АКТУАЛЬНОСТЬ
Научные разработки последних лет вселяют надежду на успех в области диагностики, лечения и реабилитации ревматических заболеваний на ранних стадиях, в том числе потому, что именно раннее выявление этих патологий служит определяющим фактором благоприятного прогноза [1]. Ревматические заболевания могут начинаться в любом возрасте, но, как правило, дебютируют в молодости. Системность поражения, хроническое, неуклонно прогрессирующее течение, развитие стойкой постоянной нетрудоспособности и жизнеугрожающих осложнений являются теми особенностями заболеваний опорно-двигательного аппарата, которые делают крайне актуальным вопрос их своевременной диагностики и адекватного лечения.
Ведущим клиническим проявлением ревматических заболеваний выступает суставной синдром, однако наряду с ним большого внимания заслуживают и экстраартикулярные симптомы, такие как вовлечение кожи и ее придатков, которые могут свидетельствовать о генерализованной воспалительной реакции [2, 3]. Кожные проявления при ревматических патологиях разнообразны и зачастую отражают активность основного заболевания, эффективность проводимого лечения и позволяют оценить прогноз; кроме того, они могут быть результатом побочного действия назначаемых препаратов, что также является важной информацией для клинициста [4]. Например, известно, что длительное применение таких лекарственных средств, как пеницилламин, аллопуринол, тиазидные диуретики, кеторолак, препараты золота, сульфаниламиды, фенитоин, пенициллины, амфетамин, может служить причиной развития васкулита [5].
Отметим, что при ревматоидном артрите, системной красной волчанке, дерматомиозите и других системных заболеваниях соединительной ткани именно поражения кожи часто выступают первыми симптомами болезни, в связи чем особую значимость при обследовании пациентов приобретает такой физикальный метод, как осмотр.
Цель настоящей статьи – повышение степени осведомленности врачей-терапевтов и врачей общей практики в вопросе кожных проявлений ревматических заболеваний для улучшения качества диагностики и лечения этих заболеваний. Статья основана на изучении материалов зарубежных и отечественных исследований с использованием данных литературы преимущественно за последние 5–10 лет.
ОСТРАЯ РЕВМАТИЧЕСКАЯ ЛИХОРАДКА
Согласно современным представлениям, острая ревматическая лихорадка (ОРЛ) является системным воспалительным заболеванием соединительной ткани с преимущественным поражением сердечно-сосудистой системы, которое развивается через 2–3 нед после острой респираторной инфекции, вызываемой β-гемолитическим стрептококком группы А, преимущественно у генетически предрасположенных детей и подростков 5–17 лет. Исходом ОРЛ нередко становится развитие хронической ревматической болезни сердца с возможным формированием ревматического порока сердца. По данным одного из исследований, среди симптомов ревматической лихорадки лидирующие позиции по частоте развития занимают кардит (91%), суставной синдром (57%) и хорея (41%) – проявление нейроревматизма. В последнее время отмечается гиподиагностика острой и повторной ревматической лихорадки [6].
При общем осмотре больных с ревматической лихорадкой можно выявить кольцевидную эритему и ревматические узелки – редкие, но специфические кожные проявления данного заболевания. Кольцевидная эритема – высыпания бледно-розового цвета в виде колец, не возвышающихся над кожей, безболезненные и бледнеющие при надавливании (рис. 1). Подкожные ревматические узелки округлые, плотные, безболезненные образования, варьирующие по размерам от 2 мм до 1–2 см. Они образуются в местах костных выступов (вдоль остистых отростков позвонков, краев лопаток) или по ходу сухожилий (обычно в области голеностопных суставов). Иногда они представляют собой скопления, состоящие из нескольких узелков. Нередко подкожные ревматические узелки сочетаются с тяжелым кардитом [7].

