В настоящее время в мире насчитывается около 850 млн пациентов с хронической болезнью почек (ХБП) [1]. По данным крупного эпидемиологического исследования, в 2016 г. ХБП занимала 16-е место в мире среди основных причин смертности; при этом ожидается, что к 2040 г. она переместится на 5-е место [2, 3]. ХБП является неблагоприятным предиктором смерти от болезней системы кровообращения, что связано с разными причинами, в том числе взаимным негативным влиянием кардиоренальных взаимоотношений при этих заболеваниях [4, 5]. Это подтверждается тем, что основной причиной смерти пациентов, страдающих патологией почек, выступают фатальные сердечно-сосудистые события. Они вносят существенный вклад в структуру смертности пациентов с ХБП, получающих лечение программным гемодиализом, где этот показатель составляет 39% [6, 9].
Стоит отметить, что ключевое значение в развитии сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний при ХБП отводится эндотелиальной дисфункции. Ее распространенность среди пациентов обсуждаемой группы значительно превышает таковую в общей популяции. Это объясняется вкладом различных факторов, таких как прогрессирование атеросклероза, уменьшение активности эндотелиальной синтазы оксида азота, оксидативный стресс, уремическая интоксикация и системный воспалительный процесс [7]. Последний, в свою очередь, характеризуется повышенным уровнем провоспалительных цитокинов. Одним из важнейших представителей этой группы является интерлейкин-6 (ИЛ-6), известный как центральный регулятор воспалительного процесса, играющий существенную роль в обеспечении иммунного ответа и ответа острой фазы [8]. В нескольких работах была продемонстрирована сильная корреляционная связь этого молекулярного маркера с сердечно-сосудистой заболеваемостью и смертностью у пациентов, получающих заместительную почечную терапию [9].
Благодаря открытиям в области изучения патогенеза ХБП, в последнее время все большее внимание уделяется коррекции связанных с ней осложнений, в том числе саркопении. Установлено, что прогрессирование саркопении у пациентов с ХБП представляет собой мультифакторный процесс и также ассоциировано с системным воспалением. Так, в когортном исследовании CRIC (Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort study) признаки системного воспаления были обнаружены у 86% больных с ХБП и саркопенией, при этом значительное повышение маркеров воспаления (ИЛ-6, ИЛ-1β, фактора некроза опухоли-альфа и др.) отмечалось у 12% исследуемой группы [10, 11].
Рядом авторов было установлено, что уровень ИЛ-6 был повышен в почечной ткани пациентов с диабетической нефропатией, гломерулонефритами и др. [12]. Подоциты, эндотелиальные клетки, мезангиальные клетки и эпителиальные клетки канальцев экспрессируют ИЛ-6. В этих типах клеток передача сигналов ИЛ-6 может способствовать их пролиферации, дифференцировке и индуцировать тубулоинтерстициальный фиброз [13].
Согласно имеющимся данным, ИЛ-6 участвует в развитии как острого поражения почек, так и ХБП. Высокий уровень циркулирующего ИЛ-6 у пациентов с острым повреждением почек служит прогностическим фактором повышения смертности [14, 15]. Кроме того, в ряде исследований обнаружено, что в возникновении и прогрессировании ХБП определенную роль играет повышение содержания ИЛ-6 как в сыворотке крови, так и в почечной ткани.
Вместе с тем механизм повышения уровня ИЛ-6 у пациентов с ХБП до конца не ясен, однако обсуждается его связь с формированием дисфункции эндотелия. Отмечается, что с прогрессированием ХБП и нарушением клиренса ИЛ-6 его уровень возрастает, и он продолжает оказывать на эндотелий свое негативное влияние, приводя к сердечно-сосудистому ремоделированию [8]. При этом данный провоспалительный цитокин вызывал повреждение эндотелия главным образом за счет снижения экспрессии эндотелиальной синтазы оксида азота и адипонектина [7]. Muzasti et al. (2020) обнаружили, что высокие уровни ИЛ-6 повышали риск кальцификации сонных артерий и толщину комплекса интима-медиа (КИМ) у пациентов с ХБП 5Д [9]. В то же время его роль в этих процессах до конца не изучена, а оценка вклада ИЛ-6 в сердечно-сосудистое ремоделирование на разных стадиях ХБП представляет исследовательский интерес.
