ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Распространенность воспалительных заболеваний кишечника (ВЗК) неуклонно растет и давно уже стала серьезной проблемой общественного здравоохранения во всем мире [1–5]. Наиболее часто ВЗК представлены такими патологиями, как болезнь Крона (БК) и язвенный колит (ЯК). К менее известным формам ВЗК относится микроскопический колит (MК), который включает коллагеновый и лимфоцитарный колиты, а также неполный микроскопический колит (MКi) при невозможности четкого различения форм МК [2]. Все указанные ВЗК имеют как общие (наслаивающиеся), так и самостоятельные клинические и патологические черты. Формы заболевания в некоторой степени сходны по эпидемиологии, генетическим особенностям пациентов и клиническим проявлениям, предполагающим их возможную этиологическую общность и патогенез [5]. Поскольку естественное течение болезни, выбор тактики терапевтического и хирургического лечения, реакция на медикаментозное воздействие, осложнения, эффективность лечения, исходы заболевания, прогноз и потенциал различных ВЗК значительно различаются, точный диагноз имеет решающее значение для надлежащей терапии [6–8].
Кроме того, диагностическую дилемму для практических врачей формирует необходимость проведения дифференциальной диагностики рассматриваемой группы заболеваний с функциональными заболеваниями кишечника, так как зачастую кинические симптомы дебюта функциональных гастроинтестинальных расстройств (ФГИР) и ВЗК схожи [9]. С другой стороны, наблюдается явная недооценка симптомов ВЗК в некоторых ситуациях и задержка в диагностике (удлинение времени от появления симптомов до постановки диагноза) в случае истинных БК и ЯК, что особенно заметно при БК тонкой кишки.
На данный момент единого «золотого» стандарта для первичной диагностики и дифференциальной диагностики БК или ЯК не существует. Согласно российским клиническим рекомендациями по ведению пациентов с ВЗК [10, 11] и консенсусу Европейского общества по изучению болезни Крона и язвенного колита (European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation, ECCO), диагноз БК или ЯК как минимум должен быть основан на оценке клинических данных, результатов клинического и биохимического исследования крови, исследований кала, эндоскопических, гистологических и радиологических исследований [12]. При этом наиболее надежным методом диагностики наличия и оценки степени активности ВЗК служит эндоскопическое обследование [8, 12, 13]. Степень активности ВЗК при эндоскопическом исследовании подтверждается калькуляцией данных эндоскопии посредством утвержденных систем оценки, таких как эндоскопический индекс тяжести ЯК (UCEIS), эндоскопическая шкала Мейо (MES) для ЯК [14, 15] и простая шкала эндоскопической оценки для БК (SES-CD) [15], а также гистологической оценкой биоптатов, полученных во время данного исследования [16, 17]. Но даже после верификации ВЗК часто возникает неопределенность в дифференциации диагноза: как показывают результаты исследований, около 10% пациентов с ВЗК имеют в амбулаторных картах диагноз «неопределенный колит» [5, 18]. Помимо этого, в некоторых случаях достаточно сложно различить формы ВЗК или колит другой этиологии, что также может отрицательно влиять на эффективность дальнейшего лечения и «управление» заболеванием, снижать качество жизни пациентов и увеличивать расходы на лечение [19, 20].
Хотя эндоскопическое исследование при ВЗК и является эталоном для наблюдения за активным заболеванием, оно как процедура мониторинга не лишено определенных недостатков. Так, эндоскопические индексы оценки активности ВЗК (индекс активности болезни Крона (CDAI) и индекс Харви Брэдшоу (HBI) для БК и простой индекс клинической активности колита (SCCAI) для ЯК) не всегда коррелируют с эндоскопическими данными и заживлением слизистой оболочки кишечника [15, 19]. Показано, что почти у половины пациентов с БК с клинической ремиссией по-прежнему наблюдаются эндоскопические признаки активного заболевания, тогда как примерно у 40% пациентов с эндоскопически неактивным заболеванием отмечаются клинические симптомы [21, 22].
Таким образом, постоянно растет потребность в неинвазивных маркерах для диагностики, дифференциальной диагностике и прогнозирования течения ВЗК. В качестве инструмента для диагностики, дифференциальной диагностики и адекватного мониторинга ВЗК могут выступать серологические и фекальные биомаркеры. В 1998 г. рабочая группа по определению биомаркеров Национального института здоровья США определила биомаркер как «характеристику, которая объективно измеряется и оценивается в качестве индикатора нормальных биологических процессов, патогенных процессов или фармакологических реакций на терапевтическое вмешательство» [23]. Пример такого биомаркера – холестерин [24]. Идеальный биомаркер должен быть неинвазивным, чувствительным, специфичным для заболевания, простым в исполнении и экономичным.
