В 2020 г. научно-практическим советом Минздрава России были приняты и утверждены российские клинические рекомендации по ведению артериальной гипертензии (АГ) у взрослых [1]. В них к числу основных препаратов для лечения этого заболевания отнесены тиазидные и тиазидоподобные диуретики: все три основных препарата данной группы (гидрохлоротиазид, индапамид и хлорталидон) рассматриваются как возможные средства для назначения с целью контроля артериального давления (АД).
Аналогичное положение содержится и в рекомендациях Европейского общества кардиологов (ESC) и Европейского общества гипертонии (ESH) 2018 г. [2]. Оно базируется на результатах метаанализа 2015 г., в котором была показана достаточная эффективность всех трех указанных препаратов в профилактике неблагоприятных событий у больных АГ [3]. Следует отметить, что в британских и американских клинических рекомендациях приоритет отдается тиазидоподобным диуретикам, обладающим большей продолжительностью эффекта, а по некоторым данным, и большей эффективностью.
Целью настоящего исследования стал анализ эффективности тиазидных и тиазидоподобных диуретиков у пациентов с АГ в условиях рутинной клинической практики.
МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДЫ
Обследовано 409 больных, входящих в группу активного наблюдения в связи с впервые выявленной АГ: 157 (38,4%) мужчин и 252 (61,6%) женщины. Средний возраст пациентов составил 58,58±9,914 лет.
Все участники были обследованы при включении в группу активного наблюдения и затем совершали еще 4 визита наблюдения через каждые 3 мес. При каждом визите фиксировались проводимая терапия, уровни АД и частоты сердечных сокращений (ЧСС), наличие осложнений, гипертонических кризов. Пациентам проводилась эхокардиография и цветовое дуплексное сканирование (ЦДС) сонных артерий, биохимическое исследование крови, оценка индекса массы тела.
На фоне подобранной антигипертензивной терапии для контроля эффективности лечения применялось суточное мониторирование АД. Оно проводилось на оборудовании ABPM-05 Meditech в течение 24 ч с измерением АД через каждые 15 мин в дневное и через каждые 30 мин в ночное время. Рассчитывались средние значения систолического и диастолического АД за сутки, день и ночь, показатели нагрузки давлением как процент измерений, превышающих нормальные значения, и степень ночного снижения АД (%).
Долгосрочная (межвизитная) вариабельность АД оценивалась на основе его амбулаторного измерения по значению стандартного отклонения от индивидуальных средних значений и коэффициенту вариации (стандартное отклонение, отнесенное к среднему значению АД, по данным 5 измерений у каждого больного).
Статистическая обработка результатов выполнялась с использованием пакета статистических программ SPSS 23.0. Для протяженных величин рассчитывались средние и величины стандартного отклонения. Для оценки достоверности различий использовали t-критерий Стьюдента и критерий χ2 Пирсона. Для всех видов анализа достоверными считали различия при р <0,05.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
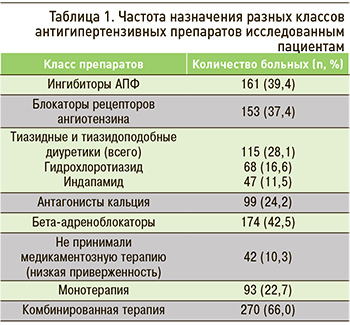 Мы проанализировали частоту назначения разных классов антигипертензивных препаратов пациентам, участвовавшим в исследовании. Данные этого анализа представлены в таблице 1.
Мы проанализировали частоту назначения разных классов антигипертензивных препаратов пациентам, участвовавшим в исследовании. Данные этого анализа представлены в таблице 1.
В качестве монотерапии использовались бета-адреноблокаторы (18 больных), антагонисты кальция (12 больных), ингибиторы АПФ (35) и блокаторы рецепторов ангиотензина (28). Диуретики в рамках монотерапии не применялись. В фиксированных или свободных комбинациях в реальной практике чаще назначали гидрохлоротиазид (68 пациентов), реже индапамид (47).
Было проведено сравнение офисного АД до начала лечения и на фоне терапии, достигнутых значений АД по данным суточного мониторирования АД (СМАД) и долгосрочной вариабельности АД на при приеме гидрохлоротиазида и индапамида (табл. 2).
Как видно из таблицы 2, исходные и достигнутые значения офисного АД и достигнутый уровень этого показателя по данным СМАД достоверно не отличались. Отмечалась тенденция к несколько большему снижению систолического АД в ночное время на фоне терапии индапамидом. Долговременная вариабельность систолического АД как по показателю индивидуального стандартного отклонения, так и по величине коэффициента вариации оказалась достоверно меньше на фоне терапии с использованием индапамида, что говорит о лучшем долговременном контроле АД в этой группе.