В связи с этим целью настоящего исследования стало изучение особенностей гемодинамики и сосудистого ремоделирования у пациентов с ХБП 3А–5Д стадий в зависимости от тяжести ХБП, а также оценка связи уровня ИЛ-6 сыворотки крови с обсуждаемыми параметрами.
МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДЫ
В исследование были включены 80 пациентов (34 (42,5%) мужчины и 46 (57,5%) женщин) с ХБП 3А–5Д стадий. Продолжительность анамнеза ХБП в среднем составила 8,69±9,33 [0,5; 37] лет, продолжительность заместительной почечной терапии методом гемодиализа – 53,60±47,41 [4; 148] мес. Распределение по возрасту среди мужчин и женщин не отличалось от нормального. Средний возраст исследуемых составил 58,9±13,1 лет.
Когорта пациентов с ХБП, включенных в исследование, была разделена на две равные группы: 1-я – додиализная, 2-я – диализная (табл. 1).

Всем больным проводилось ультразвуковое исследование сосудистых бассейнов экстракраниальных, позвоночных и почечных артерий, выполнялись следующие лабораторные исследования: общий анализ крови, расширенный биохимический анализ крови с определением общего белка, альбумина, креатинина, мочевины, мочевой кислоты, глюкозы и других показателей, общий анализ мочи.
Методом количественного иммуноферментного анализа (ИФА) (Luminex MAGPIX, США) у пациентов определялись сывороточные уровни ИЛ-6. С этой целью использовался лабораторный набор «Интерлейкин-6» (ИЛ-6) (ELISa Cloud-Clone Corp, США); диапазон измерения – 7,8–500 пг/ мл, чувствительность метода – 0,1 нг/мл.
Для оценки вероятности саркопении применялся опросник SARC-F, мышечной производительности – тест 6-минутной ходьбы (Т6МХ), мышечной силы – кистевая динамометрия (КДМ). Указанные методы рекомендованы Европейской рабочей группой по саркопении у пожилых людей (EWGSOP). Также с целью оценки выраженности саркопении применялся тест с поднятием ноги.
Статистическая обработка результатов обследования осуществлялась с помощью программ Microsoft и STATISTICA 10.0. Оценка нормальности распределения параметров в группах проводилась посредством анализа Колмогорова–Смирнова. Среди методов описательной статистики использовалось определение средней арифметической со стандартным отклонением – М±SD (при нормальном распределении), медианы и квартилей – Me [Q1; Q3] (при распределении, отличном от нормального). При нормальном распределении признака сравнение независимых выборок выполнялось с применением критерия Стьюдента, при отличии от нормального распределения – критерия Манна–Уитни. При проведении сравнения двух независимых групп использовались методы дисперсионного анализа. Корреляционный анализ осуществлялся с помощью коэффициента Пирсона (r; при нормальном распределении признака) и коэффициента Спирмена (rS; при распределении, отличном от нормального). Коэффициент корреляции считали значимым при р <0,05.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Среди причин, вызвавших развитие ХБП в группе обследуемых, были артериальная гипертензия (33,8%), хронический тубулоинтерстициальный нефрит (30%), сахарный диабет (18,8%), хронический гломерулонефрит (15%), а именно IgA-нефропатия (6,25%), мембрано-пролиферативный гломерулонефрит (3,75%), мембранозный гломерулонефрит (1,25%) и быстро прогрессирующий гломерулонефрит (2,5%), а также аутосомно-доминантная поликистозная болезнь почек (10%), ишемическая нефропатия (3,8%). Ишемическая болезнь сердца была выявлена у 38,8% пациентов, острый инфаркт миокарда в анамнезе – у 10%, ХСН в качестве осложнения наблюдалась в 48,8% случаев, острое нарушение мозгового кровообращения в анамнезе – у 7,5%, тромбоэмболия легочной артерии – у 1 больного. При подсчете индекса массы тела ожирение было констатировано у 30% респондентов.