К возможным дерматологическим признакам ревматизма и ОРЛ относится и узловатая эритема – болезненные подкожные участки красного или фиолетового цвета, неправильной формы, которые чаще всего локализуются на голенях. Она встречается также при некоторых системных заболеваниях (саркоидоз, туберкулез, неспецифический язвенный колит и др.) [8] и часто является показателем активности патологического процесса. В литературе описано и такое необычное проявление при ревматической лихорадке, как пурпура Шейнлейна–Геноха – пятнистая сыпь или крапивница, переходящая в пальпируемую пурпуру, которая располагается обычно на нижних конечностях и ягодицах [9, 10].
РЕВМАТОИДНЫЙ АРТРИТ
Ревматоидный артрит (РА) – воспалительное заболевание суставов с аутоиммунным патогенезом и системным поражением. Внесуставные проявления РА являются серьезной диагностической и терапевтической проблемой, поскольку связаны с плохим прогнозом и требуют раннего выявления и своевременного лечения [11]. Кожные проявления этого заболевания клинически характеризуются полиморфными элементами, такими как пустулы, буллы, абсцессы, папулы, включая классические ревматоидные узелки, бляшки и язвы, а гистологически – воспалительными инфильтратами, богатыми нейтрофилами [12, 13]. При ювенильном идиопатическом артрите основные кожные симптомы включают мимолетную сыпь, ревматоидные узелки, а также бляшечный и каплевидный псориаз [14].
Синдром Фелти наблюдается у 1% больных серопозитивным РА и, наряду с характерной клинико-лабораторной картиной заболевания, сопровождается спленомегалией, ревматоидными узлами, синдромом Шегрена, кожным васкулитом, периферической нейропатией, нейтропенией и гиперпигментацией кожи нижних конечностей [15].
СИНДРОМ ШЕГРЕНА
Синдром Шегрена (GSS) – хроническое гетерогенное аутоиммунное заболевание с широким спектром клинических проявлений. Он характеризуется лимфоцитарной инфильтрацией экзокринных желез, что приводит к ксеростомии и сухому кератоконъюнктивиту (ксерофтальмии). Первичный синдром Шегрена – второе по частоте заболевание соединительной ткани после РА, которым страдают женщины. Болезнь может начинаться с экстрагландулярных признаков, таких как неэрозивный полиартикулярный артрит, феномен Рейно, поражение периферической или центральной нервной системы, заболевание почек, интерстициальная пневмония и даже васкулит [16]. Общие кожные симптомы синдрома Шегрена включают ксероз (рис. 2, 3), кольцевидную эритему, гипергаммаглобулинемическую пурпуру и иммунологические воспалительные состояния, такие как васкулит (лейкоцитокластический и крапивница; рис. 4).
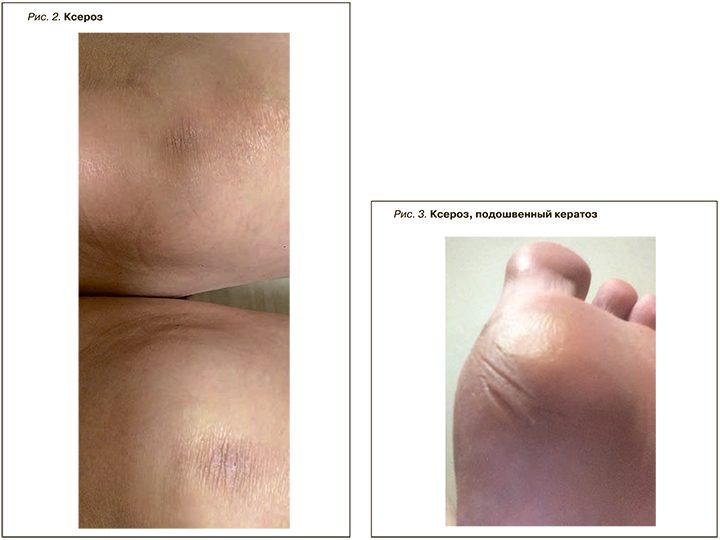
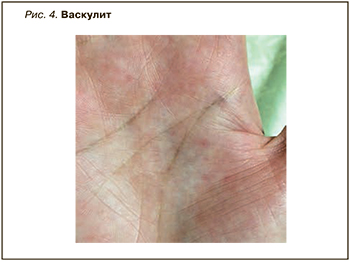
Поражение кожи при синдроме Шегрена относительно распространено и может присутствовать в форме различных проявлений, в частности ксеродермии, дерматита век, кольцевидной эритемы и кожного васкулита. Клинические признаки васкулита зависят от степени поражения кожи и кровеносных сосудов и варьируют от петехий до пальпируемой пурпуры и обширных экхимозов [17,18]. У многих пациентов с синдромом Шегрена отмечаются признаки системной сухости носа, трахеи, влагалища и кожи, что позволяет предположить поражение и других желез. Дополнительные кожные симптомы этого заболевания – livedo reticularis, локализованный узловой кожный амилоидоз. К дерматологическим последствиям поликлональной реактивности относится васкулит, а проявления пролиферации B-клеток варьируют от инфильтратов плазматических клеток до B-клеточной лимфомы [19, 20].