Rogler G. и Biedermann L. [25] с клинической точки зрения выделяют четыре ситуации, в которых биомаркеры могут быть полезными: 1) когда установлен диагноз ВЗК и необходима помощь в дифференциации БК и ЯК; 2) для прогностической оценки тяжести ВЗК или течения болезни и раннего принятия решения о наилучшем лечении; 3) при определении активности заболевания во время течения болезни, мониторинге и управлении продолжающимся лечением; 4) после операции для прогнозирования или диагностики рецидива заболевания.
В фокусе внимания этой работы – различные иммунологические маркеры сыворотки/плазмы крови, их эффективность и место в диагностике ВЗК, роль в дифференциальной диагностике БК и ЯК. Добавление исследований таких маркеров к эндоскопическим, рентгенографическим и даже морфологическим исследованиям позволит клиницистам диагностировать и лечить ВЗК более эффективно и экономично.
Настоящий обзор литературы по биомаркерам в диагностике ВЗК основан на результатах анализа статей, содержащихся в базах данных PubMed, Springer и Scopus за период 1990–2022 гг. Индивидуальный поиск в базе данных PubMed выполнялся по ключевым словам «биомаркер», «маркер», «воспалительное заболевание кишечника», «болезнь Крона», «язвенный колит», «протеомика», «липидомика». Ссылки, использованные в найденных статьях, затем проверялись на предмет дальнейших исследований, представляющих потенциальный интерес. Тезисы были проверены на соответствие критериям.
БЕЛКИ ПЛАЗМЫ
С-реактивный белок (СРБ) – хорошо известный неспецифический маркер воспаления. При БК его уровень обычно повышается, особенно при пенетрирующей и абсцедирующей формах, однако при ЯК показатель имеет меньшее диагностическое и прогностическое значение. У больных ЯК повышенный уровень СРБ наблюдается редко и, безусловно, служит индикатором тяжелого течения заболевания [25].
Другие белки острой фазы, такие как α1 кислый гликопротеин (AGP, орозомукоид), фибриноген, микроглобулин β2, амилоид А сыворотки (аполипопротеин липопротеидов высокой плотности (ЛПВП), принадлежит к семейству реагентов острой фазы), эотаксин-1 (CCL11, селективный хемоаттрактант, играющий важную роль в активации и привлечении эозинофилов в собственную пластинку кишечника), α2-глобулин и α1-антитрипсин в настоящее время изучаются как индикаторы ВЗК, но пока не нашли широкого применения в клинической практике [26].
СЕРОЛОГИЧЕСКИЕ МАРКЕРЫ – АНТИТЕЛА
Широко известно, что у пациентов с ВЗК выявляются сывороточные антитела (АТ), которые играют вспомогательную роль в диагностике. Подобные АТ как самостоятельно, так и в сочетании были признаны возможными параметрами для диагностики и дифференциальной диагностики ВЗК, но точное клиническое значение их в плане диагностики/течения/прогнозирования болезни четко не определено. Маркеры антител при ВЗК можно разделить на две группы: аутоантитела, представляющие собой АТ к кишечным и некишечным самостоятельным компонентам, и микробные АТ – АТ к различным микроорганизмам, включая бактерии, дрожжи и грибки. К наиболее известным группам аутоантител относятся DNase-sensitive-pANCA и АТ к гликопротеинам поджелудочной железы (PAb).
DNase-sensitive-pANCA – дезоксирибонуклеаза (ДНКаза)-чувствительные перинуклеарные антинейтрофильные цитоплазматическкие АТ, являющиеся АТ против гранул цитоплазмы нейтрофилов. «Золотым» стандартом выявления ANCA служит реакция непрямой иммунофлюоресценции. Как субстрат для этой реакции используются нейтрофилы, фиксированные с помощью этанола. АТ обнаруживаются с помощью непрямой иммунофлюоресценции в качестве базового скринигового теста. Этот метод позволяет выделить два основных типа свечения ANCA: цитоплазматический тип (cANCA) и перинуклеарный тип (pANCA) в зависимости от вида антигенных мишеней, с которыми связываются данные аутоантитела. Антигеном, который соответствует pANCA, считается гистон 1, тогда как антиген cANCA – это протеиназа 3 и миелопероксидаза [24].
