Мультидисциплинарный подход к изучению патогенеза и терапии хронического болевого синдрома является одним из приоритетных направлений современной медицины. Ревматологические заболевания, основным проявлением которых служит хронический болевой синдром, в этом плане не исключение.
Анкилозирующий спондилоартрит (АС) – хроническое воспалительное заболевание из группы спондилоартритов, характеризующееся обязательным поражением крестцово-подвздошного сочленения и/или позвоночника с потенциальным исходом в анкилоз, с частым вовлечением в патологический процесс энтезисов и периферических суставов [1]. Распространенность АС по миру следующая: 0,24% от общей популяции в Европе, 0,17% – Азии, 0,32% – Северной Америке, 0,1% – Латинской Америке и 0,07% – Африке [2]. Если остеоартрит и ревматоидный артрит остаются самыми частыми причинами суставной боли, то АС относят к наиболее трудно диагностируемым причинам специфической боли в спине. Согласно статистике, правильный диагноз, а значит и терапию, пациент с АС получает в среднем через 7–10 лет после дебюта заболевания [3–5].
В патогенезе заболевания принимают участие как воспалительные, так и остеопролиферативные изменения в виде синдесмофитов и анкилоза, которые видны при рентгенологическом исследовании. Согласно современной классификации, выделяют 2 формы аксиального спондилоартрита (аксСпА): с радиографическими признаками сакроилеита (анкилозирующий спондилит) и без радиографических признаков в крестцово-подвздошных сочленениях (нерентгенологический аксСпА – нр-аксСпа).
Магнитно-резонансную томографию (МРТ) часто используют для диагностики АС. Исследование в Т2-режиме с подавлением жира позволяет выявить воспалительные изменения в виде отека костного мозга в области крестцово-подвздошных сочленений (остеит). При использовании Т1-режима выявляются поствоспалительные изменения: жировая дистрофия, эрозия, склероз и анкилоз.
Соотношение мужчин и женщин с АС составляет 2:1–3:1, с нр-аксСпа – 1:1,9 [6, 7].
Согласно критериям Международного общества по изучению спондилоартритов от 2009 г. (ASAS – The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society, 2009) [8], признаком АС выступает воспалительная боль в спине, под которой понимают хроническую боль (длящуюся более 3 мес), имеющую хотя бы 4 из 5 следующих характеристик:
- возраст начала до 40 лет;
- постепенное начало;
- ночная боль (во второй половине ночи);
- уменьшение боли после физических упражнений;
- отсутствие улучшения на фоне отдыха.
Кроме того, для воспалительной боли в нижней части спины характерно наличие перемежающейся боли в ягодицы, утренняя скованность более 30 мин и хороший ответ на терапию нестероидными противовоспалительными препаратами (НПВП).
Большое значение в патогенезе заболевания имеет неблагоприятная наследственность, одним из главных маркеров которой является антиген HLA-B27. АС начинается, как правило, в третьей декаде жизни, на 5 лет ранее у HLA-B27-позитивных пациентов по сравнению с HLA-B27-негативными [9, 10]. Определение HLA-B27, наряду с нейровизуализацией, служит важным диагностическим критерием АС. Распространенность HLA-B27 в популяции (8%) отражает распространенность АС (0,5–5%) [11].
На сегодняшний день проводимая противовоспалительная терапия (НПВП, глюкокортикостероиды) пациентов с АС зачастую недостаточно купирует болевой синдром. В связи с этим обращает на себя внимание наличие у ряда пациентов особых качественных характеристик боли. Так, описывая свои жалобы, пациенты могут использовать следующие дискрипторы: ощущение онемения, покалывания, усиление болевых ощущений при прикосновении в области пораженных отделах позвоночника. Это позволяет заподозрить у ряда больных с АС наличие центральной сенситизации (ЦС), участвующей в патогенезе хронического болевого синдрома.
