Диагностика
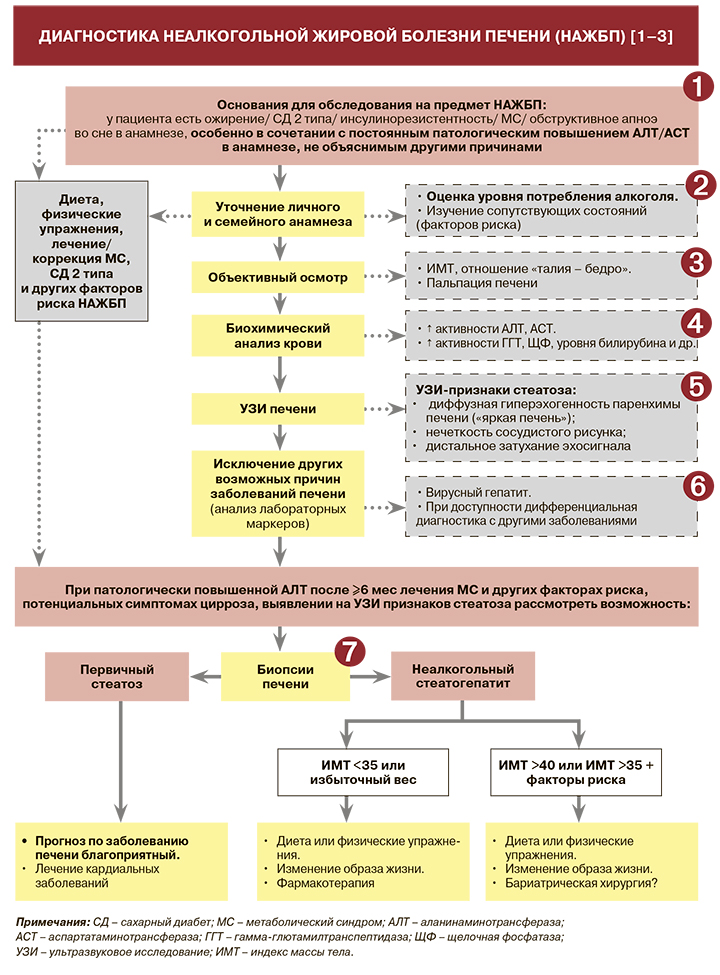
1.
• В большинстве случаев неалкогольная жировая болезнь печени (НАЖБП) не проявляется какими-либо специфическими симптомами, но часть пациентов может предъявлять жалобы на повышенную утомляемость, ноющую боль или дискомфорт в области правого подреберья без четкой связи с приемом пищи [1, 2].
• У некоторых больных в клинической картине на первый план выходят проявления метаболического синдрома (МС): висцеральное ожирение, признаки нарушения обмена глюкозы, дислипидемии и артериальной гипертензии [2].
• В тяжелых случаях, когда НАЖБП приводит к развитию цирроза печени, возникают симптомы печеночной недостаточности и/или портальной гипертензии: увеличение размеров живота, отеки, геморрагический синдром, энцефалопатия и др. [2].
2.
• Детальный анамнез уровня употребления алкоголя пациентом с подозрением на НАЖБП крайне важен, поскольку диагностические тесты не могут выявить четкого различия между алкогольной и неалкогольной жировой болезнью печени. Согласно рекомендациям Всемирного гастроэнтерологической организации (WGO), порог употребления спиртного, позволяющий исключить алкогольный генез заболевания печени, составляет в пересчете на этанол <20 г/сут для женщин и <30 г/сут для мужчин; согласно рекомендациям Российского гастроэнтерологического общества, аналогичные показатели составляют <20 и <40 г/сут. Для оценки потребления алкоголя должны использоваться соответствующие специализированные опросники или балльные системы, например CAGE, AUDIT [1].
