ВВЕДЕНИЕ
При лечении больных старше 80 лет, кроме достижения основных целей терапии заболевания, актуальными являются такие задачи, как сохранение способности пациентов обслуживать себя самостоятельно и не зависеть от посторонней помощи при осуществлении повседневной деятельности, улучшение качества жизни, предупреждение побочных действий и осложнений от приема лекарственных средств, снижение смертности [1, 2]. Наличие синдрома старческой астении (ССА) у больных артериальной гипертензией (АГ) вносит коррективы в организацию и тактику антигипертензивной терапии (АГТ) [3]. При ее назначении врачи индивидуально учитывают общее состояние больных и потенциальную возможность развития негативных последствий в виде учащения падений из-за ортостатической гипотонии, переломов костей, усугубления деменции, усиления астенического синдрома [4–6]. На современном этапе ключевые риски антигипертензивного лечения у пациентов старше 80 лет и больных с ССА ассоциированы с опасностью выраженного снижения артериального давления (АД), сопровождающегося гипоперфузией жизненно важных органов, а при резком градиенте изменения АД – и с потерей сознания, падениями, переломами шейки бедра с длительной иммобилизацией [7, 8]. Серьезной проблемой при ведении больных старческого возраста признана связь ортостатической гипотонии с более высокой частотой неблагоприятных сердечно-сосудистых событий и с высокими цифрами смертности [9].
Следует также отметить, что АГ – одно из основных заболеваний, приводящих к развитию хронической сердечной недостаточности (ХСН) у лиц пожилого и старческого возраста. Более 80% пожилых пациентов в популяции имеют в анамнезе ХСН, которая выступает основной причиной госпитализации людей старше 65 лет [10]. Наличие ХСН значительно ухудшает прогноз в этой возрастной группе, увеличивая смертность на 33–35% в год [11].
Таким образом, практикующий врач при ведении пациентов старческого возраста с АГ, назначая АГТ, должен, с одной стороны, достичь целевых значений снижения АД, а с другой – не допустить неблагоприятных последствий, обусловленных коморбидной патологией.
Цель исследования – оценка эффективности амбулаторного лечения АГ у пациентов старческого возраста в зависимости от наличия ХСН и ССА.
МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДЫ
При амбулаторном наблюдении обследованы 320 больных АГ старше 80 лет обоего пола – 162 женщины (50,6%) и 158 (49,4%) мужчин. Медиана возраста пациентов составила 83,6 лет с межквартильным диапазоном от 81,2 до 85,8 лет. Дизайн работы соответствовал наблюдательному кросс-секционному исследованию и включал сравнительный анализ «случай–контроль».
Критериями включения пациентов в исследование были возраст старше 80 лет, наличие АГ, ХСН IIA–IIБ стадии и II–IV функционального класса.
Критерии невключения: наличие гемодинамически значимых пороков сердца, имплантированного электрокардиостимулятора, ишемической болезни сердца в анамнезе, острого нарушения мозгового кровообращения или транзиторной ишемической атаки в течение последних 6 мес, злокачественных новообразований, тяжелой патологий печени или почек.
Проведенное исследование соответствовало стандартам Хельсинкской декларации и было одобрено Этическим комитетом ФГБОУ ВО «Ростовский государственный медицинский университет» Минздрава России (протокол от 05.09.2019 № 13/19). Все лица, вошедшие в исследование, подписали письменное информированное добровольное согласие на участие в нем.
В зависимости от наличия ХСН и ССА все участники были разделены на четыре клинические группы: группа 1А– пациенты с АГ, ССА и ХСН (n=84); группа 1Б – пациенты с АГ и ССА без ХСН (n=84); группа 2А – пациенты с АГ и ХСН без ССА (n=77); группа 2Б – пациенты с АГ без ХСН и без ССА (n=75).
