ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Аутоиммунный/воспалительный синдром, вызванный адъювантами (Autoimmune/inflammatory syndrome induced by adjuvants, ASIA), впервые был описан в 2011 г. Shoenfeld Y. и Agmon-Levin N. [1]. Этот симптомокомплекс объединяет ряд состояний, характеризующихся общим механизмом развития и вызванных различными адъювантами. В литературе его называют также синдромом Шонфельда (Shoenfeld’s syndrome).
Выделение ASIA позволило впервые сгруппировать специфические состояния, в основе патогенеза которых лежит гиперергическая реакция иммунной системы в ответ на различные адъюванты. К подобным состояниям относят силиконоз, макрофагальный миофасциальный синдром, синдром Персидского залива, синдром «больного здания», поствакцинальный феномен и др. [2, 3]. С момента выделения ASIA опубликовано более 4000 посвященных ему клинических случаев [4]. Большая часть из них была ассоциирована с установкой силиконовых имплантатов и использованием косметических филлеров, содержащих минеральные масла [5–7].
Наиболее известным ревматологическим заболеванием, ассоциированным с адъювантами, является силикон-индуцированная системная склеродермия. Известны саркоидоподобные реакции, связанные с внутрикожным введением адъювантов-филлеров и нанесением татуировок. Вместе с тем мы не встретили в научной литературе случаев развития системной красной волчанки с элементами уртикарного васкулита в сочетании с саркоидоподобной гранулематозной реакцией. Описание такого клинического случая и стало целью настоящей статьи.
ОПИСАНИЕ КЛИНИЧЕСКОГО НАБЛЮДЕНИЯ
Пациентка Н., 1979 г.р., в 2021 г. в возрасте 42 лет впервые обратилась к врачу с жалобами на увеличение шейных лимфатических узлов до 6–8 мм, а также без видимых причин периодически возникающие кожные высыпания по типу эпидермального отека, впоследствии расцененного как уртикарный васкулит (рис. 1). С этого же периода пациентка отмечала выраженную общую слабость, утомляемость, значимо снижающую трудоспособность.
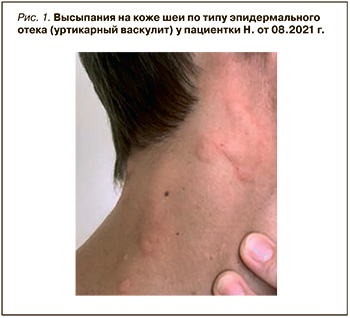
Данные анамнеза жизни: наследственность по аутоиммунным заболеваниям не отягощена, пациентка не курит, не употребляет алкоголь и наркотические препараты, инфекционными заболеваниями не страдала (за исключением легкой формы COVID-19 в 2021 г.). С 2000 по 2015 г. принимала комбинированные оральные контрацептивы (сначала дроспиренон + этинилэстрадиол, а с 2015 г. до момента обращения – дроспиренон + этинилэстрадиол + кальция левомефолат). В 2010 г. у пациентки был выявлен аутоиммунный гипотиреоз, в связи с чем ей был назначен постоянный прием левотироксина натрия 50 мкг/сут (достигнут медикаментозный эутиреоз).
С 2013 г. по май 2021 г. наблюдаемая проходила различные инвазивные косметологические процедуры: 2–3 раза в год получала инъекции ботулотоксина в область лица; в 2018 г. установила силиконовые импланты грудных желез; в июне 2021 г. ей производилось введение многочисленных филлеров на основе гиалуроновой кислоты в область лица.
С мая 2021 г. после эпизода нервно-психического перенапряжения у пациентки начали появляться высыпания на коже по типу крапивницы (впоследствии высыпания были расценены как уртикарный васкулит), с которыми пациентка обратилась к дерматологу. Проведенное лечение антигистаминными средствами (цетиризин) и энтеросорбентами (уголь активированный, полиметилсилоксана полигидрат) не дало клинического эффекта. Лечение было усилено назначением таблетированного преднизолона 60 мг/сут (1 мг/кг массы тела пациентки) с последующей постепенной полной отменой в течение 2,5 мес, но и после него также не наблюдалось какой-либо положительной динамики.
