Фибромиалгия (ФМ) – это комплексное расстройство с распространенной хронической мышечно-скелетной болью, депрессией, нарушением сна, утренней скованностью, повышенной утомляемостью [1–6, 20, 24, 30]. Для болезни характерно наличие на теле болезненных участков, так называемых болевых точек. Женщины более подвержены развитию этой болезни, чем мужчины. ФМ – заболевание, попадающее в поле зрения не только ревматологов, неврологов, специалистов по болевым синдромам, но и врачей общей практики. По данным статистики, ФМ страдают 2–5% населения. Однако, несмотря на распространенность, диагноз «фибромиалгии» в мире, в частности в России, ставится крайне редко. Это связано с необычными проявлениями болезни, недостаточной информированностью врачей и отсутствием четких диагностических критериев.
История
Хотя термин «фибромиалгия» введен сравнительно недавно, это состояние уже давно описано в научной литературе. Еще в 1904 г. W. Gowers использовал понятие «фиброзит». Во второй половине ХХ в. одни врачи считали, что фиброзит является типичной причиной развития болей в мышцах, другие полагали, что он представляет собой следствие «напряжения» или «психогенного ревматизма», а сообщество ревматологов и вовсе не принимало во внимание эту патологию.
Современная концепция ФМ была создана H.A. Smythe и Н. Moldofsky в середине 1970-х гг. Они и ввели в оборот новый термин «фибромиалгия» [26]. Авторы определили наличие локальной повышенной чувствительности, так называемые болевые точки (tender points), как характерный симптом ФМ. Кроме того, они установили, что у пациентов с ФМ часто наблюдаются нарушения сна.
Следующим этапом исследования ФМ стала разработка диагностических критериев заболевания Американской коллегией ревматологии (АКР), которые были опубликованы в 1990 г. [32]. Существенный прогресс в изучении ФМ был сделан после того, как исследователи пришли к выводу, что это состояние не обусловлено поражением или воспалением периферических тканей. Поэтому все усилия были направлены на изучение центральных механизмов патогенеза заболевания.
 Этиология и патогенез
Этиология и патогенез
Одним из важнейших механизмов формирования хронической боли при ФМ служит феномен центральной сенситизации [28, 30]. Он характеризуется тем, что после длительной периферической ноцицептивной стимуляции остается определенный уровень возбуждения в центральных сенсорных нейронах заднего рога, что поддерживает боль даже при отсутствии в дальнейшем периферической патологии. Однако в многочисленных исследованиях продемонстрировано, что центральная сенситизация может развиваться при нарушениях в центральной нервной системе (ЦНС) без периферического повреждения.
Таким примером служит как раз ФМ. То, что боль может быть результатом изменений в ЦНС и «реальным» нейробиологическим явлением, многим кажется маловероятным. Нередко пациентов с ФМ, у которых не обнаруживают периферических изменений, врачи рассматривают как симулянтов или больных истерией. Некоторые врачи в ситуациях, когда они не могут найти органической причины боли, предпочитают использовать такие диагностические ярлыки, как «психосоматические и соматоформные расстройства». Однако сегодня убедительно показано, что центральная сенситизация, а также нарушение нисходящего (норадренергического и серотонинергического) ингибиторного контроля боли возникают при ФМ не вследствие периферических изменений в мышцах, фасциях, связках или соединительной ткани, а в результате нейродинамических нарушений в ЦНС у лиц с генетической предрасположенностью под воздействием многочисленных стрессовых (физических и психических) факторов [20, 24, 28, 30]. К таким факторам относятся:
- периферические болевые синдромы;
- инфекции (парвовирус, вирус Эпштейна–Барр, клещевой боррелиоз, Q-лихорадка);
- физическая травма (например, дорожно-транспортное происшествие);
- психическое напряжение/эмоциональный стресс;
- гормональные нарушения (гипотиреоз);
- медикаменты;
- вакцины.