Одним из поводов к исследованию нейрогенных механизмов боли при АС послужил тот факт, что Food and Drug Administration (FDA) оспорило применение ингибиторов фактора некроза опухоли (ФНО-α) для лечения пациентов с нр-аксСпас [12, 13]. При отсутствии рентгенологических изменений достоверная диагностика заболевания может быть крайне затруднительной, а назначение дорогостоящего биологического лечения – мало обоснованным. Основным аргументом против назначения противовоспалительной биологической терапии было наличие часто встречающихся признаков фибромиалгии (ФМ) у больных АС, в патогенезе которой основным механизмом является ЦС.
Однако в исследовании X. Baraliakos и соавт. [14] было показано, что диагностические критерии ФМ встречаются у 24% больных АС, причем в 29% случаев при анкилозирующем спондилите и в 19% – при нр-аксСпа. Тот факт, что пациенты с нр-аксСпа не особенно предрасположены к симптомам ФМ, позволяет предположить, что широкое распространение боли происходит на поздних стадиях болезни.
На сегодняшний день проведены единичные исследования, в которых выявлено наличие невропатических дескрипторов (жжение, онемение, покалывание, ползание мурашек и др.) при АС. Исследование с участием 100 больных АС, проведенное турецкими коллегами в 2018 г. [15], показало, что 25% пациентов имели невропатическую боль по опроснику PainDETECT. Также была продемонстрирована корреляция невропатических симптомов с уровнем боли в спине и суставах, индексами BASDAI, ASDAS, BASFI и др., а также с общим показателем шкалы SF-36.
В исследовании Jung-Hye Choi [16] с участием 105 больных АС были получены более высокие цифры представленности признаков невропатической боли – 35,2%. Исследование выявило корреляцию признаков невропатической боли с возрастом, тяжестью заболевания, наличием энтезитов, поражением периферических суставов и депрессией, однако корреляция с маркерами воспаления у данных пациентов не подтвердилась.
В связи с тем что в настоящее время нет общепризнанного стандарта для оценки невропатического компонента боли (НКБ), в исследовании Kevser Gok [17] были использованы оба наиболее популярных опросников для скрининга невропатической боли DN4 и Pain DETECT. Результаты этих опросников высоко коррелировали друг с другом. Представленность НКБ по DN4 составила 31,4%. Пациенты с НКБ, определенном как по DN4, так и опроснику Pain DETECT, имели более высокую интенсивность боли по визуально-аналоговой шкале (ВАШ), усталость, индексы BASDAI, ASDAS, депрессию, тревогу и более низкое качество жизни.
Учитывая вышеизложенное, нами было проведено исследование, целью которого стало выявление невропатических дескрипторов у больных АС и определение их связи с заболеванием.
Материал и методы
В исследование приняли участие 150 пациентов с АС. Критериями включения служили:
- достоверный диагноз АС, установленный в соответствии с модифицированными Нью-Йоркскими критериями (1984) [18];
- возраст от 18 до 65 лет;
- согласие пациента на осмотр.
Критериями исключения стали наличие сопутствующих заболеваний, сопровождающихся хроническим болевым синдромом, не связанным с АС (диабетическая или алкогольная полиневропатия и др.), наличие психических заболеваний, затрудняющих адекватную самооценку болевого синдрома, эмоционального состояния и заполнение опросников, а также отказ пациента от осмотра врача невролога.
 У всех пациентов были оценены ревматологический (активность заболевания и функциональные нарушения по индексам BASDAI, BASFI и BASMI) и неврологический статусы, оценка интенсивности боли по ВАШ, определение НКБ по диагностическим опросникам невропатической боли (DN4, Pain DETECT), оценка эмоционально-аффективной сферы (опросник HADS) и оценка качества жизни по опроснику EQ-5D.