Установлено, что содержание перинуклеарных ANCA (pANCA) значительно возрастает при ЯК, при этом их титры изменяются в зависимости от активности заболевания [27]. Joossens S. et al. в проспективном исследовании обнаружили, что у 64% пациентов с ЯК были положительные pANCA и отрицательные ASCA [28]. В то же время примерно у 25% пациентов с эндоскопически или гистопатологически подтвержденной БК, локализованной в левых отделах толстой кишки и сопровождающейся симптомами, аналогичными ЯК, уровень pANCA в плазме крови повышен, что ограничивает эффективность pANCA при дифференциальной диагностике ВЗК [29]. В отличие от ряда предшествующих работ, недавно опубликованное ретроспективное поперечное исследование с участием 2550 человек в Австралии показало, что серопозитивность pANCA была обнаружена у более чем 80% больных с ВЗК и при этом не различалась у пациентов с БК и ЯК, а комбинированное использование pANCA и ASCA не позволяло дифференцировать подтипы ВЗК в этой когорте [30].
Основным антигеном cANCA выступает фермент из группы сериновых протеаз – протеиназа-3, служащий диагностическим маркером гранулематоза Вегенера. Вместе с тем аутоантитела к нейтрофильной протеиназе 3 (PR3), возможно, могут быть полезным серологическим маркером для дифференцирования субпопуляций ВЗК, поскольку показано, что частота положительных результатов PR3-ANCA у пациентов с ЯК составляет 15–40%, тогда как у пациентов с БК – лишь 0–10% [31, 32]. Считается, что сочетанное использование нескольких АТ ANCA может повысить эффективность диагностики ВЗК. Было продемонстрировано, что у пациентов с уже диагностированным БК или ЯК прогностическая ценность pANCA-отрицательного / ASCA-положительного результата составляла 95% для БК, тогда как pANCA-положительный / ASCA-отрицательный результат имел 90% прогностическую ценность для ЯК [32].
АТ к гликопротеинам поджелудочной железы (антиген-специфические панкреатические АТ, PAb) присутствуют у 20–30% пациентов с БК, но менее чем у 2–9% больных ЯК и могут в очень малом количестве обнаруживаться при состояниях, не связанных с ВЗК. Основными антигенами PAb являются гликопротеин 2 (GP2, также называемый MZGP), CUB и zona pellucida-подобные домены 1 (CUZD1) [24]. Аутоантитела к GP2 поджелудочной железы рассматриваются как многообещающие сывороточные маркеры для дифференциации БК от ЯК [25, 33]. GP2 представляет собой мембраносвязанный рецептор, расположенный в клетках микроскладок Пейеровских бляшек кишечника, который взаимодействует с fimH-положительными бактериями (GP2 распознает FimH, главный компонент ворсинок 1-го типа на внешней мембране подгруппы грамотрицательных энтеробактерий, таких как E. coli и Salmonella enterica) и опосредует специфические для бактерий иммунные ответы слизистой оболочки [32]. Богатые GP2 М-клетки в изобилии находятся в тонкой кишке, тогда как в толстой кишке встречаются редко.
Высвобождение антител к GP2 связано с воспалением подвздошной кишки, которое может объяснить более высокую экспрессию GP2 в сыворотке у пациентов с БК [29, 30]. Отмечалось также, что экспрессия PAb может иметь расовые различия. В одном исследовании было описано 46% положительных результатов PAb среди китайских пациентов с БК по сравнению с 22% у европейских пациентов [33].
АНТИМИКРОБНЫЕ АНТИТЕЛА
В клинической практике антимикробные антитела обычно не применяются, их роль в ведении пациентов с ВЗК требует дальнейшего изучения и проспективных исследований, чтобы подтвердить их полезность. К наиболее известным серологическим маркерам этой группы относятся:
- IgA и IgG ASCA – IgA и IgG АТ к маннану клеточной стенки Saccharomyces cerevisiae (пекарских дрожжей). Выявление их в диагностическом титре в большей степени характерно для БК [34, 35]. У здоровых людей циркулирующие ASCA также могут быть выявлены у 5% лиц [10]. Полагают, что при БК ASCA служат маркером риска раннего начала заболевания, фибростенозирования и пенетрации. ASCA у пациентов с БК в основном обнаруживаются, когда воспаление затрагивает терминальный отдел подвздошной кишки, однако их экспрессия относительно низкая у пациентов с изолированной БК толстой кишки. Amre D.K. et al. показали, что наличие ASCA увеличивает вероятность хирургического вмешательства при БК примерно на 10% по сравнению с ASCA-отрицательными пациентами [35], но с клинической точки зрения различие в риске 10% незначительно влияет на принятие серьезных решений о необходимости такого лечении [25].