Исследования ФМ последних двух десятилетий показали, что болевой порог зависит от степени дистресса. Многие психологические факторы, такие как сверхнастороженность, мнительность, катастрофизация, внешний локус контроля боли, могут играть важную роль в степени выраженности симптомов ФМ. Специальные исследования показали, что у пациентов с ФМ снижена серотонинергическая и норадренергическая активность. Так, при исследовании цереброспинальной жидкости (ЦСЖ) у пациентов с ФМ выявлено снижение уровня серотонина и его основного метаболита – 5-гидроксииндолуксусной кислоты, а также 3-метокси-4-гидроксифенилгликоля – активного метаболита норадреналина [13]. В подтверждение этих данных говорит тот факт, что препараты, которые одновременно повышают уровни серотонина и норадреналина (трициклические антидепрессанты, дулоксетин, милнаципран, трамадол), обладают эффективностью в лечении ФМ. Кроме того, при ФМ определяется повышенное содержание субстанции P, эндогенных опиоидов, глутамина и нейротрофических факторов в ЦСЖ, как известно, способствующих повышению возбудимости нейронов [30]. Нейробиологические доказательства того, что ФМ является состоянием с повышенной болевой чувствительностью (центральная сенситизация) и нарушениями процессов восприятия, подтверждаются результатами аппаратных методов диагностики: однофотонной эмиссионной компьютерной томографии и функциональной магнитно-резонансной томографии [13, 20, 24, 30].
В последние годы проведено много исследований, выявляющих у пациентов с ФМ патологию тонких периферических волокон, однако роль этих изменений в патогенезе болевого синдрома при ФМ пока остается дискуссионной [17].
Клиническая картина
Основной симптом ФМ – хроническая боль, не обусловленная какой-либо патологией скелетно-мышечного аппарата, которая беспокоит пациента не менее 3 мес. Эта боль имеет диффузный характер, распространяется по всему телу выше и ниже талии. Обычно пациенты описывают свое состояние как «я чувствую, что у меня болит везде» или «я себя ощущаю постоянно простуженным». Как правило, с их слов, боль распространяется по всем мышцам, но иногда они также отмечают боль и припухлость в суставах. Кроме того, больные часто жалуются на парестезии, онемение, покалывание, жжение, ощущение ползания мурашек по коже, особенно в области ног и рук.
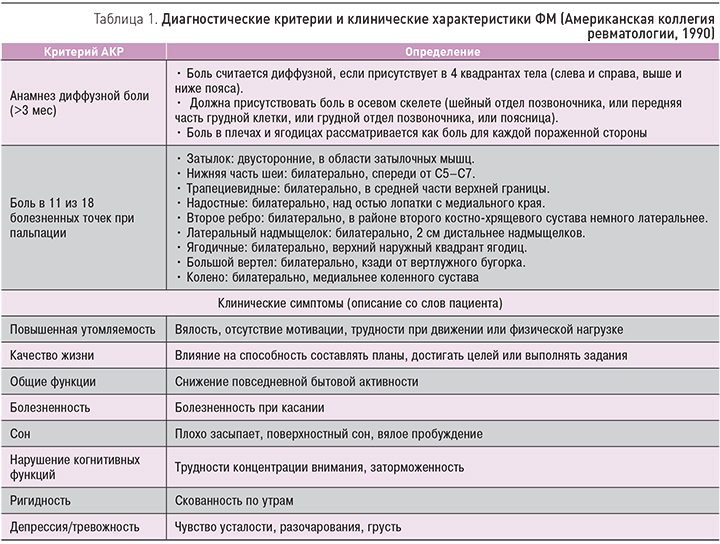
У пациентов с ФМ при физикальном обследовании обнаруживается повышенная чувствительность или болезненность в определенных точках тела (tender points). Исследование этих точек требует опыта: врач должен знать, где именно пальпировать и с какой силой. Всего, согласно критериям АКР, определено 9 пар болезненных точек (рис).
Давление, производимое в болезненных точках при исследовании, должно составлять 4 кг/см – это то давление, при котором белеют ногтевые ложа исследователя. При выполнении пальпации 18 болезненных точек рекомендуется оказывать равномерное давление на парные точки и с тем же усилием пальпировать другие участки тела для сравнения чувствительности. У больных ФМ в болезненных точках наблюдается повышенная чувствительность по сравнению с другими участками тела.