Данные объективного исследования на амбулаторном осмотре (28.09.2021): состояние удовлетворительное, температура тела 36,6 °С, сознание ясное. Рост 169 см, масса тела 60 кг. Кожные покровы сухие, на коже туловища и конечностей уртикарные высыпания диаметром от 1 до 15 см, местами сливные. Пальпируются лимфатические узлы: шейные – до 1 см, подмышечные – до 1,5–2 см, паховые – до 1,5 см; лимфоузлы подвижные, безболезненные, не спаянные с окружающими тканями. Периферических и полостных отеков нет. Остальные данные осмотра без особенностей.
С учетом лимфаденопатии пациентке было рекомендовано выполнение ультразвукового исследования (УЗИ) щитовидной железы, лимфоузлов шеи и органов брюшной полости.
При УЗИ органов брюшной полости от 29.09.2021 в структуре обеих долей печени визуализировались множественные гиперэхогенные образования размером 6–12 мм с четкими контурами овальной или неправильной формы (гемангиомы?). По ходу сосудистых пучков брюшного отдела аорты определялись множественные увеличенные лимфоузлы максимальным размером до 12–20 мм с гиперплазией мозгового слоя. Согласно заключению УЗИ органов брюшной полости, выявлены очаговые образования печени (гемангиомы?) без отрицательной динамики относительно предшествующего исследования. Определена лимфаденопатия брюшной полости.
При УЗИ щитовидной железы от 29.09.2021 были обнаружены признаки аутоиммунного тиреоидита, региональные лимфоузлы с обеих сторон с измененной гипоэхогенной структурой, размерами до 5–25 мм.
С учетом выявленной диффузной лимфаденопатии пациентка была направлена на консультацию к гематологу 29.09.2021, который констатировал наличие периферической, внутрибрюшной лимфаденопатии (лимфопротиферативное заболевание?), сделал предположение о наличии неходжкинской лимфомы неуточненной.
В рамках дообследования пациентке были рекомендованы проведение мультиспиральной компьютерной томографии (МСКТ) органов шеи, грудной клетки, брюшной полости, малого таза с внутривенным контрастированием, исключение системных и лимфопролиферативных заболеваний, обследование на инфекции (гепатиты В, С, ВИЧ).
Данные серии МСКТ шеи, органов грудной клетки, области молочных желез, органов брюшной полости, забрюшинного пространства и малого таза с внутривенным контрастированием от 29.09.2021: мягкие ткани шеи структурны, объемных образований не найдено, выявлены множественные увеличенные лимфатические узлы поверхностных и глубоких групп, немногочисленные подчелюстные лимфоузлы с двух сторон (до 9 мм), углочелюстные узлы с двух сторон по передней поверхности шеи до 8–9 мм. Над- и подключичные лимфатические узлы не увеличены.
При МСКТ органов грудной клетки были обнаружены немногочисленные лимфатические узлы (паратрахеальные, бифуркационный, правые бронхопульмональные, парааортальные) до 10 мм в диаметре (рис. 2).
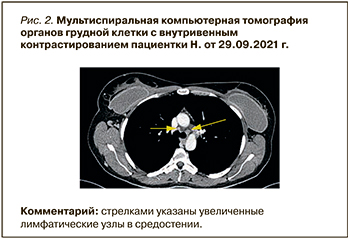
Результаты МСКТ области молочных желез: состояние после аугментационной маммопластики, в молочных железах соотношение жировой и железистой ткани 1/1, патологических изменений не выявлено. Справа дифференцируется имплант под большой грудной мышцей, размерами 10,9×3,9×12,7 см; контуры четкие, ровные, капсула сохранена; содержимое однородное, плотностью +38HU. Слева дифференцируется имплант под большой грудной мышцей, чуть смещенный латерально (асимметрично), размерами 11,7×4,4×12,4 см; контуры четкие, ровные, капсула сохранена; содержимое однородное, плотностью +38HU. В правой подмышечной области лимфоузлы увеличены: до 15 штук 5–22 мм с утолщенной капсулой, субпекторально справа, под малой грудной мышцей; глубоко дифференцируются увеличенные лимфатические узлы 5–10 мм. В левой подмышечной области лимфоузлы также увеличены: до 15 штук от 5–24 мм с утолщенной капсулой, субпекторально слева, под малой грудной мышцей; глубоко дифференцируются увеличенные лимфатические узлы 5–11 мм.