У всех пациентов были оценены ревматологический (активность заболевания и функциональные нарушения по индексам BASDAI, BASFI и BASMI) и неврологический статусы, оценка интенсивности боли по ВАШ, определение НКБ по диагностическим опросникам невропатической боли (DN4, Pain DETECT), оценка эмоционально-аффективной сферы (опросник HADS) и оценка качества жизни по опроснику EQ-5D.
На момент обследования все пациенты, включенные в исследование, получали терапию НПВП, сульфасалазином и имели достоверный двусторонний сакроилеит на обзорном снимке таза.
Для статистической обработки данных использовались параметрические и непараметрические методы в программе Statistica 10, Copyright StatSoft, Inc. 1984–2011 (Basic statistics and Tables, Nonparametrics statistics). Кроме того, использовались методы выявления связи между признаками: метод корреляции Спирмена. Статистически значимыми считались различия при р <0,05.
Результаты и обсуждение
Средний возраст обследованных больных АС составил 34,63±10,34 года, средняя длительность заболевания 7,85±6,6 года, индексы BASDAI, BASFI и BASMI 4,95±2,21 балла, 4,08±2,79 и 2,34±1,83 балла соответственно. Показатели тревоги соответствовали 6,56±3,72, а депрессии 4,73±2,98 баллов, качество жизни EQ-5D – 0,34±0,31, а средняя интенсивность боли составляла 4,60±2,10 балла по ВАШ. Показатели невропатической боли по DN4 – 1,61±1,39 балла и Pain Detect – 5,17±4,77 балла.
На основании невропатического опросника DN4 были выделены 2 группы обследуемых:
- I группа – больные, достоверно не имеющие НКБ (DN4 <4 баллов, отрицательный невропатический тест);
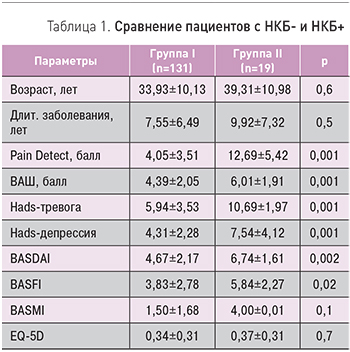
- II группа – пациенты с признаками невропатической боли (DN4 ≥4 баллов, положительный невропатический тест). НКБ определялся у 13% (n=19) пациентов. Выделенные группы не отличались по возрасту, продолжительности заболевания индексу BASMI и качеству жизни.
Группу больных с DN4 ≥4 баллов отличала более интенсивная боль по шкале ВАШ (6,01±1,91; p=0,001) по сравнению с группой больных, не имевших невропатического компонента, где интенсивность боли составила 4,39±2,05 балла (табл. 1).
У пациентов с НКБ+ достоверно была более высокой активность заболевания (BASDAI 6,74±1,61) и функциональные нарушения (BASFI 5,84±2,27). II группа достоверно также отличалась по уровню тревоги (10,69±1,97 vs 5,94±3,53) и депрессии (7,54±4,12 vs 4,31±2,28), причем показатели соответствовали наличию клинически значимой тревоги и наличию субклинической депрессии у этих больных.
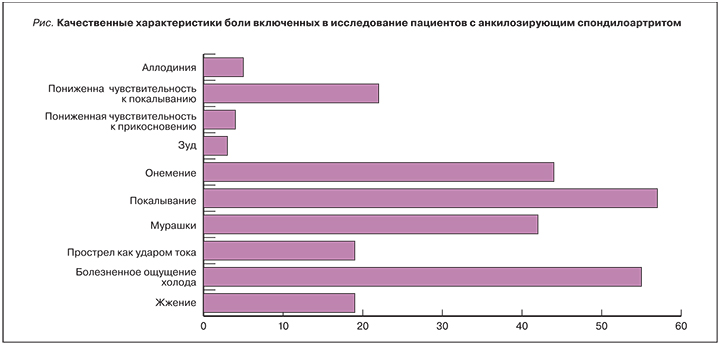
Анализируя качественные характеристики боли пациентов, принявших участие в исследовании по опроснику DN4, наиболее часто были выявлены следующие характеристики: болезненное ощущение холода, покалывание, онемение, ползание мурашек, пониженная чувствительность к покалыванию. Причем данные характеристики чаще были характерны пациентам группы II (болезненное ощущение холода 34%, покалывание 40%, онемение 34%, ползание мурашек 30%, пониженная чувствительность к покалыванию 17%), что соответствовало критериям разделения на группы (рис.).
