Воспалительные заболевания кишечника (ВЗК) – язвенный колит (ЯК) и болезнь Крона (БК) – занимают одно из первых мест в структуре заболеваний желудочно-кишечного тракта. Пик заболеваемости ЯК и БК приходится на самый активный трудоспособный возраст – 20–40 лет, а тяжесть течения приводит к временной потере трудоспособности в молодом возрасте и к инвалидизации больных, в связи с чем проблема ВЗК имеет большую медико-социальную значимость. За последние три десятилетия XX в. почти во всех западных странах было отмечено увеличение числа случаев БК и ЯК.
Причины возникновения БК и ЯК до сих пор до конца не выяснены, однако данные последних исследований позволяют предположить, что в патогенезе ВЗК основной является комбинация наследственных факторов, состояния микробиоты кишечника, иммунного ответа и окружающей среды, приводящая к чрезмерному патологическому иммунному ответу у генетически предрасположенных лиц. Установлена взаимосвязь ВЗК с множеством факторов окружающей среды, таких как применение антибактериальных препаратов, перенесенные кишечные инфекции в детском и более старшем возрасте и особенности питания [1–3]. Принимая во внимание данные исследований общегеномных ассоциаций (GWAS), было высказано предположение, что нарушение регуляции врожденной и адаптивной иммунной систем способствует развитию ВЗК. На сегодняшний день выявлены 163 локуса генов, ассоциированных с развитием ВЗК [4, 5]. Было показано, что выявленные генетические факторы риска взаимодействуют друг с другом в различных путях развития заболеваний. Точно так же были выявлены генетические факторы риска возникновения внекишечных проявлений ВЗК, некоторые из которых имели связь с ВЗК. Весьма вероятно, что, кроме вышеупомянутого перекреста генетических локусов риска, ВЗК и внекишечные проявления также имеют общий механизм развития [5]. Частота внекишечных проявлений ВЗК составляет от 6 до 50% [6, 7], при этом у 25% больных выявляются комбинации нескольких внекишечных проявлений. Системные осложнения ВЗК, снижая трудоспособность и качество жизни больных, могут представлять угрожающие для жизни состояния (например, первичный склерозирующий холангит – ПСХ, венозные тромбоэмболии – ВТЭ, выраженный стеноз дыхательных путей и пр.). Некоторые внекишечные проявления, такие как ирит и увеит, чаще встречаются у женщин, тогда как ПСХ и анкилозирующий спондилит – у мужчин [8]. Патогенез внекишечных проявлений ВЗК до сих пор не выяснен. Считается, что слизистая оболочка кишечника при ВЗК может запускать иммунный ответ во внекишечных участках вследствие общих эпитопов, например, кишечные бактерии и синовиальная оболочка [9, 10]. Конкордантность внекишечных проявлений отмечается у 70% семей, в которых болен один взрослый и один ребенок и у 84% семейных пар, где больны родные братья и сестры [11–15]. Несмотря на все эти данные, остается не ясным, почему фенотип ВЗК включает так много внекишечных проявлений, и почему у определенных пациентов развиваются определенные внекишечные проявления, а у других – нет.
Многогранность клинической картины, сложность диагностики, отсутствие настороженности врачей общей практики относительно возможных внекишечных проявлений приводит к большому числу диагностических ошибок и, следовательно, к потере драгоценного времени для назначения адекватного лечения, поэтому для клиницистов важно знать все многообразие внекишечных симптомов ВЗК.
КЛАССИФИКАЦИЯ ВНЕКИШЕЧНЫХ ПРОЯВЛЕНИЙ ВЗК
Существуют различные подходы к классификации системных проявлений ВЗК. А.И. Парфенов приводит следующую классификацию [16]:
- Патогенетически связанные с воспалением кишечника артриты, афтозный стоматит, эписклерит, узловатая эритема и гангренозная пиодермия, которые не требуют специального лечения.
- Генетически связанные с HLA-B27 анкилозирующий спондилит, сакроилеит, увеит, ПСХ, которые требуют специального лечения.
- Связанные с нарушением всасывания мочекаменная и желчекаменная болезни, анемия, нарушение свертывания крови и другие заболевания, которые также требуют специального лечения.
 Другая классификация рассматривает внекишечные проявления либо в связи, либо вне связи с активностью основного заболевания (табл. 1).
Другая классификация рассматривает внекишечные проявления либо в связи, либо вне связи с активностью основного заболевания (табл. 1).
С клинических позиций удобнее рассматривать внекишечные осложнения ВЗК в соответствии с их локализацией (табл. 2).
