Введение
В настоящее время реабилитация больных после перенесенной пневмонии, ассоциированной с новой коронавирусной инфекцией, вызванной SARS-CoV-2, во всем мире представляет важную проблему: 84% переболевших нуждается в реабилитации [1, 2]. Информационный дефицит клинических и анамнестических характеристик постковидного состояния в регионах Российской Федерации приводит к возникающим недостаткам в организации медицинской помощи на местах. Это может сопряжено с неадекватным использованием имеющегося потенциала реабилитационных отделений и реабилитационных факторов ввиду недостаточных данных об эпидемиологии и клинике у больных после COVID-19.
В литературе хорошо освещены вопросы клиники и лечения пневмонии в целом, однако вопросы эпидемиологии, диагностики заболевания, качества жизни, когнитивные и эмоциональные аспекты, лечение с учетом индивидуальных особенностей изучены недостаточно [3]. Комплексное исследование этих проблем позволит предложить систему мероприятий, направленных на совершенствование реабилитации, улучшение качества жизни и организации помощи людям, страдающим после новой коронавирусной инфекции.
По данным литературы, в течение первых 6 мес после госпитализации по поводу новой коронавирусной инфекции, вызванной SARS-CoV-2, у большинства пациентов происходит выздоровление, однако часто сохраняются остаточные явления, которые потенциально могут привести к инвалидности. У 60–80% пациентов, прошедших реабилитацию, удается достигнуть восстановления утраченных функций [4, 5].
Квалифицированная реабилитация для пациентов, перенесших COVID-19, помогает не только минимизировать последствия заболевания, но и максимально быстро вернуться к привычному образу жизни. Реабилитация предполагает индивидуальный подход, учитывает возраст, коморбидные состояния. Пандемия затронула все слои населения, и реабилитация должна быть доступна лицам разных возрастов и социального статуса. Анализ группы лиц, проходящих реабилитацию, позволит сфокусировать усилия на наиболее хорошо отвечающих группах и разработать реабилитационные программы. Клинические рекомендации по реабилитации после новой коронавирусной инфекции, вызванной SARS-CoV-2 включают физические тренировки, обучение и изменением поведения, воздействие физических факторов и другие технологии, направленные на улучшение физического и психологического состояния пациентов, независимо о пола, возраста и сопутствующих заболеваний [6, 7].
Тем не менее, по-прежнему необходимы дополнительные исследования влияния различных технологий реабилитации на различные группы пациентов по возрасту, полу, тяжести перенесенной пневмонии, степени поражения легочной ткани с целью повышения эффективности легочной реабилитации после COVID-19.
Целью работы было провести анализ пациентов после новой коронавирусной инфекции, вызванной SARS-CoV-2, осложненной вирусной пневмонией, в фазе реконвалесценции, получающих медицинскую реабилитацию согласно временным методическим рекомендациям «Медицинская реабилитация при новой коронавирусной инфекции (COVID-19)» [6], выработать рекомендации для дальнейшего проведения реабилитации в домашних условиях.
Материалы и методы
Проведено ретроспективное исследование историй болезни в отделении медицинской реабилитации АО «Санаторий "Чувашиякурорт"» (г. Чебоксары, Чувашская Республика) в период с 09.2020 по 06.2021 гг. В исследование были включены 357 человек, поступивших на 3-й этап реабилитации после перенесенной пневмонии, ассоциированной с новой коронавирусной инфекцией в период с октября 2020 г. по июнь 2021 г. Пациенты поступили на 3-й этап медицинской реабилитации на основании направления участкового врача прикрепленной медицинской организации. В зависимости от результата оценки по шкале реабилитационной маршрутизации (ШРМ) определяется маршрутизация пациента: 0–1 балл – пациент не нуждается в проведении реабилитационных мероприятий; 2–3 балла – реабилитационные мероприятия проводятся амбулаторно или в условиях дневного стационара; 4–6 баллов – медицинская реабилитация проводится в стационарных условиях [8]. Программа реабилитации осуществлялась в течение 10 дней в рамках территориальной программы ОМС. У всех пациентов в данных выписок из историй болезни присутствовал диагноз «J12.8 Другая вирусная пневмония». Тяжесть пневмонии определялась в соответствии с временными методическими рекомендациями «Медицинская реабилитация при новой коронавирусной инфекции (COVID-19)» [6].