Данные МСКТ органов брюшной полости: печень не увеличена, контуры ее ровные, четкие, структура и плотность (+112 HU) однородные. В левой доле печени во 2-м сегменте на фоне неизмененной паренхимы при ангиографии дифференцируется единичная зона пониженной плотности (+77HU) 5 мм; в 7-м сегменте наблюдаются 3 аналогичные структуры до 10 мм (+81 HU) – атипичные гемангиомы. Селезенка увеличена, селезеночный индекс 720, перфузия селезенки неравномерная, без очаговых изменений, селезеночная вена прослеживается фрагментарно в воротах. Надпочечники без патологических изменений, обычной структуры и размеров. Поджелудочная железа и почки не изменены.
Данные МСКТ органов малого таза: в паховой области с двух сторон дифференцируются увеличенные узлы до 10–22 мм (без ядра). Лимфатические узлы малого таза увеличены: слева в наружной подвздошной области дифференцируется до 8 штук 7–28 мм, справа – до 10 штук 7–28 мм.
Результаты лабораторных методов исследования от 07.10.2021: в клиническом анализе крови выявлены хроническая железодефицитная анемия легкой степени тяжести (гемоглобин минимальный – 103 г/л), периодическое повышение скорости оседания эритроцитов (СОЭ) до 40–50 мм/ч.
В общем анализе мочи периодически определялся мочевой синдром в виде минимальной эритроцитурии, протеинурии (0,2–1,65 г/л) – около 2 лет; суточную потерю белка пациентка не выполнила.
В биохимическом анализе крови обнаружено снижение уровня сывороточного железа в 2 раза, остальные показатели в пределах референсных значений.
В серологическом анализе крови был выявлен высокий титр антител SARS-CoV-2 IgG (более 50 ВГН), антитела к ВЭБ IgG ядерным белкам (22,7 КП); данных в пользу наличия ВИЧ-инфекции, гепатитов В и С, сифилиса, туберкулеза (квантиферроновый тест), вирусных инфекций (герпеса, цитомегаловирусной инфекции) получено не было.
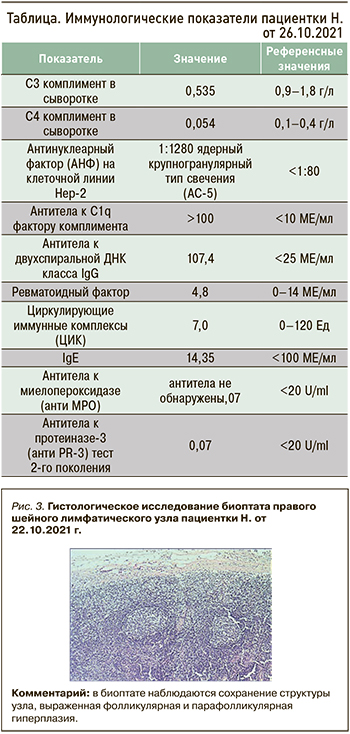
В иммунологическом анализе крови установлены снижение уровня С3 и С4 комплемента в сыворотке, увеличение уровней антител к С1q фактору комплимента, антител к двуспиральной ДНК класса IgG, антинуклеарного фактора на клеточной линии с ядерным крупногранулярным типом свечения. Иммуноблот антинуклеарных антител показал наличие положительного результата аутоантител к специфическому антигену к SS-A (60 кДа); другие антитела обнаружены не были (табл.).
В соответствии с рекомендациями гематолога 15.10.2021 пациентке была выполнена биопсия правой шейной области (эксцизионная). Результаты гистологического и цитологического исследования биоптата правого шейного лимфатического узла: макроскопически 2 лимфатических узла эластичной консистенции, бледно-розового цвета 13×9×5 и 8×4×5 мм. Микроскопически рисунок строения сохранен, в корковом слое расположены вторичные лимфоидные фолликулы с центрами размножения реактивного вида, окруженные четкой зоной мантии. Капсула утолщена, фиброзирована, очагово инфильтрирована нейтрофильными гранулоцитами. Под капсулой вокруг сосудов очагово в паракортикальной зоне найдены мелкие очаги некроза со скоплениями гранулоцитов и гистиоцитов. Также встречаются рыхлые скопления гистиоцитов по типу гранулем (рис. 3 и 4).
