ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Спондилоартриты (СпА) – группа хронических воспалительных заболеваний, характеризующаяся поражением крестцово-подвздошных сочленений (КПС) и/или позвоночника с потенциальным исходом в анкилоз, с частым вовлечением в патологический процесс энтезисов и периферических суставов, с поражением не только опорно-двигательного аппарата, но также глаз (увеит, иридоциклит), кишечника (болезнь Крона и язвенный колит), сосудов (аортит) и кожи (псориаз) [1]. Распространенность СпА в разных странах варьирует от 9 до 30 человек на 10 000 населения [1, 2].
Сопутствующие заболевания при СпА не только усугубляют их течение, но и ограничивают проведение необходимой патогенетической терапии, что приводит к снижению трудоспособности пациентов, а в редких случаях и к летальному исходу. Известно, что своевременная диагностика коморбидных заболеваний при СпА имеет решающее значение для выбора адекватной терапии и улучшения функциональной активности пациентов.
В связи с тем что дебют заболевания у большинства пациентов с СпА развивается в молодом возрасте (пик заболеваемости – до 45 лет), необходимо разработать такой алгоритм лечения, который бы обеспечивал высокий уровень качества жизни больных с учетом коморбидной патологии и благоприятный прогноз течения основного заболевания. На фоне длительной терапии базисными противовоспалительными препаратами (БПВП) и нестероидными противовоспалительными препаратами (НПВП) могут возникать нежелательные явления, требующие изменения тактики лечения СпА. Наиболее часто среди них встречаются НПВП-гастропатии, энтеропатии, язвенная болезнь желудка и интерстициальный нефрит. У пациентов, рефрактерных к приему НПВП и БПВП, назначенная терапия генно-инженерными биологическими препаратами (ГИБП) может сопровождаться нарастанием количества случаев инфекционных процессов (бактериальных, вирусных, грибковых).
Известно, что наиболее часто встречаемыми и жизнеугрожающими коморбидными состояниями при СпА являются кардиоваскулярные заболевания. У пациентов с СпА отмечается повышенный риск сердечно-сосудистой и цереброваскулярной смертности по сравнению с аналогичными показателями в общей популяции. Так, шведское популяционное когортное исследование показало повышенную вероятность смертности от всех причин у пациентов с анкилозирующим спондилитом (АС) с поправкой на возраст и пол (относительный риск (ОР) 1,60; 95% доверительный интервал (ДИ): 1,44–1,77), при этом основной причиной смерти выступали именно сердечно-сосудистые заболевания (ССЗ) [3]. В крупном популяционном исследовании, проведенном в Канаде, было установлено, что риск сердечно-сосудистой смерти у мужчин с СпА был более высоким, чем у женщин (ОР 1,46 против 1,24 соответственно) [4]. Итогом выполненных исследований стала разработка предикторов высокого риска смертельных исходов при СпА, которые включали мужской пол, пожилой возраст, сахарный диабет или хроническую болезнь почек, а также низкий уровень образования пациентов [5].
В общей популяции наиболее распространенным индексом для оценки сердечно-сосудистого риска служит модель прогнозирования риска кардиоваскулярных заболеваний Systematic COronary Risk Evaluation (SCORE), адаптированная для пациентов с ревматическими заболеваниями с использованием поправочного коэффициента 1,5. Однако применение этого увеличивающего коэффициента не всегда помогает в реальной оценке вероятности возникновения значимых сердечно-сосудистых событий.
Высокая частота коморбидной патологии была подтверждена в исследовании ASAS-COMOSPA с участием 3923 пациентов с СпА: среди сопутствующих заболеваний у участников чаще других отмечались артериальная гипертензия (34%), гиперхолестеринемия (27%), остеопороз (13%), язвенная болезнь желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки (11%) [6].
В свою очередь, в проведенном Zhao S.S. et al. в 2020 г. метаанализе 40 исследований было установлено, что наиболее распространенными сопутствующими заболеваниями при СпА были артериальная гипертензия (совокупная распространенность 22,3%), гиперлипидемия (17,1%), ожирение (13,5%), а также другие ССЗ (12,3%) [7].
Возникновение кардиоваскулярной патологии у больных СпА связывают с хроническим системным Th1–Th17-опосредованным воспалением, которое сопровождается повышением уровня таких провоспалительных цитокинов, как фактор некроза опухоли-альфа (ФНО-α), интерлейкин 2 (ИЛ-2), ИЛ-6, ИЛ-8, ИЛ-17; эти цитокины влияют на процессы неоангиогенеза, резистентности к инсулину, а также активацию мононуклеарных клеток и адгезию тромбоцитов [8–10].