Разделение пациентов по показателям опросника Pain DETECT, несмотря на средний показатель 5,17±4,77 (означающий отсутствие НКБ), было следующим:
- 0–12 баллов – 120 пациентов (нет невропатической боли);
- 12–18 баллов – 27 пациентов (неопределенная невропатическая боль);
- 18–38 баллов (высоко вероятная невропатическая боль) – 3 пациента.
Следовательно, наличие НКБ было выявлено у 30 пациентов с АС.
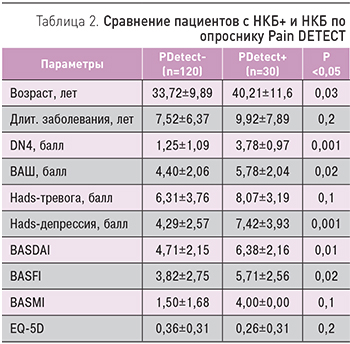
Пациенты с НКБ по опроснику Pain DETECT достоверно были старше остальных, имели более выраженную интенсивность боли по ВАШ, более высокие баллы по DN4, субклиническую депрессию, а также более высокую активность заболевания и худшие функциональные нарушения (табл. 2).
Корреляционный анализ (по Спирмену) достоверно показал прямую взаимосвязь возраста пациента и баллов по опросникам невропатической боли (r=+0,86 и r=+0,75; p <0,05), а также прямую связь с выраженностью тревоги и депрессии (r=+0,096 и r=+0,98; p <0,05). Поскольку тревога и депрессия влияют на показатели DN4 и Pain Detect, то данную прямую взаимосвязь можно объяснить увеличением эмоционально-аффективных нарушений с длительностью хронического заболевания. Также установлено, что выраженность функциональных нарушений (BASFI) напрямую взаимосвязана с активностью заболевания (BASDAI) (r=+0,99; p <0,05). Интенсивности боли по ВАШ достоверно коррелировала с выраженностью невропатической боли по DN4 и Pain Detect (r=+0,92 и r=+0,99; p <0,05). Однако, по данным корреляционного анализа, активность заболевания и функциональные нарушения не влияли на выраженность невропатического компонента, как и интенсивность боли по ВАШ (0,37, r >0,05).
Неврологическое обследование не выявило у пациентов поражения соматосенсорной нервной системы в обеих группах, но у 63 пациентов из 150 при пальпации паравертебральных мышц преимущественно в грудном и поясничном отделах позвоночника диагностирован распространенный мышечно-тонический синдром. Оценка чувствительных нарушений в зоне мышечного напряжения выявила гипералгезию (повышенную чувствительность к покалыванию) у 25 человек и была чаще представлена в группе с НКБ+ (56 vs 44%), гипостезию (пониженную чувствительность к покалыванию) у 7 пациентов (5 человек с НКБ+ и 2 НКБ-), аллодинию (болезненное восприятие неболевого стимула) у 5 исследуемых (3 с НКБ+).
Концепция ЦС изучается на различных моделях хронической боли. Показано, что при отдельных заболеваниях она может являться основной причиной развития боли, например, при ФМ, когда источник боли отсутствует. Однако чаще в клинической практике отмечаются overlap-синдромы, когда признаки воспалительной или невропатической боли перекрываются с болью, обусловленной ЦС. Можно выделить подгруппы среди пациентов с хронической болью, имеющих черты ЦС, среди пациентов с болью в спине, остеоартритом, ревматоидным артритом, теннисным локтем, болью в плече и головной болью [19]. ЦС у этих пациентов также может определять ответ на лечение, что побуждает клиницистов определять симптомы ЦС.