• Наряду с ожирением, сахарным диабетом (СД) 2 типа, инсулинорезистентностью, МС, обструктивным апноэ во сне в анамнезе, к факторам, повышающим вероятность развития НАЖБП, относятся синдром поликистозных яичников; гипотиреоз; гипогонадизм; гипопитуитаризм; панкреатодуоденальная резекция; подвздошно-тонкокишечный анастомоз; отягощенный семейный анамнез; дефицит витамина D; прием ряда лекарственных средств (тамоксифена, метотрексата, амиодарона, синтетических эстрогенов и др.) [1, 2]. Наивысший риск НАЖБП отмечается в возрастной группе 40– 65 лет, хотя болезнь встречается даже у детей младше 10 лет [1].
3.
• При объективном осмотре, как правило, выявляют признаки ожирения. У больных со стеатозом и неаклогольным стеатогепатитом (НАСГ) обнаруживают умеренное увеличение печени, край ее закруглен, консистенция тестоватая [1]. При выраженном фиброзе печень становится плотной, на стадии цирроза могут наблюдаться «печеночные знаки», спленомегалия, гепатомегалия, асцит, паукообразные ангиомы, пальмарная эритема, желтуха, печеночная энцефалопатия [1, 2].
4.
• Основные возможные изменения в биохимическом анализе крови у пациентов с НАЖБП приведены в таблице. Следует отметить, что степень повышения активности аланинаминотрансферазы (АЛТ) и аспартатаминотрансферазы (АСТ) не является точным критерием оценки тяжести НАЖБП и не коррелирует со степенью стеатоза и фиброза печени. Принято считать, что вероятность НАСГ выше, если активность сывороточных трансаминаз превышает верхнюю границу нормальных значений более чем в 2 раза, однако и при нормальных показателях активности трансаминаз нельзя с уверенностью исключить НАСГ и фиброз печени [4, 5].
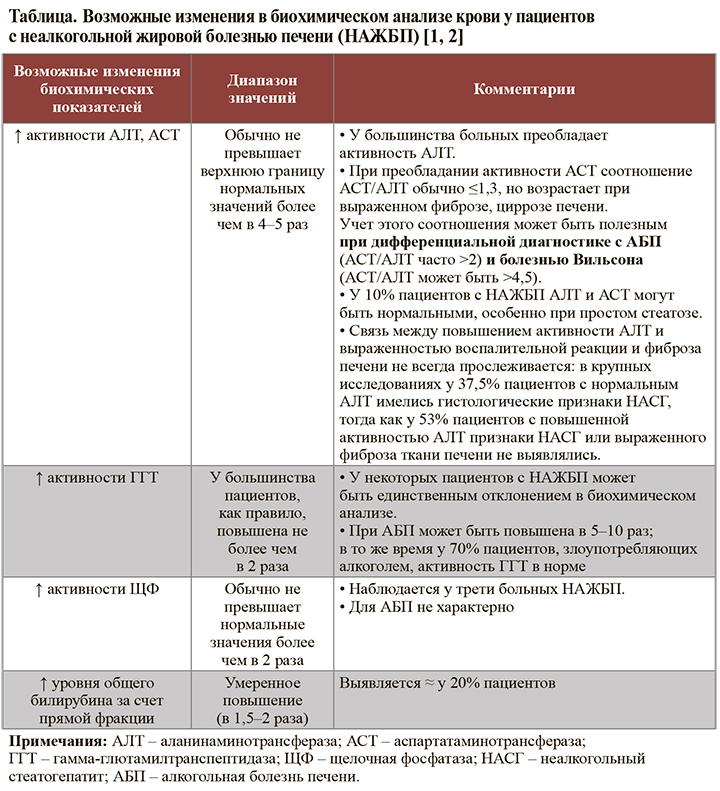
• У пациентов с циррозом при нарушении синтетической функции печени, наряду с АСТ >АЛТ, обнаруживают и такие биохимические признаки, как снижение уровня альбумина и увеличение протромбинового времени, повышение уровня общего билирубина и международного нормализованного отношения [2].