 Болезненные точки отражают зоны повышенной чувствительности к болевым стимулам, а не являются следствием локального воспаления или поражения тканей. Наличие положительной реакции более чем в 11 из 18 болезненных точек определено в качестве диагностического критерия ФМ на основании анализа статистических данных больших популяций больных. В то же время не обязательно у всех пациентов с ФМ будет отмечаться повышенная чувствительность более чем в 11 точках. Тем не менее обследование болезненных точек считается важной частью изучения функционирования скелетно-мышечной системы у пациентов с подозрением на ФМ.
Болезненные точки отражают зоны повышенной чувствительности к болевым стимулам, а не являются следствием локального воспаления или поражения тканей. Наличие положительной реакции более чем в 11 из 18 болезненных точек определено в качестве диагностического критерия ФМ на основании анализа статистических данных больших популяций больных. В то же время не обязательно у всех пациентов с ФМ будет отмечаться повышенная чувствительность более чем в 11 точках. Тем не менее обследование болезненных точек считается важной частью изучения функционирования скелетно-мышечной системы у пациентов с подозрением на ФМ.
Следует подчеркнуть, что ФМ – это не только болевой синдром. Это состояние также сопровождается целым комплексом беспокоящих пациента неболевых нарушений. Так, наряду с хронической диффузной болью другим типичным симптомом заболевания выступает повышенная утомляемость. Этот симптом наиболее ярко проявляется при пробуждении, но встречается и во второй половине дня. Незначительная физическая нагрузка способна резко усилить боль и усталость, хотя и длительный отдых и отсутствие активности также могут обострять симптоматику. Пациенты с ФМ по утрам чувствуют скованность в теле и ощущают себя не выспавшимися, даже если спали 8–10 ч. Такие больные обычно спят некрепко, часто просыпаются и трудно засыпают. Обычно они говорят: «Неважно, сколько времени я спал, но у меня ощущение, будто меня переехал грузовик».
Определенную роль в развитии клинической картины ФМ играют поведенческие и психологические факторы. Установлено, что распространенность психиатрических сопутствующих заболеваний у пациентов с ФМ может достигать от 30 до 60%, а частота психических расстройств еще выше. Депрессия и тревожные расстройства – наиболее распространенные состояния. Кроме того, у большинства пациентов наблюдаются когнитивные нарушения. Например, обычно больные описывают свои проблемы с концентрацией или вниманием как туман в голове.
Диагностика
Как уже отмечалось, в 1990 г. АКР были разработаны критерии диагностики ФМ (табл. 1) [32].
Хотя эти критерии не предназначены для использования в клинических условиях, а только в рамках исследований, они тем не менее обеспечивают более чем 85%-ную точность в дифференциальной диагностике пациентов с ФМ.
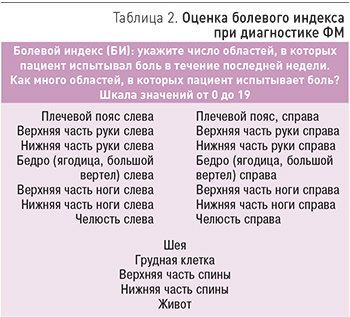
В 2010 г. были предложены новые диагностические критерии ФМ, ассоциированные с двумя параметрами: болевым индексом (БИ) и показателями по шкале тяжести симптомов (ШТС) [33]. Согласно этим критериям, для диагностирования ФМ у пациента должны определяться 3 следующих признака:
- широко распространенный БИ ≥7 и общий счет по ШТС ≥5 или БИ 3–6 и ШТС ≥9;
- симптомы должны быть представлены на одном уровне, по крайней мере в течение 3 мес;
- у пациента не должно быть другого расстройства, способного объяснить боль.
Для расчета БИ больному предлагается указать, в каких конкретно из 19 областей тела он испытывал боль за последнюю неделю (табл. 2). Для каждой области присваивается 1 балл, общий счет БИ может колебаться от 0 до 19.
В свою очередь, ШТС представляет собой сумму тяжести 3 признаков (утомляемость, нарушение сна, когнитивные симптомы) + общей степени выраженности соматических симптомов. Финальная оценка колеблется от 0 до 12 баллов. Для каждого из этих 3 симптомов определяют выраженность его в течение последней недели по следующей шкале:
- 0 баллов – нет нарушений;
- 1 балл – легкие и незначительные нарушения, обычно малозаметные или преходящие;
- 2 балла – умеренной выраженности и значительные нарушения, много раз появляющиеся и/ или постоянные умеренной выраженности;
- 3 балла – тяжелые нарушения, постоянные, длительные, жизнеугрожающие.