Физическая работоспособность оценивалась при помощи теста 6-минутной ходьбы (TШХ) при поступлении и выписке. Изменение физической подготовки оценивалось в изменении дистанции ТШХ (в м и в процентах) от первого ко второму исследованию [9, 10]. Для оценки выраженности одышки использовались шкала Борга и степень дыхательной недостаточности (ДН). Всем пациентам проводилась оценка по Госпитальной шкале тревоги и депрессии (HADS), которая содержит 14 пунктов, каждому из которых соответствует 4 варианта ответов, отражающих степень нарастания симптоматики. При интерпретации результатов учитывается суммарный показатель по каждой подшкале, при этом выделяются 3 области значений:
- 0–7 – норма (отсутствие достоверно выраженных симптомов тревоги и депрессии);
- 8–10 – субклинически выраженная тревога/депрессия;
- 11 и выше – клинически выраженная тревога/депрессия [11].
Критериями исключения из исследования стали наличие хронической сердечной недостаточности, эпилептических приступов, возраст пациентов старше 85 лет.
Для сравнения пациентов по возрасту были выделены возрастные категории: 1-я группа – до 40 лет; 2-я группа – 40–49 лет; 3-я группа – 50–59 лет; 4-я группа – 60–69 лет; 5-я группа – 70–79 лет.
Программа реабилитации включала: занятия лечебной физкультурой (получили 100% пациентов); сухие углекислые ванны (70%); магнитотерапия на аппаратах «Мультимаг», «Полимаг» («Еламед», Елатьма, Россия) (67%); галотерапия (100%); массаж грудной клетки и шейно-воротниковой зоны (100%); психологическая реабилитация в виде первичной консультации психолога и последующая индивидуальная и групповая психотерапия (83%); грязевые аппликации (были назначены 35% пациентам со среднетяжелой и тяжелой степенью поражения легочной ткани для улучшения притока крови к легким) [12–15].
Статистическая обработка результатов проводилась с применением программы StatSoft STATISTICA 10.0.1011 Eneterpise. Критерий Шапиро–Уилка использовался для проверки нормальности распределения количественных признаков. Выборочные параметры, приводимые далее, имеют следующее обозначение: n – объем анализируемой группы, Р – величина статистической значимости различий.
При оценке различий между связанными выборками выполняли сравнение с помощью методов непараметрической и параметрической статистики – критерия Вилкоксона, парного теста Стьюдента (для связанных выборок).
Результаты
Доля мужчин составляла 28,8% (103 человека), женщин – 71,2% (254 человек). Медиана давности пневмонии составляла 9,3 мес, медиана возраста пациентов – 60 лет. Самую большую возрастную группу составили пациенты 60–69 лет: среди мужчин на их долю пришлось 28,1%, среди женщин – 36,6%; меньше всего пациентов оказалось в группе старше 80 лет. На втором месте были пациенты в возрасте 50–59 лет – 26,2% среди мужчин и 30,3% среди женщин (рис. 1).
