Таурин (2-аминоэтансульфоновая кислота) представляет собой конечный продукт обмена аминокислот, содержащих серу (метионина, цистеина, гомоцистеина, цистина). Главную роль в синтезе таурина у животных играет фермент цистеинсульфинат-декарбоксилаза, однако его активность у человека ограничена. Источником таурина служит животная пища, морепродукты [1, 54]. В тканях млекопитающих таурин является важным природным компонентом – это наиболее распространенная свободная аминокислота в сердце, сетчатке, скелетных мышцах, головном мозге и лейкоцитах [51].
Есть огромное количество данных, которые раскрывают большой потенциал таурина в качестве лекарственного средства.
Множество исследований доказывает значение таурина в защите нервных клеток [9].
Поскольку таурин мал и мобилен, он не может быть химически «меченным»; его визуализируют с помощью обычных методов иммуногистохимии. При объединении многочисленных косвенных измерений стало известно, что таурин играет важную роль в функционировании мозга у здорового и больного человека, а также может выступать в качестве нейроосмолита, нейромодулятора и, возможно, нейропередатчика. Нейрохимические функции таурина будут существенно лучше прояснены за счет прямого метода визуализации изменений, связанных с физиологическими и патологическими процессами в головном мозге, в местах локальной концентрации таурина вблизи клеточного пространственного разрешения в естественных условиях или на месте в срезах ткани. Таким образом, разработан химически специфический рентгеновский флуоресцентный томограф (XFI) для визуализации сульфонатной группы таурина на срезе тканей. Насколько известно, с его помощью получено первое неискаженное изображение распределения таурина в головном мозге при разрешении 20 мкм. С помощью визуализации содержания таурина в мозжечке и гиппокампе головного мозга крыс было установлено, что потери таурина в уязвимом секторе гиппокампа СА1 (Cornus ammonis 1) после ишемии могут быть ключевым фактором в замедленной нейродегенерации после мозгового ишемического инсульта [13].
НЕЙРОПРОТЕКТОРНОЕ ДЕЙСТВИЕ ТАУРИНА
Таурин обладает эффективным нейропротекторным действием после церебрального гипоксическо-ишемического повреждения у новорожденных крыс [59].
Давно доказано, что таурин – мощный защитник от индуцированных глутаматом повреждений нейронов при инсульте. Нейропротекция может быть результатом нескольких механизмов. Многие авторы предполагают, что НАДФH-оксидаза (NOX), основной источник супероксида, индуцированного активацией рецепторов N-метил-D-аспартат (NMDA), участвует в процессе окислительного стресса. Обнаружено, что N-метил-D-аспартат-индуцированный окислительный стресс за счет увеличения уровня реактивной формы кислорода способствовал гибели клеток в пробирке. Культуры нейронов, приготовленные с добавлением таурина, показали более низкий процент клеточной смерти, также снизился уровень реактивной формы кислорода. Более того, таурин ослабил экспрессию белков NOX 4/NOX 2 и их ферментативную активность, а также снизил внутриклеточную интенсивность кальция во время NMDA-индуцированной травмы нейронов. Кроме того, таурин также показал нейропротекторное действие, заключающееся в угнетении NOX, против H2O2-индуцированного повреждения. Таким образом, авторы предполагают, что защитный эффект таурина против активных форм кислорода во время NMDA-индуцированной травмы нейронов связан с угнетением NOX (вероятно, кальций-зависимым образом) [16].
После анализа вышеуказанных нейропротекторных свойств таурина было бы правильно предположить его пользу при лечении последствий черепно-мозговой травмы (ЧМТ). Для оценки этой пользы была создана модель ЧМТ для крыс с помощью устройства ударного действия жидкости. Таурин (200 мг/кг) вводили путем внутривенной инъекции 1 раз в день в течение 7 дней после перенесенной травмы. Было установлено, что с помощью таурина было улучшено мозговое кровообращение как в левом, так и в правом полушариях через 30 мин, а затем и через 7 дней после травмы. Неврологическое повреждение было предотвращено через 7 дней после начала введения таурина. При этом митохондриальные цепные комплексы транспорта электронов I и II показали большую активность. Улучшение с помощью таурина мозгового кровотока может снизить отек и предотвратить повышение внутричерепного давления. Важно отметить, что таурин устранил состояние гиперкоагуляции [51]. Следовательно, можно смело предполагать его регенераторную роль при ЧМТ [12, 51].