Наличие АГ определяли, учитывая анамнез заболевания пациента, данные амбулаторной карты, а также результаты офисного измерения АД методом С.Н. Короткова. Измерение АД выполнялось на обеих руках троекратно, с интервалом 1–2 мин, в положении сидя, после 5-минутного отдыха [12].
Диагноз ХСН устанавливался на основании симптомов и клинических признаков, уровня N-концевого пропептида натрийуретического гормона В-типа (маркера сердечной недостаточности) и данных эхокардиографии в соответствии с национальными клиническими рекомендациями по диагностике и лечению ХСН от 2020 г. [13]. ССА выявляли с помощью опросника «Возраст не помеха», согласно которому о вероятном наличии этого синдрома можно судить, если результат составляет ≥3 баллов [14].
С учетом патофизиологических особенностей АГ в старческом возрасте при оценке эффективности АГТ в качестве цели лечения рассматривается уровень систолического артериального давления (САД) 130–139 мм рт.ст., а у пациентов со старческой астенией – 140–150 мм рт.ст. [14]. Рекомендуется рассмотреть уменьшение интенсивности АГТ вплоть до ее отмены у пациента с ССА в случае снижения САД менее 130 мм рт.ст. У этой категории пациентов инициация АГТ должна начинаться с одного препарата в низкой дозе; переходить к комбинированной терапии следует только при неэффективности монотерапии, применяя при этом не более 3 антигипертензивных препаратов.
Ортостатическая проба в рамках исследования проводилась путем перевода пациента в вертикальное положение после положения лежа на спине не менее 7 мин. Через 1, 2, 3 мин после изменения положения тела регистрировались АД и частота сокращений сердца (ЧСС). Критериями ортостатической гипотонии служили снижение САД >20 мм рт.ст. (либо >30 мм рт.ст., если исходное САД превышало 160 мм рт.ст. в положении лежа) и/или диастолического артериального давления (ДАД) ≥10 мм рт.ст. или регистрация САД <90 мм рт.ст. [5]. У части пациентов наличие ортостатической гипотонии доказывали с помощью суточного мониторирования АД. Ограничения при проведении исследования отсутствовали.
Статистический анализ полученных данных осуществлялся с помощью программы STATISTICA 12.0 (StstSoft, США). Проверку на нормальность распределения величин проводили с применением критерия Шапиро–Уилка. Количественные показатели представлены в виде медианы и межквартильного диапазона. Множественные межгрупповые различия определялись посредством дисперсионного анализа по критерию Краскела–Уоллиса, попарные – по критерию Манна–Уитни с поправкой на число сравниваемых пар. При множественных попарных сравнениях автоматически корректировался табличный уровень критериев, а доверительная вероятность имела разделительное значение для выявления статистически значимых различий (<0,05). Различие между долями определялось с помощью построения таблиц сопряженности и критерия Хи-квадрат Пирсона. Событийную вероятность (пациенты с госпитализацией в течение 12 мес наблюдения) в динамике анализировали по методу Каплана–Мейера, а влияние различных факторов на событие оценивали с использованием регрессионного анализа Кокса.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Все пациенты с АГ и ХСН (группы 1А и 2А) имели III стадию гипертонической болезни (ГБ). У преобладающего большинства больных групп 1Б и 2Б диагностировали III стадию ГБ (92,9 и 94,7% соответственно). II стадию ГБ имели 7,1% пациентов в 1Б и 5,3% в группе 2Б, при этом различия между группами были статистически значимы (p <0,05; табл. 1). У всех пациентов клинических групп отмечался очень высокий сердечно-сосудистый риск, а длительность АГ превышала 20 лет.
При сравнительном анализе распределения стадий ХСН не было выявлено статистически значимого различия между пациентами с ССА и без этого синдрома (p >0,05). Оценка распространенности ФК ХСН в исследуемых группах продемонстрировала более высокий процент встречаемости ХСН III ФК при наличии ССА (61,9 против 45,5%, р=0,036) и ХСН II ФК у пациентов без ССА (41,6 против 28,6%, p=0,041).
