Таргетная терапия тяжелой бронхиальной астмы (ТБА) открыла новую эру и дала новые возможности в лечении самых тяжелых пациентов. Сегодня доступно пять биологических препаратов – моноклональных антител для лечения ТБА с учетом фенотипов и эндотипов, а также характерных специфических биомаркеров. К таким биомаркерам относятся прежде всего уровень эзинофилии в крови и мокроте, уровень общего и специфических иммуноглобулинов Е (IgE), уровень FeNO в выдыхаемом воздухе и периостин [1–4].
Моноклональные антитела применяются для лечения ТБА с Т2-типом воспаления (аллергическим и неаллергическим) у пациентов, которые находятся на 5-й ступени терапии согласно рекомендациям GINA. Эти пациенты получают высокие дозы ингаляционных глюкокортикостероидов (ИГКС) в комбинации с длительно действующими β2-агонистами (ДДБА), а также используют другие группы препаратов – теофиллины, антилейкотриены, пероральные глюкокортикостероиды (ПГКС). При этом у них отмечаются частые обострения заболевания (≥2 раз в год), в том числе с госпитализацией, стойкое снижение показателей объема форсированного выдоха за первую секунду (ОФВ1) менее 80% от должного, а также отсутствие контроля симптомов астмы по данным валидированных опросников [5–6].
В развитии Т2-воспаления участвует большое количество цитокинов. Основным цитокином, регулирующим весь жизненный цикл эозинофила, является интерлейин-5 (IL-5). Кроме того, важную иммунологическую роль играют и другие Т2-цитокины, такие как IL-4 и IL-13. При наличии атопии вырабатываются общий и специфические IgE. Роль моноклональных антител заключается в блокировании основных цитокинов; таким образом тормозится каскад реакций, способствующих активации клеток воспаления и развитию основных симптомов бронхиальной астмы [7–11].
Анти-IL-5 моноклональные антитела меполизумаб и реслизумаб нацелены на лечение ТБА с высоким уровнем эозинофилии в периферической крови. Бенрализумаб связывается и блокирует рецептор к IL-5 и тоже направлен на лечение эозинофильной ТБА. Дупилумаб действует на сигнальный путь Т2-воспаления при ТБА с участием IL-4 и IL-13. Омализумаб – первое гуманизированное моноклональное антитело, которое используют для лечения IgE-зависимой ТБА и идиопатической крапивницы [1, 9, 11].
Основная задача врача – выявить пациента, которому такая терапия необходима, и подобрать тот вариант лечения, который будет максимально эффективен.
ОМАЛИЗУМАБ
Более 50 лет назад был открыт IgE и определена его ведущая роль в развитии аллергических заболеваний и формировании противогельминтной защиты. С тех пор проведено огромное количество клинических исследований, посвященных оценке эффективности и безопасности анти-IgE препаратов для лечения IgE-зависимых аллергических заболеваний, прежде всего атопической бронхиальной астмы.
В основе таких аллергических заболеваний, как бронхиальная астма, аллергический ринит и конъюнктивит, пищевая сенсибилизация, атопический дерматит и крапивница, лежит IgE-зависимая реакция гиперчувствительности 1 типа, при этом отмечается значительное повышение уровня общего IgE [12, 13].
Омализумаб – первое моноклональное рекомбинантное гуманизированное антитело, комплементарное к IgE. Это лекарственное средство ингибирует связывание свободного IgE с высоко афинными рецепторами на поверхности тучных клеток и базофилов. Такой механизм действия предотвращает IgE-зависимый каскад аллергических реакций и выработку медиаторов воспаления. Кроме того, снижается чувствительность IgE-рецепторов на поверхности клеток-мишеней, что приводит к уменьшению выраженности аллергической реакции у пациентов [1, 14].
Омализумаб показан для лечения среднетяжелой/тяжелой атопической бронхиальной астмы с подтвержденной повышенной чувствительностью к аэроаллергенам, отсутствием контроля симптомов заболевания на фоне базисной терапии высокими дозами ИГКС/ДДБА и уровнем IgE в сыворотке крови от 30 до 1500 МЕ/мл у пациентов с 6 лет. Также он применяется для лечения идиопатической крапивницы. Препарат вводится подкожно, в дозе от 150 до 375 мг 1 раз в 2–4 нед. Омализумаб выпускается в форме лиофилизата для приготовления раствора (согласно данным инструкции по применению).
