Хроническая болезнь почек (ХБП) – это хорошо известный, независимый фактор риска сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний из-за своей роли в гипертрофии левого желудочка (ЛЖ) и патогенезе коронарного атеросклероза [1]. Сердечно-сосудистый риск увеличивается постепенно с ухудшением функции почек [1, 2]. В последнее десятилетие было продемонстрировано, что на ранних стадиях ХБП [1, 3] может увеличить риск сердечно-сосудистой заболеваемости и смертности в долгосрочной перспективе больше [1], чем риск прогрессии ХБП [4, 5, 11]. У пациентов с ХБП 1–3-й стадий риск развития сердечно-сосудистых осложнений в 25–100 раз выше, чем риск развития ХБП 5д-стадии [1]. Сердечно-сосудистый фактор риска, такой как артериальная гипертензия (АГ), начинает развиваться на ранних стадиях ХБП [1, 6]. Недостаточно контролируемая АГ считается одним из наиболее важных факторов риска для прогрессии ХБП [1, 7, 8].
Благодаря суточному мониторированию артериального давления (СМАД) появилось больше данных о связи между циркадными изменениями АД и повреждением органов-мишеней. При анализе данных мониторирования АД важной задачей для уточнения степени риска развития осложнений в утренние часы является оценка динамики АД в утренние часы, так как именно в этот период происходит наибольшее число сердечно-сосудистых событий (инфаркт миокарда, эпизоды безболевой ишемии миокарда, инсульты, злокачественные аритмии) [9, 10]. Таким образом, нарушение функции почек – важный независимый предиктор неблагоприятного исхода и сердечно-сосудистых осложнений у больных ХБП, находящихся на гемодиализе. С увеличением почечной дисфункции возрастает и риск сердечно-сосудистых осложнений.
Целью нашего исследования стало изучение прогностического значения вариабельности артериального давления (АД) на исходы у больных хронической болезнью почек (ХБП) 5д-стадии.
МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДЫ
 Были обследованы 100 больных ХБП, получающих программный гемодиализ в возрасте от 21 до 68 лет (средний возраст 49,7±12,75 года). Среди них 54 мужчины (средний возраст 48,8±13,15 года) и 46 женщин (средний возраст 50,7±12,32 года). При анализе факторов риска неблагоприятного прогноза у больных, находящихся на заместительной почечной терапии гемодиализом, подавляющее большинство (60%) имели АГ, тогда как на долю ожирения, наследственного анамнеза (сахарный диабет 1, 2 типа) и курения приходилось 10, 3 и 5% соответственно.
Были обследованы 100 больных ХБП, получающих программный гемодиализ в возрасте от 21 до 68 лет (средний возраст 49,7±12,75 года). Среди них 54 мужчины (средний возраст 48,8±13,15 года) и 46 женщин (средний возраст 50,7±12,32 года). При анализе факторов риска неблагоприятного прогноза у больных, находящихся на заместительной почечной терапии гемодиализом, подавляющее большинство (60%) имели АГ, тогда как на долю ожирения, наследственного анамнеза (сахарный диабет 1, 2 типа) и курения приходилось 10, 3 и 5% соответственно.
Критериями включения в исследование являлись наличие ХБП 5д-стадии, нахождение на лечении программным гемодиализом, информированное согласие на проведение исследования. Критерии исключения составляли тяжелые хронические заболевания легких, осложненные дыхательной недостаточностью III степени, циррозы печени, тяжелые формы ожирения, хроническая сердечная недостаточность III функционального класса, жизнеугрожающие аритмии, возраст больных 18 лет и менее, злокачественные новообразования, системные заболевания соединительной ткани, неудовлетворительная приверженность лечению.
Пациенты получали комбинированную антигипертензивную терапию: бета-адреноблокаторы – 49%, антагонисты рецепторов ангиотензина II – 6%, ингибиторы АПФ – 44%, блокаторы кальциевых каналов – 44%, средства центрального действия (моксонидин) – 28%.
 СМАД осуществляли с помощью системы для холтеровского мониторирования АД Astokard-Holtersystem-2F Expert фирмы Astokard (Россия). Манжету монитора накладывали на среднюю треть плеча поверх тонкой рубашки, что необходимо из гигиенических соображений, а также для предупреждения возникновения неприятных ощущений или раздражения кожи при частых сжатиях. Программирование частоты измерений проводили с учетом времени сна и бодрствования пациента. Измерения АД выполняли раз в 15 мин в дневное время и раз в 30 мин ночью. При обследовании пациентов с АД, превышающим 180−190 мм рт.ст., интервалы между измерениями были увеличены до 30 мин днем и до 60 мин ночью, что не приводит к статистически значимым изменениям основных показателей суточного профиля АД и сказывается преимущественно на показателях вариабельности.