Поражения костно-суставной системы
Артропатии, связанные с ВЗК, относятся к группе спондилоартритов. Согласно классификации Международного общества по спондилоартритам (2009), спондилоартропатии разделяются на аксиальные и периферические в зависимости от преобладающих симптомов. Диагноз аксиальной спондилоартропатии (АС) основан на данных МРТ или рентгенологических признаках сакроилеита, ассоциированных с клиническими симптомами боли в нижних отделах спины. Рентгенологические признаки сакроилеита распространены при ЯК и БК и составляют 20–50%, но прогрессирующий анкилозирующий спондилит с синдесмофитами отмечается только у 1–10% пациентов.
 Периферические артриты при ВЗК являются воспалительными артропатиями, но, в отличие от псориатического артрита и других воспалительных артропатий, эти поражения носят неэрозивный характер. На основании анамнеза и вовлечения суставов в патологический процесс эмпирически были определены два разных типа ВЗК-ассоциированных периферических артропатий. Тип 1 определяется при наличии боли в суставах с признаками отека или наличием выпота, с поражением менее 5 суставов, главным образом крупных опорных суставов нижних конечностей. Симптомы, как правило, возникают остро и длятся менее 10 нед без стойкого поражения суставов и обычно коррелируют с обострением ВЗК. При типе 2 поражаются более 5 суставов преимущественно верхних конечностей с симметричным поражением. Симптомы могут сохраняться в течение нескольких месяцев и лет, независимо от активности ВЗК. Диагноз устанавливается на основании клинических данных по характерным признакам воспаления и при исключении других специфических форм артрита. Лучевые методы исследования позволяют исключить деформацию сустава в связи с остеоартритом, ревматоидным артритом и системными заболеваниями соединительной ткани. ВЗК-ассоциированный периферический артрит необходимо дифференцировать от артралгии, связанной с отменой кортикостероидов, остеонекроза вследствие приема кортикостероидов, волчаночноподобного синдрома, ассоциированного с применением инфликсимаба. При ВЗК могут отмечаться энтезопатии и дактилиты (опухание пальцев рук или ног). Последний характерен для спондилоартрита и встречается в 2–4% случаев.
Периферические артриты при ВЗК являются воспалительными артропатиями, но, в отличие от псориатического артрита и других воспалительных артропатий, эти поражения носят неэрозивный характер. На основании анамнеза и вовлечения суставов в патологический процесс эмпирически были определены два разных типа ВЗК-ассоциированных периферических артропатий. Тип 1 определяется при наличии боли в суставах с признаками отека или наличием выпота, с поражением менее 5 суставов, главным образом крупных опорных суставов нижних конечностей. Симптомы, как правило, возникают остро и длятся менее 10 нед без стойкого поражения суставов и обычно коррелируют с обострением ВЗК. При типе 2 поражаются более 5 суставов преимущественно верхних конечностей с симметричным поражением. Симптомы могут сохраняться в течение нескольких месяцев и лет, независимо от активности ВЗК. Диагноз устанавливается на основании клинических данных по характерным признакам воспаления и при исключении других специфических форм артрита. Лучевые методы исследования позволяют исключить деформацию сустава в связи с остеоартритом, ревматоидным артритом и системными заболеваниями соединительной ткани. ВЗК-ассоциированный периферический артрит необходимо дифференцировать от артралгии, связанной с отменой кортикостероидов, остеонекроза вследствие приема кортикостероидов, волчаночноподобного синдрома, ассоциированного с применением инфликсимаба. При ВЗК могут отмечаться энтезопатии и дактилиты (опухание пальцев рук или ног). Последний характерен для спондилоартрита и встречается в 2–4% случаев.
Периферический артрит при ВЗК обычно асимметричный и олигоартикулярный, встречается у 5–20% больных, чаще при БК, особенно при колите Крона. В целом прогноз благоприятный, эрозивный характер поражения и хроническое течение отмечены лишь у небольшого количества пациентов. При поражении осевого скелета прогноз менее благоприятный, что связано с течением АС, а не с ВЗК. Классическая АС является прогрессирующим состоянием со структурными поражениями и нарушением движения, влияющими на качество жизни. Важно выявить АС на раннем этапе, чтобы предотвратить ее прогрессирование и возникновение изменений, выявляемых рентгенологически, которые наблюдаются в 10–20% случаев в течение 2 лет у пациентов с повышенным С-реактивным белком или активным воспалением по данным МРТ [20–23].
Терапия пациентов с осевой АС должна проводиться с участием ревматологов. Эффективными методами лечения являются применение физиотерапевтических процедур и короткие курсы нестероидных противовоспалительных средств (НПВС), но длительное применение НПВС не рекомендовано. Для лечения периферического артрита достаточной является терапия ВЗК, хотя короткие курсы НПВС или местное введение стероидов приводит к облегчению симптомов. Пероральные кортикостероиды эффективны коротким курсом и должны быть отменены при возможности. Сульфасалазин и метотрексат могут играть положительную роль при персистирующем артрите [24], терапия, направленная на подавление фактора некроза опухоли альфа (ФНО-α), является эффективной в резистентных случаях [25].