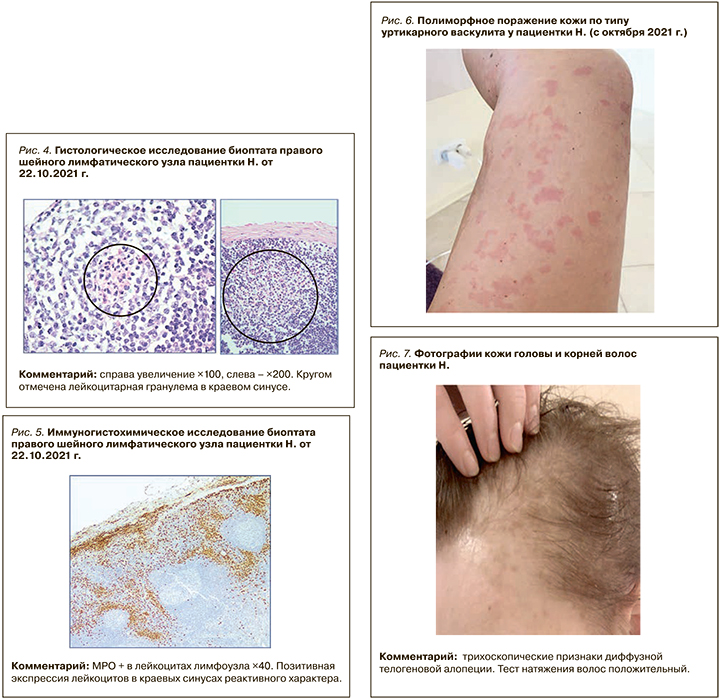
При окраске по Цилю–Нильсену кислотоустойчивая микрофлора не обнаруживалась. В паракортикальной зоне среди лимфоцитов мелкого размера рассеяны крупные клетки активированного типа, немногочисленные эозинофильные гранулоциты, гистиоциты.
При иммуногистохимическом исследовании (ИГХ) результаты окрашивания антителами CD20, CD3, CD5 соответствовали нормальному распределению B- и Т-клеточных зон лимфоидной ткани. В B-клетках центров размножения отмечалась экспрессия CD10, экспрессия Bcl-2 отсутствовала. Абберантная экспрессия циклина D1 не наблюдалась. Экспрессия CD30 отмечалась в активированных клетках паракортикальной зоны; CD68 маркирует гистиоциты, CD123 – скопления плазмоцитоидных дендритических клеток в паракортикальной зоне и под капсулой вблизи очагов некроза, МРО-гранулоциты (рис. 5).
При окрашивании антителами к Mast cell tryptase были выявлены единичные тучные клетки. С тканью биоптата было проведено контрольное ИГХ исследование – неспецифическое окрашивание отсутствовало.
Заключение: в объеме исследованного материала признаки опухолевого роста не обнаружены. В лимфоузлах – картина гранулематозного и очагового гнойно-некротического лимфаденита.
При повторном обсуждении результатов биопсии результаты были расценены как признаки саркоидоподобной гранулемы инородного тела.
С октября 2021 г. у пациентки начал изменяться характер высыпаний: появились диффузное полиморфное поражение кожи по типу уртикарного васкулита (рис. 6), выраженная алопеция (рис. 7).
С учетом отсутствия данных в пользу инфекционного процесса, онкологических и гематологических заболеваний пациентка была осмотрена ревматологом, после чего ей был выставлен диагноз системной красной волчанки подострого течения; активность заболевания была расценена как высокая. Из клинических симптомов отмечались уртикарный кожный васкулит, преходящий ангионевротический отек, синдром хронической усталости, генерализованная лимфаденопатия с саркоидоподобными гранулемами.
Также был установлен иммунологический синдром: положительные антитела к ДНК; положительный антинуклеарный фактор; гипокомплементемия С3–4; повышение антител С1q.
В связи с наличием саркоидоподобных гранулем было высказано предположение о волчаночноподобном синдроме, ассоциированном с силиконом (ASIA-синдроме). Пациентке рекомендована терапия азатиоприном 150 мг/сут и метилпреднизолоном 16 мг/сут на 10 дней с последующим снижением дозы до 2 таблеток. На фоне лечения у пациентки появились жалобы на усиление слабости, сердцебиения, прибавку массы тела, одутловатость лица по типу синдрома Иценко–Кушинга, артралгии. Также она отметила увеличение яркости высыпаний, из-за чего самостоятельно постепенно отменила прием назначенных препаратов. Суммарно принимала назначенные лекарственные средства приблизительно 3 мес.
Спустя 3 мес после полной отмены терапии при повторной МСКТ была выявлена отчетливая положительная динамика в виде уменьшения размеров лимфоузлов в зоне сканирования. Кожные высыпания у пациентки стали появляться реже, постепенно отметился рост волос на коже головы.