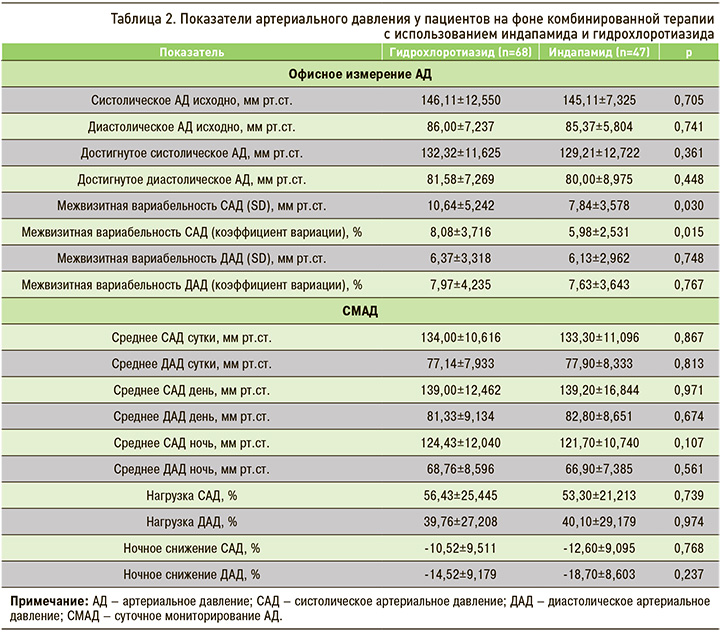
Также немаловажной представляется тенденция к лучшему контролю ночного АД у пациентов, получающих тиазидоподобный диуретик индапамид. Хотя различия в ночном уровне АД и не достигали статистической значимости, однако пользу от назначения диуретика более длительного действия может продемонстрировать клинический пример.
ОПИСАНИЕ КЛИНИЧЕСКОГО СЛУЧАЯ
Пациентка М., 1942 г.р. Рост 157 см, вес 70 кг, индекс массы тела 28,40 (предожирение).
Жалобы: колебания показателей АД до 170/100 мм рт.ст. (периодически отмечается снижение АД до 95–110/70 мм рт.ст.), слабость, головокружение, шаткость при ходьбе.
Особенности анамнеза: много лет страдает гипертонической болезнью (ГБ) с максимальным АД 180/100 мм рт.ст. Физическую нагрузку переносит удовлетворительно, одышка и боль в области сердца не беспокоят. Инфаркты и инсульты отрицает, в 2019 г. перенесла транзиторную ишемическую атаку (ТИА). Находилась в стационаре с 06.11 по 13.11.2019 по поводу ГБ 2 ст. Пережила неосложненный гипертонический криз, купированный на догоспитальном этапе. В стационаре пациентке были проведены эхокардиография (ЭхоКГ), компьютерная томография головного мозга, анализ крови, мочи. В стационаре подобрана гипотензивная терапия, пациентка выписана с улучшением. Хронические заболевания: стенозы брахиоцефальных артерий (БЦА) до 50%. Не курит. Отягощенная наследственность по сердечно-сосудистым заболеваниям. Рекомендованное лечение принимает нерегулярно из-за скачков давления.
Данные ЭхоКГ от 14.01.2019: полости не расширены, фракция выброса в норме, гипертрофия левого желудочка (ГЛЖ), межпредсердная перегородка (МПП) в верхней трети представлена утолщенной, неоднородной эхогенности структурой размерами 1,6×1,7 см (липоматоз? миксома?). Для оценки межпредсердной перегородки рекомендована чреспищеводная ЭхоКГ.
Данные ЭхоКГ от 30.03.2020: полости сердца не расширены. Липоматоз МПП. Локальная и глобальная сократительная функция левого желудочка сохранена (фракция изгнания около 60%). Давление в легочной артерии в пределах нормы.
В настоящее время пациентка принимает телмисартан 80 мг + гипотиазид 12,5 мг (фиксированную комбинацию), лерканидипин 20 мг днем, ацетилсаллициловую кислоту 75 мг, розувастатин 20 мг, ситуационно моксонидин.
Аллергологический анамнез: кашель при лечении ингибиторами АПФ.