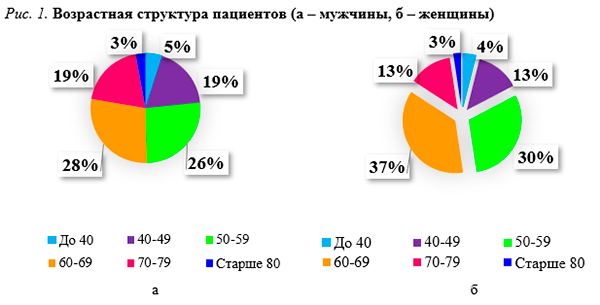
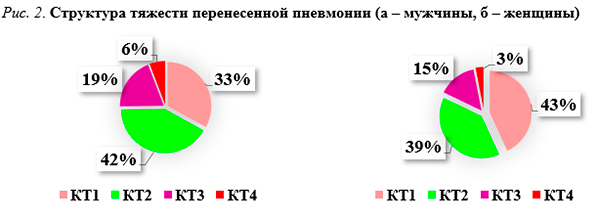
Среди лиц, поступивших на реабилитацию, присутствовали пациенты с разной степенью тяжести перенесенной пневмонии: у 40,6% наблюдались незначительные изменения (КТ-1), у 40,1% – нарушения средней степени тяжести (КТ-2); у 16,2% – тяжелой степени (КТ-3), у 3,1% – крайне тяжелые нарушения (КТ-4).
У мужчин чаще всего в анамнезе присутствовала пневмония КТ 2 степени – 41,8%. На втором месте (33%) по частоте встречалась пневмония КТ 1 степени, значительно реже пациенты переносили пневмонию с КТ 3 степени (19,4%) и КТ 4 степени (5,8%). Это согласуется со статистикой тяжести поражения легочной ткани больных с COVID-19, которая показывает преобладание средней степени тяжести поражения легких.
У женщин чаще выявлялась в анамнезе пневмония с тяжестью КТ-1 – в 43,7% случаев. КТ 2 степени встречалась в 39,3%, КТ-3 – в 15%, а КТ-4 – лишь в 2% (рис. 2).
В возрастной группе до 40 лет у мужчин КТ-1 встречается в 2,9 раза чаще, чем КТ-2 и КТ-3.
В возрастных группах 40–49 лет и 50–59 лет КТ-1 и КТ-2 наблюдались с равной частотой, число лиц с КТ-3 было меньше, а случаи КТ-4 выявлены не были.
У лиц от 60 до 69 лет чаще всего в анамнезе присутствовала пневмония КТ 2 степени, реже – КТ 1 степени; тяжелые двусторонние пневмонии КТ-3 и КТ-4 отмечались в единичных случаях. В возрасте 70–79 лет соотношение КТ-1 : КТ-2 : КТ-3 : КТ-4 составило 2 : 4 : 1 : 0,5.
У женщин в возрасте до 40 лет чаще имела место пневмония КТ 1 степени, случаи КТ-4 выявлены не были.
В возрасте 40–49 лет КТ 1 степени встречалась в 2 раза чаще, чем КТ 2 степени. При этом случаи КТ 3 степени и КТ 4 степени регистрировались очень редко.
У пациенток в возрасте 50–59 лет и 60–69 лет частота КТ-1 и КТ-2 была сопоставима, КТ-3 и КТ-4 выявлялись в единичных случаях. В возрастной группе 70–79 лет соотношение КТ-1 : КТ-2 : КТ-3 : КТ-4 составило 3 : 2 : 1 : 0,2.
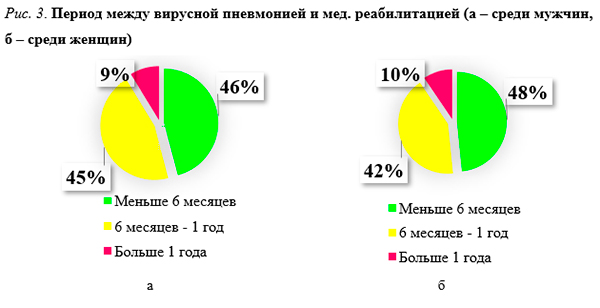
Промежуток времени от 2 до 6 мес после выписки из стационара или закрытия законченного случая составил 43,7% от общего числа пациентов. В промежутке от 6 до 12 мес за медицинской реабилитацией обратилось 44,2% (n=158), после 1 года – только 8,5% (n=30; рис. 3). Обращение за медицинской реабилитацией в сопоставимые промежутки времени между вирусной пневмонией и медицинской реабилитацией происходило примерно с равной частотой у мужчин и у женщин.