СИСТЕМНАЯ КРАСНАЯ ВОЛЧАНКА
Системная красная волчанка (СКВ) – аутоиммунное заболевание неизвестной этиологии с мультивариабельными проявлениями, течением и прогнозом, характеризующееся гиперпродукцией широкого спектра органоспецифических аутоантител и иммунных комплексов, вызывающих иммуновоспалительное повреждение внутренних органов с развитием полиорганной недостаточности. Кожные высыпания, как правило, выступают ведущим симптомом в клинической картине СКВ. В 20–33% случаев болезнь начинается именно с кожного синдрома, в результате чего больные первично направляются на дерматологический прием [21]. Волчаночная «бабочка», петехии на кистях рук, телеангиэктазии, энантема слизистой оболочки полости рта вместе с другими клинико-инструментальными показателями могут рассматриваться в качестве маркеров высокой степени активности СКВ. Обнаружение эритемы на крупных суставах, сетчатого ливедо, синдрома Рейно подразумевает целенаправленное обследование опорно-двигательного аппарата у этих больных.
Вариантом тяжелого поражения кожи при СКВ является токсический эпидермальный некролиз, долгое время считавшийся симптомом тяжелой лекарственной аллергии [22, 23].
По данным некоторых исследований, у 5–25% пациентов кожная красная волчанка может прогрессировать до СКВ [24].
УЗЕЛКОВЫЙ ПОЛИАРТЕРИИТ
Узелковый полиартериит – некротический васкулит, поражающий сосуды среднего размера, к основным проявлениям которого относятся потеря веса, лихорадка, периферическая невропатия, поражение почек, опорно-двигательного аппарата, желудочно-кишечного тракта и/или кожи, гипертония и/или сердечная недостаточность [25]. При узелковом полиартериите кожный синдром развивается практически у всех больных; при этом соответствующие изменения очень разнообразны и могут протекать по типу геморрагической сыпи, характерной также для тромбоцитопенической пурпуры или мультиформной эритемы.
Классическими кожными изменениями при рассматриваемом заболевании считаются древовидное или сетчатое ливедо (стойкие цианотичные пятна в виде ветвей дерева или выраженной мраморности), подкожные или внутрикожные узелки и локальные отеки. Ливедо встречается у большинства больных, располагается чаще на дистальных отделах конечностей, но иногда распространяется на лицо, грудную клетку, ягодицы. Подкожные узелки размером от 0,5 до 1 см располагаются по ходу сосудов, при этом они болезненны при пальпации. Болезненные плотные отеки локализуются на кистях, стопах, над лодыжками, в области лучезапястных, локтевых, голеностопных, коленных суставов; в процессе развития болезни они могут исчезать, но чаще на их месте формируется некроз кожи. Поверхностные некрозы представляют собой инфаркты и кровоизлияния в подногтевое ложе, дигитальные некрозы подушечек пальцев. Добавим, что в литературе описаны случаи развития при узелковом полиартериите глубоких инфарктов кожи – кожных язв с вовлечением глубоких подкожных структур, некрозов и гангрены фаланг пальцев и/или периферических тканей (носа, языка, мочек ушей и др.) [26–28].