В настоящее время основным клиническим инструментом для определения признаков ЦС являются опросники невропатической боли. Эти опросники позволяют зафиксировать наличие и выраженность таких чувствительных феноменов, как онемение, жжение, покалывание, ползание мурашек, аллодиния и т.д. Если у пациента нет в настоящее время или в анамнезе признаков заболевания соматосенсорной нервной системы и эти чувствительные расстройства локализованы вне определенной анатомической зоны, обусловленной этим поражением (анатомически нелогичны), то наличие этих признаков свидетельствует о ЦС.
В исследовании Q. Wu и соавт. [20] был оценен НКБ с помощью опросника Pain DETECT и было показано, что 11 из 17 пациентов с АС имели НКБ. При нейровизуализации у этих пациентов обнаружено истончение серого вещества первичной сенсомоторной коры, инсулы передней поясной извилины, цингулярной коры и дополнительной моторной зоны и увеличение серого вещества в таламусе и скорлупе. Были показаны корреляции шкалы Pain DETECT с изменениями в сером веществе. Таким образом, было доказано участие в патогенезе хронического болевого синдрома у ряда пациентов с АС смешанных механизмов: ноцицептивной и ЦС.
В другом исследовании того же автора изучено влияние терапии ингибитором ФНО-α на болевые ощущения, утомляемость и качество жизни, а также результаты МРТ пациентов с АС. Ингибитор ФНО оказывал наибольшее влияние на интенсивность боли, активность заболевания и в меньшей степени на усталость. Кроме того, было показано, что при применении ингибитора ФНО-α уменьшались показатели шкалы Pain DETECT и происходили изменения на МРТ [21]. Эти факты свидетельствуют о взаимосвязи воспалительных изменений с ЦС.
Заключение
Полученные нами данные говорят о наличии смешанного характера болевого синдрома у 13% больных по скрининговому опроснику DN4 или 20% по Pain Detect, причем нейропатический компонент боли достоверно чаще встречается у пациентов с более высокой интенсивностью боли по ВАШ и активностью заболевания, клинически выраженной тревогой, депрессией и большими функциональными нарушениями.
Полученные нами данными сопоставимы с результатами Kevser Gok [17], который в своем исследовании показал, что пациенты с НКБ+ имели более высокие интенсивность боли по ВАШ и индекс BASDAI, более выраженную депрессию, тревогу и более низкое качество жизни.
Неврологическое обследование пациентов с АС не выявило поражения соматосенсорной нервной системы, однако наличие нейропатических дескрипторов (болезненное ощущение холода 34%, покалывание 40%, онемение 34%, ползание мурашек 30%, пониженная чувствительность к покалыванию 17%), клинически значимой тревоги (10,69±1,97) позволяет говорить о наличии у этих пациентов (19 человек) боли при ЦС.
Еще одним значимым моментом в понимании смешанного характера боли у ряда больных с АС служит эффективность комплексной терапии с применением препаратов центрального действия – антиконвульсантов. В литературе описаны случаи эффективного лечения антиконвульсантами пациентов с достоверным АС, длительно страдающих от выраженного болевого синдрома, у которых результативность использования базисной терапии, НПВП и наркотических опиодов была минимальной [22].
Таким образом, наличие признаков ЦС у 13–20% пациентов с АС открывает новые возможности использования комплексной терапии для более эффективного купирования болевого синдрома. Добавление к основному лечению препаратов центрального действия (антиконвульсантов и/или антидепрессантов), возможно, позволит улучшить качество жизни пациента путем уменьшения выраженности болевого синдрома. Клиническое использование препаратов центрального действия в терапии боли при АС носит единичный характер и требует дальнейших клинических исследований.


