Острые респираторные заболевания (ОРЗ) и прежде всего острые респираторные вирусные инфекции (ОРВИ) чаще всего возникают как результат ослабления иммунной защиты при переохлаждении. Острый назофарингит (МКБ- 10 диагнозы J00–J06), или «простуда», является одним из самых распространенных инфекционных заболеваний верхних дыхательных путей. Общие симптомы простуды включают боль или резь в горле, насморк, чихание и кашель. Заболевание иногда сопровождается порозовением роговицы глаз, мышечными болями, усталостью, недомоганием, головными болями, мышечной слабостью и потерей аппетита. В большинстве случаев симптомы сохраняются в течение одной недели в острой форме, а затем, как правило, ослабевают в течение 1–2 нед.
Ослабление иммунной защиты делает организм восприимчивым к атаке вирусов, вызывающих грипп, и болезнетворных бактерий (стрептококки, стафилококки, гемофильная палочка и др.). Антибиотики подавляют рост бактерий в активной фазе деления, но в то же время увеличивают детоксикационную нагрузку на печень, вызывают дисбактериозы, аллергические реакции и способствуют развитию резистентных бактериальных штаммов. Частые изменения в генетических структурах вирусов (в частности, РНК-вирусов) создают трудности при производстве эффективных вакцин и способствуют формированию устойчивости к известным антивирусным препаратам. Комбинированная терапия лекарственными средствамии (антигистамин–деконгестант, антигистамин–анальгетик, анальгетик–деконгестант, антигистамин–анальгетик–деконгестант, антибиотики и т.д.), несмотря на доказанную эффективность [1], представляет собой ярко выраженный пример полипрагмазии.
 Поэтому одним из важнейших направлений профилактики и терапии ОРЗ и ОРВИ является нормализация функционирования иммунной системы. Общеизвестно, что дефициты определенных микронутриентов, особенно сочетанные дефициты, представляют собой одну из широко распространенных причин дисфункции иммунной системы. Адекватное потребление таких эссенциальных микронутриентов, как цинк, витамины А, С, D, E, B6, B12 и др. имеет важное значение для поддержания иммунитета [2]. Таким образом, препараты на основе жизненно важных микронутриентов представляют собой важную опцию при лечении и профилактике ОРВИ и ОРЗ. Средства, наиболее часто рекомендуемые для стимуляции иммунитета, включают «ощелачивающую» диету, цинк, витамин С и пробиотики. Эти нутрицевтики достоверно более эффективны, чем плацебо, в уменьшении числа эпизодов ОРВИ, длительности заболевания и частоты применения антибиотиков [3, 4].
Поэтому одним из важнейших направлений профилактики и терапии ОРЗ и ОРВИ является нормализация функционирования иммунной системы. Общеизвестно, что дефициты определенных микронутриентов, особенно сочетанные дефициты, представляют собой одну из широко распространенных причин дисфункции иммунной системы. Адекватное потребление таких эссенциальных микронутриентов, как цинк, витамины А, С, D, E, B6, B12 и др. имеет важное значение для поддержания иммунитета [2]. Таким образом, препараты на основе жизненно важных микронутриентов представляют собой важную опцию при лечении и профилактике ОРВИ и ОРЗ. Средства, наиболее часто рекомендуемые для стимуляции иммунитета, включают «ощелачивающую» диету, цинк, витамин С и пробиотики. Эти нутрицевтики достоверно более эффективны, чем плацебо, в уменьшении числа эпизодов ОРВИ, длительности заболевания и частоты применения антибиотиков [3, 4].
Сочетание высоких доз витамина С и органических солей цинка является перспективным направлением разработки нутриентных препаратов для лечения ОРВИ и других ОРЗ. И витамин С, и цинк играют важную роль в поддержании как здоровья в целом, так и иммунной защиты в частности. Витамин С (аскорбиновая кислота) повышает адаптационные возможности организма и его сопротивляемость инфекциям за счет поддержки нормальной скорости выработки антител. Цинк необходим для нормального функционирования тимуса (вилочковой железы) – основного органа иммунной системы, вырабатывающего Т-лимфоциты, необходимые для уничтожения бактерий и вирусов. Потребление обоих микронутриентов с пищей, как правило, недостаточно (50–70% минимальной суточной нормы). В настоящей статье рассмотрены молекулярно-клеточные механизмы и доказательная база эффектов цинка и витамина С в качестве средств терапии и профилактики ОРЗ.