В дальнейшем пациентка проводила самостоятельное наблюдение, что не позволило уточнить особенности состояния почек и верифицировать генез протеинурии.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Адъюванты – вещества, стимулирующие, ускоряющие и пролонгирующие иммунный ответ при совместном введении с антигеном. Они используются для синтеза антител и выработки иммунитета в здоровом организме. Свойствами адъювантов обладают органические (холестерин, бактериальные полисахариды и липополисахариды, лецитин, крахмал), неорганические (гидроксид алюминия, фосфат алюминия, хлорид кальция, фосфат кальция и др.) и синтетические вещества (силикон и другие кремниево-органические соединения). Сами по себе адъюванты не иммуногенны и не вызывают синтез «антиадъювантных» антител; они выступают своего рода «депо», способными длительное время сохраняться как внеклеточно, так и внутриклеточно, оказывая стимулирующее действие на иммунокомпетентные клетки [8, 9].
Широкое распространение и применение адъювантов в последнее время обусловливают повышенную частоту развития ASIA. В настоящее время патогенез ASIA недостаточно изучен. Perricone С. et al. [9] считают, что в основе развития этого синдрома лежит цепочка биологических и иммунологических реакций, возникающих в ответ на предшествующее воздействие адъювантов и приводящих к развитию аутоиммунных состояний у лиц с генетической предрасположенностью. Например, длительное воздействие силикона ассоциировано с развитием силиконоза, а воздействие гидроксида алюминия — с макрофагальным миофасциальным синдромом. По мнению авторов [9], адъюванты вызывают аутоиммунные реакции через разные патогенетические механизмы. Так, адъювант (чаще это алюминий) обеспечивает создание эффекта депо и доставку антигенов, их накопление и медленное выведение из места введения. Антиген-презентирующие клетки иммунной системы активируются, обеспечивая медленный постоянный синтез антител плазматическими клетками. Другие адъюванты (по существу, лиганды для паттернраспознающих рецепторов) активируют клетки врожденного иммунитета через Toll-подобные-рецепторы антигенпрезентирующих клеток. Как следствие, индуцируется синтез цитокинов и хемокинов, которые играют ключевую роль в возникновении, распространении и прогрессировании иммунных реакций. В-третьих, активация представителей NOD-like-рецепторов врожденного иммунитета, таких как NLRP3 и NLRC4, вызывает формирование инфламмасом, которые активируют синтез провоспалительных цитокинов, в первую очередь интерлейкинов (ИЛ)-1β и ИЛ-18, обеспечивающих хроническое воспаление. Четвертый путь активации иммунитета осуществляется через прямую активацию главного комплекса гистосовместимости адъювантами. И наконец, адъюванты усиливают и изменяют иммунный ответ организма на антигены. Этот ответ осуществляется двумя субклассами лимфоцитов – Т и В. Th1-лимфоциты обеспечивают главным образом клеточный ответ, который защищает организм от внутриклеточных болезнетворных микроорганизмов. С одной стороны, именно Th1-лимфоциты синтезируют интерферон-γ, который активирует макрофаги и приводит к опсонизации антител В-клетками. Действие цитотоксических лимфоцитов также направлено на устранение инфицированных клеток. С другой стороны, Th2-лимфоциты отвечают за гуморальный иммунитет и устранение внеклеточных болезнетворных микроорганизмов. Этот субкласс лимфоцитов синтезирует провоспалительные цитокины, в частности ИЛ-4, которые способствуют синтезу антител В-клетками. Этот механизм приводит к активации нейтрофилов и фибробластов.
В связи с вышесказанным вполне закономерным выглядит обнаружение нейтрофильно-лимфоцитарной инфильтрации в лимфатических узлах нашей пациентки. Суммарно в развитии аутоиммунных реакций, вызванных адъювантами, следует выделять следующие звенья: повреждение иммунной системы «хозяина»; поликлональную активность В-лимфоцитов ; воздействие на клеточный иммунитет G; воздействие на регуляторные клетки иммунитета; воздействие на вирус-индуцированные антитела; молекулярную мимикрию; активацию иммунного ответа на один эпитоп в процессе иммунного ответа на другой; распространение эпитопов; антиидиопатическую сеть; изменение антигенов хозяина; экспрессию HLA-групп антигенов (семейных антигенов); модификацию поверхностей антигенов; индукцию новых антигенов; взаимодействие с Toll-подобными рецепторами; транслокацию антигенов; выброс воспалительных цитокинов.