- Анти-OmpC – АТ к порину наружной мембраны Escherichia coli.
- АТ к пептиду I2 (анти-I2, возможный антиген – белок Pseudomonas spp., Pseudomonas fluorescens).
- Анти-CBir1 (возможный антиген – бактериальный (клостридиальный?) флагеллин).
- АТ к флагеллину A4-Fla2 и Fla-X.
Исследования известных микробных АТ допускают их более высокую специфичность для БК, чем для ЯК [36], однако сообщалось, что анти-I2 был обнаружен и у пациентов с воспалительным энтеритом, не относящимся к ВЗК (в 19% случаев) [37]. Существует предположение, что титры и количество микробных АТ тесно связаны с клиническими фенотипами БК: так, пенетрирующий фенотип распространен среди анти-OmpC-положительных пациентов, БК тонкой кишки, стриктурирующий и пенетрирующий фенотипы – среди анти-CBir1-положительных пациентов, а стриктурирующий фенотип и необходимость хирургического вмешательства на тонкой кишке являются обычными для анти-I2-положительных пациентов [36, 37].
Сходные результаты были получены в многоцентровом проспективном исследовании педиатрических пациентов с БК, где использовались четыре антитела: ASCA, анти-OmpC, анти-CBir1 и анти-I2 [38]. Более того, в исследованиях было установлено, что чем выше количество положительных антител, тем больше вероятность того, что стриктура и пенетрация развиваются как осложнения БК: когда все четыре АТ (ASCA, анти-OmpC, анти-CBir1 и анти-I2) положительны, частота подобных осложнений БК в 11 раз выше, чем в том случае, когда все эти четыре маркера отрицательны [39]. С другой стороны, необходимость в раннем хирургическом вмешательстве и частые осложнения, связанные с послеоперационным паучитом, были обнаружены в pANCA-положительных случаях ЯК без выявления антимикробных АТ [40].
Диагностическое значение других известных серологических микробных АТ, таких как антиманнобиозидные (AMCA), антиламинорибиазидные АТ (ALCA), антихитобиозидные (ACCA), антиламинарные (Anti L) и антихитиновые (Anti C) АТ, АТ против колониестимулирующего фактора гранулоцитарных макрофагов (анти-GM-CSF) и др., пока полностью не исследовано.
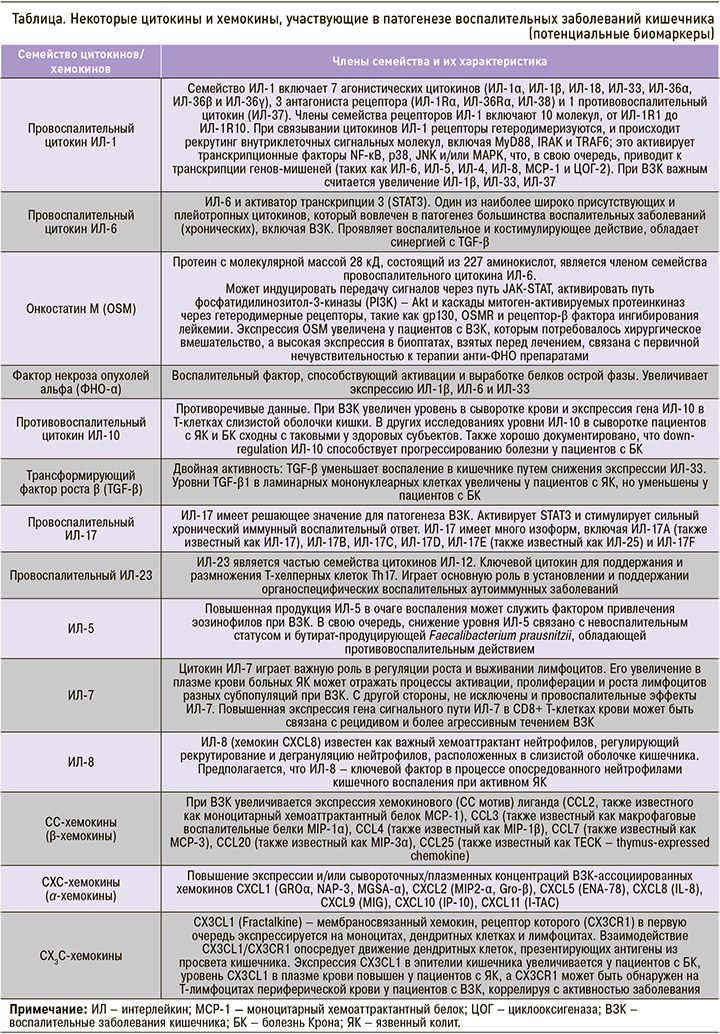
СЕРОЛОГИЧЕСКИЕ МАРКЕРЫ – ЦИТОКИНЫ И ХЕМОКИНЫ