Суммарно этот раздел ШТС может быть оценен от 0 до 9 баллов.
Кроме того, для окончательного подсчета ШТС у больного необходимо оценить наличие следующих соматических симптомов: мышечной боли (миалгии), синдрома раздраженной кишки, утомления/усталости, расстройства мышления или памяти, мышечной слабости, головной боли, боли/рези в животе, онемения/покалывания, головокружения, нарушения сна, депрессии, запора, боли внизу живота, тошноты, нервозности, боли в грудной клетке, расплывчатого видения, лихорадки, сухости во рту, зуда, визинга (шумного дыхания), феномена Рейно, крапивницы/рубцов, звона в ушах, рвоты, изжоги, язв в ротовой полости, утраты/изменения вкуса, сухости в глазах, одышки, утраты аппетита, сыпи, фоточувствительности, нарушения слуха, легкого ушиба,облысения, учащенного мочеиспускания, болезненного мочеиспускания. В общей сложности оценивают 40 симптомов. Предлагается следующая градация наличия этих признаков:
- 0 баллов – нет симптомов;
- 1 балл – мало симптомов;
- 2 балла – умеренное число симптомов;
- 3 балла – большое число симптомов.
 Суммарная оценка по ШТС с учетом соматической симптоматики может колебаться от 0 до 12 баллов.
Суммарная оценка по ШТС с учетом соматической симптоматики может колебаться от 0 до 12 баллов.
Как видно, в новых критериях в меньшей степени делается акцент на наличие тендерных точек и уделяется значительное внимание неболевым феноменам и коморбидности.
В 2011 г. были модифицированы критерии диагностики ФМ, предложенные АКР в 2010 г., в результате чего был разработан опросник, при помощи которого пациент может самостоятельно производить расчет БИ и оценку по шкале ШТС [34]. В 2016 г. были опубликованы результаты сравнения новых критериев ФМ, разработанных специалистами AКР, при использовании их докторами (версия AКР, 2010) и пациентами (версия AКР, 2011). Доказано, что БИ и оценка по ШТС валидны как при врачебном осмотре, так и при самооценке пациентами [12, 35].
Лечение
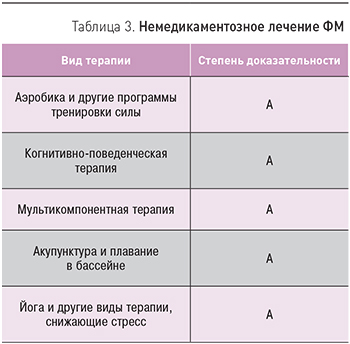
В течение последних десятилетий все больше исследователей подчеркивали важность комплексного рассмотрения факторов, связанных с ФМ. Были разработаны различные виды многопрофильных программ лечения ФМ, хотя эти программы, как правило, имеют ряд общих компонентов, в том числе физические упражнения, образовательную часть и некоторые виды когнитивного лечения для улучшения психофизиологической адаптации. Доказанная эффективность многопрофильных терапевтических программ свидетельствует о том, что сочетание медикаментозного лечения, физической нагрузки и когнитивно-поведенческого компонента является методом выбора для лечения всех пациентов с ФМ. В 2010 г. были опубликованы международные рекомендации по лечению ФМ, основанные на принципах доказательной медицины [22].
Немедикаментозная терапия
Просвещение. Информация и убеждение имеют большое значение для лечения ФМ. Отсутствие внятного объяснения симптомов часто вызывает у пациента страх, будто происходит что-то серьезное, но пока еще не выявленное, и что симптомы будут постепенно усугубляться, приводя к опасным последствиям. Следовательно, врач должен дать больному информацию о природе ФМ, ее возможных причинах (описанных ранее), а также лечении, которое считается наиболее эффективным и безопасным при ФМ.