Результаты общего осмотра: общее состояние удовлетворительное. Сознание ясное. Кожные покровы бледно-розовые. Пальпация грудной клетки безболезненная. Пастозность голеней. Система органов дыхания: дыхание через нос свободное. Частота дыхания 17/мин. Аускультативно: дыхание везикулярное, хрипы не выслушиваются Сердечно-сосудистая система: тоны звучные, ритм правильный. Патологические шумы не выслушиваются. ЧСС 76/мин без дефицита пульса. АД d=s 100/70 мм рт.ст. (примерно за 1 ч до визита приняла моксонидин 0,2 мг в связи с повышением АД до 170/100 мм рт.ст.). Система органов пищеварения: живот не увеличен, участвует в дыхании, при пальпации мягкий, безболезненный. Печень не увеличена. Стул неустойчивый. Система мочевыделения: мочеиспускание не нарушено.
Данные электрокардиографии (ЭКГ) от 20.07.2020: синусовый ритм с ЧСС 84/мин. Редкие предсердные экстрасистолы, в том числе парные. Резкое отклонение электрической оси сердца влево. Блокада передней ветви левой ножки пучка Гиса. Признаки ГЛЖ. При сравнении с ЭКГ от 16.07.2020 регистрируются единичные предсердные экстрасистолы.
Диагноз основного заболевания: ГБ 3 ст., риск 4. ТИА от 2019 г. Атеросклероз аорты, коронарных артерий, стенозирующий атеросклероз БЦА. Липома верхней трети МПП. Полипы желудка, толстого кишечника. Хронический гастродуоденит.
Пациентке проведено СМАД (на оборудовании ABPM-05 Meditech).
Протокол СМАД: исследование выполнено на фоне терапии. За время мониторирования АД регистрировалось умеренное стойкое повышение систолического АД в дневные часы за счет умеренных значений и стойкое повышение этого параметра ночью за счет умеренно выраженной гипертонии.
Отмечалось стойкое незначительное повышение диастолического АД ночью и единичные эпизоды его незначительного повышения днем. Зарегистрированы единичные эпизоды снижения диастолического АД до 45–48 мм рт.ст. в дневные и вечерние часы.
Максимальное АД 184/105 мм рт.ст.
Минимальное АД 112/45 мм рт.ст.
Среднесуточное АД 142/74 мм рт.ст.
Среднедневное АД 138/70 мм рт.ст.
Средненочное АД 146/76 мм рт.ст.
Временной гипертонический индекс (норма 25%): 74% для систолического АД, 50% для диастолического.
Суточный индекс (норма 10–20%): +6 % для систолического АД, +9 % для диастолического.
Среднесуточная ЧСС 85 уд./мин (от 73 до 110 уд./мин).
Таким образом, контроль за АД оказался недостаточным, с преобладанием повышения АД в ночное время. По данным СМАД, а также с учетом данных о резких колебаниях АД в течение суток было принято решение о коррекции терапии: гидрохлоротиазид заменили на индапамид. В качестве препарата индапамида использован Индап® (ПРО.МЕД.ЦС Прага а.о.) в дозировке 1,25 мг утром (1/2 табл. 2,5 мг). Прием телмисартана был перенесен на вечернее время.
Произведенная замена позволила улучшить контроль за АД и снизить его ночные показатели. Это было подтверждено данными СМАД, выполненного через 4 нед (на оборудовании ABPM-05 Meditech).
Протокол СМАД:
- максимальное систолическое АД 156 мм рт.ст. (08:00);
- максимальное диастолическое АД 92 мм рт.ст. (08:00);
- минимальное систолическое АД 114 мм рт.ст.;
- минимальное диастолическое АД 61 мм рт.ст.;
- среднесуточное АД 132/72 мм рт.ст.;
- среднедневное АД 138/76 мм рт.ст.;
- средненочное АД 128/68 мм рт.ст.;
- временной гипертонический индекс: 36% для систолического АД, 27% для диастолического;
- суточный индекс: 7% для систолического АД, 3% для диастолического АД;
- среднесуточная ЧСС 65 уд./мин (от 57 до 77 уд./мин).
Как видно из приведенных данных, переход к свободной комбинации препаратов с использованием индапамида как диуретика более длительного действия (по сравнению с гидрохлоротиазидом), а также изменение режима приема блокатора рецепторов ангиотензина позволили не только существенно снизить АД в ночное время, но и в значительной степени нормализовать суточный ритм АД.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Тиазидные и тиазидоподобные диуретики блокируют Na-Cl котранспортер на апикальной мембране в дистальных собирательных трубочках. В дистальных собирательных трубочках происходит реабсорбция от 5 до 7% гломерулярного фильтрата. Кроме того, этот отдел нефрона ответственен за экскрецию кальция и концентрацию мочи.