Сахарный диабет (СД) часто выступает одной из основных причин когнитивных нарушений, ухудшения памяти и нейродегенеративных повреждений. Таурин может снижать нейрональный апоптоз и гибель клеток глии при СД, а также у животных, не страдающих вышеуказанным заболеванием. Результаты исследований показали, что животные, которые получали таурин, показали более высокую производительность в поведении и памяти, а обогащенная среда оказывает положительное воздействие, особенно у не страдающих диабетом животных. Исходя из этих данных, таурин может иметь важный нейростимулирующий и нейропротекторный эффект [38].
Известно, что последствия наркоза часто связаны с расстройством когнитивных функций. Изофлуран, широко используемый ингаляционный анестетик, может вызвать нейрокогнитивный дефицит, особенно у пожилых пациентов после операции. Недавние исследования показали, что изофлуран вызывает стресс эндоплазматического ретикулума (ER) и последующий апоптоз нейронов головного мозга, что способствует когнитивным расстройствам. Предварительное лечение таурином предотвращает когнитивные нарушения, вызванные изофлураном путем ингибирования ER стресс-опосредованной активации апоптоза в гиппокампе на модели старых крыс [57].
Исследование концентрации таурина в организме имеет перспективу в контексте изучения некоторых заболеваний. К примеру, при помощи магнитно-резонансной спектроскопии (МРС) было установлено повышение уровня таурина, холина и глутамат, и уменьшение N-ацетиласпартата у 2-летней девочки с фебрильными судорогами и левым блефароптозом. Биопсия мозга подтвердила диагноз ювенильной ксантогранулемы. Следовательно, при повышенной концентрации таурина и глутамата при МР-спектроскопии следует учитывать наличие ксантогранулемы [33].
Вышеуказанные данные подтверждают нейропротекторные свойства таурина.
ВЛИЯНИЕ ТАУРИНА НА СЕРДЕЧНО-СОСУДИСТУЮ СИСТЕМУ
Таурин – наиболее распространенная серосодержащая аминокислота, хорошо известная в качестве средства улучшения метаболического статуса у животных [8, 50]. Ряд исследований доказывают, что таурин оказывает эффективное действие против метаболического синдрома, которое заключается в следующем:
- восстановлении уровня триглицеридов для предотвращения ожирения;
- снижении резистентности к инсулину, регулирующему метаболизм глюкозы;
- снижении уровня холестерина (особенно снижении уровня липопротеинов очень низкой плотности + липопротеинов низкой плотности и повышение уровня липопротеинов высокой плотности).
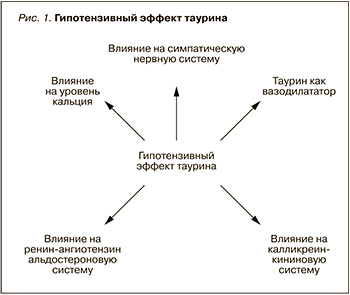 Немаловажна роль таурина и в регуляции сердечно-сосудистой системы (рис. 1), который складывается из следующих аспектов:
Немаловажна роль таурина и в регуляции сердечно-сосудистой системы (рис. 1), который складывается из следующих аспектов:
- влияния на ренин-ангиотензин-альдостероновую систему (РААС). Множество исследований подтверждают роль таурина в регуляции РААС [28, 42, 43]. Таурин ингибирует повышение артериального давления (АД), вызванное сбоем активности ренин-РААС, а также сводит к минимуму повышение в сыворотке крови уровня цитокинов, эндотелина, нейропептида Y и тромбоксана В2 [20]. Таурин может предотвратить увеличение систолического АД, вызванное введением нандролона деканоата [41];
- влияния на калликреин-кининовую систему [21];
- влияния на симпатическую нервную систему. Тауриновые добавки были наиболее чувствительны к ганглионарной блокаде и центральному адренергическому торможению, в то время как тауриновое истощение более чувствительно к центральному и периферическому адренергическому торможению. Авторы утверждают, что перинатальный дисбаланс таурина может привести к аномальным вегетативным реакциям нервной системы у взрослых самцов крыс [25]. Таурин понижает кровяное давление непосредственно через подавление высвобождения нор-адреналина из периферической симпатической нервной системы [15][34];