У пациентов с АГ на фоне ССА значительно чаще, чем у больных без ССА, имели место сопутствующие хроническая болезнь почек и фибрилляция предсердий, причем независимо от наличия ХСН. При межгрупповом анализе среди «хрупких» пациентов (т.е. имевших ССА) в группе 1А в сравнении с группой 1Б статистически значимо чаще встречались анемия (23,8 против 10,7%, p=0,033) и сахарный диабет 2-го типа (31% против 17,9%, p=0,042). При межгрупповом сравнении «крепких» пациентов (т.е. без ССА) в 2А и 2Б группах статистически значимых различий частоты встречаемости анемии и сахарного диабета 2-го типа выявлено не было (p >0,05).
По результатам офисных измерений АД в группе 1А отмечались более высокие значения САД (р=0,047), более низкие величины ДАД (р <0,001) и ЧСС (р=0,042) в сравнении с пациентами группы 2А (табл. 2).
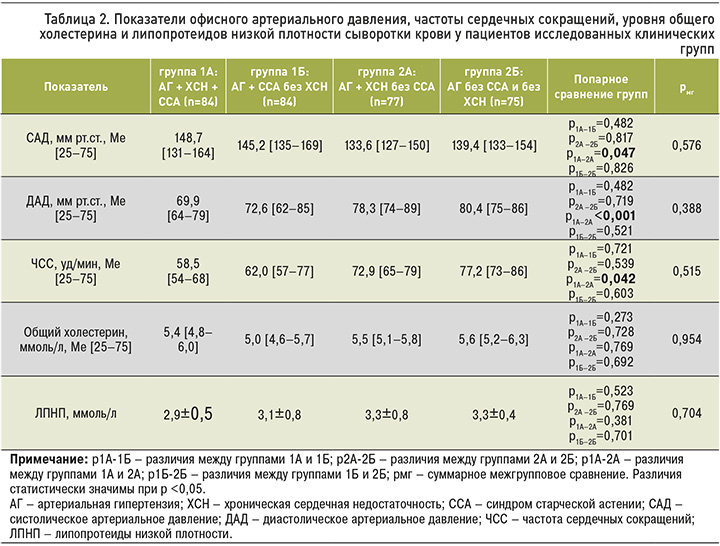
В группах 1Б и 2Б при отсутствии ХСН различия величин САД и ДАД между «хрупкими» и «крепкими» пациентами выявлены не были (p >0,05). По уровню общего холестерина и липопротеидов низкой плотности сыворотки крови межгрупповых различий также установлено не было (р=0,954 и р=0,704 соответственно).
В настоящее время не существует единого мнения о целевом диапазоне АД у пациентов с АГ и ССА. Однако имеющиеся данные поддерживают назначение АГТ «крепким» пациентам пожилого и старческого возраста и схожесть тактики их ведения с более молодыми пациентами с АГ; при этом рекомендуемые целевые уровни АД более высокие – 130–139/70–79 мм рт.ст. [12]. Для лечения АГ у пациентов пожилого и старческого возраста, включая пациентов со старческой астенией, рекомендуется использовать ингибиторы АПФ (ИАПФ), блокаторы рецепторов ангиотензинаII (БРА), блокаторы кальциевых каналов (БКК, производные дигидропиридина пролонгированного действия), тиазидные и тиазидоподобные диуретики в низких дозах. Бета-адреноблокаторы (ББ) этим пациентам следует назначать только при наличии установленных показаний.