Результаты некоторых биохимических показателей крови в исследуемых группах в виде медианы и квартилей (Me [Q1; Q3]) представлены в таблице 2.
Значения лабораторных показателей крови пациентов, ранжированных по стадиям ХБП, приведены в таблице 3.
Референсные значения ИЛ-6 составляют 0–7 пг/ мл. При этом в общей когорте пациентов его уровень был выше нормальных значений в 85% случаев (в 1-й группе – у 92,5% пациентов, во 2-й группе – у 77,5% пациентов). Средние значения ИЛ-6 в общей когорте пациентов равнялись 18,8±2 пг/мл, что более чем вдвое превышало нормальные значения этого показателя. Несмотря на большую частоту встречаемости повышенного уровня ИЛ-6 в додиализной группе исследования, количественная оценка продемонстрировала статистически достоверные различия в его концентрациях между 1-й и 2-й группами: 13,1±0,9 и 24,5±3,8 пг/ мл соответственно.
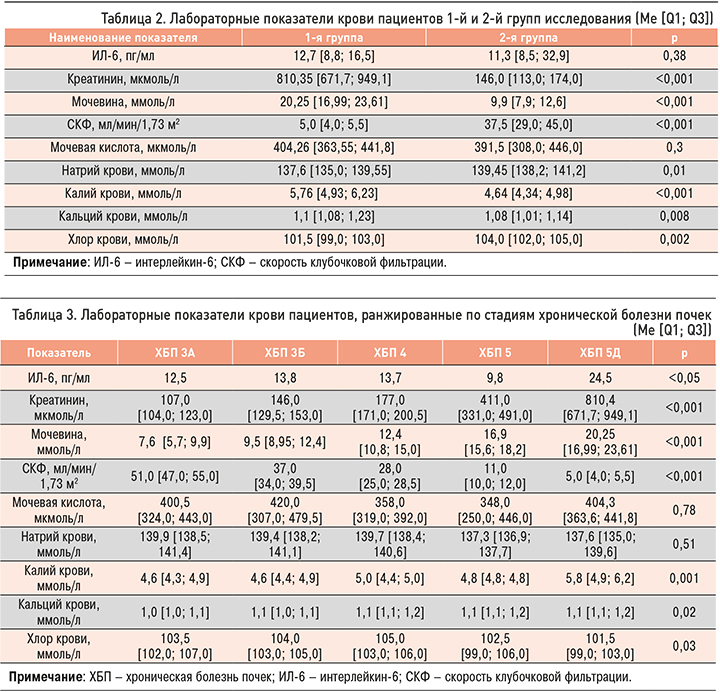
Уровень ИЛ-6 нарастал по мере снижения скорости клубочковой фильтрации (СКФ), что выражалось сильной обратной корреляционной связью. По всей видимости, это было связано с нарушением его клиренса, а также потенцированием системного воспалительного процесса в ответ на усиление уремической интоксикации (рис. 1).
У всех пациентов оценивалась вероятность развития саркопении и показатели мышечной производительности и силы. Количество баллов, набранных по опроснику SARC-F, было достоверно выше во 2-й группе по сравнению с 1-й: 2,85±2,3 против 1,85±1,9 (p <0,05).
Мышечная сила, определенная с помощью КДМ на правой и левой руках пациентов, была статистически значимо выше в 1-й группе, чем во 2-й: 29,7±11 против 26,4±12,1 (p <0,05) и 27,7±10,2 против 24,9±11,4 (p <0,05) соответственно.
Значения пробы с поднятием правой и левой ног также были выше в 1-й группе по сравнению со 2-й: 46,4±18,6 против 43,9±16,2 (p <0,05) и 45,6±18,6 против 42,8±16,2 (p <0,05) соответственно.
По результатам Т6МХ, расстояние, пройденное респондентами, было значимо больше в 1-й группе по сравнению со 2-й: 360,2±75,6 против 224±102,7 (p <0,05). Таким образом, распространенность саркопении в 1-й группе составила 12,5%, во 2-й – 42,5%.