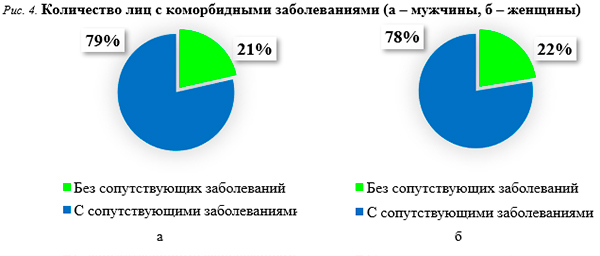
Число пациентов, не имеющих сопутствующих заболеваний, на момент реабилитации составило 79 человек (22,1%); среди них – 57 женщин всех возрастов и 22 мужчины в возрасте от 30 до 60 лет. Количество пациентов, имеющих сопутствующие заболевания, равнялось 278 человек (77,9%) – 197 женщин и 81 мужчина (рис. 4).
При поступлении 56% пациентов имели жалобы на боли. Чаще всего преобладали боли в грудной клетке, боли в спине. Медиана по визуальной аналоговой шкале (ВАШ) у поступивших на реабилитацию женщин возрастной группы 40–49 лет составляла 3,00, после реабилитации – 1,00; в возрастных группах 50–59 и 60–69 лет аналогичные показатели равнялись 2,00 (до реабилитации) и 0,00 (после реабилитации). Медиана по ВАШ среди поступивших на реабилитацию мужчин возрастных групп 40–49, 60–69 и 70–79 лет составляла 2,00 до реабилитации и 0,00 после, но различия в показателях между этими тремя группами статистически не значимы (табл. 1).
|
Таблица 1. Показатели боли по визуальной аналоговой шкале в разных возрастных группах исследования (Me (Q1; Q3)) |
|||||
|
Возраст |
ВАШ |
Женщины |
p |
Мужчины |
p |
|
40–49 |
До реабилитации |
3,00 (0; 3) |
0,011 |
2,00 (0,00; 2,00) |
0,067* |
|
После реабилитации |
1,00 (0; 1) |
0,00 (0,00; 0,00) |
|||
|
Дельта |
2,00 |
2,00 |
|||
|
50–59 |
До реабилитации |
3,00 (0; 3) |
0,005 |
2,00 (0,00; 2,00) |
0,043 |
|
После реабилитации |
0,00 (0; 2) |
0,50 (0,00; 1,00) |
|||
|
Дельта |
3,00 |
0,50 |
|||
|
60–69 |
До реабилитации |
2,00 (0; 2) |
0,002 |
2,00 (0,00; 2,00) |
0,067* |
|
После реабилитации |
0,00 (0; 0) |
0,00 (0,00; 0,00) |
|||
|
Дельта |
2,00 |
2,00 |
|||
|
70–79 |
До реабилитации |
0,50 (0; 2) |
0,017 |
0,50 (0,00; 0,5) |
0,179* |
|
После реабилитации |
0,00 (0; 0,5) |
0,00 (0,00; 0,5) |
|||
|
Дельта |
0,50 |
0,50 |
|||
|
Примечание: различия между группами статистически значимы при р <0,05. * – Различия статистически не значимы (р>0,05). |
|||||
При анализе результатов по госпитальной шкале тревоги и депрессии было выявлено, что субклинически выраженная тревога (8–10 баллов) присутствовала у 67 женщин и 50 мужчин, клинически выраженная тревога (>11 баллов) – у 42 женщин.
Субклинически выраженная депрессия (8–10 баллов) была выявлена у 84 женщин и 59 мужчин, клинически выраженная депрессия (>11 баллов) – у 34 женщин. По частоте проявлений тревоги и депрессии значимых возрастных различий не выявлено.
У поступивших на реабилитацию пациентов 282 человека (78,9%) имели оценку 3 балла по ШРМ, 75 (21,1%) – 2 балла. Показатели ШРМ и теста 6-минутной ходьбы до лечения и у мужчин, и у женщин в каждой возрастной группе были сопоставимы.