Просвещение включает обсуждение различий между острой и хронической болью. Острую боль следует рассматривать как сигнал о «вреде», о потенциальном повреждении или опасности для организма. В случае хронической боли при ФМ она уже не является признаком повреждения организма. Таким образом, пациент понимает различие между «болью» и «повреждением». Необходимо постепенно увеличивать физическую активность и выполнять упражнения. У пациентов с ФМ часто физическая активность ассоциируется с болью, а в результате этого возникает опасение, что она может ухудшить их состояние. Понятно, что этот страх ведет к избеганию активности, чтобы предотвратить усиление боли, усталости и травматизации. Имеется в виду представление о том, что, если что-то причиняет страдание или боль, этого следует избегать. Таким образом, основное внимание в процессе лечения уделяется тому, чтобы разорвать связь между физической активностью и болью. Для этого мы поощряем пациентов постепенно увеличивать физическую активность, повышая выносливость и снижая утомляемость. Нужно предупредить пациентов о том, что программа восстановления, вероятно, вызовет боль, так как мышцы действительно начинают болеть при работе после многих месяцев или даже лет бездействия, но важно объяснить, что эти упражнения не нанесут им вреда.
 Концентрация внимания на улучшении функций, а не на болезни. Лечению пациента с ФМ часто препятствуют его твердая уверенность в том, что у него соматическая патология, которую необходимо исправить или вылечить. Эта убежденность может помешать положительной динамике в процессе терапии, где основное внимание уделяется реабилитационной модели и стремлению добиться функционального улучшения. Лучше всего обсуждать такие убеждения пациента и вместе признать, достаточно ли они сильны, т.е. несовместимы со стратегией лечения, которая сосредоточена на самоуправлении. Если пациент и психотерапевт согласны приступить к терапии, то она всегда должна быть направлена на функциональные улучшения, а не на этиологию или излечение.
Концентрация внимания на улучшении функций, а не на болезни. Лечению пациента с ФМ часто препятствуют его твердая уверенность в том, что у него соматическая патология, которую необходимо исправить или вылечить. Эта убежденность может помешать положительной динамике в процессе терапии, где основное внимание уделяется реабилитационной модели и стремлению добиться функционального улучшения. Лучше всего обсуждать такие убеждения пациента и вместе признать, достаточно ли они сильны, т.е. несовместимы со стратегией лечения, которая сосредоточена на самоуправлении. Если пациент и психотерапевт согласны приступить к терапии, то она всегда должна быть направлена на функциональные улучшения, а не на этиологию или излечение.
Управление физическими симптомами с помощью релаксации. Для пациентов с ФМ релаксация служит неотъемлемой частью поведенческой программы самоуправления. Существует много различных методов, чтобы помочь пациентам обучиться релаксации (например, контролируемое дыхание, прогрессивная мышечная релаксация и аутогенная тренировка), при этом ни один из них нельзя считать лучшим. Кроме того, разным людям подходят разные методы в зависимости от их индивидуальных особенностей.
Сон. Нарушение сна – распространенный симптом ФМ. Мы рекомендуем пациентам придерживаться гигиены сна. Эта программа включает следующие правила поведения:
- установить постоянное время пробуждения;
- вставать с постели после пробуждения;
- избегать несовместимого со сном поведения в постели;
- не ложиться днем в разобранную постель и избегать активной деятельности непосредственно перед отходом ко сну, поскольку это может помешать засыпанию.
При наличии выраженных расстройств сна рекомендовано применение снотворных препаратов. Среди них в отношении пациентов с ФМ наиболее изученными являются зопиклон и мелатонин. Мелатонин, наряду с положительными клиническими эффектами, оказывает нормализующее влияние на структуру сна при полисомнографическом исследовании.
Физическая активность. Физические упражнения в качестве терапии ФМ могут показаться парадоксом, однако исследования показывают, что классические симптомы этого заболевания регрессируют на фоне аэробных нагрузок, растяжки, йоги. Обзор 16 исследований, сосредоточенных на физических упражнениях при ФМ, показал однозначно положительные результаты [21]. Рекомендуются регулярные нагрузки в виде прогулок, аэробной гимнастики, плавания, упражнений на растяжку. Силовые упражнения при этом противопоказаны.