• К диагностически значимым биохимическим отклонениям, характерным для НАЖБП в рамках МС, относятся:
– увеличение содержания триглицеридов (≥1,7 ммоль/л);
– снижение уровня холестерина липопротеидов высокой плотности (<0,9 ммоль/л у мужчин и <1,0 ммоль/л у женщин) [6].
5.
• Ультразвуковое исследование (УЗИ) печени имеет преимущества при диагностике НАЖБП на стадии цирроза печени, особенно у пациентов без клинических симптомов поражения печени [7].
• Из других методов визуализации в диагностике НАЖБП можно использовать компьютерную и магнитно-резонансную томографию (КТ и МРТ) [1, 2].
• Ни один из визуальных методов не позволяет идентифицировать жировое накопление в печени, если оно <33%, различить НАСГ и поражение печени алкогольного генеза, а также не позволяет дифференцировать стеатоз печени и НАСГ [1, 2].
6.
• Наряду с алкогольной болезнью печени (см. пункт 2 и таблицу) при обследовании пациента с подозрением на НАЖБП необходимо (при любых ресурсах здравоохранения) проведение дифференциальной диагностики с вирусным гепатитом (поверхностный антиген гепатита В, антитела или HCV-РНК вируса гепатита С, IgM антител к гепатиту А). При этом следует учитывать, что НАЖБП может сосуществовать с НАЖБП [1, 2].
• По возможности (при наличии необходимых ресурсов) также следует исключить следующие заболевания:
– болезнь Вильсона (уровни сывороточного церулоплазмина, суточной экскреции меди с мочой, осмотр офтальмологом с целью выявления кольца Кайзера–Флейшера, генетическое исследование на предмет мутации в гене АТР7В);
– лекарственное поражение печени (тщательное изучение лекарственного анамнеза, использование шкалы CIOMS/RUCAM);
– наследственный гемохроматоз (уровень сывороточного железа, процента насыщения трансферрина железом/общей железосвязывающей способности сыворотки и ферритина, генетическое исследование на предмет мутации в гене HFE, окраска на железо по Перлсу при морфологическом исследовании ткани печени);
– аутоиммунный гепатит и первичный билиарный цирроз у женщин (уровни g-глобулинов при электрофорезе белков сыворотки крови, IgG, антинуклеарного фактора, ANA, antiLKM-1, ASMA и, соответственно, уровни сывороточных IgМ и АМА-M2) [1, 2].
7.
• WGO также рекомендует рассмотреть проведение биопсии печени при наличии ≥1 из следующих диагностических находок:
– цитопения;
– спленомегалия;
– патологический ферритин в сыворотке в отсутствии процента насыщения трансферрином;
– клинические признаки хронического заболевания печени;
– ожирение + возраст старше 45 лет или патологически повышенные уровни АСТ/АЛТ;
– необъяснимая гепатомегалия [1].
• Несмотря на инвазивность, определенный потенциал ошибок в образцах и противоречивую гистологической интерпретацию, биопсия печени остается «золотым стандартом» диагностики стеатоза, воспаления и оценки стадии фиброза при НАЖБП. Этот метод позволяет с высокой степенью достоверности подтвердить наличие НАЖБП, провести дифференциальный диагноз между стеатозом и НАСГ, оценить стадию фиброза и на основании результатов гистологического исследования составить прогноз дальнейшего течения заболевания, а также исключить другие причины поражения печени [1, 2].
• Из-за сложностей в правильной интерпретации результатов биопсии печени лучшим вариантом является обращение к специалисту по гепатопатологии с опытом гистологической диагностики [1].