Цитокины, хемокины и факторы роста, которые являются растворимыми сигнальными молекулами иммунной системы, играют важную роль в патофизиологии ВЗК, участвуя в процессах воспаления, дифференцировки клеток, процессах хемотаксиса, миграции лимфоцитов, нейтрофилов и других иммунных клеток к поврежденным тканям. Некоторые цитокины обладают местным действием и могут выявляться в основном в тканях, другие могут быть обнаружены на системном уровне. Этот факт способствовал выдвижению гипотезы о различии уровней цитокинов в кровотоке у пациентов с ВЗК и без, что может иметь существенное диагностическое или прогностическое значение при оценке активности заболевания [41]. Sands B.E. было отмечено, что при многих патологиях комбинации воспалительных цитокинов выступают прогностическими факторами воспалительного состояния и, следовательно, адекватными биомаркерами для неинвазивного мониторинга активности заболевания [42].
Цитокины имеют ключевое значение в патогенезе ВЗК, контролируя воспаление кишечника и активность заболевания, и могут быть лучшими прогностическими маркерами активности болезни, чем фекальный кальпротектин и СРБ [42, 43]. Исследования уровней цитокинов при ВЗК на фактических участках воспаления в кишечнике привели к формированию парадигмы, согласно которой ЯК является Th2-ассоциированным заболеванием, тогда как при БК основную роль играют цитокины Th1/Th17, управляющие воспалительной реакцией [44]. Предполагается, что эта дихотомия лишь частично проявляется на системном уровне, и многие из классических цитокинов врожденного и адаптивного иммунитета не могут быть найдены в сыворотке крови пациентов с ВЗК или в контроле. Korolkova O.Y. et al. [41] изучали уровень 23 цитокинов в сыворотке крови у пациентов с ЯК и БК: значительных различий в цитокиновом профиле между этими двумя заболеваниям получено не было. Возможно, исследованные цитокины ограничены участками ткани воспаления, имеют относительно короткий период полураспада и проявляют себя в кровотоке только в случае значительной прогрессии заболевания. Тем не менее при оценке цитокинового/хемокинового статуса исследователи чаще всего концентрируются на сравнении одной или обеих форм ВЗК с контрольными группами. В недавнем исследовании у больных с ЯК анализ цитокинового профиля выявил значимое повышение концентраций интерлейкинов (ИЛ) ИЛ-5, ИЛ-7, ИЛ-12, ИЛ-10 и хемокинов CCL3/MIP-1α, CXCL8/IL-8, CXCL11/I-TAC и CX3CL1/Fractalkine [45]. Кроме того, доля фолликулярных Т-хелперов 2 (Tfh2), способных переключать класс синтезируемых B-клетками антител с IgM на IgG и IgA, у пациентов с ЯК была значимо повышена по сравнению с контролем [45].
Некоторые исследованные цитокины и хемокины сыворотки/плазмы крови, участвующие в патогенезе ВЗК и представляющие интерес как потенциальные биомаркеры этих заболеваний, приведены в таблице [45, 46].