Нарушение минеральной плотности костной ткани и остеопороз отмечаются у больных ВЗК мужского и женского пола в 20–50% случаев. Диагноз остеопороза у взрослых устанавливается при значении Т-критерия менее 2,5 по данным радиографической денситометрии костной ткани. Остеопороз является фактором риска переломов и показанием, при котором пациенты должны получать лечение. Наряду с лечением активного ВЗК у женщин в постменопаузе и у пациентов со спонтанными переломами в анамнезе регулярное применение бифосфонатов и другая терапия могут предотвратить дальнейшую потерю костной ткани [26].
Поражения кожи
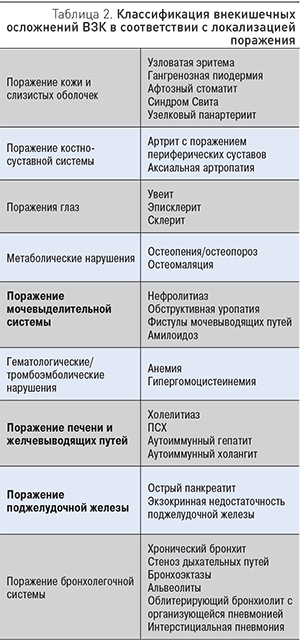
 Кожные проявления отмечаются у 2–34% больных ВЗК. Чаще всего они представлены узловатой эритемой и гангренозной пиодермией, которые определяются как реактивные (иммуноопосредованные) внекишечные проявления. Узловатая эритема (рис. 1) чаще поражает нижние конечности, однако описаны случаи локализации на туловище и верхних конечностях [6].
Кожные проявления отмечаются у 2–34% больных ВЗК. Чаще всего они представлены узловатой эритемой и гангренозной пиодермией, которые определяются как реактивные (иммуноопосредованные) внекишечные проявления. Узловатая эритема (рис. 1) чаще поражает нижние конечности, однако описаны случаи локализации на туловище и верхних конечностях [6].
Узловатая эритема диагностируется на основании клинических данных, в атипичных случаях может быть рекомендована биопсия кожи. Терапия обычно сводится к лечению обострения ВЗК, в тяжелых случаях требуются системные кортикостероиды. Рецидивирующие и резистентные формы поражения кожи можно лечить иммуномодуляторами или препаратами, ингибирующими ФНО-α.
Узловатая эритема, как правило, коррелирует с обострением ВЗК, но не всегда с тяжестью заболевания кишечника; чаще встречается у женщин и при БК по сравнению с ЯК [6]. Этиология ее неизвестна, однако имеются указания на тесную связь с определенными HLA-локусами 6 хромосомы (HLA-В). Патогенез заболевания до конца не ясен. Предполагают, что узловатая эритема может быть проявлением реакции гиперчувствительности IV типа, т.к. практически у 40% больных могут быть идентифицированы триггеры [27].
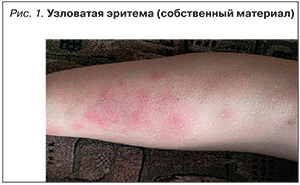
 Гангренозная пиодермия (рис. 2) встречается у 1–10% больных и чаще при ЯК, чем при БК. Гангренозная пиодермия может возникать на любом участке тела, включая гениталии, но чаще всего поражает голени.
Гангренозная пиодермия (рис. 2) встречается у 1–10% больных и чаще при ЯК, чем при БК. Гангренозная пиодермия может возникать на любом участке тела, включая гениталии, но чаще всего поражает голени.
Патофизиология неизвестна, но считается, что при гангренозной пиодермии отмечаются патологическая функция нейтрофилов и нарушение клеточного иммунитета [28]. Изменения кожи часто возникают после травмы [29]. Гангренозная пиодермия может протекать параллельно обострению ВЗК или возникать независимо, имеет тенденцию к рецидивированию после успешного лечения более чем в 25% случаев, часто в том же самом месте. Лечение включает применение системных кортикостероидов, инфликсимаба или адалимумаба, а также топические или пероральные ингибиторы кальциневрина [30, 31].
Синдром Свита относится к острым нейтрофильным дерматозам, включающим гангренозную пиодермию, но отличается от последней внешним видом, распространением и гистологическими проявлениями. Чаще встречается у женщин и у пациентов с поражением толстой кишки, а также при наличии других внекишечных проявлений [32].