Показано, что моноклональные антитела, нейтрализующие ИЛ-17, могут улучшать исходы у пациентов с псориатическим артритом и сопутствующими ССЗ [19]. Эта гипотеза дополнительно подтверждается моделью атеросклероза, воспроизведенной на животных, в которой ингибирование ИЛ-17A вызывало предотвращение прогрессирования сердечно-сосудистого поражения и стабилизацию атеросклеротических бляшек [20].
В связи с широкой распространенностью коморбидной патологии при СпА возникает закономерный вопрос: влияют ли сопутствующие заболевания на активность и исходы СпА? Согласно данным Британского регистра, у 44% пациентов имелось как минимум одно сопутствующее заболевание, причем каждая дополнительная коморбидность увеличивала индекс BASDAI на 0,40 балла (95% ДИ: 0,27–0,52), а вертебральные боли на 0,53 балла (95% ДИ: 0,37–0,68). Выяснилось, что депрессия, сердечная недостаточность и язвенная болезнь были стабильно связаны с высокими показателями активности СпА.
Таким образом, основная цель лечения больных СпА – не только достижение ремиссии или низкой активности этого заболевания, но и стабилизация течения сопутствующих патологий. При этом требуются дальнейшие исследования, посвященные повышению эффективности консервативной терапии не только самих СпА, но и коморбидных заболеваний, гетерогенность которых нередко создает значительные трудности в выборе стратегии лечения данной категории пациентов.
Цель настоящего исследования – оценить частоту встречаемости коморбидной патологии и ее влияние на активность СпА у пациентов, получающих терапию ГИБП.
МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДЫ
Дизайн исследования. В статистический анализ были включены 146 пациентов, преимущественно мужского пола (77 человек – 52,7%), которые страдают заболеваниями группы СпА (в соответствии с критериями ASAS от 2009 г.) и получают генно-инженерную биологическую терапию блокаторами ФНО-α.
Этические аспекты. Все пациенты подписывали форму информированного согласия на участие в исследовании. Все данные пациента обезличивались и обрабатывались в обезличенном виде. Исследование было одобрено комитетом по этике ФГБОУ ВО СЗГМУ им. И.И. Мечникова.
Анализ активности болезни и коморбидности. Для определения активности заболевания использовались индексы BASDAI (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index) и ASDAS (Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score) по С-реактивному белку (ASDASСРБ) на 0, 24, 52-й неделе, а также функциональный индекс BASFI (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index) на этапе включения в исследование [4, 5]. Из лабораторных методов оценки воспалительной активности проводилась оценка уровня СРБ высокочувствительным методом (мг/л). Индексы сердечно-сосудистого риска определялись на основании шкалы SCORE с использованием поправочного коэффициента для пациентов с ревматическими заболеваниями.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
Клиническая характеристика пациентов с СпА, находящихся на терапии ГИБП из группы ингибиторов ФНО-α, представлена в таблице 1. Всем участникам исследования терапия ГИБП была назначена в связи с высокой активностью основного заболевания, неэффективностью или наличием противопоказаний к НПВП и БПВП.
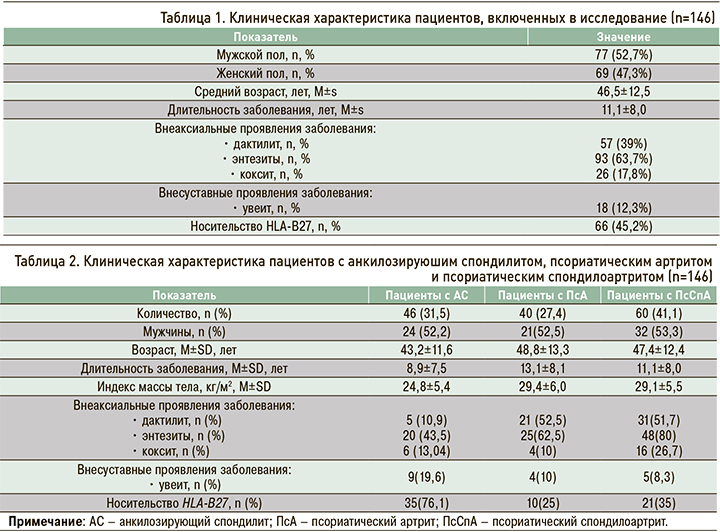
Участники исследования были разделены на 3 группы в зависимости от ранее верифицированного диагноза. В первую группу вошли 46 пациентов с анкилозирующим спондилитом (АС), отвечающих модифицированным Нью-Йоркским критериям этого заболевания (1984), во вторую – 40 пациентов с псориатическим артритом (ПсА), соответствующие критериям CASPAR (Classification criteria of Psoriatic Arthritis, 2006), в третью – 60 пациентов с псориатическим спондилоартритом (ПсСпА), одновременно отвечающие модифицированным Нью-Йоркским критериям для АС и критериям CASPAR для ПсА. Клиническая характеристика трех групп больных приведена в таблице 2.