- вазодилатирующего действия. В рандомизированном двойном слепом плацебо-контролируемом исследовании было оценено влияние таурина на метаболические показатели, такие как уровень АД, толщина интима-медиа сонной артерии, лодыжечно-плечевой индекс (ЛПИ), индекс массы тела (ИМТ) и биохимические показатели у людей с прегипертензивным статусом. В исследовании приняли участие 120 пациентов, которые принимали таурин в дозе 1,6 г/ сут и плацебо в течение 12 нед. Таурин значительно снизил клинику высокого нормального АД при 24-часовом мониторировании АД. Кроме того, добавки с таурином значительно улучшили эндотелий-зависимую и эндотелий-независимую вазодилатацию; также наблюдалось снижение толщины интима-медиа сонной артерии у прегипертезивных участников. В то же время применение таурина повлекло за собой увеличение в плазме уровня H2S и концентрации таурина [50];
- влияния на уровень Ca2+. Давно доказано, что кофеин обладает психоактивными свойствами, увеличивает бодрость, энергию и способность к концентрации. Сочетание кофеина и таурина может повышать плазменный уровень кальция и снижать уровень С-реактивного белка в плазме. Кроме того, таурин при сочетании с нифедипином проявляет синергизм в отношении снижения в плазме крови уровней Са2+ и С-реактивного белка.
Следовательно, таурин может служить дополнением в лечении артериальной гипертензии [36].
Многие современные изопропиламидные производные таурина (тауритман, таурепар) могут быть использованы в качестве кардиотропных препаратов для лечения хронической сердечной недостаточности (ХСН), стабильной стенокардии, хронической ИБС и других заболеваний сердечно-сосудистой системы [2]. Таурин может выступать в качестве препарата для лечения ХСН вследствие антагонизма к катехоламинам и ангиотензину II [22]. Диетическое употребление таурина и магния значительно увеличивает число эндотелиальных клеток-предшественников и снижает уровни свободных радикалов и реактивного вещества тиобарбитуровой кислоты и у здоровых мужчин. Сравнительный анализ показал, что таурин и магний снижают риск заболеваний сердечно-сосудистой системы [24].
Сердечный канал IKs (основной ток реполяризации в сердце) быстро и энергично реагирует на стимуляцию симпатической нервной системы, чтобы обеспечить достаточное количество времени для диастолы в виде сопровождающих ускоренную частоту сердечных сокращений. В кардиомиоцитах канал IKs представляет собой макромолекулярный комплекс, состоящий из α- (Kcnq1) субъединицы и модуляторной β- (KCNE1) субъединицы, а также межклеточных белков, критических для контроля состояния фосфорилирования комплекса [23]. Есть предположение, что несколько синдромов длительного интервала QT, связанных с мутацией каналов IKs, приводят к сдвигу зависимости напряжения канала и ускоряют его закрытие. Аналог жирной кислоты N-арахидоноил таурин восстанавливает различные мутантные каналы даже при том, что мутации в разных доменах канала IKs происходят при помощи различных молекулярных механизмов. Поэтому N-арахидоноил таурин является интересным соединением, которое может подтолкнуть развитие будущих активаторов каналов IKs для лечения синдрома длительного интервала QT, вызванного различными мутациями канала IKs [29].
ТАУРИН И УГЛЕВОДНЫЙ ОБМЕН
Ранее мы затронули связь таурина и СД. Рассмотрим подробнее роль таурина в регуляции уровня глюкозы в крови.
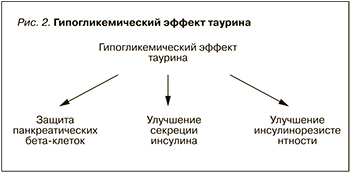 Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание, – это доказанные протекторные свойства таурина в отношении панкреатических бета-клеток (рис. 2). При лабораторном исследовании на мышах было установлено, что таурин регулирует морфофизиологию β-, α- и δ-клеток и гомеостаз глюкозы при нормальных и диабетических условиях. Авторы утверждают, что таурин может быть потенциальным терапевтическим средством для сохранения эндокринной функции поджелудочной железы при ожирении и СД [45]. Тауриновые добавки улучшают функцию островковых клеток у особей и без диабетического ожирения, причем без изменения эндокринной морфометрии поджелудочной железы. Вышеуказанный эффект может быть связан с защитным эффектом таурина при цитокин-индуцированных островковых дисфункциях, а также улучшением экспрессии белка протеинкиназы B и сигнального пути ERK [39].