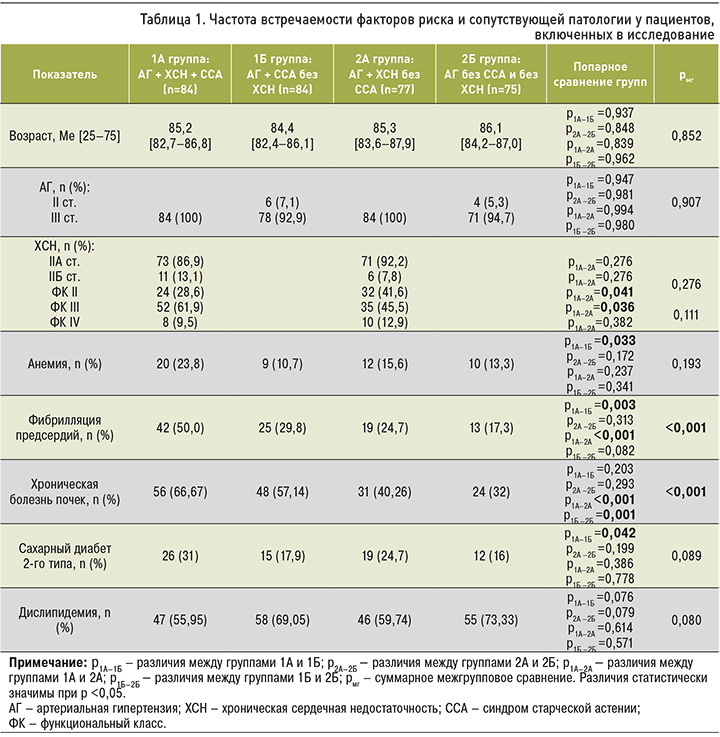
Частота встречаемости АГТ в виде моно- и комбинированной терапии у пациентов каждой исследованной группы представлена на рисунке 1. Как видно, в группе участников с АГ, ХСН и ССА АГТ отсутствовала в 14,3% случаев, что превышало соответствующий показатель у пациентов с АГ и ХСН без ССА (р=0,05). Среди пациентов без ХСН статистически значимо бóльшая доля «хрупких» пациентов не принимала АГТ в сравнении с «крепкими» больными (11,9 против 2,7%, р=0,028). Множественное межгрупповое различие (р=0,031) сформировалось в основном за счет частой отмены АГТ в группах 1А и 1Б по сравнению с «крепкими» пациентами групп 2А и 2Б. Отмена АГТ отмечалась в большем проценте случаев по причине развития ортостатической гипотонии.
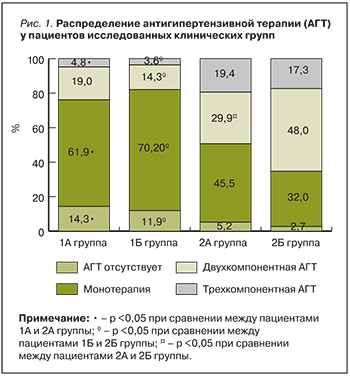
Суммарно монотерапия антигипертензивными средствами применялась в группе 1А в 61,9% случаев, что на 16,4% больше, чем у пациентов группы 2А (р=0,037). Среди участников исследования с АГ без ХСН монотерапия значимо чаще имела место у «хрупких» пациентов, нежели у «крепких» (70,2 против 32%, р <0,001).
Следует отметить, что среди «крепких» больных с АГ без ХСН двухкомпонентная АГТ регистрировалась чаще в сравнении с «крепкими» пациентами с ХСН (48 против 29,9%, р=0,022), а также в сравнении с «хрупкими» пациентами без ХСН (48 против 14,3%, р <0,001).
Трехкомпонентная АГТ значимо чаще назначалась в группе «крепких» пациентов с АГ и ХСН в сравнении с «хрупкими» больными с АГ и ХСН (на 14,6%, р=0,004). Похожие результаты отмечены и у пациентов с АГ без ССА и без ХСН относительно больных АГ с ССА без ХСН (на 13,7%, р=0,004).
Характеристика АГТ у пациентов каждой группы приведена в таблице 3.