ГЕНЕТИЧЕСКИЕ И ЭПИГЕНЕТИЧЕСКИЕ МАРКЕРЫ
Понимание механизмов заболевания на системном уровне, открытие сложных биомаркеров и в конечном итоге составление личного омического профиля в перспективе является возможным благодаря быстрому развитию технологий молекулярных измерений. Примечательно, что новые технологии секвенирования теперь облегчают анализ вариаций генома и ответов транскриптомов на такой глубине, которая была немыслима всего несколько лет назад. За последнее десятилетие был достигнут огромный прогресс в развитии и совершенствовании протеомных технологий, с помощью полногеномного поиска ассоциаций (GWAS) и трансэтнических исследований полностью идентифицировано более 200 локусов восприимчивости к ВЗК, выявлены новые полиморфизмы одиночных нуклеотидов (SNP) [47]. Было обнаружено, что некоторые моногенные дефекты изменяют иммунный гомеостаз кишечника с помощью нескольких механизмов, таких как нарушение эпителиального барьера и эпителиального ответа, снижение клиренса бактерий у нейтрофильных гранулоцитов и других фагоцитов. Другие SNP-дефекты индуцируют гипервоспаление или аутовоспаление или нарушают селекцию и активацию T- и B-клеток. Несомненно, будущие исследования функциональных и экспрессивных локусов (локусы количественных признаков экспрессии, eQTL) улучшат наше понимание патогенеза ВЗК, а внедрение секвенирования нового поколения (NGS) позволит идентифицировать каждую генетическую вариацию по всему геному человека в одном эксперименте [47].
Существующие достижения уже открывают возможности для долгожданного персонализированного медицинского подхода к лечению ВЗК и предоставляют новые идеи, такие как новые биомаркеры-кандидаты для БК. Например, Hong S.N. et al., применяя методику секвенирования РНК (RNA-seq), выявили транскриптомные различия между нормальной слизистой оболочкой, невоспаленной слизистой оболочкой и воспаленной слизистой оболочкой у пациентов с БК [48]. При этом было продемонстрировано наибольшее кратное различие экспрессии гена CXCL1 между исследуемыми группами пациентов с БК: экспрессия гена CXCL1 (член семейства CXC-хемокинов, который обладает нейтрофильной хемоаттрактантной активностью и экспрессируется в основном в нейтрофилах, макрофагах и эпителиальных клетках в кишечнике и сыворотке крови) существенно увеличивалась при активном воспалении. На основании полученных данных было высказано предположение, что данный ген имеет функциональную связь с БК, а измерение уровней экспрессии транскриптов гена может использоваться в качестве потенциального биомаркера данного заболевания и оценки степени воспаления [48]. Следует отметить, что авторы протеомных исследований отстаивают важность заборов образцов как крови, так и ткани кишечника для изучения протеомики у пациентов с ВЗК.
Эпигенетика описывает взаимодействия генов с окружающей средой, влияющие на экспрессию генов, но без изменений в последовательности ДНК. В конце прошлого века был открыт ряд малых некодирующих РНК (мнРНК, non-coding RNA, ncRNA), не участвующих напрямую в синтезе белка, но имеющих большое значение в регуляции экспрессии генов на разных уровнях [49]. Со времени открытия мнРНК их механизмы и функции так до конца и не определены. МнРНК обнаружены во всех типах организмов, включая даже вирусы и бактерии. Непосредственно в клетке мнРНК обычно локализованы в ядре и цитоплазме, реже в ДНК-содержащих органеллах (митохондриях и пластидах), где и происходит их синтез. Пока не существует четкой классификации мнРНК, которая существует, например, для белков. Основной фактор разграничения мнРНК по классам – их распространенность в конкретных типах организмов, клеточная локализация и взаимодействие с сопровождающими белковыми комплексами. Малые некодирующие РНК (мнРНК) – короткие РНК, участвующие в регуляции экспрессии генов, иммунитете клетки и посттранскрипционных модификациях РНК [50].
Среди всего разнообразия мнРНК наибольший интерес в плане биомедицинского применения вызывают три класса малых РНК: малые интерферирующие РНК (миРНК), микроРНК и piwi-interacting РНК (пиРНК). Главная функция миРНК – подавление экспрессии (сайленсинг, или замалчивание) генов посредством ингибирования процесса трансляции таргетного белка [49]. Недавние исследования показали, что миРНК опосредуют воспалительные реакции и функцию кишечного барьера в патогенезе ВЗК. Имеющиеся данные исследований мнРНК позволяют предположить об их применении в двух основных областях – диагностике и терапии заболеваний. В ходе дальнейших исследований важно не только найти строго специфичные маркеры различных заболеваний, сконструировать высокоспецифичные терапевтические РНК, но и найти эффективный способ их доставки.