При анализе разных возрастных категорий выявлено, что у пациентов в возрасте 40–49 лет оценка по ШРМ составляла 3,0±0,2 балла, результат ТШХ равнялся 381 м. В возрастной группе 50–59 лет аналогичные показатели составили 2,84±0,3 балла и 337 м, в группе 60–69 лет – 2,96±0,2 балла и 371 м.
Мужчины в возрасте до 50 лет при поступлении (до лечения) имели лучшие показатели по шкале Борга (2,29±0.47), чем женщины того же возраста (2,46±0,49). В возрастной группе после 50 лет зарегистрирована тенденция к более высоким показателям по этой шкале у женщин (до лечения – 2,49±0,52), по сравнению с мужчинами (до лечения – 2,69±0,41; табл. 2).
|
Таблица 2. Результаты при поступлении по ШРМ и шкале Борга |
||||
|
Возраст |
ШРМ |
Шкала Борга |
||
|
Женщины |
Мужчины |
Женщины |
Мужчины |
|
|
До 40 |
3,00±0,00 |
3,00±0,00 |
2,51±0,50 |
2,22±0,44 |
|
40–49 |
3,00±0,00 |
3,00±0,00 |
2,41±0,49 |
2,37±0,50 |
|
50–59 |
3,00±0,00 |
3,00±0,00 |
2,41±0,56 |
2,43±0,50 |
|
60–69 |
2,97±0.16 |
3,00±0,00 |
2,55±0,50 |
2,78±0,42 |
|
70–79 |
3,00±0,00 |
3,00±0,00 |
2,51±0,50 |
2,88±0,33 |
|
Примечание: р <0,05. |
||||
При оценке переносимости пациентами физических нагрузок по шкале Борга было выявлено снижение уровня одышки с умеренной до легкой в возрастной группе 40–49 у мужчин на 64,0% (до лечения – 3,0±0,5 балла; р=0,0023), у женщин – на 22,6% (до лечения – 3,1±0,3 балла; р=0,012).
Анализ результатов ТШХ при поступлении показал разницу у женщин и мужчин в возрасте до 40 лет – 384,0±12,58 и 402,5±17,07 м соответственно. В остальных возрастных группах достоверные различия между женщинами и мужчинами выявлены не были: так, в возрасте 40–49 лет результаты ТШХ составили 386,61± 36,18 и 391,75±10,15 м, 50–59 лет – 390,23±27,67 и 384,37±14,41 м, 60–69 лет – 377,76±26,69 и 372,95±20,00 м, 70–79 лет – 374,25±24,54 и 372,22±23,86 м.
Общий средний прирост показателей ТШХ среди женщин равнялся 106,22 м, среди мужчин – 102,25 м (табл. 3).
|
Таблица 3. Результаты теста 6-минутной ходьбы (м) до и после поступления на реабилитацию |
|||||
|
Возрастной период |
Тест 6 минутной ходьбы |
Женщины |
р |
Мужчины |
р |
|
До 40 лет |
До реабилитации |
384,00±12,58 |
0,007
|
402,5±17,07 |
0,007
|
|
После реабилитации |
464,00±39,26 |
548,75±43,41 |
|||
|
Дельта |
80,0 |
|
146,25 |
|
|
|
40–49 |
До реабилитации |
386,61±36,18 |
0,018
|
391,75±10,15 |
0,006
|
|
После реабилитации |
504,19±38,75 |
512,81±35,21 |
|||
|
Дельта |
114,69 |
|
128,06 |
|
|
|
50–59 |
До реабилитации |
390,23±27,67 |
0,006
|
384,37±14,41 |
0,006
|
|
После реабилитации |
491,55±30,83 |
511,30±34,21 |
|||
|
Дельта |
103,34 |
|
124,77 |
|
|
|
60–69 |
До реабилитации |
377,76±26,69 |
0,006
|
372,95±20,00 |
0,006
|
|
После реабилитации |
474,36±36,75 |
443,33±35,26 |
|||
|
Дельта |
100,26 |
|
76,44 |
|
|
|
70–79 |
До реабилитации |
374,25±24,54 |
0,006
|
372,22±23,86 |
0,007
|
|
После реабилитации |
481,825±32,87 |
459,55±30,42 |
|||
|
Дельта |
111,03 |
|
93,3 |
|
|
Обсуждение
Проведенный анализ показал, что доля женщин в общей популяции больных на третьем этапе реабилитации более чем в 2,5 раза превышает число мужчин. Можно предположить, что меньшее число мужчин при прохождении реабилитации связанно с тем, что на этот период лист нетрудоспособности не выдается. Другая причина кроется в психологических особенностях мужского населения, меньше обращающих внимание на собственное здоровье и имеющих более тяжелые условия труда при наличии опасных и вредных факторов.