Вместе с тем при изучении уровней ИЛ-6 среди пациентов с саркопенией и ХБП в 1-й и 2-й группах достоверных различий установлено не было (18,3 против 20,3; p=0,66). Вероятно, это связано с небольшим объемом выборки, а также влиянием программного гемодиализа на обсуждаемый показатель. Однако уровень этого клинического маркера превышал нормальные значения более чем в 2 раза.
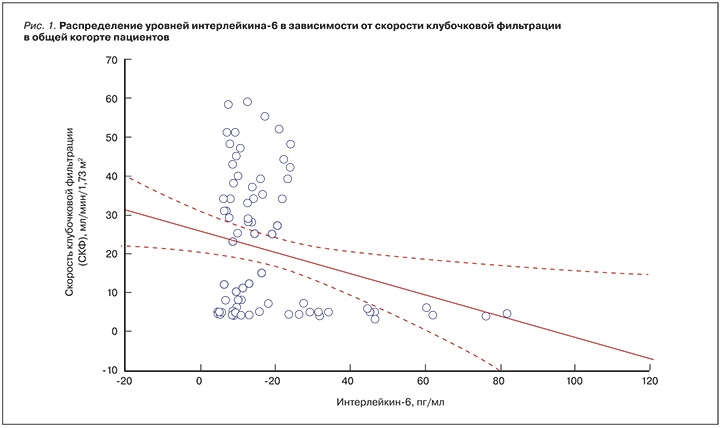
Изучение гемодинамики в бассейнах экстракраниальных, позвоночных и почечных артерий и их ветвей в обсуждаемых группах больных выявило ряд особенностей. Так, почечный кровоток во всех сосудистых зонах, начиная от устьев почечных артерий и до междольковых зон, был значительно снижен во 2-й группе по сравнению с 1-й. Обнаружено, что увеличение скорости кровотока в междольковых артериях сопровождалось повышением сывороточных уровней ИЛ-6 (табл. 4).
При оценке зависимости показателей кровотока в экстракраниальных артериях от СКФ было установлено, что уменьшение СКФ сопровождалось снижением скорости кровотока в общей сонной артерии в диастолу. В то же время высокие значения ИЛ-6 были ассоциированы со снижением скорости кровотока в общей и внутренней сонных артериях в диастолу (рис. 2).
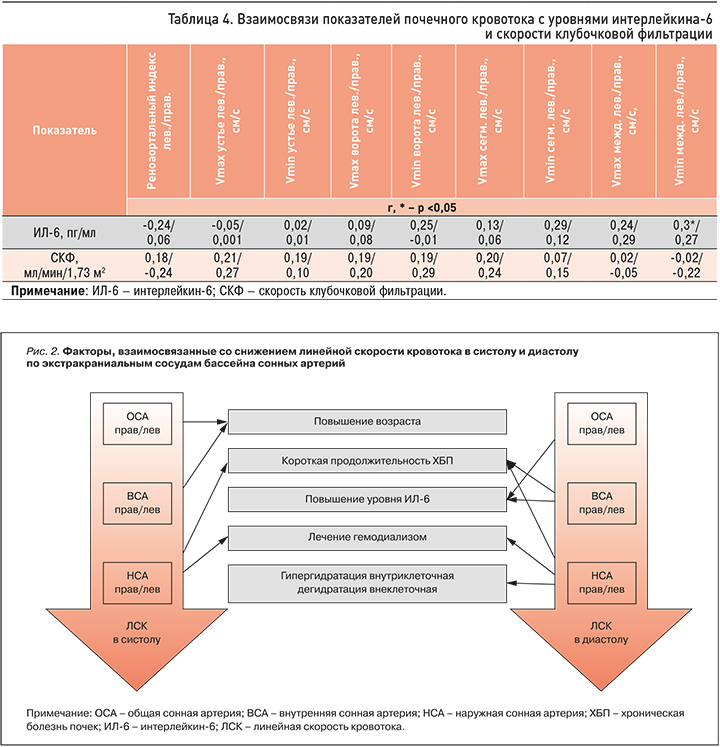
Нами проведено изучение особенностей ремоделирования общей сонной артерии с оценкой толщины КИМ посредством логит-регрессионного анализа. Степень выраженности ХБП, определяемая с помощью СКФ, не показала своего значимого влияния на толщину КИМ. Вместе с тем повышение ИЛ-6 было связано с увеличением этого показателя.
