в патологическом количестве и пароксизмами ФП с деформациями грудной клетки (рис. 3).
Далее у лиц молодого возраста основной и контрольной групп, у которых выявлялась ЖЭ, мы провели оценку ТРС (табл. 1).
Как видно из табл. 1, для лиц с МВ характерно достоверно более частое выявление патологических значений начала и наклона ТРС.
При оценке продолжительности интервала QT учитывались только его корригированные значения, рассчитанные с учетом частоты сердечных сокращений (QTc) [23]. Как видно из табл. 2, были выявлены существенные различия продолжительности интервала QTc у лиц с МВ – все значения этого показателя у юношей основной группы оказались статистически выше по сравнению с контрольной группой. Превышение QTc более 480 мс выявлено у пятой части юношей с МВ и вовсе не определялось в группе контроля (различия достоверны).
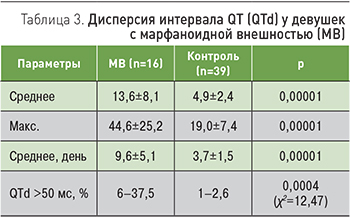
Другим показателем, характеризующим высокий риск аритмических событий, является дисперсия интервала QT (QTd). Этот параметр рассчитывается как разница продолжительности самого длинного и самого короткого интервала QT в 12 общепринятых отведениях. Была проанализирована QTd в течение суток у девушек с МВ (табл. 3).
Как следует из табл. 3, девушкам с МВ свойственны достоверно более высокие значения дисперсии интервала QT. Превышение порога QTd в 50 мс выявлено у трети лиц основной группы и практически не встречалось в контрольной(р=0,0004).
Таким образом, для лиц с большим числом высокоспецифичных КП (МВ) как в молодом, так и в старшем возрасте характерно более частое выявление патологического числа НЖЭ и ЖЭ, а также пароксизмов ФП.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Суммируя полученные данные, следует отметить высокую распространенность желудочковых НРС у лиц молодого возраста с МВ. У таких пациентов значимо чаще выявляются одиночные и парные ЖЭ в патологическом количестве. Однако некоторые авторы склонны относить подобные НРС к вариантам нормы у лиц молодого возраста без органических заболеваний сердца. В то же время в контрольной группе, сформированной из лиц с единичными КП дизэмбриогенеза, названные НРС практически не встречались. Это подтверждает предположение о связи НРС в молодом возрасте с КП ННСТ, участвующими в алгоритме диагностики МВ.
Следует отметить и тот факт, что характер выявленных нами аритмий при МВ, оцененной согласно уточненному алгоритму, аналогичен НРС у пациентов с СМ. Последние работы выявили связь между НРС у пациентов с СМ и наличием мутаций фибриллина FBN [24]. Между тем алгоритм диагностики СМ подразумевает выявление наиболее специфичных для этого заболевания признаков (шкала системного вовлечения соединительной ткани), основными из которых являются КП. При этом наибольший диагностический вес имеют арахнодактилия и деформации грудной клетки. Между тем эти КП входят в алгоритм диагностики МВ. Таким образом, нам представляется весьма перспективным предложенное Э.В. Земцовским [13] понятие диспластического континуума при СМ, где в качестве фибриллинопатии рассматривается и МВ.
Выявленная нами склонность лиц с МВ к формированию клинически значимых НРС подтверждается более частым выявлением в этой группе и других признаков ЭНМ. Так, у 21% лиц с МВ выявляется удлинение корригированного интервала QT, что является мощным самостоятельным предиктором желудочковых НРС. Увеличение продолжительности электрической систолы желудочков мы склонны объяснять относительным увеличением толщины миокарда у лиц с МВ [25] и повышенным тонусом симпатического отдела вегетативной нервной системы [20]. С увеличением массы миокарда левого желудочка связано, вероятно, и то, что у трети девушек с МВ выявляется повышение дисперсии интервала QT, что практически не встречалось у лиц с единичными КП. Это свидетельствует о высокой вероятности нарушений электрических процессов в миокарде и также может рассматриваться как предиктор НРС у лиц с МВ.
Неразрывно с НРС следует рассматривать и такой маркер ЭНМ, как ТРС. Нами показано, что у лиц с МВ достоверно чаще выявляется отсутствие физиологической реакции синусового узла на ЖЭ – отсутствие увеличения частоты синусового ритма сразу после ЖЭ и замедление темпов урежения ритма в последующем. Это может рассматриваться как свидетельство вегетативной дисфункции синусового узла и как причина развития клинически значимых НРС.
Таким образом, мы показали, что для лиц с МВ характерно более частое выявление предикторов развития ЖЭ, что уже в молодом возрасте проявляется более частой регистрацией клинически значимых желудочковых НРС.
ВЫВОДЫ
Для лиц с МВ молодого возраста характерно частое выявление большого числа предсердных экстрасистол и ЖЭ на фоне признаков ЭНМ, таких как удлинение и повышение дисперсии интервала QT, а также патологических значений ТРС.
У пациентов старших возрастных групп с признаками МВ существенно возрастает риск развития суправентрикулярных и желудочковых аритмий высоких градаций, а также пароксизмов ФП.