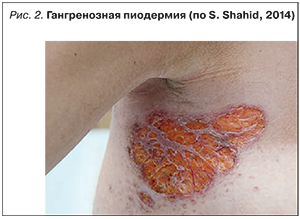
 Синдром Свита (рис. 3) характеризуется появлением плотных красных и болезненных воспалительных бляшек, узелков или папул, обычно поражающих верхние конечности, лицо или шею. Появление высыпаний часто сопровождается лихорадкой и лейкоцитозом в периферической крови и, как правило, ассоциировано с активностью заболевания кишечника. При гистологическом исследовании пораженных участков обнаруживается выраженная периваскулярная инфильтрация полиморфноядерными гранулоцитами без признаков васкулита.
Синдром Свита (рис. 3) характеризуется появлением плотных красных и болезненных воспалительных бляшек, узелков или папул, обычно поражающих верхние конечности, лицо или шею. Появление высыпаний часто сопровождается лихорадкой и лейкоцитозом в периферической крови и, как правило, ассоциировано с активностью заболевания кишечника. При гистологическом исследовании пораженных участков обнаруживается выраженная периваскулярная инфильтрация полиморфноядерными гранулоцитами без признаков васкулита.
В терапии синдрома Свита эффективны системные кортикостероиды, при резистентных или часто рецидивирующих случаях возможно применение иммуносупрессантов [33].
Анти-ФНО-индуцированные поражения кожи
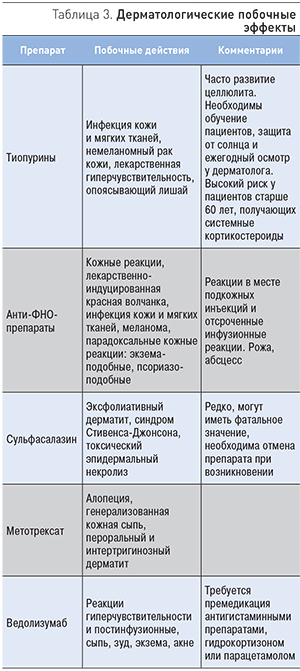
Иммуномодуляторы и анти-ФНО-препараты могут индуцировать побочные реакции со стороны кожи, такие как инфекции, злокачественные образования, аллергические реакции и парадоксальное воспаление (табл. 3).
Поражения глаз
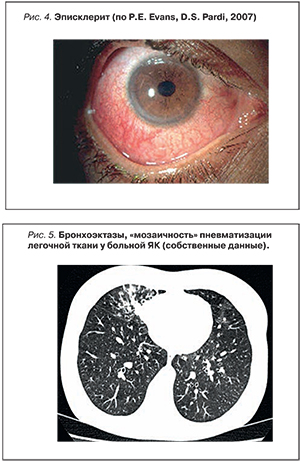
Частота офтальмологических поражений у больных ВЗК составляет 4–12%, по некоторым данным – достигает 29%. Воспалительные заболевания глаз (эписклерит, склерит, увеит) связаны с активацией и инфильтрацией клеток врожденной и адаптивной иммунных систем в тканях или внутриглазных структурах. В некоторых случаях это может быть связано со склеритом с фибриноидным некрозом и васкулитом. Генетические ассоциации, подтверждающие активацию врожденной иммунной системы при увеите, включают взаимосвязь с мутацией NOD2 и MHC класс I, полипептид-связанная последовательность A (MICA) [34].
Обычный эписклерит (рис. 4) не требует наблюдения у офтальмолога. Дифференциальная диагностика с увеитом и склеритом (рис. 5) основана на отсутствии выраженной боли в глазах, светобоязни, затуманенного зрения и ослабления зрения. В то время как эписклерит отражает активность ВЗК, увеит может протекать независимо от активности кишечных симптомов и других внекишечных проявлений и может предшествовать дебюту заболевания кишечника. Эписклерит может проходить самостоятельно. Для облегчения симптомов используют топические или системные НПВС или топические стероиды. Терапия склерита должна проводиться офтальмологом и включать топические или системные стероиды, при необходимости – иммуносупрессоры и анти-ФНО-препараты.
 Поражения печени и желчевыводящих путей
Поражения печени и желчевыводящих путей
У 30% больных ВЗК наблюдаются патологические изменения печеночных ферментов крови, при этом необходимо проводить дифференциальную диагностику между ПСХ, лекарственно-индуцированным поражением и другими заболеваниями печени, не связанными с ВЗК. Независимо от наличия клинических симптомов холестаза, в случае сохраняющихся необъяснимых изменений биохимических печеночных показателей, необходимо проведение магнитно-резонансной холангиографии (МРТ). При нормальных результатах МРТ у пациентов с ВЗК с подозрением на ПСХ необходимо проведение биопсии печени для диагностики ПСХ малых протоков.