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание, – это доказанные протекторные свойства таурина в отношении панкреатических бета-клеток (рис. 2). При лабораторном исследовании на мышах было установлено, что таурин регулирует морфофизиологию β-, α- и δ-клеток и гомеостаз глюкозы при нормальных и диабетических условиях. Авторы утверждают, что таурин может быть потенциальным терапевтическим средством для сохранения эндокринной функции поджелудочной железы при ожирении и СД [45]. Тауриновые добавки улучшают функцию островковых клеток у особей и без диабетического ожирения, причем без изменения эндокринной морфометрии поджелудочной железы. Вышеуказанный эффект может быть связан с защитным эффектом таурина при цитокин-индуцированных островковых дисфункциях, а также улучшением экспрессии белка протеинкиназы B и сигнального пути ERK [39].
Второе – это способность таурина индуцировать синтез инсулина. Он улучшает секрецию этого вещества в ответ на поступление питательных веществ и деполяризующих агентов. Таурин усиливает секреторную способность островков поджелудочной железы за счет улучшения экспрессии белка и ингибирования АТФ-чувствительных калиевых каналов, а также повышения содержания синтаксина 1 (Synt-1) [48].
Есть данные, свидетельствующие о том, что тауроурсодеоксихолевая кислота (TUDCA) потенцирует синтез инсулина из панкреатических бета-клеток через путь цАМФ/PKA (протеинкиназа А) [49]. TUDCA представляет собой тауриновый конъюгат урсодезоксихолевой кислоты (УДХК). Она также является гидрофильной желчной кислотой для лечения некоторых холестатических заболеваний печени. Несколько исследований показали, что TUDCA служит антиапоптическим агентом для ряда нейродегенеративных заболеваний, в том числе бокового амиотрофического склероза, болезни Альцгеймера, болезни Паркинсона и болезни Хантингтона. Кроме того, TUDCA играет важную роль в защите от гибели клеток при некоторых заболеваниях сетчатки, таких как пигментный ретинит. Все большее число доклинических и клинических исследований подчеркивают потенциальную пользу этой простой желчной кислоты, которая используется в китайской медицине на протяжении более чем 3000 лет [47].
Третье: таурин улучшает инсулинорезистентность. Нарушение обмена таурина тесно связано с ожирением, резистентностью к инсулину и СД. Для исследования его действия было задействовано 711 участников с избыточным весом или ожирением (возраст 30–70 лет; 60% женщин), которые имели генетическую предрасположенность к СД. Было обнаружено, что базовые уровни таурина в крови значительно модифицировали клинику СД при генетической предрасположенности, в частности вызывали изменения уровня глюкозы натощак, инсулина, показатели оценки инсулинорезистентности (HOMA-IR) в течение 2-летнего диетического вмешательства независимо от потери веса. Высокие базовые уровни таурина у участников с наименьшей генетической предрасположенностью к СД были связаны с меньшим снижением показателей уровня глюкозы и HOMA-IR, при этом более выраженное снижение уровня инсулина и HOMA-IR наблюдалось среди генетически предрасположенных лиц. Эти данные свидетельствуют о том, что уровень таурина в крови может дифференцированно модулировать действие генов, связанных с СД, для улучшения чувствительности к инсулину среди пациентов с избыточной массой тела [58].
Хроническая гипергликемия зачастую связана с нарушением тестикулярной функции. Было проведено исследование с целью изучить защитные эффекты и возможные механизмы действия таурина и пиоглитазона против диабет-индуцированной дисфункции яичек у крыс. Нормальные и диабетические крысы получали таурин
(100 мг/кг) или пиоглитазон (10 мг/кг) перораль-но – ежедневно в течение 6 нед. Таурин и пиоглитазон способствовали снижению уровня сахара в крови, провоспалительных цитокинов, а также увеличению уровня циркулирующего инсулина, тестостерона, ЛГ, ФСГ. Кроме того, оба средства значительно уменьшили перекисное окисление липидов и повреждение ДНК, одновременно увеличив активность антиоксидантных ферментов в семенниках крыс, страдающих СД. Также таурин и пиоглитазон оказывали защитное действие против диабета, вызванного повреждением яичек, путем ослабления гипергликемии, воспаления, окислительного стресса и повреждения ДНК [3].