МОЛЕКУЛЯРНЫЕ МЕХАНИЗМЫ ДЕЙСТВИЯ ЦИНКА НА ИММУНИТЕТ
Негативное воздействие дефицита цинка на здоровье человека включает замедление роста, нарушение функции иммунных клеток, более высокие уровни воспаления и окислительного повреждения клеток, когнитивные нарушения, инсулинрезистентность и др. Препараты цинка успешно используются для лечения острой диареи у детей, болезни Вильсона–Коновалова, ОРЗ, дегенерации макулы. Дефицит цинка резко отрицательно сказывается на активности тимулина (Zn-зависимый гормон, участвующий в дифференцировке Т-лимфоцитов и повышении активности Т- и NK-лимфоцитов) и функционировании лимфоцитов типа Th1 (способствуют развитию клеточного иммунного ответа, активируя Т-киллеры и стимулируя секрецию γ-интерферона) [5, 6]. Основные механизмы воздействия цинка на иммунитет включают модуляцию вирус-рецепторных взаимодействий, активацию Т-клеток и других лимфоцитов, уменьшение апоптоза и корректировку секреции цитокинов [7]. Большинство вирус-рецепторных взаимодействий происходит при посредничестве всего лишь одного клеточного рецептора, который взаимодействует с конкретным участком вирусного капсида [8]. Структура белковой оболочки, например, риновируса-14 позволяет предположить существование по крайней мере 360 Zn-связывающих сайтов на поверхности капсида. Связывание цинка этими сайтами изменит молекулярную поверхность капсида и потенциально может предотвратить взаимодействие капсида с клетками человека [9].
Противодействие иммунной системы вирусным инфекциям требует достаточного количества иммунокомпетентных активных Т-лимфоцитов. Дефицит цинка сокращает количество периферийных и тимусных Т-клеток, ослабляет их пролиферативный ответ, а также ухудшает функционирование Т-клеток-помощников и цитотоксических Т-клеток, приводя к атрофии тимуса, лимфопении, увеличению скорости инфицирования и большей продолжительности инфекций [10]. На молекулярном уровне цинк стимулирует автофосфорилирование белка тирозинкиназы Lck через взаимодействия с цитоплазматическими петлями CD4 и CD8, что приводит к активации Т-клеток, которые затем более интенсивно атакуют вирусные частицы [11].
Другим возможным путем активации Т-клеток является воздействие тимулина – цинк-связывающего пептидного гормона, состоящего из 9 аминокислот (последовательность аминокислот pEAKSQGGSN) [12]. Тимулин регулирует дифференцировку незрелых Т-клеток в вилочковой железе и улучшает функционирование зрелых Т-клеток [13]. Тимулин также оказывает, судя по всему, нейроэндокринные эффекты через увеличение секреции адренокортикотропного гормона [14], который в свою очередь активирует секрецию кортикостероидов, вовлеченных в реакцию на стресс, общий иммунный ответ, энергетический метаболизм и синтез белков. Помимо стабилизации структуры гормона, цинк также способствует увеличению секреции тимулина [15].
Антиапоптотическое действие ионов цинка как на уровне тимуса, так и на периферии приводит к увеличению числа Т-клеток, способствуя, таким образом, дальнейшему укреплению иммуностимулирующего эффекта. Было показано, что цинк ингибирует проапоптотические каспазы-3, -6 и -9 [16]. Кроме того, цинк увеличивает соотношение Bcl-2/Bax, тем самым повышая устойчивость клеток к апоптозу [17]. Одним из возможных молекулярных механизмов ингибирования каспазы-3 цинком является действие XIAP белка (X-связанного ингибитора апоптоза). XIAP представляет собой основной эндогенный ингибитор каспазы-9, -3 и -7. Структура XIAP домена в комплексе с каспазой-3 свидетельствует о том, что механизм торможения обусловлен блокадой субстрат-связывающего кармана каспазы. Домен BIR2 белка XIAP, который непосредственно ингибирует каспазу, является цинк-зависимым. Дефицит цинка приведет к нарушению структуры этого домена и к ослаблению ингибирования каспазы [18], стимулируя увеличение апоптоза Т-лимфоцитов.