• Наряду с биопсией печени существуют неинвазивные методы диагностики НАЖБП и оценки степени фиброза – тесты ФиброМакс, ФиброМетр, эластометрия и др. [2]. При этом, как отмечается в рекомендациях WGO, ни один из неинвазивных методов не может дать результаты, позволяющие исключить другие возможно имеющиеся заболевания, или стадию НАЖБП в прогностических целях [1]. В конечном итоге НАЖБП – это диагноз исключения, и часто для подтверждения диагноза, стадии заболевания (стеатоз, НАСГ), дифференциальной диагностики и определения срочности агрессивной терапии необходимо проведение биопсии печени [1].
• Как отмечается в клинических рекомендациях EASL–EASD–EASO, оптимальный план ведения пациентов с НАЖБП пока не определен. Необходимо учитывать не только риск прогрессирования заболевания печени и сопутствующих метаболических нарушений, но и экономические аспекты. Мониторинг должен включать рутинный биохимический анализ, оценку сопутствующих патологий и неинвазивную оценку фиброза. У пациентов со стеатозом без ухудшения метаболических факторов риска мониторинг рекомендуется проводить каждые 2‒3 года, у пациентов с НАСГ и/или фиброзом – ежегодно, а у больных с НАСГ/ циррозом – каждые 6 мес. Биопсию печени можно повторить по показаниям через 5 лет [3].
Лечение

1.
• При избыточной массе тела необходимо добиваться ее плавного уменьшения: первоначально – на 10% и не более чем на 0,5–1,0 кг в неделю. Быстрое снижение веса может привести к прогрессированию стеатогепатита и другим нежелательным последствиям. В то же время уменьшение массы тела на 10% является облигатным условием для клинически значимого уменьшения и регресса некровоспалительных изменений в печени [2]. Результаты метаанализа свидетельствуют о корреляции похудания со снижением выраженности стеатоза и/или уровня сывороточных трансаминаз. Уменьшение массы тела на 4–14% ассоциировано со статистически значимым уменьшением содержания триглицеридов (ТГ) в гепатоцитах (35–81%) [8, 9].
• Пациентам с неалкогольной жировой болезнью печени (НАЖБП) подходит средиземноморский тип питания: потребление большого количества фруктов (с учетом их калорийности), овощей, рыбы, ограничение потребления жирного «красного» мяса [2, 3]. Необходимо стремиться к снижению калорий на 25% от нормальной диеты (≈2500 калорий в день) в зависимости от возраста и пола пациента. Диета с умеренным ограничением калорий и модифицированным подбором питательных макроэлементов показывает лучшие результаты по сравнению с очень низкокалорийной диетой [1].
2.
• Пациентам с НАЖБП показаны умеренные аэробные нагрузки, например ходьба в среднем темпе не менее 20 мин не реже 5 раз в неделю, плавание, езда на велосипеде. От бега следует воздержаться, пока не будут достигнуты нормальные показатели индекса массы тела (ИМТ) [2].
• При выполнении умеренных физических нагрузок рекомендуется ориентироваться на достижение частоты сердечных сокращений до 60–75% от возрастного максимума [1].
• Регулярное выполнение адекватных физических упражнений приводит к улучшению гистологической картины печени при неалкогольном стеатогепатите (НАСГ) даже без клинически значимого снижения массы тела, а также способствует уменьшению сывороточного уровня холестерина [10].
3.
Критерии, определяющие возможность хирургического лечения морбидного ожирения (эндоскопическая установка внутрижелудочных баллонов, регулируемое бандажирование желудка, гастрошунтирование и др.):
– ИМТ >40 кг/м2 (независимо от наличия сопутствующих заболеваний);
– ИМТ >35 кг/м2 при наличии тяжелых заболеваний, на течение которых можно воздействовать путем уменьшения массы тела [11].
4.
• К факторам высокого риска прогрессирования фиброза при НАСГ относятся возраст >50 лет, сахарный диабет (СД), метаболический синдром, повышение аланинаминотрансферазы (АЛТ) [3].
• Пациентам без НАСГ или фиброза рекомендованы только здоровое питание и физическая активность без фармакотерапии [3].