Степень блокады Na-Cl транспортера тиазидными диуретиками не одинакова: она выше у тиазидоподобных препаратов и ниже у гидрохлоротиазида. Отличаются и фармакокинетические свойства диуретиков: гипотензивное действие гидрохлоротиазида развивается уже через 2 ч после приема, пик действия наступает через 4 ч, а общая продолжительность действия составляет до 12 ч. У индапамида длительность эффекта составляет 18–24 ч, у хлорталидона – до 48 ч. Имеются и другие значимые различия между препаратами: например, индапамид исходно является липофильным соединением, что обеспечивает ему высокую биодоступность, а затем, метаболизируясь через глюкуронирование, становится гидрофильным. Такие существенные различия в свойствах тиазидных и тиазидоподобных диуретиков дают основания обсуждать и возможные различия в эффективности препаратов [4].
В настоящее время накоплено большое количество данных о потенциально более высокой антигипертензивной эффективности тиазидоподобных препаратов. В некоторых метаанализах было показано существенное преимущество тиазидоподобных диуретиков перед гидрохлоротиазидом: например, в плане профилактики и обратного развития гипертрофии миокарда тиазидоподобные препараты оказались 2 раза более эффективными [5]. Кроме этого, было продемонстрировано, что терапия тиазидоподобными диуретиками может способствовать лучшему контролю за АД, не вызывая при этом ухудшения электролитного баланса и биохимических параметров крови [6].
В Новой Зеландии был проведен анализ эффективности применяемого там тиазидного диуретика бендрофлюметиозида и тиазидоподобного препарата хлорталидона в реальной практике. Оказалось, что при использовании тиазидоподобного диуретика в качестве стартовой терапии удается достичь уменьшения риска неблагоприятных исходов, а при использовании тиазидного – нет [7]. В метаанализе 14 рандомизированных исследований, опубликованном в 2015 г., было установлено, что различия в снижении АД на фоне терапии стандартными дозами индапамида и гидрохлоротиазида составляют около 5 мм рт.ст. При этом риск побочных метаболических эффектов препаратов сопоставим [8].
В проведенном нами исследовании существенных различий в достигнутых значениях АД при назначении гидрохлоротиазида и индапамида зарегистрировано не было, однако на фоне назначения индапамида оказалась достоверно ниже долгосрочная вариабельность АД. Ранее в исследовании X-CELLENT было показано, что индапамид, как и амлодипин, могут уменьшать суточную вариабельность АД по данным мониторирования. При этом блокатор рецепторов ангиотензина кандесартан в монотерапии на этот параметр существенно не влиял, несмотря на в целом сопоставимое антигипертензивное действие [9]. Отметим, что вариабельность АД может рассматриваться как важный дополнительный показатель хорошего контроля за АД. Она может лучше характеризовать степень контроля АД, чем достигнутые значения офисного АД, что может иметь ключевое значение, например, с точки зрения профилактики инсульта [10].
Интересна и возможность нормализовать суточный ритм АД при использовании тиазидоподобных диуретиков. Известно, что на фоне антигипертензивной терапии до 30% больных имеют повышение АД в ночное время («маскированная гипертония») [11]. Один из возможных путей эффективной борьбы с «маскированной гипертонией» – замена тиазидных диуретиков на более длительно действующие тиазидоподобные.
В приведенном нами клиническом случае замена гидрохлоротиазида на индапамид привела к дополнительному снижению АД преимущественно в ночное время без эпизодов гипотонии. Следует отметить, что пациентка применяла свободную комбинацию препаратов, позволившую нормализовать суточный ритм АД. Подобные же результаты были получены ранее в исследовании, где сравнивались два режима применения свободной комбинации азилсартана и индапамида: одной группе пациентов оба препарата назначались утром, другая группа получала индапамид утром, а азилсартан вечером. Оба режима приема препаратов позволили достичь достоверного снижения уровня АД в течение суток, но только прием азилсартана в вечернее время позволил нормализовать ночное АД [12].
Следует подчеркнуть, что в представленном случае была использована половина от рекомендованной для лечения АГ суточной дозы индапамида. Такая доза назначалась с целью уменьшения риска эпизодов гипотонии, которые у пожилой больной отмечались на фоне приема комбинаций с использованием гидрохлоротиазида. Для пожилых пациентов использование низких доз диуретиков особенно важно с точки зрения безопасности этих препаратов [13].
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Таким образом, наличие лекарственной формы индапамида в виде делимой таблетки может иметь практическую ценность при лечении АГ у пожилых пациентов, поскольку это позволяет назначать препарат в низких дозах и в необходимых сочетаниях.