СИСТЕМНАЯ СКЛЕРОДЕРМИЯ
Системная склеродермия (ССД) – редкое заболевание соединительной ткани с неизвестным и сложным патогенезом. Ее можно разделить на две формы: локализованная склеродермия (морфея, линейная склеродермия или склеродермия en coup de saber) и системный склероз. Локализованная склеродермия – заболевание кожи и подкожной клетчатки, приводящее к образованию участков утолщенной кожи, при биопсии которых выявляется фиброз кожи. В свою очередь, системный склероз связан с несколькими системными проявлениями и поражением внутренних органов и связан с повышенной смертностью. Антинуклеарные антитела (ANA) могут присутствовать более чем в 90% случаев системного склероза, и по крайней мере одно из более специфических аутоантител (анти-центромерные, анти-SCL70 и анти-РНК-полимераза III) обнаруживается примерно в 70% случаев. Органами, наиболее часто поражающимися при склеродермии, являются кожа, желудочно-кишечный тракт, легкие, почки, скелетные мышцы и перикард [29].
Особую драматичность приобретает течение склеродермии при поражении легких и почек. Клинические проявления интерстициального поражения легких в случае ССД неспецифичны и могут существенно различаться у пациентов – от бессимптомного течения до быстропрогрессирующей дыхательной недостаточности [30]. Поражение почек в 10% случаев ССД может сопровождаться острой почечной недостаточностью, которая прогрессирует до терминальной стадии в 50% случаев [31].
Что касается поражения кожи при ССД, то оно протекает в несколько стадий. Прежде всего возникает плотный отек ткани, который часто начинается с пальцев и изменяет их форму – они белеют и превращаются в сосископодобные образования. Дальше идет индурация, уплотнение этих областей, причем такой процесс может быть не только на руках. Иногда при ССД могут наблюдаться очаговые изменения в виде «следа сабельного удара». Бывает, что дерматологические поражения затрагивают туловище, и тогда больной ощущает чувство сдавления как бы корсетом или панцирем, кожа при этом нередко пигментируется. В этом периоде у больных зачастую появляются множественные телеангиэктазии. Дальнейшее развитие изменений кожи при ССД заключается в ее атрофии, она становится блестящей, натянутой [32]. При локализации процесса на лице обостряются контуры носа, появляются кисетообразные складки вокруг рта («кисетообразный рот»), сужение ротовой щели («рыбий рот»), при этом может быть затруднено его открывание. По мере уплотнения кожи на кистях рук и пальцах образуются сгибательные контрактуры, что, наряду с изменениями и атрофией самой кожи, делает кисти больных похожими на «птичью лапку» и носит название склеродактилии или акросклероза [33].
ДЕРМАТОМИОЗИТ
Дерматомиозит – системное прогрессирующее заболевание, характеризующееся преимущественным поражением поперечнополосатой и гладкой мускулатуры с нарушением двигательной функции, а также кожи. Типичные его клинические симптомы – прогрессирующая симметричная мышечная слабость в проксимальных отделах верхних и нижних конечностей, миалгии, болезненность мышц при пальпации, трудности при осуществлении любых движений, боли в суставах, гелиотропная сыпь, наличие синдрома Готтрона в области разгибательной поверхности суставов пальцев рук [34].