СМАД осуществляли с помощью системы для холтеровского мониторирования АД Astokard-Holtersystem-2F Expert фирмы Astokard (Россия). Манжету монитора накладывали на среднюю треть плеча поверх тонкой рубашки, что необходимо из гигиенических соображений, а также для предупреждения возникновения неприятных ощущений или раздражения кожи при частых сжатиях. Программирование частоты измерений проводили с учетом времени сна и бодрствования пациента. Измерения АД выполняли раз в 15 мин в дневное время и раз в 30 мин ночью. При обследовании пациентов с АД, превышающим 180−190 мм рт.ст., интервалы между измерениями были увеличены до 30 мин днем и до 60 мин ночью, что не приводит к статистически значимым изменениям основных показателей суточного профиля АД и сказывается преимущественно на показателях вариабельности.
Статистическую обработку полученных результатов проводили с использованием статистических пакетов программ SPSS Statistics 17.0 и Statistica (версия 6.0). Тестирование параметров распределения проводили с помощью критериев Колмогорова–Смирнова, асимметрии и эксцесса. Непрерывные переменные представлены в виде M±m (среднее±стандартная ошибка среднего) или Me (25–75‰) в зависимости от вида распределения (параметрического или непараметрического). При сравнении дискретных переменных использовался χ²-критерий Пирсона с коррекцией на непрерывность по Йетсу, двусторонний точный критерий Фишера. Для оценки изменения дискретных переменных в динамике применялся χ²-критерий Макнемара. Для всех проведенных анализов различия считали достоверными при двустороннем уровне значимости р <0,05.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
В процессе проспективного наблюдения в течение 12 мес у обследованных больных оценивали взаимосвязь наличия и выраженности повышения АД и смертности от всех причин и комбинированной конечной точки у больных ХБП, находящихся на гемодиализе.
Для оценки изменений цифр АД в течение суток применяли СМАД. Оценивая результаты суточного мониторирования АД у пациентов, получающих программный гемодиализ, следует отметить увеличение среднего систолического (САД) как дневного, так и ночного АД до 2-й степени. Обращает на себя внимание значительное увеличение индекса времени как систолического (САД) дневного и ночного АД, так и дневного и ночного ДАД в среднем во всей группе пациентов (что свидетельствует о недостаточной эффективности терапии). При оценке вариабельности АД и величине степени ночного снижения АД отклонений от нормативных значений в среднем обнаружено не было, однако выявлено преобладание так называемого non-dipper-типа. У исследуемых больных отмечалось увеличение средней скорости утреннего подъема АД. Величина утреннего подъема АД в среднем по группе пациентов не превышала нормативных значений. Статистически значимых гендерных различий в показателях СМАД выявлено не было.
 При динамической оценке показателей СМАД после года проспективного наблюдения выявлено статистически значимое увеличение уровней САД дневного, ДАД дневного, САД ночного, ДАД ночного (где р <0,001, р=0,004, р <0,00, р=0,044 соответственно). Достоверной динамики в изменении показателей циркадного ритма АД по сравнению с первичными показателями выявлено не было, что свидетельствует о неэффективности терапии АГ, а ввиду нарастания цифр АД можно говорить о возрастании риска неблагоприятных исходов у пациентов, находящихся на хрониогемодиализе при проспективном наблюдении в течение года (табл.).
При динамической оценке показателей СМАД после года проспективного наблюдения выявлено статистически значимое увеличение уровней САД дневного, ДАД дневного, САД ночного, ДАД ночного (где р <0,001, р=0,004, р <0,00, р=0,044 соответственно). Достоверной динамики в изменении показателей циркадного ритма АД по сравнению с первичными показателями выявлено не было, что свидетельствует о неэффективности терапии АГ, а ввиду нарастания цифр АД можно говорить о возрастании риска неблагоприятных исходов у пациентов, находящихся на хрониогемодиализе при проспективном наблюдении в течение года (табл.).