Диагностика синдрома ASIA основана на больших и малых критериях, сформулированных Shoenfeld Y. и Agmon-Levin N. [1], с учетом наиболее типичных проявлений заболевания. Большие критерии включают внешние факторы (инфекции, вакцинации, силикон); предшествующие клиническим симптомам типичные клинические проявления: миалгию, миозит и мышечную слабость, артралгию или артриты, синдром хронической усталости (неэффективный сон, нарушения сна), неврологические нарушения, преимущественно связанные с демиелинизацией нервных волокон, нарушения интеллекта и памяти, лихорадку, сухость во рту. Устранение повреждающего фактора приводит к ремиссии заболевания.
К малым критериям ASIA относят появление аутоантител или антител к предположительному адъюванту, другие клинические проявления (синдром раздраженной кишки), специфические HLA (HLA DRB1, HLA DQB1), признаки аутоиммунного заболевания (системной красной волчанки, ревматоидного артрита, системной склеродермии, васкулитов и др.)
Первоначальные критерии ASIA были позднее дополнены Zafrir Y. et al. [10] на основании наблюдения 93 пациентов, предъявлявших жалобы на нервно-психические расстройства, патологию опорно-двигательного аппарата, желудочно-кишечного тракта и постоянную усталость. По данным анализа 300 случаев установленного ASIA, было выявлено, что среди аутоиммунных заболеваний у данной группы пациентов встречались фибромиалгия (15,6%), системная красная волчанка (13%), васкулиты (5,3%) [7]. Таким образом, выявленный у нашей пациентки антительный ответ после введения множественных адъювантов соответствует общему представлению об индуцированной системной красной волчанке.
Среди васкулитов, сопутствующих ASIA, описаны гигантоклеточный артериит, реже – ANCA-васкулит, болезнь Бехчета, болезнь Шенлейна–Геноха. Лабораторные исследования позволили обнаружить у 155 (51,7%) пациентов присутствие антинуклеарных антител (ANA), а именно anti-SSA, anti-Sm, anti-dsDNA, anti-SSB. У 4 пациентов были найдены антифосфолипидные антитела. Ревматоидный фактор был позитивным у 8% пациентов, а anti-CCP выявлен только у одного больного. Описаны случаи развития ASIA с проявлениями системной красной волчанки, ревматоидного артрита, склеродермоподобного синдрома, а также гранулематозного васкулита, похожего на гранулематоз с полиангиитом [11–13]. Следовательно, ASIA часто протекает под маской различных ревматических заболеваний. Интересно, что в описанных в литературе случаях, а также в нашем наблюдении определяется сочетание аутоиммунного процесса с В-клеточной антительной активацией и наличием саркоидоподобных гранулем в коже или лимфатических узлах, что не встречается при классической, «неиндуцированный» системной красной волчанке.
Наиболее распространенной причиной развития ASIA является силикон. Это кремний-органический каучук с молекулярной массой 28 Да, который принято считать инертным материалом. Изделия из силикона широко применяются в различных сферах медицины. Самый распространенный пример его использования силикона в медицине – имплантаты грудных желез, которые впервые начали устанавливать в 60-е гг. XX в. при реконструктивных операциях. Все силиконовые соединения составлены из неорганической кремний-кислородной цепи -Si-O- Si-O- Si-O- Si-O-… К атомам кремния в этой цепи крепятся боковые органические группы. Меняя длину основной кремний-кислородной цепи, варьируя боковыми группами и перекрестными связями, получают силиконы с различными свойствами. Добавим, что диоксид кремния, образующийся в результате окисления силикона, также дает адъювантный эффект [14].
Исследования на моделях животных (мыши) с коллаген-индуцированным артритом и экспериментальной волчанкой, выполненные Schaefer C. et al. [15, 16], показали взаимосвязь присутствия имплантированного силикона с повышением уровня ИЛ-2. У животных с волчанкой отмечали повышение уровня антител к ДНК. Установлено, что имплантация силикона стимулирует выработку специфических антител, а наличие предшествующего коллаген-индуцированного артрита способствует еще большему повышению титра антител к силикону. Эти данные позволили сделать вывод, что присутствие силикона может провоцировать и обострять течение аутоиммунных заболеваний. Однако количество циркулирующих биологически активных веществ не оказывало значительного влияния на клиническое течение индуцированных заболеваний у животных.