Симптом Гoттpoнa представляет собой узелки или бляшки, порой c симптомами шелушения, либо большие пятна красного или розового цвета, локализованные на сгибательных суставных поверхностях, преимущественно кистей рук (межфаланговых или пястно-фаланговых), а также локтевых и коленных суставов. Гелиотропная сыпь при дерматомиозите имеет лиловый цвет и располагается под бровями (по типу очков) или на верхней области конечностей, спины и ключицы, на животе, ягодицах, бедрах и голенях. Также могут выявляться темные бордово-синие разветвляющиеся эритемы. Начальный симптом дерматомиозита –это покраснение и припухание кожи y границ ногтей. При дерматомиозите, отягощенном кальцинозом, появляются гнойные раны, наполненные крошкообразной массой, – признак отложения кальциевых депозитов под кожей [35,36].
СПОНДИЛОАРТРИТЫ
Спондилоартриты (СпА), такие как псориатический артрит, аксиальный СпА/анкилозирующий спондилит, реактивный артрит, и СпА, ассоциированные с воспалительными заболеваниями кишечника, могут иметь характерные кожные проявления [37]. Связанные со СпА кожные заболевания могут предшествовать поражению суставов, указывать на снижение эффективности текущего системного лечения или даже быть обусловлены самим лечением. Кожный васкулит может выступать внесуставным проявлением анкилозирующего СпА, связанным с повреждением цитокинами и аутоантителами эндотелиальной стенки сосудов в активную фазу воспаления [38].
ПСОРИАЗ
Псориаз – системное заболевание аутоиммунной природы, которым страдают примерно 125 млн человек во всем мире. Пациенты с псориазом часто болеют воспалительным артритом, кардиометаболическими заболеваниями и психическими расстройствами.
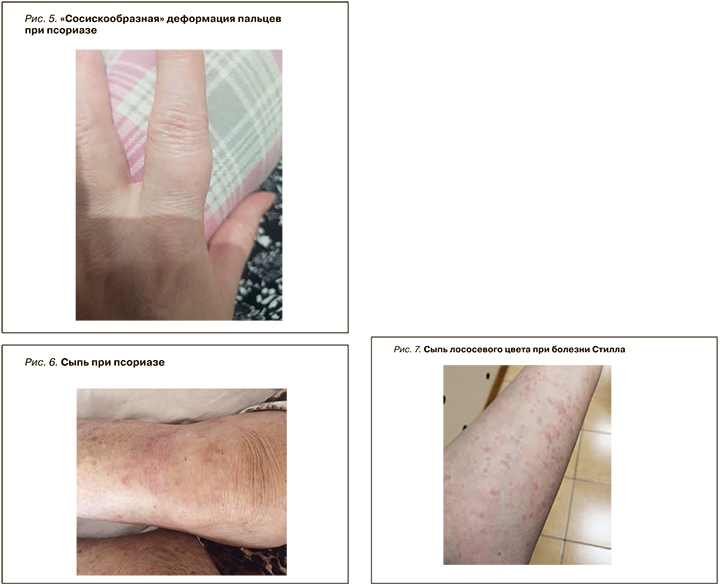
Наиболее распространенный вариант заболевания – бляшечный псориаз [39]. Наряду с типичной сыпью, для псориаза характерна «сосискообразная» деформация пальцев (рис. 5) и багрово-цианотичное окрашивание кожи над воспаленными суставами (рис. 6). К другим патогномоничным признакам относят точечные дефекты ногтевой пластины – «симптом наперстка», а также поражения ногтевой пластины, внешне сходные с изменениями при микозе. Псориаз ногтей имеет распространенность от 10 до 82% и может существенно влиять на качество жизни пациентов [40]. Согласно другим данным, поражение ногтей встречается у 80–90% больных псориазом; при этом данный симптом свидетельствует о тяжелой форме заболевания и коррелирует с развитием псориатического артрита [41, 42].