Когнитивно-поведенческая терапия. Хотя когнитивно-поведенческая терапия не излечивает, она помогает людям добиться контроля своих симптомов и восстановить контроль своей жизни. Она сконцентрирована на мыслях, чувствах и поведении человека. В ней также рассматривается роль внешних факторов в поддержании и усугублении симптомов и трудоспособности. При проведении когнитивно-поведенческой терапии следует уделить внимание повышению осознания пациентами собственной негативной структуры мышления, например катастрофических мыслей, рассуждений по принципу «черное и белое» или нереалистично глобального или негативного мышления, фильтрации или искаженному пониманию негативной информации и нереалистичным оценкам контроля своего состояния и самоэффективности. Необходимо приложить усилия для того, чтобы пациенты выработали более адаптивное восприятие, которое дает больше надежды или веры в то, что они сами могут кое-что сделать для улучшения ситуации.
Специально проведенный анализ различных немедикаментозных методов лечения ФМ показал, что достоверной эффективностью обладают когнитивно-поведенческая терапия и различные виды физической активности (табл. 3) [22]. На фоне проведения терапии с помощью этих методов лечения отмечалось стойкое улучшение симптомов ФМ на протяжении одного года и более.
Медикаментозная терапия
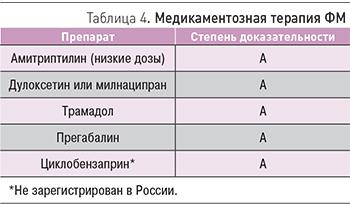
Согласно рекомендациям 2010 г., наиболее эффективными и безопасными лекарственными средствами в терапии ФМ служат антидепрессанты, прегабалин, трамадол и циклобензаприн (табл. 4) [22].
Антидепрессанты. Среди лекарственных препаратов одними из первых для лечения болевого синдрома при ФМ были использованы трициклические антидепрессанты (ТЦА). Было показано, что амитриптилин способен купировать интенсивность болей, укреплять сон и снижать утомляемость больных ФМ [19]. При этом антидепрессанты из группы селективных ингибиторов обратного захвата серотонина (СИОЗС) (флуоксетин, сертралин, циталопрам, пароксетин) показали низкую эффективность в ходе рандомизированных, плацебо-контролируемых исследований при ФМ [19].
Ингибиторы обратного захвата серотонина и норадреналина (ИОЗСН) (венлафаксин, дулоксетин, милнаципран) оказались более эффективными, чем СИОЗС. Как и ТЦА, они ингибируют обратный захват серотонина и норадреналина, однако в отличие от ТЦА практически не влияют на другие рецепторы. Такая избирательность приводит к снижению побочных эффектов и лучшей переносимости ИОЗСН.
Данные по венлафаксину говорят о его успешном применении для лечения невропатической боли и ФМ [36]. В исследовании с использованием дулоксетина отмечалось более выраженное снижение общего балла по шкале тяжести ФМ (FIQ) и 30%-ное снижение боли у 54% пациентов, принимавших препарат, по сравнению с 33% больных из группы плацебо [7].
Дулоксетин утвержден FDA (Food and Drug Administration) в качестве средства из группы CИОЗСН для лечения большого депрессивного расстройства, невропатической боли при сахарном диабете и ФМ.
Милнаципран, который широко используется в качестве антидепрессанта, утвержден FDA для лечения ФМ. В ходе 12-недельного рандомизированного клинического исследования (РКИ) 125 пациентов с ФМ получали либо милнаципран (1 или 2 раза в сутки в дозах до 200 мг/сут), либо плацебо [23]. Всего у 37% пациентов с ФМ удалось достичь 50%-ного снижения боли на фоне двукратного приема, у 22% – на фоне однократного приема и у 14% – в группе плацебо.
Несмотря на то что многие хронические болевые синдромы, включая ФМ, сопровождаются депрессией, некоторые исследования показали, что анальгетическая активность антидепрессантов не зависит от их влияния на эмоциональный статус больных [7, 19, 23, 31, 36]. Метаанализ результатов 18 РКИ подтвердил, что антидепрессанты могут снизить интенсивность боли при ФМ, уменьшить депрессию, утомляемость, восстановить сон и повысить качество жизни [19].