ПСХ относится к наиболее распространенным внекишечным поражениям печени, встречается у 4–5% больных. ПСХ связан с 4-кратным повышением риска развития колоректальной неоплазии (дисплазия и рак) у пациентов с ВЗК как до, так и после трансплантации печени [35]. После подтверждения диагноза ПСХ у больных ВЗК обязательно проведение колоноскопии 1 раз в 1–2 года. При наличии признаков аутоиммунного гепатита (повышение трансаминаз, высокий уровень IgG, повышение аутоиммунных антител ANA, SMA, LKM) у больных ПСХ рекомендовано проведение пункционной биопсии печени. Необходимо учитывать наличие IgG4-ассоциированного склерозирующего холангита при повышении IgG4 и/или соотношения IgG4/IgG.
При ПСХ не существует доказательной терапии, которая могла бы отсрочить трансплантацию печени, развитие холангиокарциномы или летального исхода. Хотя препараты урсодеоксихолевой кислоты в дозе 15–20 мг/кг улучшают показатели холестаза, необходимо избегать назначения высоких доз препарата. У пациентов с признаками аутоиммунного гепатита следует рассмотреть возможность назначения кортикостероидов и/или иммуносупрессоров.
Помимо ПСХ, у пациентов ВЗК могут развиться неалкогольная жировая болезнь печени (НАЖБП), лекарственно-индуцированное поражение печени, тромбоз портальной и печеночной вен, абсцесс печени, амилоидоз печени и гранулематозный гепатит. Частота НАЖБП составляет 1,5–55% у больных ЯК и 1,5–39,5% у больных БК. К факторам риска развития НАЖБП относятся метаболический синдром и такие ВЗК-ассоциированные факторы, как интраабдоминальные абсцессы, свищевая форма заболевания, тяжесть поражения толстой кишки, нутриционная недостаточность, дефицит белка и некоторые препараты (метотрексат, кортикостероиды).
 Лекарственно-индуцированные поражения печени встречаются у больных ВЗК, поэтому лабораторный мониторинг необходимо проводить каждые 1–3 мес. Препараты 5-аминосалициловой кислоты (5-АСК) не так часто оказывают повреждающее действие на печень, однако имеют место случаи развития хронического гепатита. У 10% пациентов, принимающих метотрексат, отмечается повышение аминотрансфераз. Ожирение и употребление алкоголя являются дополнительными факторами риска развития лекарственно-индуцированного поражения печени у пациентов, получающих метотрексат. Гепатотоксичность азатиоприна и 6-меркаптопурина составляет, по разным данным, от 3 до 15%. У 81% пациентов, имеющих гепатотоксичные реакции при приеме азатиоприна, отмечается хорошая переносимость 6-меркаптопурина. Тиопурины (включая 6-тиогуанин) могут вызывать повреждение сосудистого эндотелия печени, приводя к развитию вено-окклюзионной болезни, пелиозу печени и узловой регенеративной гиперплазии. У пациентов с высоким уровнем гамма-глутамилтранспептидазы и тромбопенией необходимо проведение пункционной биопсии печени для исключения вышеуказанных состояний. Изредка азатиоприн и 6-меркаптопурин могут вызывать тяжелую холестатическую желтуху, которая сохраняется даже после отмены препарата. В литературе описаны несколько тяжелых случаев анти-ФНО-индуцированного аутоиммунного гепатита и холестатического поражения печени [36, 37]. Вторичный амилоидоз печени является редким осложнением ВЗК, частота его составляет до 0,9% при БК и до 0,07% при ЯК. Длительное активное воспаление кишечника может привести к отложению амилоида в сосудах и синусоидах печени. Специфической терапии амилоидоза в данном случает не существует, кроме лечения основного заболевания, хотя был отмечен прямой эффект анти-ФНО-терапии на содержание амилоида в крови [38]. Развитие гранулематозного гепатита при ВЗК может быть внекишечным проявлением БК или ассоциированным с приемом сульфасалазина и такими воспалительными заболеваниями, как первичный билиарный цирроз, саркоидоз, болезнь Вегенера, инфекция или лимфома [39]. Редким осложнением ВЗК является абсцесс печени.