 Стимуляция цинком изменяет внутриклеточную передачу сигнала от клеточных рецепторов, детектирующих патогены (так называемых Toll-подобные рецепторы, TLR), активация которых приводит к секреции провоспалительных цитокинов. С другой стороны, сложные взаимодействия между цинком, сигнальными каскадами окиси азота и циклических нуклеотидов наряду с ингибированием связанной с рецептором интерлейкина-1 киназы-1 и κB киназы приводит к снижению уровней провоспалительных цитокинов [19]. Средние уровни 1a-рецептора TNF (фактор некроза опухоли) и рецептора ICAM-1 (молекула клеточной адгезии) в плазме существенно снижались при терапии ацетатом цинка у пациентов, участвовавших в рандомизированном исследовании [20]. Данный эффект связан, вероятно, с уменьшением активации NF-κB киназы через ингибирование фосфорилирования I-κВ киназой. Среди иммуномодулирующих эффектов цинка, имеющих прямое отношение к защите от вирусной инфекции, важнейшим является стимуляция ионами цинка продукции интерферонов α и γ [21]. Помимо иммуностимулирующего эффекта, ионы цинка способствуют защите эпителия легких при воспалительном стрессе. У крыс с дефицитом цинка снижалась общая концентрация белка в легких, что соответствует ослабленной регенерации легочной ткани [22]. Истощение внутриклеточного цинка также повышает активность каспазы-3, что ведет к активации апоптоза и, следовательно, к структурному повреждению легочного эпителия [23]. Дотации цинка (50 мг/сут, 8 нед) детям с бронхиальной астмой, находящимся на терапии ингаляционными стероидами (n=284), значительно ослабляет клинические симптомы (кашель, хрипы и одышку) и улучшает параметры спирометрии (ФЖЕЛ, ОФВ1, ОФВ1/ФЖЕЛ) [24].
Стимуляция цинком изменяет внутриклеточную передачу сигнала от клеточных рецепторов, детектирующих патогены (так называемых Toll-подобные рецепторы, TLR), активация которых приводит к секреции провоспалительных цитокинов. С другой стороны, сложные взаимодействия между цинком, сигнальными каскадами окиси азота и циклических нуклеотидов наряду с ингибированием связанной с рецептором интерлейкина-1 киназы-1 и κB киназы приводит к снижению уровней провоспалительных цитокинов [19]. Средние уровни 1a-рецептора TNF (фактор некроза опухоли) и рецептора ICAM-1 (молекула клеточной адгезии) в плазме существенно снижались при терапии ацетатом цинка у пациентов, участвовавших в рандомизированном исследовании [20]. Данный эффект связан, вероятно, с уменьшением активации NF-κB киназы через ингибирование фосфорилирования I-κВ киназой. Среди иммуномодулирующих эффектов цинка, имеющих прямое отношение к защите от вирусной инфекции, важнейшим является стимуляция ионами цинка продукции интерферонов α и γ [21]. Помимо иммуностимулирующего эффекта, ионы цинка способствуют защите эпителия легких при воспалительном стрессе. У крыс с дефицитом цинка снижалась общая концентрация белка в легких, что соответствует ослабленной регенерации легочной ткани [22]. Истощение внутриклеточного цинка также повышает активность каспазы-3, что ведет к активации апоптоза и, следовательно, к структурному повреждению легочного эпителия [23]. Дотации цинка (50 мг/сут, 8 нед) детям с бронхиальной астмой, находящимся на терапии ингаляционными стероидами (n=284), значительно ослабляет клинические симптомы (кашель, хрипы и одышку) и улучшает параметры спирометрии (ФЖЕЛ, ОФВ1, ОФВ1/ФЖЕЛ) [24].