Антиконвульсанты-габапентиноиды. Прегабалин, лиганд α2-δ кальциевых каналов, применяемый для лечения невропатической боли, был первым препаратом, утвержденным FDA и для терапии ФМ. Также он является первым и пока единственным препаратом в России, официально зарегистрированным для лечения этого заболевания. Прегабалин связывается с α2-δ-участком потенциалозависимых кальциевых каналов в ЦНС. Вследствие уменьшение притока кальция внутрь нейронов снижается высвобождение субстанции P, глутамата и норадреналина, что обеспечивает анальгезирующее и анксиолитическое действия прегабалина. Активность этого препарата ограничена нейронами и не влияет на сосудистые кальциевые каналы.
В ходе крупного РКИ с участием 528 пациентов с ФМ прегабалин показал значительное снижение балла боли, повышал качество сна, снижал утомляемость и улучшал общее самочувствие [15]. Участники исследования получали плацебо или одну из доз прегабалина (150, 300 или 450 мг/сут) в течение 8 нед. У всех пациентов, принимавших препарат, наблюдалось улучшение в течение 2 нед, которое сохранялось вплоть до окончания исследования.
В последующем 6-месячном плацебо-контролируемом исследовании участвовали 566 пациентов с ФМ, завершивших 6-недельное открытое исследование и ответивших на лечение (респондеры) [16]. Проводилась монотерапия прегабалином в дозах 300, 450 или 600 мг/сут (2 раза в сутки). В результате было показано, что ответная реакция на лечение прегабалином является протяженной во времени.
В двух других крупных РКИ, где лечение продолжалось 13–14 нед, было показано, что монотерапия прегабалином эффективна для уменьшения интенсивности боли при ФМ в дозировках 300, 450 и 600 мг/сут [9, 25].
Также эффективность прегабалина в лечении ФМ оценивалась в ходе метаанализа результатов шести РКИ, в которых приняли участие более 2000 пациентов с ФМ [29]. Показано, что прегабалин вызывал снижение боли при ФМ, улучшал сон и повышал качество жизни, но не влиял на тяжесть депрессивного настроения. Кроме того, у пациентов с ФМ, получавших прегабалин, отмечалось снижение утомляемости и тревожности.
Габапентин, чьи фармакологические свойства сходны с прегабалином [8], применяли в ходе 12-недельного РКИ с участием 150 пациентов с ФМ [18]. В группе габапентина отмечалось достоверное снижение среднего балла интенсивности боли по сравнению с группой плацебо. Кроме того, габапентин значительно улучшал балл по шкале тяжести ФМ (FIQ), шкале самостоятельной оценки пациентом своего состояния (PGIC) и по шкале оценки качества сна. По сравнению с плацебо, габапентин приводил к значительному повышению частоты встречаемости седативного эффекта, дурноты и головокружения. Однако, по современным рекомендациям 2010 г., эффективность габапентина для лечения ФМ не достигает уровня доказательности А.
Трамадол. Трамадол – это анальгетик центрального действия, который связывается с μ-опиоидными рецепторами и ингибирует обратный захват норадреналина и серотонина. Комбинация парацетамола с трамадолом в соотношении 8:1 показала синергизм обоих препаратов в условиях доклинических моделей боли. В ходе 13-недельного многоцентрового РКИ трамадол/парацетамол в дозах 37,5 мг/325 мг купировали боль при ФМ более эффективно, чем плацебо [11]. Все нежелательные явления, зарегистрированные в ходе этого исследования (транзиторные и несерьезные нежелательные явления), представляли собой хорошо известные осложнения трамадола: головокружение, тошнота, рвота, запор, сонливость, головная боль и слабость.
Местные анестетики. Существует опыт использования в лечении пациентов с ФМ системных форм лидокаина: однократные и курсовые инфузии этого анестетика в дозах 5–7 мг/кг приводили к достаточно заметному снижению боли [10].
В ходе недавнего РКИ пациентам с ФМ выполняли инъекции лидокаина в дозе 50 мг в болевую точку в области трапециевидной мышцы. В результате было отмечено не только локальное снижение боли в месте инъекции, но и общий анальгезирующий эффект [27]. Данное исследование показало важную роль периферических тканей в развитии гипералгезии при ФМ и доказало возможность клинического применения локальных инъекций анестетиков для купирования боли при этом заболевании.
Заключение
На сегодняшний день все специалисты подчеркивают необходимость комплексной мультимодальной терапии ФМ, основанной на принципах биопсихосоциального подхода и включающей как фармакологические, так и нелекарственные методы.