Лекарственно-индуцированные поражения печени встречаются у больных ВЗК, поэтому лабораторный мониторинг необходимо проводить каждые 1–3 мес. Препараты 5-аминосалициловой кислоты (5-АСК) не так часто оказывают повреждающее действие на печень, однако имеют место случаи развития хронического гепатита. У 10% пациентов, принимающих метотрексат, отмечается повышение аминотрансфераз. Ожирение и употребление алкоголя являются дополнительными факторами риска развития лекарственно-индуцированного поражения печени у пациентов, получающих метотрексат. Гепатотоксичность азатиоприна и 6-меркаптопурина составляет, по разным данным, от 3 до 15%. У 81% пациентов, имеющих гепатотоксичные реакции при приеме азатиоприна, отмечается хорошая переносимость 6-меркаптопурина. Тиопурины (включая 6-тиогуанин) могут вызывать повреждение сосудистого эндотелия печени, приводя к развитию вено-окклюзионной болезни, пелиозу печени и узловой регенеративной гиперплазии. У пациентов с высоким уровнем гамма-глутамилтранспептидазы и тромбопенией необходимо проведение пункционной биопсии печени для исключения вышеуказанных состояний. Изредка азатиоприн и 6-меркаптопурин могут вызывать тяжелую холестатическую желтуху, которая сохраняется даже после отмены препарата. В литературе описаны несколько тяжелых случаев анти-ФНО-индуцированного аутоиммунного гепатита и холестатического поражения печени [36, 37]. Вторичный амилоидоз печени является редким осложнением ВЗК, частота его составляет до 0,9% при БК и до 0,07% при ЯК. Длительное активное воспаление кишечника может привести к отложению амилоида в сосудах и синусоидах печени. Специфической терапии амилоидоза в данном случает не существует, кроме лечения основного заболевания, хотя был отмечен прямой эффект анти-ФНО-терапии на содержание амилоида в крови [38]. Развитие гранулематозного гепатита при ВЗК может быть внекишечным проявлением БК или ассоциированным с приемом сульфасалазина и такими воспалительными заболеваниями, как первичный билиарный цирроз, саркоидоз, болезнь Вегенера, инфекция или лимфома [39]. Редким осложнением ВЗК является абсцесс печени.
Поражения поджелудочной железы
Больные ВЗК имеют повышенный риск развития острого панкреатита (ОП) и экзокринной недостаточности поджелудочной железы. При ВЗК могут возникать две формы ОП. В первом случае острое воспаление связано с общими патогенетическими путями, например, аутоиммунным панкреатитом, идиопатическим панкреатитом, гранулематозным панкреатитом и панкреатитом, ассоциированным с ПСХ. Во втором случае ОП может возникнуть в результате терапии ВЗК или вследствие ассоциированных состояний, например, билиарного панкреатита, лекарственно-индуцированного панкреатита, панкреатита при БК с поражением двенадцатиперстной кишки, панкреатита после проведения эндоскопической ретроградной холангиопанкреатографии или энтероскопии [40]. Отмена препарата приводит к быстрому разрешению симптомов. Данный побочный эффект может ограничить терапевтические возможности для дальнейшего ведения пациентов. Хронический панкреатит при ВЗК морфологически характеризуется наличием патологии панкреатического протока, иногда с образованием псевдокист, и в большинстве случаев отсутствием кальцинатов в паренхиме поджелудочной железы.
Поражения нервной системы
Распространенность неврологических поражений при ВЗК, по данным отчетов различных центров, составляет от 3 до 39%, однако эти данные малочисленны в связи с небольшим размером выборки и погрешностями в проводимых исследованиях. Периферическая нейропатия является редким проявлением, ассоциированным с ВЗК. Возможными причинами могут быть дефицит микроэлементов и витаминов, прием препаратов, например, метронидазола. У пациентов с ВЗК поражения центральной нервной системы отмечаются чаще, чем в общей популяции. Развитие этих проявлений связывают с тромбозом венозных синусов, острым нарушением мозгового кровообращения и центральной демиелинизацией [41]. Демиелинизация может усугубляться при лечении анти-ФНО-препаратами и является противопоказанием для начала анти-ФНО терапии [42].
Поражения сердечно-сосудистой системы
У больных ВЗК повышен риск развития ишемической болезни сердца, цереброваскулярных осложнений и мезентериальной ишемии, особенно у женщин. К развитию атеросклероза и патологии коронарных сосудов предрасполагает системное воспаление, что было доказано на примере ревматоидного артрита и ВЗК [43, 44]. В крупном мета-анализе смертности от сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний у больных ВЗК с участием 63 983 пациентов не было доказано повышения смертности в сравнении с общей популяцией [45]. Однако в популяционных исследованиях, проведенных в Дании и Финляндии, было показано, что смертность от сердечно-сосудистых осложнений выше у больных ВЗК в период активности заболевания в сравнении с общей популяцией [46]. Гипергомоцистеинемия, известный фактор риска артериального и венозного тромбоза, в 4 раза чаще встречается у больных ВЗК, чем в общей популяции [47]. Более того, состояние гиперкоагуляции, связанное с системным воспалением, содействует раннему атеросклерозу и поэтому повышает риск артериальных тромботических явлений [48].