Наиболее часто при применении омализумаба отмечаются такие нежелательные явления, как реакции в месте инъекции (боль, отек, эритема и зуд), головные боли, реже фарингит, кашель и др. Анафилактические и другие острые аллергические реакции (в том числе ангионевротический отек), согласно данным инструкции по применению, встречаются редко.
На фоне терапии омализумабом отмечается улучшение качества жизни пациентов, уменьшение частоты обострений и обращений за экстренной медицинской помощью, снижение частоты применения системных ГКС и коротко действующих бронхолитиков. При этом омализумаб в меньшей степени оказывает влияние на функцию легких [14–17].
По данным клинических исследований, первичная конечная точка эффективности омализумаба – это предотвращение развития обострений бронхиальной астмы, которое наблюдается в том числе на фоне применения других моноклональных антител при лечении заболеваний с Т2-типом воспаления. Омализумаб способствует сокращению частоты обострений на фоне вирусной инфекции. Длительное его применение способствует снижению эозинофилии в мокроте, уменьшению толщины ретикулярной базальной мембраны, улучшению функции легких [14–17].
Согласно данным обзора Cochrane, в котором были рассмотрены результаты 25 исследований по оценке эффективности подкожного введения омализумаба с включением 6382 больных атопической бронхиальной астмой, в период с 16-й по 60-й неделю применения препарата отмечалось значимое снижение риска развития обострения заболевания (26% в группе плацебо vs 16% в группе омализумаба), уменьшение числа госпитализаций на 28–60-й неделе лечения (3% в группе плацебо vs 0,5% в группе омализумаба), небольшое, но тем не менее достоверное снижение дозы ингаляционных ГКС для базисной терапии в группе омализумаба, а также снижение потребности коротко действующих бронхолитиках. Однако статистически достоверных различий по такому параметру, как снижение дозы ПГКС, между группами обнаружено не было [1].
МЕПОЛИЗУМАБ
IL-5 регулирует весь жизненный цикл эозинофилов, дифференцировку, активацию, миграцию и рекрутинг. При развитии бронхиальной астмы в дыхательных путях формируется эозинофильное воспаление, которое стимулирует выработку воспалительных цитокинов и способствует развитию отека слизистой, продукции слизи и ремоделированию дыхательных путей. В клинических исследованиях анти-IL-5 препаратов было показано прямое действие на ключевые звенья патогенеза бронхиальной астмы, приводящее к нормализации уровня эозинофилов в бронхиальном дереве и периферической крови [1, 18, 19].
Меполизумаб – гуманизированное моноклональное антитело IgG1k, которое связывается и блокирует IL-5, препятствуя его связыванию со специфическим рецептором на поверхности эозинофилов. Меполизумаб применяется в качестве дополнительной поддерживающей терапии ТБА у пациентов с 6 лет эозинофильным профилем, а также для лечения эозинофильного гранулематоза с полиангиитом (синдром Чарджа–Стросс) у больных старше 18 лет. Препарат вводится в фиксированной дозе 100 мг подкожно (1 флакон) у детей старше 12 лет и взрослых и в дозе 40 мг у детей 6–12 лет 1 раз в 4 нед. Форма его выпуска – лиофилизат для приготовления инъекционного раствора.
Главным биомаркером для назначения меполизумаба служит уровень эозинофилов в периферической крови от 150 кл/мкл на момент инициации лечения или 300 кл/мкл в анамнезе за предыдущие 12 мес (согласно данным инструкции по применению).
Среди нежелательных явлений при использовании меполизумаба чаще всего отмечаются реакции в месте инъекции, головная боль и назофарингит. Тяжелые анафилактические реакции в ходе клинических исследований зафиксированы не были. Данные о развитии редких анафилактических реакций были получены уже в ходе постмаркетингового периода наблюдения. Кроме того, по данным клинических исследований, у меполизумаба отмечается крайне низкий уровень иммуногенности. У 6% пациентов за 4,5 года наблюдений отмечалось появление антител, у 1 пациента были выявлены нейтрализующие антитела, при этом наличие антител не повлияло на эффективность меполизумаба (согласно данным инструкции по применению) [20].
Меполизумаб на сегодняшний день обладает длительной, почти 5-летней базой клинических наблюдений. В исследованиях MENSA и DREAM было показано снижение частоты клинически значимых обострений на фоне терапии этим препаратом, а также выявлена закономерность повышения эффективности меполизумаба в плане снижения частоты клинически значимых обострений бронхиальной астмы при увеличении исходного уровня эозинофилии крови на момент инициации терапии. Так, в исследовании MENSA было показано, что при исходном уровне эозинофилов в периферической крови 150 кл/мл снижение частоты обострений составляет 53%, а при уровне 500 кл/мкл – уже 73% [21, 22]. В исследовании SIRIUS через 32 нед наблюдалось статистически значимое снижение дозы ПГКС на ≥50% и на ≥5 мг в сутки [20]. В двух пролонгированных исследованиях COLUMBA и COSMOS была показана безопасность и эффективность длительного применения меполизумаба в течение 52 нед [23, 24].