Полученные данные свидетельствовали о том, что прогрессирование темпов ХБП и, как следствие, системного воспалительного процесса, в том числе на фоне уремической интоксикации, сопровождалось нарушением гемодинамики в бассейне сонных артерий (рис. 3).
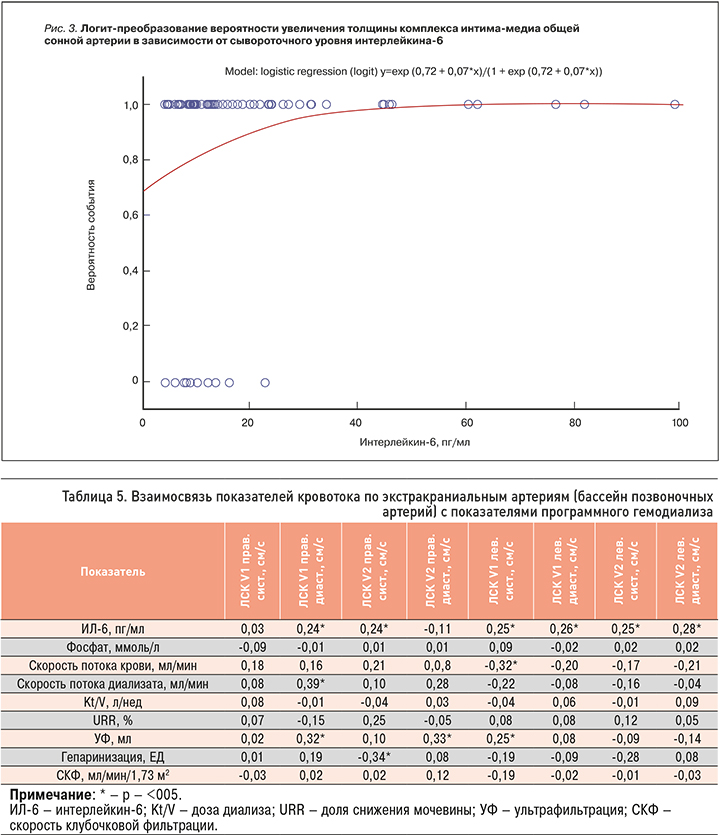
При оценке линейной скорости кровотока (ЛСК) в бассейне позвоночных артерий было установлено, что она в большей степени зависела от уровня уремической интоксикации, чем ЛСК в бассейне сонных артерий (табл. 5). В частности, повышение уровня ИЛ-6 сопровождалось увеличением ЛСК кровотока в позвоночных артериях в V1 и V2 сегментах как в систолу, так и в диастолу.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Проведенное исследование показало, что по мере прогрессирования ХБП отмечается снижение кровотока в сосудистых бассейнах сонных, позвоночных и почечных артерий. Вместе с тем происходит потенцирование системного воспалительного процесса, ключевым регулятором которого в обсуждаемой группе больных является ИЛ-6. Он реализует свою провоспалительную активность и вносит значимый вклад в развитие и прогрессирование эндотелиальной дисфункции и сосудистого ремоделирования. Это проявляется нарушением центральной и периферической гемодинамики, что усугубляет кардиоренальные взаимоотношения и негативно сказывается не только на течении основного заболевания, но и прогнозе в целом.
В то же время обнаружена высокая распространенность саркопении как одного из серьезных осложнений ХБП. В этой подгруппе пациентов также определялись высокие уровни ИЛ-6, превышающие нормальные значения более чем в 2 раза. Несмотря на то что достоверных различий в его уровне у пациентов с верифицированной саркопенией в 1-й и 2-й группах выявлено не было, этот аспект представляет исследовательский интерес, поскольку саркопения выступает неблагоприятным предиктором фатальных сердечно-сосудистых событий у пациентов с ХБП.
Полученные данные создают предпосылки для дальнейшего изучения вопроса о связи таких процессов, как оксидативный стресс, системное воспаление и уремическая интоксикация, а также оценки их интегративной роли в прогрессировании ХБП и сердечно-сосудистом ремоделировании.