Поражения бронхолегочной системы
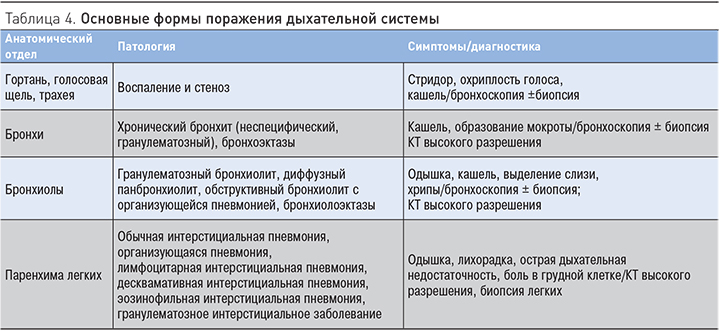
Дыхательная и пищеварительная системы в силу эмбрионального родства имеют общие компоненты иммунной системы слизистых оболочек [49]. Cледовательно, дефекты иммунных систем эпителия и слизистых оболочек, ассоциированные с ВЗК, могут затрагивать различные отделы респираторной системы. Перенос иммунных клеток из участков воспаления кишечника на периферические и затем внекишечные поверхности слизистых оболочек может быть причиной воспаления в респираторной системе. Благодаря широкому внедрению компьютерной томографии высокого разрешения в область диагностики респираторной патологии у больных ВЗК установлено, что бронхолегочные проявления при ЯК и БК включают множество различных заболеваний, затрагивающих разные отделы бронхиального дерева, легочную паренхиму и плевру. Использование функциональных методов исследования позволило установить субклиническое вовлечение респираторной системы у больных ВЗК, не имеющих респираторных симптомов и отклонений при рентгенологическом исследовании легких. По данным различных авторов и нашим собственным данным [50], нарушение функции внешнего дыхания выявляется почти у половины больных ВЗК с преимущественной обструктивной патологией на уровне мелких бронхов. Формирование бронхоэктазов отмечено многими исследователями как наиболее частая патология при ВЗК. В табл. 4 отражены основные варианты поражения респираторной системы.
Интерстициальная пневмония, связанная с ВЗК, была описана как самая распространенная форма пневмонии. Помимо ВЗК-ассоциированных бронхолегочных осложнений, приведенных в таблице, поражение паренхимы легких могут вызывать инфекционные возбудители или лекарственные препараты (салицилаты, метотрексат, тиопурины, анти-ФНО-средства). Лекарственно-индуцированные поражения легких у больных ВЗК неоднократно упоминались в литературе и были связаны чаще с приемом препаратов 5-АСК или метотрексата. Салицилаты (сульфасалазин, месалазин, 5-АСК) вызывают различные типы интерстициального поражения легких [51]. Почти в половине случаев в анализе крови выявляют эозинофилию. В большинстве случаев месалазин- или сульфасалазин-индуцированные поражения легких возникают при системном применении препаратов, однако имеется сообщение об эозинофильной пневмонии, развившейся у больной ЯК при использовании суппозиториев с месалазином [51].
Метотрексат может вызывать тяжелый пневмонит или фиброз легких. У пациентов, получающих терапию препаратами анти-ФНО, были зафиксированы случаи гранулематозного воспаления, схожего с саркоидозом [52]. Это парадоксальное воспаление можно купировать отменой препаратов анти-ФНО и/или назначением кортикостероидов. Дифференциальная диагностика ВЗК-ассоциированных, лекарственно-обусловленных и инфекционных поражений легких чрезвычайно важна, т.к. требует различных подходов к лечению.
Поражения мочеполовой системы
Распространенность почечной недостаточности достигает 15% у больных с БК или ЯК. Пациенты с ВЗК, особенно с БК, предрасположены к развитию камней в почках, состоящих из солей мочевой кислоты или оксалатов кальция. Вторичный амилоидоз (АА тип) – редкое, но тяжелое осложнение ВЗК. Пациенты с повышенным риском развития амилоидоза – это мужчины с БК в форме илеоколита и/или перианальной формой. Имеются сообщения о случаях тубулоинтерстициального нефрита, включая гранулематозный интерстициальный нефрит, в качестве внекишечного проявления ВЗК. Сульфасалазин и 5-АСК могут вызывать токсическое поражение почек (гломерулонефрит, нефротический синдром и интерстициальный нефрит). Салицилаты могут вызывать острый или хронический интерстициальный нефрит независимо от принимаемой дозы [53]. Циклоспорин может приводить к острой почечной недостаточности вследствие констрикции приносящих артериол, вызывая снижение кровоснабжения почек и скорости клубочковой фильтрации [54]. Необходимо проводить мониторинг лабораторных показателей с целью раннего выявления токсического влияния препаратов. Отмена препарата приводит к регрессу изменений.