5.
• Повышение чувствительности тканей к инсулину – одна из главных целей комплексного лечения НАЖБП [2]. При этом сахароснижающие препараты не имеют среди официальных показаний к применению НАЖБП (НАСГ), т.е. их назначение при этом заболевании является off-label.
• В исследовании PIVENS с участием пациентов без явного СД пиоглитазон, по сравнению с витамином E и плацебо, улучшал все гистологические показатели (за исключением фиброза) и в сравнении с плацебо чаще приводил к регрессу НАСГ [12]. Гистологический эффект наблюдался вместе с улучшением уровня АЛТ и частичной коррекцией инсулинорезистентности. Аналогичные результаты были получены в двух меньших и более коротких рандомизированных клинических исследованиях (РКИ) [13, 14], хотя длительное применение пиоглитазона официально не оценивалось. Следует учитывать вероятность серьезных побочных эффектов глитазонов (увеличение массы тела, переломы костей у женщин и, реже, хроническая сердечная недостаточность). Несмотря на профиль безопасности и переносимости, пиоглитазон можно использовать у некоторых пациентов с НАСГ, особенно при СД 2 типа [3].
• Спектр положительных эффектов метформина, помимо повышения чувствительности тканей к инсулину, включает уменьшение массы тела (за счет центрального аноректического действия), стимуляцию β-окисления жирных кислот, снижение концентрации ТГ, общего холестерина (ХС) и ХС ЛПНП в сыворотке крови [2]. При этом данных о гистологической эффективности метформина при НАСГ недостаточно, этот препарат слабо воздействует на содержание жира в печени [3].
• В ходе небольшого экспериментального исследования по применению ежедневных инъекций лираглутида, который влияет на взаимодействие глюкозы–инсулина, была достигнута гистологическая ремиссия НАСГ без ухудшения фиброза [15].
6.
• Как и сахароснижающие средства, гиполипидемические препараты при НАЖБП применяются off-label. Среди статинов при НАЖБП наиболее хорошо изучены эффективность и безопасность симвастатина и аторвастатина в дозе 20–40 мг на ночь, а также правастатина, ловастатина, розувастатина. Согласно последним данным, статины редко вызывают поражение печени, поэтому контроль активности трансаминаз с целью мониторинга гепатотоксичности не показан [2]. Более того, их прием даже может значительно снизить уровень аминотрансфераз [16].
• Фенофибрат может назначаться с целью коррекции повышенного уровня ТГ – в виде монотерапии или в сочетании со статинами. Эффективность фенофибрата при лечении НАЖБП показана в нескольких небольших клинических исследованиях, однако необходима дополнительная оценка его роли в исследованиях с изучением гистологических параметров [17].
• Омега-3 полиненасыщенные жирные кислоты (ПНЖК) могут применяться для лечения гипертриглицеридемии у пациентов с НАСГ. Предварительные данные небольших или неконтролируемых исследований позволяют предположить, что омега-3 полиненасыщенные жирные кислоты (ПНЖК) могут уменьшать содержание жира в печени [18], однако считать их препаратами выбора для терапии НАЖБП/НАСГ до получения результатов рандомизированных клинических исследований преждевременно [2].
7.
• В упомянутом исследовании PIVENS прием витамина Е (800 МЕ/сут) снижал выраженность стеатоза, воспаления, баллонной дистрофии и стимулировал регресс НАСГ у 36% пациентов (+15% относительно плацебо) [12]. Витамин Е возможно использовать у пациентов с НАСГ без цирроза и СД, однако дать определенные рекомендации пока не представляется возможным: необходимы дальнейшие исследования. Долгосрочная безопасность витамина E вызывает сомнения, поскольку отмечается увеличение общей смертности, частоты геморрагического инсульта и рака простаты у мужчин старше 50 лет [3].
8.