Согласно рекомендациям GINA, при отсутствии эффективности выбранного биологического препарата необходимо провести смену препарата через 4 мес неэффективной терапии [25]. В этом плане показательно 32-недельное многоцентровое открытое несравнительное исследование OSMO с участием больных ТБА с эозинофильным фенотипом, у которых не был достигнут контроль над заболеванием, несмотря на получение высоких доз ИГКС, других препаратов и омализумаба (≥4 мес). В результате проведенной замены омализумаба на меполизумаб на 32-й неделе у 77 и 79% пациентов были достигнуты минимальные клинически значимые различия (ACQ-5: ≥0,5 балла; SGRQ: ≥4 балла), а также отмечалось значимое снижение частоты обострений на 64% [26].
РЕСЛИЗУМАБ
Реслизумаб – второе после меполизумаба анти-IL-5 моноклональное антитело, одобренное FDA и EMA для лечения ТБА с эозинофильным профилем [1].
Реслизумаб – гуманизированное моноклональное антитело IgG4k, которое блокирует IL-5, препятствуя его связыванию со специфическим рецептором на поверхности эозинофилов. Этот препарат показан больным ТБА (18 лет и старше) с эозинофильным профилем и исходным уровнем эозинофилов крови 400 кл/мкл и выше. Он вводится инфузионно внутривенно 1 раз в 4 нед. При этом требуется индивидуальный подбор дозы из расчета 3 мг/кг массы тела.
Среди наиболее часто возникающих нежелательных реакций на реслизумаб отмечены миалгия и повышение креатинфосфокиназы (КФК). Также зафиксированы легкие анафилактические реакции (3 случая в исследовании BREATH). Кроме того, у 5,4% пациентов встречается образование незначительного уровня антител (согласно данным инструкции по применению) [27–29].
Эффективность Реслизумаба была изучена в программе из 4 клинических рандомизированных исследований BREATH. В них была показана эффективность препарата в плане снижения частоты клинически значимых обострений, улучшения качества жизни и снижения потребности в коротко действующих бронхолитиках. На фоне применения реслизумаба наблюдается снижение частоты клинически значимых обострений до 59%, в том числе обострений, требующих госпитализации, на 34%. Кроме того, отмечается прирост показателей ОФВ1 до 126 мл, а также улучшение качества жизни по данным опросника ACQ7 на 0,25 балла у пациентов с уровнем эозинофилии 400 кл/мкл. Влияние реслизумаба на снижение дозы ПГКС в рамках клинических исследований не определялось [22].
БЕНРАЛИЗУМАБ
В отличие от других анти-IL-5 моноклональных антител, бенрализумаб не действует на IL-5 напрямую, а блокирует альфа-рецептор на поверхности эозинофилов и базофилов. При отсутствии связывания с IL-5 происходит апоптоз клеток (эозинофилов и базофилов) в результате антителозависимой клеточно-опосредованной цитотоксической реакции за счет активации рецепторов клеток-киллеров, макрофагов и нейтрофилов [1, 11, 30].
Бенрализумаб – гуманизированное фукозилированное моноклональное антитело IgG1k. Он применяется у взрослых больных ТБА с эозинофильным фенотипом в качестве дополнительной поддерживающей терапии при уровне эозинофилии в периферической крови ≥300 кл/мкл. Форма выпуска препарата – раствор для подкожного введения в предзаполненном шприце. Рекомендуемая доза составляет 30 мг. Препарат вводится один раз в 4 нед (первые 3 инъекции), затем – один раз в 8 нед (согласно инструкции по применению).
Эффективность и безопасность бенрализумаба была изучена в ряде рандомизированных клинических исследований. В исследовании CALIMA и SIROCCO были включены больные ТБА, принимающие высокие дозы ИГКС в комбинации с ДДБА, с частыми обострениями (≥2 в год), а также исходным уровнем эозинофилии ≥300 кл/мкл [31, 32]. На фоне терапии отмечалось значимое снижение частоты обострений – на 28% (CALIMA) и на 51% (SIROCCO) по сравнению с плацебо. Помимо этого, наблюдался более длительный период до развития первого обострения и улучшение показателей по контролю симптомов ТБА в соответствии с данными валидированных опросников AQLQ и ACQ6 [30, 31]. В исследовании ZONDA была показана эффективность бенрализумаба в отношении снижения дозы ПГКС на 75% [32].