Корреляция не была зарегистрирована между длительностью периода между лечением и реабилитацией, между полом и степенью поражения легочной ткани.
Из общего числа реабилитируемых можно выделить принципиально разные по дальнейшей тактике ведения группы пациентов:
1. Пациенты с полным восстановлением, у которых произошло восстановление нарушенной дыхательной функции и функции сердечно-сосудистой системы.
2. Пациенты с высоким уровнем тревожности и депрессии, нуждающиея в дальнейшей психологической диагностике и лечении.
3. Пациенты со сниженными адаптационными резервами, у которых не восстановилась толерантность к физической нагрузке, функции внешнего дыхания. Для уточнения причин снижения физиологических ресурсов, затрудняющих восстановление (возраст, тяжесть перенесенной пневмонии, сопутствующие заболевания), требуется проведение дальнейших исследований.
Необходимо рассмотреть вопрос о дальнейшей поддержке и стратегиях по минимизации психосоциальных последствий COVID-19 после выписки. Для полноценной и максимальной эффективной реабилитации курс в 10 дней недостаточен. Продолжить лечение может помочь дистанционная реабилитация. В последние годы быстрое развитие информационно-коммуникационных технологий вместе с носимыми устройствами сделало возможной цифровую дистанционную реабилитацию, эффективность и безопасность которой не уступают традиционной реабилитации [16, 17]. Это позволит рационально использовать кадровые ресурсы, своевременно проводить лечебно-диагностические и реабилитационные мероприятия.
Выводы
1. Выявлено, что доля женщин (71,2%), поступивших на медицинскую реабилитацию, почти в 3 раза превышала долю мужчин (28,8%).
2. В структуре пациентов, поступивших на амбулаторную реабилитацию, преобладают пациенты с легкой степенью тяжести пневмонии – КТ-1 (145 человек: 111 женщин и 34 мужчины). Отмечено, что у женщин в анамнезе наибольшей была частота выявления КТ-1 (43,7%), а у мужчин – КТ-2 (41,8%).
3. При анализе временного промежутка между первым и третьим этапом реабилитации установлено, что наибольшее число пациентов обратилось за помощью в период 6–12 мес – 44,2%; в период от 2 до 6 месяцев этот показатель составил 43,7%. Большое количество пациентов с затянувшейся медицинской реабилитации имеет риск ухудшения качества жизни и развития постковидных осложнений.
4. Признаки тревоги и депрессии среди женщин встречались чаше, чем среди мужчин. Статистически значимые различия оказались характерны только для признаков депрессии.
Таким образом, для полноценной реабилитации и сокращения времени ожидания необходимо увеличивать число реабилитационных коек на 2-м этапе реабилитации и количество квот на 3-й этап. На реабилитацию приходят лица с разным ковидным анамнезом, разным коморбидным фоном, различным промежутком от лечения до реабилитации, различной физической работоспособностью. Все эти факторы целесообразно учитывать мультидисциплинарной бригаде для достижения поставленных целей в комплексной реабилитации пациентов после перенесенной пневмонии, ассоциированной с новой коронавирусной инфекции, вызванной SARS-CoV-2.