Перинатальное истощение таурина с последующим высоким потреблением сахара влияет на ренин-ангиотензиновую систему и уровень глюкозы у взрослых самок крыс. Проведенные исследования указывают, что перинатальный дисбаланс таурина изменяет взаимодействие ренин-ангиотензиновой системы и эстрогена по регуляции глюкозы и инсулина у взрослых самок крыс [42].
ДРУГИЕ ЭФФЕКТЫ ТАУРИНА
Таурин выполняет важную функцию и в других существенных биологических процессах, таких как конъюгация желчных кислот, осморегуляция, стабилизация мембран клеток. Более того, ослабление апоптоза и его антиоксидантной активности имеет решающее значение для цитопротекторного эффекта таурина. Таурин достигает особенно больших концентраций в тканях, подвергающихся воздействию повышенных уровней окислителей. Это позволяет предположить, что он может играть важную роль в воспалительных процессах, связанных с окислительным стрессом. В самом деле в месте воспаления таурин реагирует с хлорноватистой кислотой, порожденной нейтрофильной миелопероксидазой (MPO). Эта реакция приводит к образованию менее токсичного таурина хлорамина (TauCl). TauCl и таурин бромамин (Tau-NHBr), продукт реакции таурина с бромноватистой кислотой (HBrO), оказывают антимикробное и противовоспалительное действие [10, 31]. Однако их роль в патогенезе воспалительных заболеваний не ясна. Есть предположение, что стимулирование эозинофилов может быть источником Tau-NHBr, а, как мы указывали ранее, таурин в изобилии присутствует в лейкоцитах [53].
Доказано, что пропионобактерии угрей, потенциальные возбудители акне, чрезвычайно чувствительны к таурин бромамину (Tau-NHBr). Поскольку актуальные антибиотики связаны с появлением устойчивых бактерий, Tau-NHBr может стать хорошим кандидатом для местной терапии угрей. В исследовании для сравнения эффекта Tau-NHBr был использован 1% гель клиндамицина как одно из наиболее распространенных средств местного лечения вульгарных угрей. Через 6 нед сопоставимые сокращения угревых поражений в группах исследования составили 65% у Tau-NHBr и 68% у клиндамицина соответственно. Поэтому Tau-NHBr может быть использован в качестве средства для местного лечении угрей, особенно у пациентов, у которых уже развилась устойчивость к антибиотикам [32].
Есть данные, свидетельствующие, что комбинация таурин + симвастатин может оказывать хорошее противовоспалительное действие [30].
Таурин доказал свою эффективность в защите печеночных и почечных клеток.
Существует множество лекарственных средств и токсических веществ, которые пагубно влияют на морфофункциональные свойства печени.
К препаратам, которые используются против воспалительных заболеваний, относится сульфасалазин. Однако его серьезными побочными эффектами являются поражения почек и печени. Таурин может служить потенциальным защитным средством с терапевтическими возможностями против побочных эффектов сульфасалазина [18].
Чрезмерное воздействие фторида негативно отражается на здоровье человека, в частности, на почках, которые выступают одними из основных органов, участвующих в его выведении из организма. Введение таурина значительно снизило фторид-опосредованное уменьшение абсолютного веса и соматического индекса почек у облученных крыс. Таурин в значительной степени предотвращал повышение в плазме фторид-индуцированных мочевины и креатинина, восстановил фторид-опосредованное снижение уровня трийодтиронина, тироксина и отношение трийодтиронина к тироксину. Кроме того, таурин смягчил фторид-опосредованное снижение почечного антиоксидантного статуса за счет значительного повышения антиоксидантной активности ферментов, а также уровня глутатиона. Наконец, таурин ингибировал фторид-индуцированное окислительное повреждение почек путем заметного снижения уровня перекиси водорода и малонового диальдегида, а также улучшил архитектуру почек у обработанных крыс. Соответственно таурин защищает организм от фторид-индуцированной почечной токсичности [4].
Таурин эффективно облегчает метимазол-индуцированное поражение печени [17].