У 13% пациентов отмечалось появление антител к препарату. Среди нежелательных реакций чаще всего отмечаются реакции в месте инъекции, головная боль и назофарингит. Также наблюдалось развитие более тяжелых реакций, таких как анафилакция, ангиотек и крапивница [33].
ДУПИЛУМАБ
Дупилумаб – рекомбинантное человеческое моноклональное антитело IgG4, которое блокирует передачу сигналов IL-4 и IL-13 путем специфического связывания с IL-4Rα-субъединицей, общей для рецепторных комплексов IL-4 и IL-13. Дупилумаб применяется в качестве дополнительной поддерживающей терапии бронхиальной астмы среднего и тяжелого течения у пациентов в возрасте ≥12 лет с эозинофильным фенотипом или у пациентов с гормонозависимой бронхиальной астмы, получающих ПГКС. Также препарат назначается для лечения атопического дерматита среднетяжелого и тяжелого течения у взрослых пациентов при недостаточном ответе на терапию топическими лекарственными препаратами или в случае, когда такие препараты не рекомендованы [1, 11, 34].
Дупилумаб выпускается в виде предзаполненного шприца с предохранителем для иглы, содержащего раствор для подкожного введения (200 мг/шприц и 300 мг/шприц). Начальная доза препарат 400 мг (2 инъекции по 200 мг), далее по 200 мг каждые 2 нед. Доза может быть увеличена до 300 мг каждые 2 нед (согласно данным инструкции по применению).
В исследования по эффективности и безопасности дупилумаба включали пациентов с Т2-воспалением. На фоне терапии препаратом отмечалось снижение частоты клинически значимых обострений. При этом более выраженный эффект (на 67%) регистрировался у пациентов с исходной эозинофилией в периферической крови ≥300 кл/мкл. Кроме того, наблюдалось снижение уровня FeNO на 48% в выдыхаемом воздухе даже у больных с исходным уровнем эозинофилии в периферической крови <300 кл/мкл. Около 70% пациентов на фоне терапии дупилумабом смогли снизить дозу ПГКС, а почти половина больных смогла вовсе отказаться от их применения (исследование VENTURE). Несмотря на снижение дозы ПГКС, у больных, получавших дупилумаб, отмечалось значимое снижение частоты обострений (на 59%) заболевания даже при исходном уровне эозинофилов <150 кл/мкл [1, 11, 35].
У 5–9% пациентов отмечалось появление антител к дупилумабу, приблизительно у 2–4% антитела стойко сохранялись, примерно у 1–2% выявлялись нейтрализующие антитела. У одного больного была обнаружена сывороточная болезнь, еще у одного – реакция, подобная сывороточной болезни (<0,1%), которые ассоциировались с высокими титрами антител. Среди нежелательных явлений при применении дупилумаба часто встречаются развитие герпеса и конъюнктивита, реакции в месте инъекции, редко эозинофильная пневмония и анафилактические реакции [35].
Сводные сравнительные данные биологических таргетных препаратов для лечения ТБА отражены в таблице 1.

СРАВНЕНИЕ ЭФФЕКТИВНОСТИ И БЕЗОПАСНОСТИ МОНОКЛОНАЛЬНЫХ АНТИТЕЛ
Прямые сравнительные исследования head to head, посвященные сравнению эффективности и безопасности биологических молекул, не проводились. Однако было выполнено несколько непрямых сравнительных анализов.
Agache I. et al. под эгидой EAACI был проведен непрямой сравнительный анализ исследований по пяти биологическим молекулам для лечения ТБА [1]. Для него были использованы данные PUBMED, EMBASE и библиотеки Cochrane. Всего были оценены 3441 цитата из проведенных исследований в период с 2011 по 2019 г. и 145 полных публикаций. Публикации содержали данные по эффективности и безопасности биологических молекул. Все исследования были рандомизированными и содержали группу сравнения с плацебо или интервенционную группу. Продолжительность наблюдения составляла от 12 до 56 нед. В исследования были включены пациенты 12–75 лет, в случае с омализумабом – с 6 лет [1].