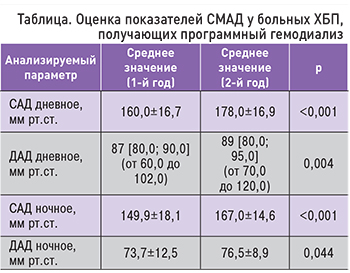
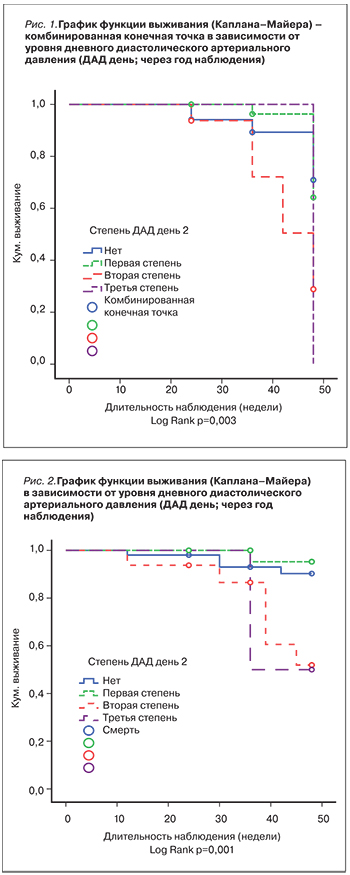
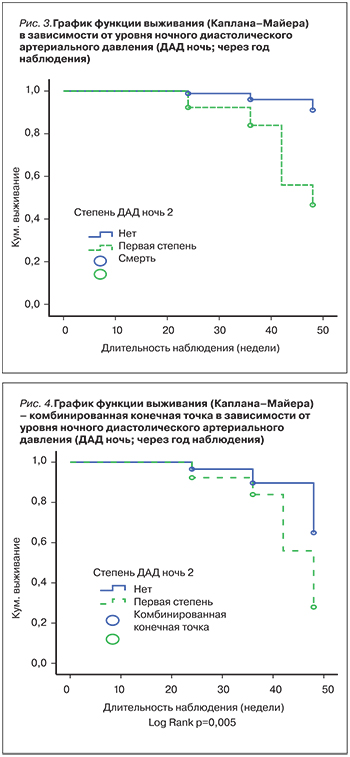
Выявлено возрастание смертности при повышении уровня ДАД дневного, ДАД ночного, САД ночного (р=0,001, р=0,001, р=0,002 соответственно), а также увеличение комбинированной конечной точки при повышении степени этих же показателей (р=0,004, р=0,024, р=0,017 соответственно). Таким образом, при проведении суточного мониторирования после годового проспективного наблюдения отмечена прямая зависимость неблагоприятных исходов в зависимости от степени повышения АД. Графики функции выживания в зависимости от результатов СМАД в динамике представлены на рис. 1–4.
Таким образом, существует независимая связь между недостаточным снижением ночного АД и повышенным риском сердечно-сосудистых осложнений в популяциях с почечной недостаточностью.
Также проведена сравнительная оценка комбинированной антигипертензивной терапии после года проспективного наблюдения. Отмечено уменьшение частоты применения используемых ранее групп препаратов, в частности бета-адреноблокаторов с 49 до 38%, антагонистов рецепторов ангиотензина II с 6 до 4%, ингибиторов АПФ с 44 до 40%, блокаторов кальциевых каналов с 44 до 35%, средств центрального действия (моксонидина) с 28 до 15%, у больных, получающих программный гемодиализ.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Примерно у 80% больных ХБП, находящихся на программном гемодиализе, наблюдается АГ, которая сочетается с повышенной частотой сердечно-сосудистой смертности и является основным предиктором ишемической болезни сердца у больных уремией [11]. Можно отметить существенное, статистически значимое увеличение частоты госпитализации в зависимости от степени увеличения среднего дневного САД, а также возрастание числа неблагоприятных исходов (смертности) в зависимости от степени повышения среднего дневного и ночного ДАД [12].
В общей популяции отношение между САД, ДАД и сердечно-сосудистыми катастрофами является линейным. Напротив, у больных ХБП 5д-стадии эта взаимосвязь выражается кривой U-образной формы. Низкое САД до диализа (менее 110 мм рт.ст.) связано с низкой выживаемостью, равно как и САД более 180 мм рт.ст. ассоциируется с неблагоприятным исходом [11, 13–15]. Среди больных ХБП [7, 16] и пациентов, получающих лечение гемодиализом [9–11], отсутствие суточных колебаний АД и снижения АД ночью отмечается у 74–82% пациентов. Но иногда ночные цифры АД у этих пациентов могут быть выше, чем днем. Так, у обследованных нами пациентов с ХБП 5д-стадии отмечалось нарушение циркадного ритма суточного профиля АД, а также было выявлено возрастание смертности при повышении уровня дневного и ночного ДАД и ночного САД, что совпадает со многими международными исследованиями. Таким образом, существует независимая связь между недостаточным снижением ночного АД и повышенным риском сердечно-сосудистых катастроф в популяциях больных ХБП. В то же время ХБП является важным независимым фактором риска развития и прогрессирования сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
У больных, находящихся на программном гемодиализе, отмечается увеличение среднего как дневного, так и ночного САД и ДАД с нарушением циркадного ритма изменения АД в течение суток. Выявлено значительное увеличение индекса времени как дневного и ночного САД, так и дневного и ночного ДАД в среднем во всей группе пациентов, а также преобладание так называемого non-dipper-типа и увеличение средней скорости утреннего подьема АД у исследуемых пациентов, что свидетельствует о высокой степени риска неблагоприятных событий. Выявлено возрастание смертности при повышении уровня как дневного, так и ночного ДАД и ночного САД, а также увеличение комбинированной конечной точки при повышении степени этих же показателей. Таким образом, нарушение циркадного ритма суточного профиля АД в сочетании с недостаточной коррекцией АГ имеет неблагоприятное прогностическое значение у больных, получающих программный гемодиализ. Полученные данные позволят лучше оценить клиническое значение нарушений суточного профиля АД, возникающих у больных на заместительной почечной терапии, тем самым выявить важность адекватной коррекции АГ с целью уменьшения частоты развития неблагоприятных исходов.



