ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Распространенность сахарного диабета (СД) во всем мире растет с угрожающей скоростью. Число человек с этим заболеванием среди взрослого населения в России, по данным IDF (International Diabetes Federation), в 2017 г. составило 8 455 300 человек [1]. Что же касается распространенности сахарного диабета 1 типа (СД1) в России, то она, по данным Федерального регистра сахарного диабета от 31.12.2016, составила 199 298 человек в возрасте старше 18 лет, за год было зарегистрировано 5430 новых случаев СД1 среди взрослого населения [2].
У пациентов с СД1 выявляют следующие хронические осложнения: диабетическую невропатию у 33,6%, диабетическую ретинопатию (ДР) – у 27,2%, диабетическую нефропатию (ДН) – у 20,1%, артериальную гипертензию – у 17,1%, диабетическую макроангиопатию – у 12,1%, синдром диабетической стопы – у 4,3%, ишемическую болезнь сердца – у 3,5%, цереброваскулярные нарушения – у 1,5%, инфаркт миокарда – у 1,1% пациентов [2]. В связи с декомпенсацией ежегодно госпитализируют от 10 до 30% от общего числа пациентов с СД1.
Крайними формами декомпенсации СД являются диабетический кетоацидоз (ДКА) и гипергликемический гиперосмолярный синдром (ГГС). Их патогенез связан с абсолютным или относительным дефицитом инсулина и повышенными уровнями контринсулярных гормонов, которые приводят к изменению метаболизма углеводов, жиров, белков, а также к развитию различной степени осмотического диуреза и обезвоживания, кетоза и кетоацидоза [3]. Причинами декомпенсации СД являются недостаточная терапия инсулином (снижение дозы или неадекватная схема введения инсулина), инфекции (чаще всего пневмонии или инфекции мочеполового тракта) [4, 5], инфаркт миокарда, цереброваскулярные нарушения, легочная эмболия, панкреатит, злоупотребление алкоголем [5] и наркотиками [6, 7], прием некоторых лекарственных средств [8]. Имеются сообщения о случаях развития кетоацидоза как первичного проявления акромегалии [9].
Другое жизнеугрожающее состояние, гипогликемическую реакцию, может вызвать нерациональная инсулинотерапия, нарушение режима питания и физической активности. У пациентов с повторными эпизодами гипогликемии риск смертности увеличен в 6 раз по сравнению с пациентами, которые не испытывали тяжелых гипогликемий. У данных пациентов повышен риск развития ишемического инсульта головного мозга, инфаркт миокарда, нарушений когнитивных функций и потери зрения [10]. Причинами развития гипогликемии могут стать некорректная по отношению к приему пищи или физической нагрузке доза вводимого инсулина, пропуск приема пищи, снижение синтеза эндогенной глюкозы на фоне приема алкоголя, снижение массы тела и гастропарез [11, 12].
Опыт многих международных исследований показал, что высокая информированность пациентов о контроле и лечении своего заболевания помогает значительно снизить риск развития декомпенсации, свести к минимуму вероятность возникновения осложнений диабета [14], улучшить психологическое состояние и повысить экономическую эффективность лечения [15]. Было показано, что интенсивный гликемический контроль и принятие верных решений пациентами, прошедшими обучение в школе диабета, снижает риск развития ДР в 4, а раннего поражения почек – в 3 раза. Регулярный самоконтроль уровня гликемии и артериального давления у пациентов позволяет снизить риск развития фатальных сердечно-сосудистых осложнений и потери зрения более чем в 3 раза [14]. Плохая ориентированность пациентов в своем заболевании и страх перед развитием гипогликемии влияют на гликемический контроль и увеличение частоты ошибок инсулинотерапии у пациентов с СД1, причем связь между обучением и гликемическим контролем была независимой от стажа СД [16].
В нашем исследовании было уделено внимание анализу причин декомпенсации СД1 и статистики обучения пациентов в школе диабета.
МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДЫ
Мы провели ретроспективный анализ 218 историй болезней пациентов, госпитализированных в отделение реанимации и интенсивной терапии (ОРИТ) ГБУ «Городская клиническая больница им. В.П. Демихова» Москвы в связи с декомпенсацией СД1. Среди выбранных для исследования пациентов были 99 женщин и 119 мужчин (средний возраст 28,6±9,9 и 28,8±8,7 года соответственно). У 55 пациентов СД1 был диагностирован впервые. У пациентов, уже имеющих СД, стаж составил от 3 мес до 49 лет.