Было установлено, что все биологические препараты приводят к снижению частоты клинически значимых обострений. На фоне терапии бенрализумабом, меполизумабом и дупилумабом потребность в ПГКС снижается более чем на 50% для первых двух препаратов и на 29,4% – для третьего.
Изменение ОФВ1 оценивали для всех молекул, кроме дупилумаба. Так, у бенрализумаба прирост составит 140 мл, у меполизумаба – в среднем на 111 мл, у реслизумаба – на 140 мл, у омализумаба – на 3,7%.
Изменение качества жизни определялось для всех препаратов: во всех случаях было отмечено улучшение этого параметра, а также контроля симптомов бронхиальной астмы.
При оценке профиля безопасности нежелательные явления отмечались у всех биологических молекул. Тяжелые реакции чаще наблюдались при исследовании дупилумаба (1,46 случаев в среднем) и реслизумаба (4,71), реже на фоне применения бенрализумаба (0,56) и меполизумаба (0,98) [32, 35–40].
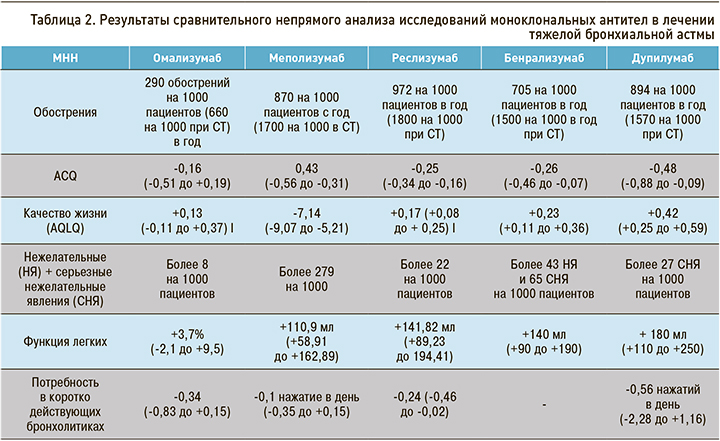
Данные сравнительного непрямого анализа исследований биологических таргетных препаратов для лечения ТБА приведены в таблице 2.
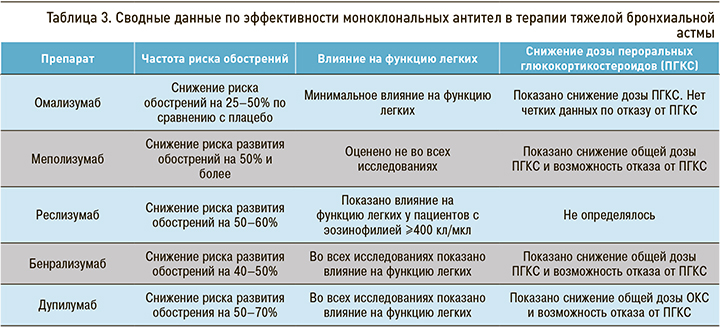
Результаты, полученные Kring J.G. et al. [41] при сравнении биологических препаратов по трем критериям эффективности терапии ТБА, представлены в таблице 3.
В непрямом сравнительном анализе публикаций о бенрализумабе и дупилумабе в PubMed, Embase, CENTRAL и SCOPUS, проведенного Ando K. et al., в качестве первичной конечной точки оценивали снижение частоты клинически значимых обострений и развитие нежелательных явлений. В качестве вторичной конечной точки определяли влияние терапии на ОФВ1 и изменение качества жизни. Было установлено, что дупилумаб и бенрализумаб достоверно снижают частоту обострений в течение года по сравнению с плацебо. При оценке результатов лечения по подгруппам в зависимости от исходного уровня эозинофилии было показано, что дупилумаб был более эффективен в снижении частоты обострений в подгруппе с уровнем эозинофилии ≥300 кл/мкл и в подгруппе со значениями этого показателя 150–300 кл/мкл. При этом обе молекулы были не эффективны при уровне эозинофилов менее 150 кл/мкл.
При сравнении влияния дупилумаба и бенрализумаба на ОФВ1 и качество жизни были получены сопоставимые данные эффективности обеих молекул при исходном уровне эозинофилов в крови ≥300 кл/мкл и более, и обе были достоверно эффективнее по сравнению с плацебо. Также не было получено достоверных данных по превалированию одной из молекул в отношении развития нежелательных явлений: как в отношении побочных реакций в целом, так и по серьезным нежелательным явлениям данные оказались сопоставимы. Таким образом, согласно результатам приведенного анализа, дупилумаб продемонстрировал лучшую эффективность в снижении частоты обострений при исходном уровне эозинофилии ≥300 кл/мкл; если величина этого показателя составляет 150 кл/ мкл, то бенрализумаб не эффективен в отличие от дупилумаба [42].