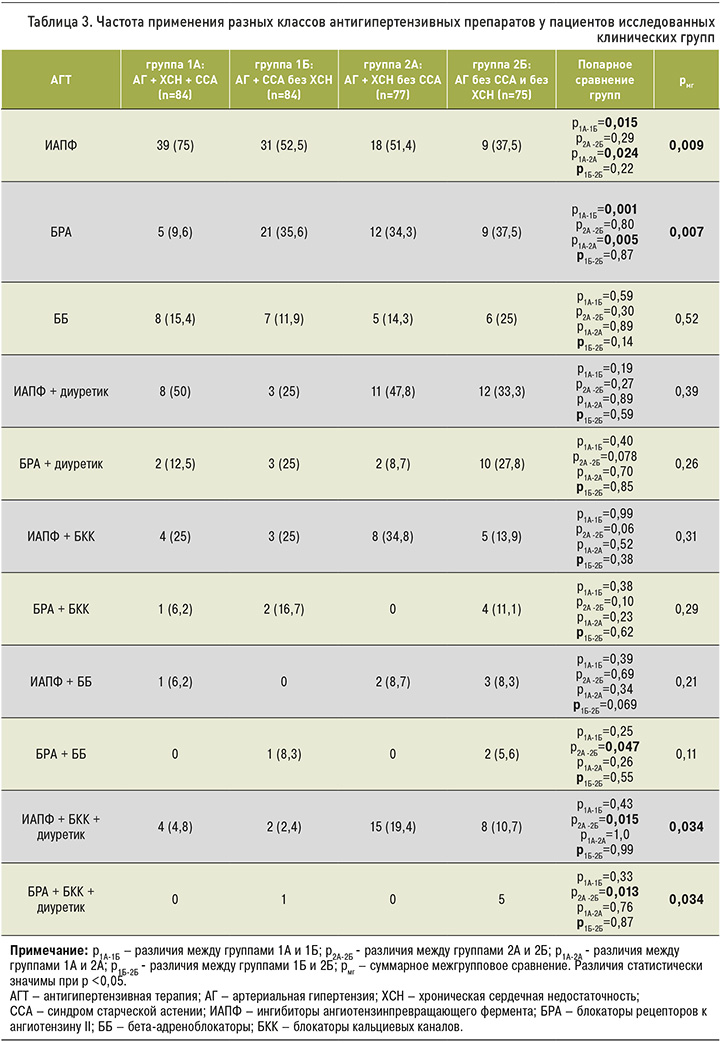
Среди пациентов исследованных клинических групп различие сформировалось по частоте использования в качестве антигипертензивных средств ИАПФ (p=0,009) и БРА (p=0,007). Так, у «хрупких» больных с АГ и ХСН ИАПФ в качестве монотерапии применялись статистически значимо чаще, чем у «хрупких» пациентов без ХСН (р=0,015) и «крепких» пациентов с ХСН (р=0,024). Монотерапия БРА в группе 1А имела наименьший процент в сравнении с пациентами групп1Б (р=0,001) и групп 2А (р=0,005).
Двухкомпонентную терапию БРА+ ББ и трехкомпонентную терапию ИАПФ + БКК + диуретик и БРА + БКК + диуретик значимо чаще получали пациенты с АГ без ССА и без ХСН относительно больных АГ с ССА без ХСН (р=0,047, р=0,015 и р=0,013 соответственно).
Снижение САД до целевого уровня в группе1А наблюдалось у 23 (27,4%), в 1Б – у 32 (38,1%), в 2А – у 33 (42,9%), в 2Б – у 46 (61,3%) участников исследования. Различие эффективности АГТ в четырех изучаемых группах было статистически значимым (р=0,0002). Доля пациентов с достижением целевого уровня САД оказалась наименьшей при АГ на фоне ХСН и ССА (27,4%) и наибольшей среди больных АГ старческого возраста без этой коморбидной патологии (рис. 2).

Ортостатическая гипотония встречалась чаще в группе 1А по результатам выполнения пробы (30,9%) и при суточном мониторировании АД (33,3%) и реже – в группе 2Б (в 14,7 и 18,7% случаев соответственно (рис. 3).