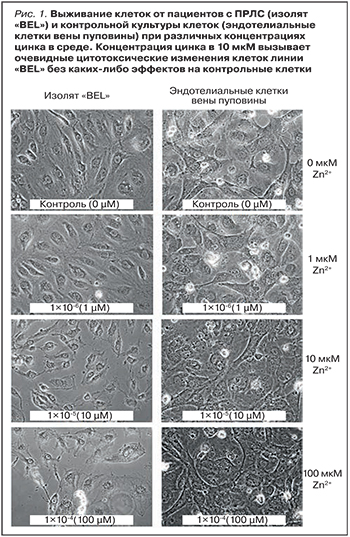
Важно подчеркнуть, что цинк предотвращает апоптоз нормально функционирующих клеток иммунной системы и, наоборот, ускоряет апоптоз абнормальных клеток: например, клеток от пациентов с пороками развития лимфатической системы (ПРЛС). Клинически ПРЛС характеризуются воспалительными эпизодами. ОРЗ верхних дыхательных путей стимулируют развитие болезненной припухлости мест локализации пороков, а цинк способствует снижению воспаления. Хлорид цинка уже при достаточно низких концентрациях (10 мкM элементарного цинка) оказывал цитотоксическое действие на линии клеток от пациентов с ПРЛС (n=10) без каких-либо очевидных эффектов на контрольные клетки (эндотелиоциты пупочной вены человека; рис. 1). Отметим, что токсическая концентрация цинка для большинства типов клеток гораздо выше и составляет ~100 мкM [25].
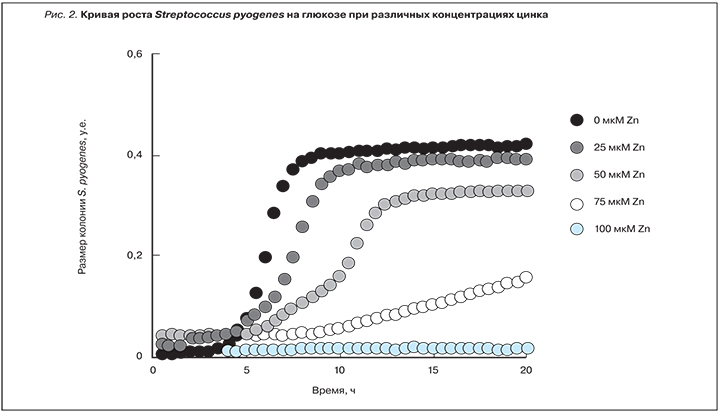
 Кроме торможения взаимодействий «вирус–рецептор», ионы цинка проявляют антибактериальный эффект. Системы врожденного иммунитета используют цинк в качестве противомикробного агента против стрептококка группы А (Streptococcus pyogenes). В частности, нейтрофилы используют ионы цинка в ответ на стрептококковую инфекцию [26]. Нейтрофилы секретируют ионы Zn2+ для обезвреживания стрептококков фагоцитами. Цинк непосредственно ингибирует рост S. pyogenes (рис. 2), ослабляя метаболизм глюкозы и снижая биосинтез липополисахаридной бактериальной капсулы [27].
Кроме торможения взаимодействий «вирус–рецептор», ионы цинка проявляют антибактериальный эффект. Системы врожденного иммунитета используют цинк в качестве противомикробного агента против стрептококка группы А (Streptococcus pyogenes). В частности, нейтрофилы используют ионы цинка в ответ на стрептококковую инфекцию [26]. Нейтрофилы секретируют ионы Zn2+ для обезвреживания стрептококков фагоцитами. Цинк непосредственно ингибирует рост S. pyogenes (рис. 2), ослабляя метаболизм глюкозы и снижая биосинтез липополисахаридной бактериальной капсулы [27].
Антимикробная активность цинкосодержащих препаратов на основе цитрата цинка и аминохелатов цинка была показана на грамположительных прокариотах рода Staphylococcus, грамотрицательных прокариотах рода Escherichia и эукариотах – грибах рода Candida. Цитрат цинка оказал выраженное антисептическое действие на все тест-культуры как на плотной, так и в жидкой питательной среде [7].
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ КЛИНИЧЕСКИХ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЙ ПРЕПАРАТОВ ЦИНКА В ТЕРАПИИ И ПРОФИЛАКТИКЕ ОРЗ
Иммуномодулирующие, антибактериальные и антивирусные эффекты ионов цинка указывают на перспективность использования препаратов цинка для терапии и профилактики ОРЗ. По данным клинических исследований и мета-анализов, пероральный прием цинка, начиная с момента появления первых симптомов ОРЗ и до выздоровления, был достоверно ассоциирован с более короткой продолжительностью простуды [28]. Напомним, что эффективность препарата, подтвержденная в результате проведения мета-анализа, представляет собой доказательность класса А [29].