Были проанализированы следующие данные: основное заболевание и его осложнения; причины декомпенсации СД; информация о посещении школы диабета; данные физикального осмотра, общего и биохимического анализов крови, общего анализа мочи, кислотно-основного состояния (КЩС); уровни гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c), микроальбумина в моче, скорость клубочковой фильтрации. Статистический анализ данных производился с помощью пакета программного обеспечения Statistica 8.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ
По причинам декомпенсации СД1 пациенты были разделены на 3 группы: пациенты, декомпенсация которых произошла на фоне нарушения рекомендаций по образу жизни (n=104); пациенты, декомпенсация который произошла из-за ошибок инсулинотерапии (n=53); пациенты с впервые выявленным СД1 (n=55).
Средний возраст пациентов в первой группе составил 28,6±8,9 года. К нарушению рекомендаций по образу жизни были отнесены следующие причины: прием алкоголя, наркотиков, пропуск приема пищи, психоэмоциональный стресс, инфекция, беременность, травма, отсутствие самоконтроля глюкозы. Первое место по частоте встречаемости заняло нарушение диеты (36,5%), второе – декомпенсация на фоне инфекции (21,2%), третье (16,3%) – прием алкоголя и психоэмоциональный стресс.
Средний возраст пациентов во второй группе составил 30,7±14,1 года. К ошибкам инсулинотерапии были отнесены пропуск введения дозы инсулина, неэффективность выбранной дозы инсулина, неисправность инсулиновой помпы, нарушение техники введения инсулина. Ведущими причинами декомпенсации были пропуск инъекции инсулина (50,9%) и неэффективность выбранной дозы инсулина (41,5%). У шестерых пациентов указания на причину декомпенсации обнаружено не было.
СД1 был диагностирован впервые у пациентов в возрасте от 18 до 58 лет. В 58,2% случаев наблюдалась его манифестация на фоне инфекционного заболевания, в 20% случаев – на фоне сильного психоэмоционального стресса, в остальных случаях причина была неизвестна.
В своем исследовании мы рассматривали следующие острые осложнения СД: ГГС, кетоз, ДКА, гипогликемическая реакция.
ГГС – острая декомпенсация СД с резко выраженной гипергликемией (уровень глюкозы плазмы – ГП >35 ммоль/л), высокой осмолярностью плазмы (>320 мосмоль/л) и резко выраженной дегидратацией при отсутствии кетонемии (<3 ммоль/л) и ацидоза (pH >7,3; бикарбонат >15 ммоль/л) [17, 18]. ГГС был диагностирован у 37 пациентов.
ДКА был диагностирован у 75 пациентов со следующими показателями: ГП >13 ммоль/л, кетонемия >5 ммоль/л, кетонурия ≥3,8 ммоль/л, метаболический ацидоз (pH ≤7,3; бикарбонат ≤18 ммоль/л, анионная разница >10–12 ммоль/л). При этом степень нарушения сознания бывает различной [18, 19].
Кетоз был диагностирован у 96 пациентов. Критерии для постановки диагноза аналогичны ДКА, но нарушения КЩС не выявляются (pH >7,3 и уровень бикарбонатов сыворотки крови >15 ммоль/л) [20].
С гипогликемической реакцией были госпитализированы 10 пациентов. У 3 пациентов гипогликемия была спровоцирована пропуском приема пищи, у 3 – ошибочной коррекцией дозы инсулина, у 4 пациентов причина выявлена не была. Критерием постановки диагноза был уровень ГП <3,9 ммоль/л [20, 21]. При этом степень нарушения сознания была различна: от спутанности до гипогликемической комы.
В группе пациентов с нарушением образа жизни наиболее частой формой декомпенсации был ДКА (46,2%), в группе пациентов с ошибками инсулинотерапии почти с равной частотой развивались ГГС (32,1%) и ДКА (34%). Впервые выявленный СД1 в 80% случаев манифестировал кетозом.
 Одним из факторов, лежащих в основе развития поздних осложнений СД, является уровень гликемии, поэтому крайне важно достижение индивидуальных для каждого пациента целевых значений HbA1c. В нашем исследовании только у 1,8% пациентов это значение было достигнуто, у остальных пациентов данный показатель варьировался в пределах 10,3±1,7%. По результатам исследования, частота диагностирования хронических осложнений составила 81,6%. Очевидно, что больший процент осложнений, чем в целом по популяции, обусловлен в том числе и неконтролируемым течением заболевания.
Одним из факторов, лежащих в основе развития поздних осложнений СД, является уровень гликемии, поэтому крайне важно достижение индивидуальных для каждого пациента целевых значений HbA1c. В нашем исследовании только у 1,8% пациентов это значение было достигнуто, у остальных пациентов данный показатель варьировался в пределах 10,3±1,7%. По результатам исследования, частота диагностирования хронических осложнений составила 81,6%. Очевидно, что больший процент осложнений, чем в целом по популяции, обусловлен в том числе и неконтролируемым течением заболевания.