Коагулопатия
У пациентов с ВЗК риск ВТЭ по меньшей мере в два раза выше, чем в общей популяции. Самыми распространенными формами ВТЭ являются тромбоз глубоких вен и эмболия легочной артерии. ВТЭ связана с активностью заболевания. Хотя риск ВТЭ выше во время госпитализации, частые тромбозы отмечаются у амбулаторных пациентов, входящих в группу высокого риска (недавняя госпитализация или оперативное лечение, активное заболевание). ВТЭ у пациентов ВЗК распространена вследствие взаимодействия приобретенных и наследственных факторов. Установленные наследственные факторы риска ВТЭ отмечаются с одинаковой частотой у пациентов с ВЗК и в общей популяции [55]. Самыми значимыми приобретенными факторами риска ВТЭ являются активность заболевания (относительная частота во время обострения заболевания в сравнении с ремиссией составляет 4,5), госпитализации (повышают риск в 6 раз по сравнению с амбулаторными пациентами), поражение толстой кишки и недавнее оперативное вмешательство (распространенность после операции составляет 2,3%). К факторам риска также относят фистулизирующий или стенозирующий типы ВЗК, длительную иммобилизацию, постановку центрального венозного катетера, применение кортикостероидов, оральных контрацептивов, курение. Гипергомоцистеинемия – потенциальный фактор ВТЭ, может быть вторичной вследствие дефицита витамина В12 и фолатов, который наблюдается у некоторых пациентов ВЗК [55]. Всем пациентам с ВЗК необходимо проведение профилактических мероприятий, особенно при госпитализации в стационар, также следует рассматривать необходимость профилактики ВТЭ после недавно перенесенного оперативного вмешательства и госпитализации, у амбулаторных пациентов с высокой активностью заболевания кишечника.
Лечение ВТЭ у пациентов с ВЗК должно проводиться согласно тем же протоколам, что и у пациентов, не страдающих ВЗК. Хотя первой линией терапии чаще всего является низкомолекулярный гепарин, допустимо применение низкодозированного нефракционированного гепарина или фондапаринукса. Длительное лечение может включать антагонисты витамина К (аценокумарол, варфарин, флуидион, фенпрокумон) или новые пероральные антикоагулянты (дабигатран, ривароксабан, апиксабан и эдоксабан). Данные об использовании этих препаратов при ВЗК отсутствуют [56]. Длительность лечения зависит от соблюдения баланса между риском рецидива (анамнез, факторы риска) и риском кровотечения, которое может быть индуцировано этой терапией. Важно помнить, что тиопурины могут снижать эффект варфарина [55]. Длительная антикоагулянтная терапия может обсуждаться у пациентов ВЗК, которые имели эпизод венозного тромбоза во время клинической ремиссии ВЗК при отсутствии провоцирующих факторов.
БИОЛОГИЧЕСКАЯ ТЕРАПИЯ ПРИ ВНЕКИШЕЧНЫХ ПРОЯВЛЕНИЯХ ВЗК
Несмотря на частые внекишечные осложнения ВЗК, данные по их лечению малочисленны и ограничиваются в основном описанием конкретных клинических случаев. Лечение внекишечных проявлений должно проводиться с учетом течения ВЗК и включать мультидисциплинарный подход. В патогенезе поражения кишечника и других органов при ВЗК важную роль играет ФНО-α-зависимый механизм, поэтому можно предположить, что антитела к ФНО имеют благоприятный эффект в терапии ВЗК и ВЗК-ассоциированных внекишечных проявлений. Существенная доказательная база в пользу применения инфликсимаба и адалимумаба при лечении ВЗК и внекишечных проявлений подтверждает обоснованность применения ингибиторов ФНО-α в клинической практике. Доказано, что внедрение нейтрализующих ФНО-α антител в клиническую практику является самым значимым достижением в лечении пациентов с ВЗК; инфликсимаб и адалимумаб быстро вошли в схему лечения как основного заболевания, так и внекишечных проявлений ВЗК. Эффективность применения других таргетных биологических агентов, например, моноклональных антител к белку интегрин α4β7 (ведолизумаб) и их положительное воздействие на исход заболевания требуют дальнейшего изучения.
Тщательное выявление и своевременная диагностика и лечение внекишечных проявлений необходимы для предотвращения инвалидизации пациентов ВЗК. Улучшение диагностики и дифференциальной диагностики внекишечных проявлений, и, следовательно, как можно более раннее назначение адекватной терапии могут предупредить развитие тяжелых осложнений и повысить качество жизни больных в целом. Лечение внекишечных проявлений должно проводиться с учетом течения ВЗК и включать мультидисциплинарный подход. Для реализации данной цели необходимо тесное сотрудничество врачей различных специальностей, которые в своей повседневной практике могут сталкиваться с подобными больными. Необходимы дальнейшие исследования по оценке прогностических маркеров и предикторов развития внекишечных проявлений ВЗК, а также влияния различных методов терапии на их течение.