Диагностика и обсуждаемые патогенетические механизмы ASIA неоднозначны. Ameratunga R. et al. [17] продемонстрировали в эксперименте неточности в диагностике этого синдрома, вследствие которых он может быть выявлен если не у всего населения, то по крайней мере у всех больных с аутоиммунными нарушениями. Авторы указывают в своем обзоре на методологические, аналитические и этические недостатки изучения ASIA в эксперименте. В связи с этим они призывают к введению моратория на изучение синдрома на животных, пока не будет получено независимое заключение об эквивалентности аутоиммунных экспериментальных моделей и ASIA человека.
Окись кремния в качестве адъюванта способна вызывать не только силикоз легких, но и ASIA, который может проявляться разными ревматическими заболеваниями [18]. Применение продуктов кремния (силиконовых протезов и медицинских консумативов) может приводить к разнообразным аутоиммунным нарушениям – силикозу, асбестозу, талькозу, силиконовым гранулемам и др. Поэтому в англоязычной литературе начали применять термин «силиконозы» для обозначения гетерогенной группы болезней, обусловленных контактом с кремнием и его производными. Захват силиконовых частиц макрофагами вызывает активацию последних и усиление синтеза провоспалительных цитокинов (ИЛ-1β, ИЛ-6 и др.). В результате этого возрастает продукция активных форм кислорода. Тем не менее силикон не может быть разрушен макрофагами, из-за чего происходят их апоптоз и дальнейшее выделение частиц силикона во внеклеточное пространство. Вследствие продолжающейся гибели макрофагов продуцируется избыточное количество ИЛ-17, приводящее к рекрутированию нейтрофилов в окружающих тканях. В лимфатических узлах силиконовые частицы инициируют хроническую активацию Т-клеток, сопровождающуюся выделением иммуноглобулинов E и G1 [19]. Выявленная нами гистологическая картина в лимфатических узлах пациентки полностью согласуется с представленными выше представлениями об индуцированной системной красной волчанке.
К побочным эффектам применения силиконовых протезов относят рубцовые контрактуры, местную кожную воспалительную реакцию, регионарную лимфаденопатию, формирование силиконовых гранулем и развитие саркоидоза, кожных силиконовых гранулем и др. Отмечается, что наиболее выраженные последствия пластических операций наблюдаются в случае применения грудных протезов, содержащих силиконовый гель. Ремиссия данных состояний достигалась путем удаления имплантатов [20, 21].
Установлено, что даже при отсутствии разрывов имплантата силикон может диффундировать в окружающие ткани. Проникновение силикона в ткани увеличивается со временем, усиливая при этом воспалительно-иммунный ответ вокруг перисиликоновой капсулы. В практике пластических хирургов хорошо известно такое осложнение, как появление подкожных узлов, что связано с развитием локальной гранулематозной реакции (силикономы). Хотя силиконовые имплантаты включены в критерии Shoenfeld Y. et al в 2011 г. [1] как причина развития ASIA, van Nunen S. et al. [22] еще в 1982 г. описали 3 клинических случая реакции на силиконовые протезы груди, предположив увеличение риска развития аутоиммунных заболеваний после подобных вмешательств. С тех пор в медицинской литературе описан ряд клинических случаев ревматоидного артрита, болезни Шегрена, системной красной волчанки и системного васкулита у пациенток, перенесших установку силиконовых грудных имплантатов [23–26].
В условиях специализированной клиники Cohen Tervaert J. и Kappel R. [18] проанализировали влияние силиконовых имплантатов на иммунную систему 32 пациентов, каждый из которых подходил под критерии ASIA. У 53% из них были диагностированы системные аутоиммунные заболевания, 47% имели иммунодефицит. Развитие жалоб и клинических симптомов происходило длительно, что предположительно было вызвано изнашиванием и/ или повреждением импланта. Многие пациенты, участвовавшие в исследовании, имели не только аутоиммунные заболевания, но и гипогаммаглобулинемию или IgG-дефицит. Данная особенность была подтверждена Csako G. et al. [27].
У пациентов с грудными имплантатами силикон может стимулировать развитие аутоиммунных заболеваний во многом за счет дисрегуляции гуморального иммунного ответа. В итоге Cohen Tervaert J. и Kappel R. подчеркивают [28–30], что импланты сами по себе безвредны, но перед их установкой необходимо тщательное обследование оперируемых для исключения возможных противопоказаний, которые впоследствии будут определяющими в развитии ASIA.