ДН была диагностирована у 19,3% пациентов. У 17 пациентов была выявлена хроническая болезнь почек (ХБП) C1, у 18 – ХБП С2, у 2 – С3а, у 4 – С3б. Было обнаружено, что частота выявления ДН была выше в группе пациентов с ошибками инсулинотерапии (p <0,05). ДР обнаруживалась при офтальмологическом осмотре в 29,8% случаев. При этом у преобладающего числа пациентов была непролиферативная форма (n=48), у 5 пациентов была диагностирована препролиферативная стадия, а у 12 – пролиферативная. Диабетическая периферическая ангиопатия (ДПА) выявлена у 56% пациентов, а периферическая симметричная полиневропатия – у 79,4%.
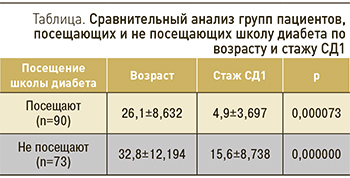
Обучение людей с СД является важным и неотъемлемым компонентом лечения диабета, который должен быть доступным для всех. По данным IDF, меньше чем половина пациентов СД и меньше чем 1 из 4 родственников больных имеют доступ к обучающим программам [22]. А те пациенты, которые имеют возможность получать образование в школе диабета, зачастую пренебрегают ею. В связи с этим был произведен анализ посещаемости школы диабета среди пациентов, вошедших в выборку. Среди пациентов с СД1 55,2% посещают школу диабета, а 44,8% – нет. Было выявлено достоверное различие в этих двух группах пациентов по возрасту и стажу заболевания (см. таблицу), различия по полу выявлено не было. Также были выявлены корреляционные связи между стажем СД1 и посещением школы диабета (r=-0,6245; p <0,05) и между возрастом пациентов и посещаемостью школы диабета (r=- 0,31; p <0,05). Таким образом, школу диабета в основном посещают более молодые пациенты и/или пациенты, имеющий меньший стаж СД (в среднем меньше 5 лет).
Мы предполагаем, что обучение пациентов и их активное участие в проводимом лечении позволит успешнее контролировать уровень гликемии и способствовать снижению риска развития хронических осложнений. При проведении сравнительного анализа среди пациентов, посещающих и не посещающих школу диабета, в отношении хронических осложнений СД было выявлено достоверное различие: среди пациентов не посещающих школу диабета в 2 раза чаще была диагностирована ДР, а ДПА выявлялась чаще на 25%, чем в группе пациентов, посещающих школу диабета. Однако полученные результаты также могут быть объяснены тем, что в группе не посещающих пациенты старше и стаж СД1 у них больше. Были выявлены корреляционные связи между стажем СД1 и ДР (r = 0,56; p <0,05); между стажем СД1 и ДПА (r = 0,31; p <0,05); между стажем СД1 и ДН (r = 0,30; p <0,05). Полученные результаты закономерны, но следует обратить внимание, что наиболее чувствительной к длительности течения заболевания оказалась патология сетчатки. Для пациентов с большим стажем СД снижение остроты зрения является колоссальной проблемой, значительно ухудшающей качество жизни.
Далее были проанализированы связи между посещаемостью школы диабета и ДР (r=-0,29); между посещением школы диабета и выявлением ДПА (r=-0,27). Выявленные корреляционные связи гораздо слабее, нежели между данными осложнениями и длительностью течения СД, однако на их наличие стоит обратить внимание, так как в отличие от стажа заболевания обучение пациентов в школе диабета является модифицируемым фактором риска поздних осложнений. Модернизация и совершенствование программ обучения, несомненно, является эффективным способом улучшения результатов лечения СД и его глобального прогноза. Дальнейшие детальные исследования и анализ клинической практики смогут подтвердить или опровергнуть наши выводы о важнейшей роли обучения пациентов СД1, что приведет к уменьшению числа госпитализаций, гипогликемических состояний, уменьшит процент отдаленных осложнений, позволит достичь стабильности и управляемости метаболическими параметрами.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
На основании полученных данных мы обратили внимание на то, что отсутствие систематического обновления знаний, недостаточное обучение пациентов с СД1 увеличивает частоту развития острых и хронических осложнений. Однако выявленная корреляция не объясняет, почему декомпенсация состояния развивалась у пациентов, которые по полученным данным посещали школу диабета.
Нам представляется, что данный факт может объясняться несколькими причинами. Так, было установлено, что количество и качество усвоения информации во многом зависит от формы подачи материала, многопрофильности обучения, индивидуального подбора программ обучения для пациентов, имеющих различный стаж диабета, возраст, пол, социально-экономическое положение, тип диабета, а также наличие просторного комфортного помещения для обучения [13]. Ошибками классических схем обучения пациентов являются:
- повторяющийся материал, который полезен пациентам с впервые выявленным СД, но снижает желание пациентов со стажем посещать данные курсы;
- избыточная интенсивность и длительность каждого занятия влечет за собой снижение внимания и неустойчивость выносимых с курса знаний;
- форма подачи материала в основном в виде лекций [13].