Многие заболевания печени связаны с окислительным стрессом, воздействием эндотоксинов и инфекций. Это может привести к развитию хронического гепатита, цирроза и рака печени. S-адеметионин в сочетании с таурином и бетаином имеет функцию антиоксиданта и может выступать в качестве дополнения к противовоспалительному действию [27]. Комбинация S-адеметионина с таурином и/или бетаином обладает гепатопротекторным действием при этанол-индуцированном повреждении печени путем поддержания гомеостаза глутатиона [26].
Существует предположение, что твердые дисперсии таурина и цинка обладают гепатопротекторными свойствами за счет механизма, связанного с уменьшением фосфорилирования JNK1-киназ и сигнал-регулируемых киназ (ERK2), которые подавляют воспаление, апоптоз и пролиферацию холангиоцитов во время холестаза [52].
Таурин также уменьшает железо-индуцированный алкогольный фиброз печени путем снижения окислительного стресса, снижения выработки воспалительных и фиброгенных медиаторов и уменьшения активации звездчатых клеток [11].
Фиброз печени становится основной причиной повышенной заболеваемости и смертности у людей с шистосомой. Для оценки роли таурина в качестве профилактического лечения шистосомоза были использованы мыши, которые принимали его вместе с питьевой водой в течение 4 нед. Таурин значительно улучшил состояние печени, уменьшил сывороточные уровни аминотрансфераз и снизил ареал печеночной гранулемы, а также предотвратил прогрессирование фиброза. Кроме того, он способствовал снижению экспрессии трансформирующего фактора роста бета 1 (TGF-бета1), фактора некроза опухоли альфа (TNF-α), белка хемотаксиса моноцитов –α1, макрофагального воспалительного белка-1α [56].
Эпидуральный фиброз – общее осложнение после ламинэктомии. Лечение таурином заметно снижает ламинэктомия-индуцированный эпидуральный фиброз на моделях крыс. Тем не менее антифиброзный эффект таурина не зависел от трансформирующего ростового фактора бета (TGF-beta)/SMAD сигнального каскада, так как не было никаких изменений в экспрессии TGF-бета и его рецепторов. Кроме того, таурин не имели почти никакого влияния на апоптоз клеток. Интересно отметить, что введение таурина значительно снизило экспрессию белка раннего ростового ответа-1 (EGR-1). Кроме того, избыточная экспрессия EGR-1 увеличила активацию фибробластов, в то время как снижение EGR-1 показывает противоположный эффект. Соответственно EGR-1 играет ключевую роль в ингибирующем действии таурина на TGF-бета-индуцированный фиброз. В итоге стоит отметить, что таурин может стать потенциальным средством профилактики эпидурального фиброза после ламинэктомии [55].
У больных СД часто наблюдается эректильная дисфункция (ЭД). Для оценки влияния таурина на диабетическую ЭД были использованы крысы с искусственно вызванным СД, и соответственно с ЭД. После 4 нед лечения таурином был сделан вывод, что тауриновые добавки улучшают эректильную функцию у крыс с диабетической ЭД, вероятно, благодаря антифиброзному действию [44].
Известна роль таурина в защите от TGF-бета1-ассоциированного развития фиброза легких после торакального облучения [40].
Существуют сведения о противоопухолевой активности таурина.
Введение бутионин сульфоксимина (BSO) приводит к сосудистым изменениям и увеличивает уровень иммунного TNF-α (в основном сонных артерий) в модели окислительного стресса. Эффект таурина на BSO-индуцированных изменениях сосудов варьируется в зависимости от емкости. Ингибирование увеличения TNF-α было достигнуто с помощью таурина в обеих сонных артериях и аорте. Эти данные указывают на то, что таурин оказывает благотворное воздействие при лечении воспалительных заболеваний, таких как атеросклероз [37].
Противоопухолевую активность таурина изучали многие авторы. В одном из исследований авторы оценили уровень таурина с помощью Bi-Digital Test O-Ring в нормальной ткани внутренних органов и тканях, пораженных опухолью. В норме концентрация таурина составила 4–6 нг. Несколько примеров аденокарциномы пищевода, желудка, поджелудочной железы, толстой кишки, простаты и легкого, а также рака молочной железы показали уровень таурина 0,0025–0,0028 нг. Самый низкий уровень таурина (0,0002–0,0005 нг) был обнаружен у детей, инфицированных вирусом Зика с микроцефалией в Бразилии. Прием таурина в дозе 175 мг 3 раза/сут пациентами среднего возраста с различными видами рака показал значительное его противоопухолевое действие с поразительно повышенной экскрецией с мочой бактерий, вирусов, грибков, асбеста, тяжелых металлов и других токсичных веществ [35].