Мета-анализ 13 плацебо-контролируемых клинических исследований подтвердил, что суточная доза цинка ≥75 мг достоверно ассоциирована с сокращением длительности ОРЗ на 42% (95% доверительный интервал [ДИ] 35–48%) [30]. Мета-анализ 16 рандомизированных исследований (n=1387) подтвердил, что дотации цинка в дозах >75 мг/сут приводили к значительному сокращению продолжительности ОРЗ (в среднем на 1,03 сут, 95% ДИ 0,34–1,72; р=0,003) [31]. Мета-анализ показал, что доля участников с симптоматикой ОРЗ после 7 дней терапии цинком достоверно снижалась до 45% (95% ДИ 20–99%; р=0,05). При приеме цинка риск тяжелого течения ОРЗ были достоверно ниже (отношение рисков [ОР] 0,64, 95% ДИ 0,47–0,88; р=0,006); частота назначения антибиотиков также снижалась (р<0,00001), а время купирования болей в горле укорачивалось [31].
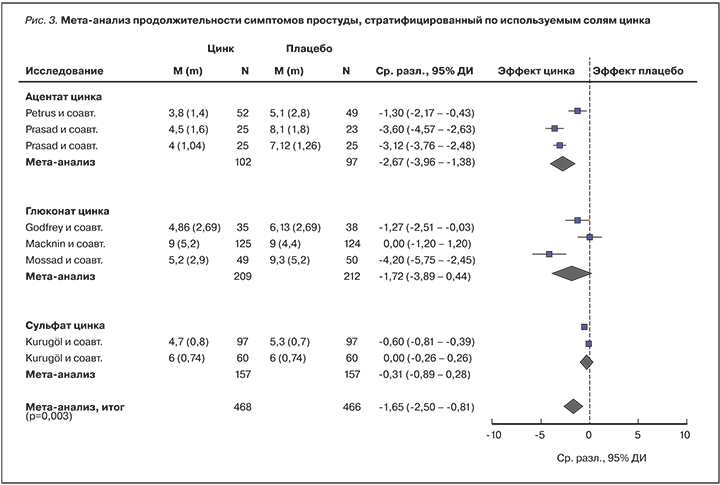
Мета-анализ 17 рандомизированных исследований (n=2121) подтвердил укорочение продолжительности симптомов ОРЗ (на 1,65 дней, 95% ДИ 0,81–2,50) и продемонстрировал значительно более выраженный эффект более высоких доз цинка (>75 мг/сут) по сравнению с его низкой дозой [32]. Данный мета-анализ также подтвердил высокую эффективность органических солей цинка (ацетат, глюконат) по сравнению с неорганическим сульфатом цинка [32]. В частности, рассасывание таблеток ацетата цинка приводит к укорочению простуды в среднем на 3-е сут (95% ДИ 2,1–3,8) независимо от возраста, пола, этнической принадлежности, статуса аллергии, курения и тяжести протекания ОРЗ (рис. 3) [33].
 Эффект воздействия ацетата цинка в составе таблеток для рассасывания на симптоматику ОРЗ может быть связан, в частности, с повышением топической доступности цинка, прежде всего в регионе слизистой оболочки зева. Неблагоприятные последствия рассасывания таблеток на основе ацетата цинка, в отличие от сульфата цинка, были незначительными (тошнота и рвота полностью отсутствовали). Поэтому ацетат цинка и другие органические соли цинка в дозах ~80 мг/сут могут быть весьма полезны для лечения простуды, если их прием начинается сразу после появления первых симптомов и продолжается в течение 2–3 нед [34]. Мета-анализ клинических испытаний органической формы цинка (ацетата цинка) показал, что его высокие дозы в форме таблеток для рассасывания (80–92 мг/сут) уменьшают продолжительность симптомов простуды. В частности, ацетат цинка сокращает продолжительность выделений из носа на 34% (от 17 до 51%), заложенности носа на 37% (от 15 до 58%), першения в горле на 33% (от 8 до 59%), охриплости на 43% (от 3 до 83%), кашля на 46% (от 28 до 64%), болей в мышцах на 54% (от 18 до 89%) [34].