• Адеметионин (S-аденозил-L-метионин) сочетает гепатопротективные, холеретические, холекинетические, детоксикационные, регенерирующие, антиоксидантные, антифибротические свойства, а также обладает нейропротективным и антидепрессивным действием. В связи с тем что одним из ключевых механизмов формирования и прогрессирования НАЖБП выступают нарушения баланса фосфотидилхолина (ФХ)/ фосфотидилэтаноламинов (ФЭА), применение адеметионина можно считать патогенетически обоснованным, поскольку как важный регулятор синтеза фосфолипидов клеточных мембран он способствует нормализации этого баланса [19].
• Для лечения госпитальных пациентов рекомендуют использовать ступенчатую терапию адеметионином: внутривенное введение длительностью до 2 нед с последующим переходом на пероральную терапию в амбулаторных условиях [2].
• В обсервационном проспективном мультицентровом исследовании у пациентов с внутрипеченочным холестазом на фоне НАЖБП (n=250) после 6-недельного курса применения адеметионина (800–1200 мг/сут) отмечалось достоверное статистически значимое улучшение биохимических показателей и клинических симптомов заболевания: – снижение ЩФ (в 1,4 раза), ГГТ (в 1,66 раз), АЛТ (в 2 раза), АСТ (в 2,1 раза); – уменьшение выраженности желтухи (на 27,1%), зуда (на 21,6%), усталости (на 43,3%) [20].
• В открытом плацебо-контролируемом исследовании с участием пациентов с внутрипеченочным холестазом адеметионин при приеме 800 мг 2 раза/сут через 15–30 дней лечения способствовал прекращению кожного зуда и нормализации или улучшению на 50% уровней общего и прямого билирубина, АЛТ, АСТ, ГГТ, ЩФ [21]. При внутримышечном (500 мг/сут) и внутривенном (800 мг/сту) введения адеметионина биохимический ответ на лечение (снижение общего и прямого билирубина, АЛТ, АСТ, ГГТ, ЩФ) уже на 7-й
• Урсодезоксихолевая кислота (УДХК) обладает гепатопротективным, антиоксидантным и антифибротическим действием. В различных РКИ прием этого лекарственного средства (15–30 мг/сут) приводил к достоверному снижению активности АЛТ, аспартатаминотрансферазы (АСТ) и гамма-глютамилтранспептидазы (ГГТ) относительно плацебо, а также уменьшению выраженности стеатоза и фиброза. Помимо этого, препарат способствовал уменьшению общего ХС, ХС ЛПНП, ТГ, токсичных жирных кислот в ткани печени и белой жировой ткани [2, 22, 23].
• Эссенциальные фосфолипиды (ЭФЛ) оказывают антиоксидантное и противовоспалительное действие, способны восстанавливать целостность клеточных мембран (регенерирующие свойства). По данным ряда клинических исследований, у больных с НАЖБП ЭФЛ уменьшают выраженность стеатоза печени (по данным УЗИ) и снижают уровень активности сывороточных трансаминаз [2, 24-26].
• В зависимости от соотношения количеств линолевой и линоленовой кислот у препаратов ЭФЛ могут отмечаться дополнительные свойства (например, гиполипидемические) [2].
• Имеются определенные данные о противовоспалительных и антифибротических свойствах силимарина (активного компонента экстракта расторопши). В небольшом плацебо-контролируемом исследовании у пациентов с НАСГ, получавших силимарин, было отмечено снижение активности сывороточных трансаминаз, однако убедительных данных о долгосрочном положительном влиянии силибилина на течение НАСГ не получено [2, 27].
• Как отмечается и в зарубежных, и российских клинических рекомендациях, в настоящее время не существует единого одобренного стандарта лечения (в том числе лекарственного) НАЖБП/НАСГ [1, 2]. При этом оговаривается высокая важность в любой попытке положительно повлиять на течение НАЖБП/НАСГ изменения стиля жизни (диета, физические упражнения) и коррекции сопутствующих состояний [1].