Таурин может быть полезным средством для профилактики нарушений функции щитовидной железы. Недавно было проведено исследование на крысах, заключающееся в изучении влияния таурина на щитовидную железу совместно с введением хлорпирифоса и свинца. Результаты показали, что введение хлорпирифоса привело к нарушению функции этого органа, что проявлялось снижением концентрации трийодтиронина и тироксина, увеличением концентрации тиреотропного гормона и дегенерацией фолликулярного эпителия щитовидной железы. Таурин снизил нарушение функции щитовидной железы и улучшил ее гистоархитектонику. Благотворное влияние таурина может быть связано с его способностью защищать организм от токсинов и окислительного стресса [5]. А также стоит отметить, что таурин уменьшает когнитивные нарушения у крыс, вызванные хроническим воздействием хлорпирифоса и ацетата свинца [6].
Известна ретинопротекторная роль таурина. Его дефицит, как известно, вызывает вырождение фоторецептора, и в последнее время было обнаружено, что это также вызывает потерю ганглиозных клеток сетчатки, подобную токсичности вигабатрина. Чтобы вызвать истощение таурина, был использован ингибитор транспортера таурина гуанидоэтан сульфат (GES) при концентрации 1% в питьевой воде. Далее была проведена спектральная оптическая когерентная томография и электроретинограмма (ЭРГ) на животных после двух месяцев лечения GES через питьевую воду. Лечение привело к значительному снижению уровня таурина в плазме и глубокой дисфункции зрительной эффективности, что было показано с помощью записи ЭРГ. Оптический анализ когерентной томографии показал, что сетчатка была тоньше в таурин-истощенной группе.
Это исследование подтверждает, что дефицит таурина вызывает потерю ганглиозных клеток сетчатки и конусов. Был также установлен градиент потери клеток в зависимости от их типа – от S-колбочек и L-колбочек до ганглиозных клеток сетчатки. Самые больше потери клеток наблюдались в дорсальной части сетчатки. При истощении таурина S-колбочки оказались более чувствительны к индуцированной светом токсичности сетчатки [14]. Применение таурина в тандеме с вигабатрином может способствовать реверсированию ретинопатии, а также смягчать или замедлять дальнейшее ухудшение [19].
АНТИОКСИДАНТНЫЕ СВОЙСТВА ТАУРИНА
Мышечная дистрофия Дюшенна представляет собой наследуемую прогрессирующую мышечную дистрофию, которая характеризуется ранним началом, симметричной атрофией мышц в сочетании с нарушениями в сердечно-сосудистой и костно-суставной системе. Известно, что антиоксиданты имеют большой потенциал в качестве адъювантной терапии у пациентов с этим заболеванием. Это относится и к таурину [7].
Появилось предположение, что дефицит аминокислоты таурина обостряет некроз миофибрилл в отношении ювенильных мышей. Введение таурина повысило его содержание в молодых дистрофических мышцах (на 40%), значительно снизило некроз миофибрилл (на 75%) и предотвратило значительное увеличение показателей в 3 маркерах воспаления. Это дает основания для дальнейших исследований использования таурина в качестве терапевтического вмешательства для защиты растущих мышц молодых мальчиков с мышечной дистрофией Дюшенна [46].
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Таким образом, к основным свойствами таурина относятся:
- цитопротекторное действие (нейропротекторная, гепатопротекторная, ретинопротекторная, нефропротекторная активность и др.);
- регуляция сердечно-сосудистой системы, гипотензивный эффект;
- гипогликемический эффект;
- восстановление уровня триглицеридов;
- снижение уровня холестерина;
- антифиброзная активность;
- противоопухолевая активность;
- антиоксидантное действие;
- противовоспалительная и антибактериальная активность.
Дальнейшее изучение биологических свойств таурина представляется перспективным для изучения альтернативных способов лечения множества заболеваний.