Эти проблемы можно решить разделением курсов для пациентов с различным стажем и результатом предыдущего обучения, уменьшением времени одного занятия и увеличением их числа для повышения качества получаемых знаний, а также возможности контроля полученных умений, внедрением в систему образования интерактивных методов преподавания, дискуссий и бесед с использованием большого количества визуального материала, печатной продукции с краткими рекомендациями.
Недостатки классических школ диабета могут восполнить технологические преимущества телемедицины и создание дистанционных платформ обучения пациентов [15]. Сервисы телемониторинга успешно протестированы и работают в странах Европы [22], Индии [23], Бразилии [24]. В некоторых медицинских центрах России внедрена система телемониторинга, однако ее распространение пока не повсеместное [25, 26]. Данные технологии направлены на сбор информации об уровне гликемии, артериального давления, принимаемых препаратах и их дозах, приемах пищи, физической активности, сопутствующей патологии с помощью смартфонов со встроенным глюкометром и специальной программой по обработке этой информации и ее передаче лечащему врачу. Новые дистанционные технологии позволят врачу структурировано получать полную информацию о состоянии пациента, течении его заболевания и поможет вовремя скорректировать терапию и рекомендации. Сводная статистика по реальной клинической практике поможет эффективно выявлять пациентов, входящих в группы риска, и осуществлять разработку индивидуализированных программ по их ведению.
Интересно, что пациенты, достигшие целевого уровня HbA1c, условно «здоровые», воспринимают обучение охотнее и более эффективно применяют полученные знания, выполняют рекомендации, чем пациенты с декомпенсацией [27]. Это указывает на вклад обучения в понимание пациентами своей роли, уверенности в своих возможностях управлять болезнью. Данный аспект замыкает порочный круг: декомпенсация СД происходит из-за отсутствия необходимых знаний и умений, а сама декомпенсация снижает желание и возможность их получения. В такой ситуации необходимо искать альтернативные подходы к обучению пациентов.
В эру информационных технологий закономерным является существование не только традиционных школ диабета, врачей-консультантов, но и дистанционных программ обучения. Международной федерацией диабета (IDF) была разработана онлайн-платформа D-NET, которая представляет собой форум, объединяющий специалистов со всего мира, и позволяет обсуждать новейшие разработки в области лечения, ухода за пациентами с диабетом и обучения [22]. Интегральный опыт и возможность в любой момент обратиться за мнением другого специалиста повышает эффективность назначаемого лечения. В нашей стране пока подобной платформы нет, однако уже началось внедрение телемедицинских систем для совместной работы специалистов разных организаций для решения трудных лечебно-диагностических задач и обмена опытом [28].
IDF были разработаны несколько онлайн-программ для обучения пациентов, в ходе которых они могут обучаться с помощью видеоуроков, получать консультации разнопрофильных специалистов и делиться друг с другом опытом самоконтроля [22]. В нашей стране предпринимаются попытки разработать похожую дистанционную обучающую платформу для пациентов с СД, однако пока данный проект не получил финансовой поддержки [29]. Дистанционное обучение должно также решить проблему обучения и консультирования пациентов, живущих на расстоянии от крупных городов.
Таким образом, низкий процент компенсации среди пациентов с СД зависит как от регулярности и возможности получения знаний о своем заболевании, так и от качества организации обучения. Внедрение в ближайшем будущем дистанционных методов обучения сможет улучшить текущее положение дел.
ВЫВОДЫ
Согласно полученным данным, ведущей причиной декомпенсации СД1, приведшей к госпитализации, является плохая ориентированность пациентов в своем заболевании. Почти половина обследованных пациентов с СД1 не обновляют свои знания, не посещают периодически школу диабета. Это объясняет низкий уровень знаний пациентов об особенностях инсулинотерапии в различных условиях, плохую приверженность лечению и нарушение рекомендаций врача. Пациенты должны принимать активное участие в управлении своим заболеванием, осуществлять регулярный самоконтроль и при необходимости проводить коррекцию доз инсулинотерапии. Пациенты должны быть хорошо информированы о возможных осложнениях в органах-мишенях, вызванных нескорректированной гликемией, и осуществлять их профилактику, получить все необходимые современные знания о тактике лечения своего заболевания. Содействие со стороны пациента, соблюдение рекомендаций при грамотно подобранной инсулинотерапии может помочь уменьшить число больных, госпитализированных в ОРИТ, и значительно улучшить прогноз в отношении хронических осложнений.
Мы полагаем, что регулярное посещение школы диабета позволит минимизировать риск развития осложнений СД1. В связи с выявленными закономерностями рекомендуется посещение школы в соответствии с алгоритмами специализированной медицинской помощи. Повышение приверженности пациентов и эффективности обучения может быть достигнуто введением новых методов образовательных программ по управлению СД.