По результатам дисперсионного анализа, включающего пол, возраст и длительность заболевания, группы пациентов были сопоставимы (p >0,05).
В исследованных группах наблюдались достоверные отличия по наличию дактилитов, энтезитов, кокситов, псориатической ониходистрофии и носительства HLA-B27 (p <0,01). Так, маркер HLA-B27 чаще выявлялся у пациентов с АС (76,1%), тогда как внеаксиальные проявления и кокситы – у пациентов с ПсСпА.
При проведении post-hoc-тестов Games–Howell удалось установить, что дактилиты наиболее часто встречались в группе ПсСпА (51,7%). При этом частота энтезитов в группах обследованных пациентов варьировала в широких пределах: 43,5% при АС, 62,5% при ПсА и 80% при ПсСпА. Это может свидетельствовать о более тяжелом течении ПсСпА. Внесуставные проявления СпА, такие как увеит, чаще отмечались в группе пациентов с АС (19,6% от общего количества человек, включенных в эту группу).
В таблице 3 отражены данные по распространенности коморбидных патологий среди пациентов трех групп. Обращает на себя внимание тот факт, что как минимум одно сопутствующее заболевание было выявлено в 85,6% случаев.
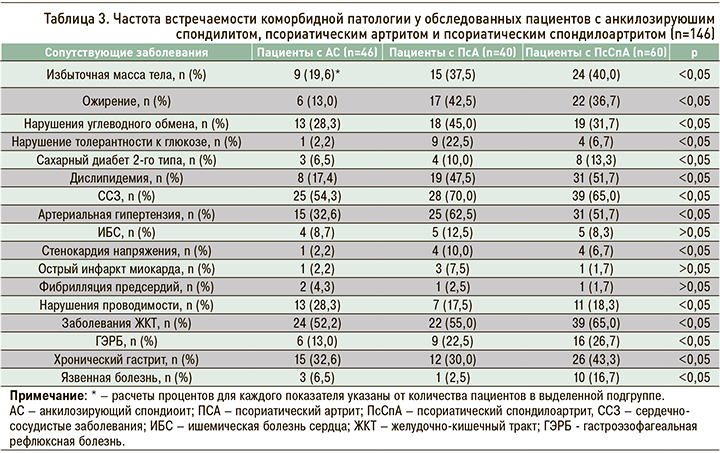
При сравнении частоты встречаемости коморбидных заболеваний были выявлены достоверные различия по всем нозологиям, указанным в таблице 3, кроме ИБС, острого инфаркта миокарда и фибрилляции предсердий (p <0,05).
Согласно полученным данным, у пациентов с СпА наиболее распространенными коморбидными патологиями были заболевания сердечно-сосудистой (63,0%) и желудочно-кишечного тракта (58,2%). Артериальная гипертензия диагностировалась в 48,6% случаев, дислипидемия – в 39,7%, а среди болезней желудочно-кишечного тракта преобладали хронический гастрит (36,3%) и ГЭРБ (21,2%). Сравнительная оценка коморбидных патологий при различных нозологических формах СпА показала, что избыточная масса тела, ожирение, дислипидемия, сахарный диабет 2-го типа, артериальная гипертензия и ИБС достоверно чаще наблюдались у пациентов с ПсСпА.
У 15,3% обследованных СпА сочетался с поражением одного органа или системы, что требовало назначения соответствующей патогенетической терапии (ингибиторов протонной помпы, диуретиков, антиаритмических и антигипертензивных препаратов).
На следующем этапе исследования был выполнен анализ частоты назначения БПВП, НПВП и ГКС, а также индексов активности BASDAI и ASDASСРБ в группах пациентов с наличием и отсутствием коморбидных заболеваний (табл. 4). В группе пациентов с коморбидными состояниями показатели активности СпА (BASDAI, ASDASСРБ) и функциональный индекс BASFI были достоверно выше (p <0,05), чем у пациентов без сопутствующих заболеваний. Не менее интересны результаты сравнения частоты приема различных лекарственных препаратов в сравниваемых группах обследованных. Так, пациенты с сопутствующими заболеваниями реже принимали НПВП по сравнению с группой пациентов без коморбидных патологий (45,6 против 79,2%), при этом системные формы ГКС получали 8,8% обследованных в группе СпА с сопутствующими заболеваниями, тогда как пациентам без коморбидности эта группа препаратов вообще не назначалась.