РЕАКТИВНЫЙ АРТРИТ
Реактивный артрит – заболевание, обычно вызываемое мочеполовой или бактериальной кишечной инфекцией. При его развитии после короткого латентного периода могут возникнуть глазные симптомы, олигоартрит и поражение слизистых оболочек. Классические кожные проявления реактивного артрита включают бленноррагическую кератодермию и циркинатный баланит, которые микроскопически сходны с пустулезным псориазом [43].
БОЛЕЗНЬ СТИЛЛА
Болезнь Стилла – редкое системное воспалительное заболевание, характеризующееся рецидивирующей гектической лихорадкой, непродолжительными высыпаниями, артритом и поражением нескольких органов, включая полисерозит, миоперикардит, поражение легких, боли в животе, неврологические заболевания. Для него очень характерна сыпь лососевого цвета (рис. 7) – кожное проявление генерализованной воспалительной реакции и важный диагностический критерий [44–46].
ГРАНУЛЕМАТОЗ С ПОЛИАНГИИТОМ
Гранулематоз с полиангиитом (устаревшее название – гранулематоз Вегенера) представляет собой системный васкулит, сопровождающийся кожными симптомами, которые могут появляться на любом этапе развития системного заболевания. Классическая клиническая триада болезни включает некротическое гранулематозное воспаление верхних и/или нижних дыхательных путей, некротический гломерулонефрит и аутоиммунный некротический системный васкулит, поражающий преимущественно мелкие сосуды. Обнаружение антинейтрофильных цитоплазматических антител, направленных против протеиназы 3 (PR3-ANCA), является высокоспецифичным диагностическим методом для гранулематоза с полиангиитом [47,48].
БОЛЕЗНЬ БЕХЧЕТА
Болезнь Бехчета – редкая форма васкулита, способная поражать сосуды любого размера, как артериальные, так венозные, что приводит к различным клиническим проявлениям. Начало этого заболевания обычно приходится на 3–4-е десятилетие жизни. Для его клинической картины характерны рецидивирующие язвы полости рта и половых органов, а также поражения глаз. При осмотре кожи выявляются папуло-пустулезные поражения и кожный васкулит, поражения, подобные синдрому Свита (острый фебрильный нейтрофильный дерматоз), гангренозная пиодермия и многоформная эритема [49, 50].
ПОДАГРА
Подагра – заболевание, вызванное нарушением пуринового обмена. Для нее типично образование тофусов, представляющих собой подкожное или внутрикожное скопление солей мочевой кислоты (уратов). Чаще они локализуются в области пальцев кистей и стоп, коленных суставов, на локтях и ушных раковинах. При длительном течении заболевания и отсутствии адекватного лечения наблюдается изъязвление кожи над тофусами со спонтанным выделением содержимого в виде крошковатой белой массы. Одним из клинических проявлений подагры может быть развитие мочекислой нефропатии и уратного нефролитиаза с исходом в хроническую почечную недостаточность [51, 52]. Среди механизмов прогрессирования сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний при подагре, помимо гиперурикемии, можно отметить также воспаление, эндотелиальную дисфункцию и окислительный стресс [53].
САРКОИДОЗ
Саркоидоз – идиопатическое мультисистемное гранулематозное заболевание, которое обычно поражает легкие, глаза, лимфатические узлы и кожу. Болезнь обычно дебютирует в возрасте около 40 лет, и почти две трети заболевших составляют женщины [54, 55]. Кожа – второй по частоте поражений орган при саркоидозе [56]. Среди множества зарегистрированных морфологических проявлений заболевания можно назвать папулы, микропапулы, бляшки, подкожные узелки, саркоидоз рубца, ознобленную волчанку, узловатую эритему, язвы и алопецию. Папулы при саркоидозе могут быть разных цветов, включая красный, красновато-коричневый, фиолетовый, полупрозрачный или гиперпигментированный. Из-за такого цветового разнообразия они имитируют другие кожные заболевания, включая красный плоский лишай или псориаз. Саркоидные поражения бессимптомны, но примерно в 10–15% случаев им может сопутствовать зуд. Также описаны такие редкие проявления заболевания, как фолликулярные, бородавчатые, ихтиозиформные, гипомеланотические и кольцевидные поражения [57, 58].