Эффект воздействия ацетата цинка в составе таблеток для рассасывания на симптоматику ОРЗ может быть связан, в частности, с повышением топической доступности цинка, прежде всего в регионе слизистой оболочки зева. Неблагоприятные последствия рассасывания таблеток на основе ацетата цинка, в отличие от сульфата цинка, были незначительными (тошнота и рвота полностью отсутствовали). Поэтому ацетат цинка и другие органические соли цинка в дозах ~80 мг/сут могут быть весьма полезны для лечения простуды, если их прием начинается сразу после появления первых симптомов и продолжается в течение 2–3 нед [34]. Мета-анализ клинических испытаний органической формы цинка (ацетата цинка) показал, что его высокие дозы в форме таблеток для рассасывания (80–92 мг/сут) уменьшают продолжительность симптомов простуды. В частности, ацетат цинка сокращает продолжительность выделений из носа на 34% (от 17 до 51%), заложенности носа на 37% (от 15 до 58%), першения в горле на 33% (от 8 до 59%), охриплости на 43% (от 3 до 83%), кашля на 46% (от 28 до 64%), болей в мышцах на 54% (от 18 до 89%) [34].
МОЛЕКУЛЯРНЫЕ МЕХАНИЗМЫ ДЕЙСТВИЯ ВИТАМИНА С НА ИММУНИТЕТ
Витамин С, пожалуй, самый известный микронутриент, ассоциированный с профилактикой ОРЗ. Аскорбиновая кислота (рис. 4), основной витамер витамина С, – известный антиоксидант, обладающий, кроме того, широким спектром биологического воздействия. Аскорбиновая кислота хорошо растворяется в воде (33 г/100 мл), характеризуется крайне низкой токсичностью (LD50 внутрь 11,9 г/кг). «Кислотой» данное соединение называется вследствие довольно низкого значения рН в растворе (константа кислотной диссоциации составляет 4,1). Биологические эффекты аскорбиновой кислоты включают антиоксидантный эффект, действие на систему глутатиона, синтез катехоламинов и кортикостероидов, синтез серотонина из триптофана, преобразование фолиевой кислоты в усвояемую гидрофолиевую кислоту, улучшение фагоцитарной активности лейкоцитов, образование антител, образование волокон коллагена (гидроксилирование пролина и лизина), стимуляция системы фибробластов, превращение холестерина в желчные кислоты [35].
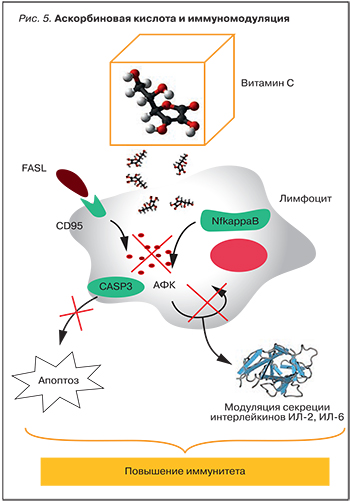
Для терапии ОРЗ особый интерес представляют иммуномодулирующие свойства аскорбиновой кислоты. Витамин C интенсивно накапливается в клетках иммунной системы и необходим для их функционирования, особенно фагоцитов и Т-клеток. Дефицит витамина приводит к снижению иммунного ответа [36]. Витамин С усиливает хемотаксис гранулоцитов, нейтрофилов и макрофагов и их фагоцитарную активность [37], также усиливая лизоцим-зависимое разрушение патогенных бактерий. Накопление витамина С в лимфоцитах оказывает значительное влияние на их выживание [38]. Аскорбиновая кислота модулирует уровни различных белков в Т-лимфоцитах в зависимости от дозы и времени воздействия. Выдерживание лимфоцитов с аскорбиновой кислотой в течение 24 ч приводит к 2-кратному увеличению уровней более 40 белков. Эти белки относятся к 5 функциональным группам: внутриклеточная сигнализация, углеводный обмен, апоптоз, транскрипция и иммунная функция [39]. Иммуномодулирующие эффекты витамина С во многом обусловлены его антиоксидантными свойствами. Аскорбиновая кислота тормозит различные формы апоптоза Т-клеток [40] через сигнальные пути FASL и Nf-κB (рис. 5).
Лиганд рецептора FAS (FASL) является одним из ключевых белков апоптоза клеток иммунной системы. Связывание лигандом FAS-рецептора (CD95) индуцирует апоптоз путем активации каспазы-3. Сигнальные пути, опосредующие этот процесс, включают увеличение уровней активных форм кислорода и высвобождение проапоптотических факторов из митохондрий, что и приводит к активации каспазы-3. Поэтому витамин C оказывает модулирующее воздействие на иммунную систему, подавляя FAS-индуцированный апоптоз лимфоцитов [41].