Длинные некодирующие РНК (LncRNA, днРНК) представляют собой некодирующие РНК, участвующие в регуляции различных внутриклеточных процессов и имеющие длину более 200 нуклеотидов [50]. За последнее десятилетие объем исследований днРНК при ВЗК увеличился, при этом была обнаружена дисрегулируемая экспрессия в образцах крови и биопсийной ткани. Было доказано, что LncRNA играют важную роль в патогенезе ВЗК, включая регуляцию кишечного эпителиального барьера, апоптоза клеток и различных процессов иммунной системы [51].
ПРОТЕОМИКА И ЛИПИДОМИКА
Протеомика и липидомика также применялись для исследования ответов иммунных клеток, связанных с ВЗК. Исследования показали участие Th17 в патогенезе ВЗК, особенно в БК-ассоциированной дисрегуляции иммунных ответов. Riaz Т. et al. сравнивали протеомы клонов Th1 и Th1/Th17 человека, полученных из биоптатов кишечника пациентов с БК [52]. Всего был определен 7401 белок; при этом 334 по-разному экспрессировались между клонами Th1 и Th1/Th17. В соответствии с их функциями в иммунных ответах цитотоксические белки, такие как гранзим B и перфорин, были более распространены в Th1, чем в Th17 клетках. Однако только подгруппа клонов клеток Th1 от пациентов с БК, охарактеризованная как CD28-положительная, и D-отрицательная группа естественных киллеров проявляли эти цитотоксические свойства; что свидетельствует о большем разнообразии опосредованного Т-клетками иммунного ответа при БК, чем ожидалось. В другом недавнем исследовании протеомный анализ регуляторных Т-клеток (CD4+ Foxp3+ Treg) позволил выявить специфический белок Themis1, сверхэкспрессия которого в Treg приводила к усилению их супрессивных функций [53, 54].
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Биомаркеры – ценные инструменты при ведении пациентов с ВЗК, а их использование для диагностики, дифференциальной диагностики и оценки прогноза заболевания – постоянно расширяющаяся область исследований. Некоторые из них способны помочь клиницистам в выборе правильной терапевтической стратегии и прогнозировании риска нежелательных явлений при ВЗК. Однако биомаркеры следует использовать только тогда, когда связанная с ними дополнительная информация действительно полезна для принятия клинических решений. В контексте ВЗК мы имеем целый ряд биомаркеров, которые были исследованы и внедрены в клиническую практику. Многие из них указывают на системное воспаление и поэтому имеют ограничения в практическом использовании, некоторые же относительно специфичны для ВЗК, например «серологические маркеры».
Следует понимать, что на сегодня не существует идеального биомаркера, который был бы патогномоничным при диагностике ВЗК, позволял бы различать подтипы ВЗК или контролировать активность заболевания и прогнозировать его течение. Более того, на данный момент нет ни одного биомаркера, который был бы достаточно чувствительным или специфичным, чтобы только по результатам его анализа можно было уверенно поставить диагноз того или иного ВЗК.
Большинство биомаркеров, применяемых в клинической практике при ведении пациентов с ВЗК, не специфично для этой группы заболеваний. Они указывают на патологические/физиологические процессы или реакции, такие как воспаление, инфильтрацию тканей лейкоцитами или острофазовую реакцию, которая может возникать во время многих других заболеваний и патофизиологических состояний. При этом один-единственный биомаркер вряд ли может служит точным критерием диагноза, учитывая сложный иммунологический патогенез ВЗК, взаимосвязь всех факторов, способствующих патогенезу, и их взаимное влияние, которые привели к концептуальному оформлению интерактома ВЗК, охватывающему аспекты иммунома, микробиома, экспосома и генома. В кишечном микроокружении, где множество компонентов ВЗК функционально взаимодействуют, никакая информация об одной молекуле, отдельном гене или отдельном микробе не может в достаточной мере объяснить всю совокупность событий, которые возникают в результате постоянной обратной связи и передачи сигналов с прямой связью [12].
Поиск биомаркеров и новых диагностических и прогностических паттернов ВЗК продолжается. Наиболее важно то, что ни одно исследование по идентификации биомаркеров не должно планироваться без независимой когорты исследований для подтверждения результатов. Включение биомаркеров в существующие модели прогнозирования или индексы заболеваний может способствовать созданию основанной на иммунологии модели прогнозирования эндоскопического статуса слизистой оболочки при ВЗК.