ДИФФУЗНЫЙ (ЭОЗИНОФИЛЬНЫЙ) ФАСЦИИТ
Диффузный (эозинофильный) фасциит – редкое заболевание соединительной ткани, для которого типичен симметричный и болезненный отек с прогрессирующим уплотнением и утолщением кожи и мягких тканей. Диагноз эозинофильного фасциита часто основывается на ассоциации характерных кожных или подкожных аномалий и утолщенной фасции с воспалительной инфильтрацией, в основном состоящей из лимфоцитов и эозинофилов. Периферическая эозинофилия присутствует часто (60–90%), но не является обязательной для диагностики [59–61].
Рецидивирующий панникулит Вебера–Крисчена – еще одно редкое заболевание из группы диффузных заболеваний соединительной ткани, сопровождающееся рецидивирующим некротическим поражением подкожно-жировой клетчатки, а также поражением внутренних органов. Чаще им болеют женщины 20–50 лет. Различают кожный и висцеральный варианты болезни.
Для панникулита Вебера–Крисчена характерно образование множественных узлов в подкожно-жировой клетчатке конечностей, реже живота, груди и лица. В течение нескольких недель происходит рассасывание узлов с образованием блюдцеобразных углублений в подкожно-жировой клетчатке вследствие ее атрофии, в которых нередко откладываются соли кальция [62].
При гигантоклеточном артериите (болезни Хортона) описан случай некроза кожи головы и языка [63].
В последнее десятилетие была выделена новая нозологическая единица – IgG4-cвязанное системное заболевание (IgG4-ССЗ). Это группа патологий, имеющих два сходных признака: повышение концентрации иммуноглобулина G (IgG) 4-го субкласса в сыворотке и формирование в различных органах и тканях инфильтрации из плазмоцитов, секретирующих IgG4, эозинофилов, развитие фибросклероза и облитерирующего флебита. IgG4-ССЗ отличается разнообразием клинических проявлений: встречаются формы заболевания как с одной локализацией поражения, так и с мультиорганными проявлениями, традиционно называемыми многоочаговым фибросклерозом [64, 65]. IgG4-ССЗ часто обнаруживается на этапе выраженных изменений в органах как случайная диагностическая находка. При отсутствии лечения заболевание приводит к фиброзу и необратимому повреждению органов. Наиболее часто IgG4-ССЗ манифестирует в виде поражения слюнных и слезных желез, лимфаденопатии и аутоиммунного панкреатита 1 типа [66].
Васкулит и аутоиммунные заболевания встречаются у 20–23% пациентов с хроническими язвами нижних конечностей. Язвы кожи, связанные с заболеваниями соединительной ткани или васкулитами, возникают на фоне широкого спектра заболеваний, включая системный склероз, СКВ, дерматомиозит, РА, антифосфолипидный синдром. Такие пациенты рефрактерны к стандартной терапии. Привлечение ревматологов к участию в диагностическом процессе позволяет выявить основное системное заболевание как причину и улучшить клинический исход у таких сложных пациентов [67, 68].
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Анализ данных литературы и наш собственный клинический опыт позволяют заключить, что поражение кожи и ее придатков часто сопутствует ревматическим заболеваниям. Огромное значение в выявлении этих изменений имеет один из физикальных методов – осмотр. Адекватная и своевременная трактовка характерных изменений кожи и ее придатков, а также междисциплинарный подход к ведению пациентов способствует повышению эффективности диагностики и лечения, профилактике осложнений, улучшению качества жизни и прогноза, снижению инвалидизации, что, несомненно, имеет огромное медико-социальное значение.