Также показано, что постоянная стимуляция В-лимфоцитов силиконом может приводить к развитию псевдолимфомы, предшествующей неходжкинской лимфоме. Необходимо заметить, что эпидемиологические данные не являются показательными в вопросе увеличения частоты встречаемости заболеваний соединительной ткани у этой группы пациентов [23, 31]. Эти данные имеют серьезные ограничения прежде всего из-за малых размеров выборки. Более того, в большинстве исследований оценивались последствия сразу после установки грудных имплантатов, что могло привести к неправильным выводам.
Сложность диагностики индуцированных аутоиммунных заболеваний заключается в том, что они развиваются через несколько месяцев/лет после имплантации. Так, Cohen Tervaert J. и Kappel R. утверждают, что между пластической операцией и развитием характерной симптоматики должно пройти определенное время (вплоть до нескольких десятков лет), так как за это время силикон мигрирует из места основной локализации и проявляет себя как адъювант [1, 11, 32, 33]. При этом адъювантный эффект со временем усиливается. Добавим, что большинство силиконовых протезов с годами стареет. Силикон диффундирует и накапливается в лимфатических узлах, легких, печени и соединительной ткани [34, 35]. Более того, при замене силиконовых протезов груди на солево-целлюлозно-смешанные имплантаты большинство пациенток отметили значительное уменьшение симптоматики [36]. В свою очередь Brown S. et al. обнаружили [35], что дефекты грудных имплантатов и появление экстракапсулярного силикона связаны с более высоким уровнем риска развития аутоиммунных состояний.
В медицинской литературе широко описаны случаи осложнения и обострения ревматологических заболеваний, наблюдаемые после вакцинации [6, 10, 37, 38]. В ASIA включен и синдром с применением гидроксида алюминия [10, 38]. По данным McGarvey P. et al. [39], синдром Гийена–Барре выступает наиболее частым поствакцинальным осложнением и ассоциирован с введением вакцин против гриппа (H1N1) и гепатита B.
Суммарно в литературных источниках активно обсуждаются 5 видов аутоиммунных нарушений при введении адъювантов: силиконозы, макрофагальный миофасциальный синдром, синдром Персидского залива и синдром «больных зданий», поствакцинальный синдром. Во всех случаях развитию аутоиммунного воспаления предшествует контакт с внутренними или внешними триггерными факторами (адъювантами) нарушения иммунитета. ASIA ассоциирован с индивидуальной генетической предрасположенностью, вероятно, связанной с носительством HLA-DRB1*01 или HLA-DRB4. Механизмы индукции аутоиммунитета могут быть разными. При этом в тканях присутствуют морфологические признаки иммунного воспаления – лимфогистиоцитарная инфильтрация, гранулематозное воспаление, склеродермоподобные изменения. Характерной особенностью является регрессия клинических, лабораторных и морфологических проявлений после удаления адъюванта.
Большое число лиц, которые с косметической целью прибегают к установке имплантов и введению адъювантов, делает крайне актуальным вопрос изучения индуцированного аутоиммунного синдрома в клинике внутренних болезней. Описанное нами появление СКВ-подобных изменений и типичных гранулематозных изменений в лимфатических узлах после имплантации силикона и введения внутрикожных филлеров у наблюдавшейся пациентки свидетельствует о клинической значимости проблемы для практического врача-ревматолога. С учетом отказа пациентки от удаления имплантов и медикаментозного лечения, несмотря на полное понимание ей рисков указанного решения для здоровья, мы имеем возможность наблюдать естественное течение процесса после короткой схемы индукционной терапии. Указанное описание является фрагментом работы, инициированной с целью лучшего понимания особенностей ASIA.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Мы наблюдали женщину, у которое произошло формирование системной красной волчанки с уртикарным синдромом и саркоидоподобными гранулемами как варианта ASIA после имплантации силиконовых имплантов грудных желез и проведения множественных внутрикожных инъекций адъювантов. Сложные патогенетические механизмы формирования иммунного ответа после введения адъювантов в ткани человека требуют внимательного изучения каждого из подтвержденных случаев ASIA с целью разработки оптимальных подходов к медицинскому ведению лиц с развившимися индуцированными аутоиммунными синдромами.
Авторы выражают благодарность коллегам за помощь в подготовке статьи, а также врачу Н.И. Лубинской, предоставившей клиническое портфолио для публикации клинического случая (с разрешения пациентки).