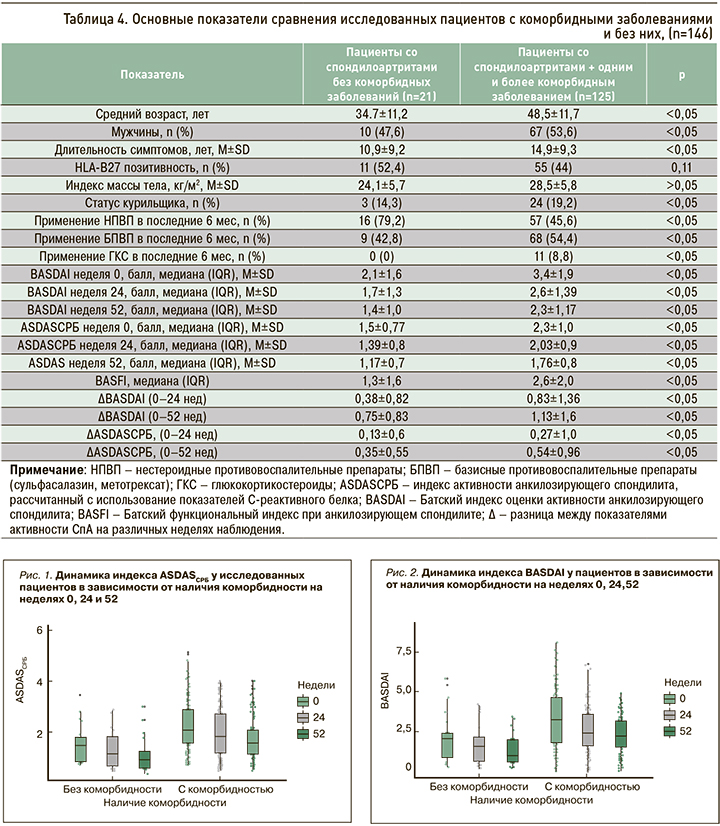
Следует отметить, что возраст пациентов и длительность СпА были значимо выше в группе с коморбидными заболеваниями, чем у пациентов без таковых. При этом снижение активности СпА по индексам BASDAI и ASDASСРБ через 24 и 52 нед лечения ГИБП у участников с отягощенным коморбидным фоном было более значимым относительно группы обследованных без коморбидности. Динамика индексов активности основного заболевания в зависимости от наличия сопутствующих патологий представлена на рисунках 1 и 2.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
В проведенном исследовании получены данные о высокой встречаемости различных коморбидных состояний у пациентов с СпА. Наиболее часто встречающимися среди них были заболевания сердечно-сосудистой системы и желудочно-кишечного тракта. При этом пациенты с коморбидностью имели более высокую активность СпА и ограниченные возможности приема НПВП из-за наличия сопутствующих заболеваний. Следует полагать, что более высокая активность СпА в группе с наличием коморбидности могла быть обусловлена отсутствием возможности перманентного приема НПВП, служащих базисными средствами для пациентов с АС. У пациентов с СпА и коморбидностью на фоне применения ингибиторов ФНО-α наблюдалось более существенно снижение индексов BASDAI и ASDAS по сравнению с пациентами без сопутствующих заболеваний. Тот факт, что у пациентов с СпА и сопутствующими патологиями, имевшими противопоказания для назначения НПВП, отмечалась более выраженная динамика снижения активности основного заболевания, скорее всего, был связан с тем, что им раньше, чем группе сравнения, назначалась генно-инженерная биологическая терапия.
Известно, что введение ГИБП в схемы лечения СпА в значительной степени повысило эффективность комплексной терапии и способствовало более частому достижению ремиссии или низкой степени активности этой группы иммуновоспалительных заболеваний. Особую значимость препараты этой группы приобретают в тех случаях, когда у пациентов имеются противопоказания или первичная неэффективность НПВП, которые относятся к патогенетически обоснованным средствам лечения АС.
Выбор стратегии лечения СпА неразрывно связан с коморбидными заболеваниями, играющими важную роль не только в течении и исходах различных клинических вариантов СпА, но и влияющих на выживаемость проводимой терапии.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Согласно результатам проведенного исследования, СпА часто ассоциированы с заболеваниями сердечно-сосудистой системы и желудочно-кишечного тракта, которые, в свою очередь, ограничивают возможность применения НПВП у пациентов этой категории. Следствием этого становится более высокая степень активности основного заболевания в случае отягощенного коморбидного фона. Подтверждения полученных в ходе исследования данных относительно активности СпА в зависимости от сопутствующих патологий можно встретить в иностранной литературе. Известно, что пациенты с коморбидными заболеваниями имеют более высокую активность СпА перед инициацией терапии ГИБП [7, 15, 19, 24]. При этом следует отметить, что наличие коморбидной патологии не влияло на скорость снижения активности иммуновоспалительного процесса при СпА в течение года наблюдения.
Вместе с тем требуются дальнейшие исследования по оценке эффективности проводимой ГИБТ с учетом имеющегося широкого круга коморбидных заболеваний у пациентов, страдающих заболеваниями из группы СпА.