Как при выполнении ортостатической пробы, так и при суточном мониторировании АД частота выявления ортостатической гипотонии в клинических группах различалась (p <0,01). Однако, значимых различий в частоте обнаружения этого осложнения АГТ при сопоставлении двух указанных методов не обнаруживалось (p >0,05), что подчеркивает целесообразность использования у пациентов ортостатической пробы вследствие более легкого ее выполнения по сравнению с мониторингом АД.
Всем участникам, включенным в исследование, у которых не были достигнуты целевые диапазоны АД, проводилась коррекция терапии с учетом наличия ССА и риска развития гипотонии. Однако через 12 мес наблюдения в группе «крепких» пациентов процент достижения целевого уровня АД статистически значимо не отличался от исходного. В группе пациентов с АГ и ССА через 12 мес САД, по данным дневников пациентов, находилось в диапазоне 140–160 мм рт.ст.
В разных клинических группах исследования была изучена частота госпитализаций пациентов вследствие сердечно-сосудистых событий в течение 12 мес наблюдения по методу Каплана–Мейера. Количество госпитализаций оказалось наиболее высоким в группе 1А, реже других госпитализировались пациенты группы 2Б (рис. 4). Анализ показал, что частота неблагоприятных событий в группах статистически значимо различалась (χ2=8,14, р=0,036). При наличии ССА у больных АГ риск неблагоприятного течения болезни с госпитализацией вследствие сердечно-сосудистых событий возрастал в 3,57 раз (отношение шансов (ОШ) 3,57, р=0,0002), при ХСН – в 4,39 раза (ОШ 4,39, р <0,0001), а при сочетании ХСН и ССА – в 7,26 раз (ОШ 7,26, р <0,0001). Отсутствие АГТ повышало риск госпитализаций пациентов в 1,93 раза (ОШ 1,93, р=0,037). Наиболее частой причиной госпитализации у пациентов с АГ и ХСН выступала декомпенсация сердечной недостаточности (р <0,05), тогда как у больных с АГ без ХСН – развитие сердечно-сосудистых событий в виде транзиторной ишемической атаки, нарушений ритма, острого коронарного синдрома (р <0,05).

Таким образом, ХСН и ССА ухудшали эффективность АГТ у больных АГ старше 80 лет ввиду более низкой частоты достижения целевых уровней АД и более частой встречаемости ортостатической гипотонии, а также по причине госпитализаций вследствие сердечно-сосудистых событий.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
1. У «хрупких» пациентов вне зависимости от наличия ХСН статистически значимо чаще отмечались отсутствие АГТ и монотерапия АГ, а также более редкое использование трехкомпонентной терапии в сравнении с «крепкими» пациентами, имевшими или не имевшими ХСН. Двухкомпонентная терапия регистрировалась в большем проценте случаев у участников исследования с АГ без ССА и без ХСН в сравнении как с пациентами с АГ и ХСН без ССА, так и больными, одновременно имевшими все эти три заболевания.
2. У «хрупких» пациентов с АГ и ХСН по сравнению с «хрупкими» больными АГ без ХСН и «крепкими» пациентами с ХСН в качестве монотерапии статистически значимо чаще использовались ИАПФ.
3. У «крепких» пациентов старше 80 лет по сравнению с «хрупкими» вне зависимости от наличия ХСН для лечения АГ чаще применялась комбинированная терапия.
4. «Крепкие» пациенты с АГ без ХСН в сравнении с «хрупкими» больными АГ без ХСН значимо чаще получали двух- (БРА + ББ) и трехкомпонентную терапию (ИАПФ + БКК + диуретик и БРА+ БКК + диуретик).
5. Наличие ХСН и ССА ухудшает эффективность АГТ у больных АГ старше 80 лет, приводит к более частому развитию ортостатической гипотонии.
6. У пациентов с АГ при наличии ССА риск госпитализаций в связи с сердечно-сосудистыми событиями повышался в 3,57, при наличии ХСН – в 4,39, а при сочетании ХСН и ССА – в 7,26 раз.