В обзор Cochrane, посвященный препаратам анти-IL-5 терапии, для оценки данных по меполизумабу было включено 4 исследования (всего 1809 пациентов с подтвержденной эозинофильной ТБА, с уровнем ОФВ1 менее 80%, частыми обострениями, уровнем эозинофилов 150 кл/мкл на момент начала терапии или 300 кл/мкл в анамнезе за последние 12 мес). Для оценки эффективности реслизумаба также оценивали данные 4 исследований (1764 пациента со среднетяжелой или тяжелой бронхиальной астмой, с уровнем эозинофилии ≥400 кл/мкл). В отношении бенрализумаба были оценены результаты 5 клинических исследований с участием 3232 пациентов, имеющих среднетяжелую и тяжелую эозинофильную бронхиальную астму и уровень эозинофилии ≥300 кл/мкл [43].
При анализе данных было показано статистически значимое снижение частоты клинически значимых обострений на фоне терапии всеми биологическими препаратами по сравнению с плацебо. При этом на фоне терапии реслизумабом не было выявлено статистически значимой разницы относительно плацебо по частоте обострений, требующих обращения за скорой медицинской помощью, в отличие от меполизумаба и бенрализумаба, которые способствовали достоверному снижению этого показателя. На фоне применения всех трех названных биологических препаратов отмечалось статистически значимое снижение уровня эозинофилии крови, улучшение показателей ОФВ1 и качества жизни. Все они показали высокий уровень безопасности, однако на фоне терапии бенрализумабом отмечалось большее по сравнению с плацебо количество клинически значимых нежелательных явлений, которые привели к прекращению терапии. Вероятно, это связано с другим механизмом влияния этого препарата на эозинофилы [43].
ПЕРСПЕКТИВЫ БИОЛОГИЧЕСКОЙ ТЕРАПИИ
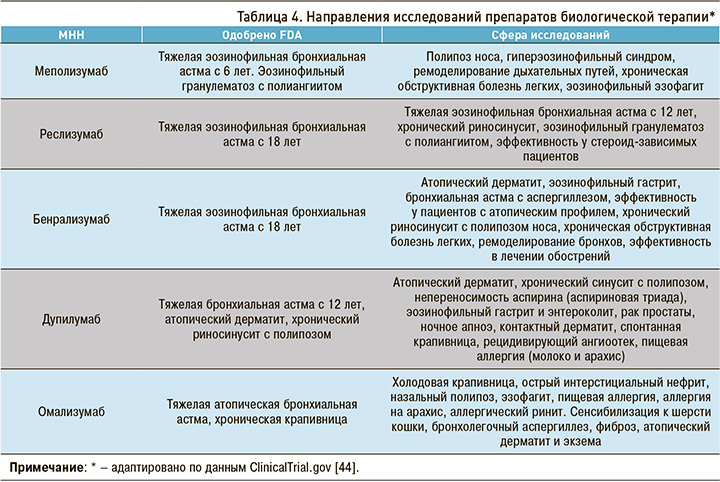
На сегодняшний день продолжаются исследования по эффективному и безопасному применению препаратов таргетной биологической терапии в лечении пациентов с другими нозологиями. В таблице 4 представлены основные векторы таких исследований.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Для лечения пациентов с ТБА в настоящее время доступны пять биологических молекул моноклональных антител, действующих на разные звенья воспаления. Доказана эффективность всех этих молекул в плане снижения частоты клинически значимых обострений, улучшения функции легких и качества жизни. Меполизумаб, бенрализумаб и дупилумаб продемонстрировали эффективность, связанную с возможностью снижения дозы ОКС на ≥50% и на ≥5 мг вплоть до полной отмены ОКС. Кроме того, показан высокий профиль безопасности всех препаратов. Наиболее изученным среди анти-IL-5 препаратов является меполизумаб. Добавим, что в ходе клинических исследований на фоне применения этого препарата не отмечено развития анафилактических реакций.
Для лечения детей применяются омализумаб и меполизумаб (с 6 лет) и дупилумаб (с 12 лет). Наблюдения в реальной клинической практике на сегодня проведены в отношении омализумба и меполизумаба. При выборе таргетной терапии необходимо убедиться и подтвердить диагноз ТБА, а также определить биомаркер, который поможет в дальнейшем при выборе таргетной терапии.