Внутриклеточный витамин С также модулирует воспалительные и апоптотические процессы посредством ингибирования активации транскрипционного фактора NF-κB [42]. Процессы, контролируемые белком NF-κB, имеют важное значение для секреции цитокинов, т.к. NF-κB регулирует экспрессию генов интерлейкинов. Активность NF-κB в значительной мере зависит от уровня активных форм кислорода, поэтому витамин C влияет на синтез интерлейкина-2 и секрецию интерлейкина-6. Аскорбат-дефицитные лимфоциты характеризуются нарушениями в синтезе интерлейкинов [43].
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ КЛИНИЧЕСКИХ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЙ ВИТАМИНА С В ТЕРАПИИ И ПРОФИЛАКТИКЕ ОРЗ
Кохрейновский мета-анализ 29 рандомизированных исследований по использованию витамина С (в дозах 0,25–2 г/сут) для профилактики простуды (n=10 708) показал 3%-ное снижение заболеваемости ОРЗ (OР 0,97, 95% ДИ 0,94–1,00; р=0,05), что указывает на слабую, но достоверную способность витамина С обеспечивать профилактику ОРЗ. Пять исследований с участием марафонцев, лыжников и солдат, действующих в субарктической местности (в общей сложности n=598), показали достоверно более выраженный профилактический эффект витамина С в отношении ОРЗ (ОР 0,48, 95% ДИ 0,35–0,64) [44, 45]. В том же кохрейновском мета-анализе было показано, что при приеме витамина С продолжительность ОРЗ у взрослых была снижена на 8% (3–12%), у детей – на 14% (7–21%). Тяжесть течения ОРЗ также снижалась при регулярном приеме витамина С в дозах >200 мг/сут. При приеме витамина С детьми в дозах от 1 до 2 г/сут заболеваемость ОРЗ падала на 18% [44], что подтверждает дозозависимое его действие.
Интересно отметить, что витамин С весьма полезен для профилактики и лечения ОРЗ у детей при сочетании с пробиотиками. В рандомизированном контролируемом исследовании дети 3–6 лет (n=57) в течение 6 мес получи Lactobacillus acidophilus CUL21 (NCIMB 30156), L. acidophilus CUL60, Bifidobacterium bifidum CUL20 и Bifidobacterium animalis lactis CUL34 в комбинации с витамином С по 50 мг/сут. По сравнению с плацебо отмечено достоверное снижение заболеваемости ОРЗ (-33%, р=0,002) и частоты пропусков при посещении детских дошкольных учреждений (-30%, р=0,007) [46].
О СОЧЕТАННОМ ПРИМЕНЕНИИ ЦИНКА И ВИТАМИНА С В ТЕРАПИИ И ПРОФИЛАКТИКЕ ОРЗ
Клетки иммунной системы, особенно фагоциты и Т-клетки, специфически концентрируют витамин С и цинк для осуществления своих функций. Дефициты цинка и витамина С в питании или неадекватная обеспеченность цинком и витамином С при повышенных нагрузках снижают противовирусный иммунитет [47]. Поэтому применение препаратов, включающих и цинк, и витамин С весьма перспективно в профилактике и терапии ОРЗ. Сочетание витамина С, цинка, чеснока, чернушки («черный тмин») и женьшеня сокращает время разрешения всех симптомов ОРЗ на 4 дня (95% ДИ 3–6; р<0,001) и снижает средний балл тяжести проявлений заболевания (р<0,01) [48].
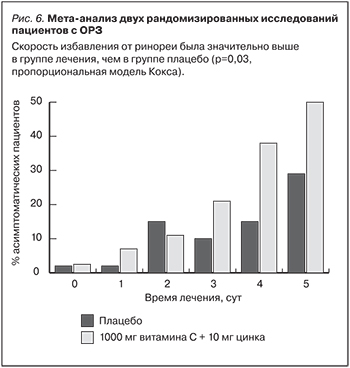
Были проведены 2 рандомизированных плацебо-контролируемых исследования с использованием шипучих таблеток цинка с витамином С (витамин С – 1000 мг, цинк – 10 мг; 1 табл./сут) [49]. Мета-анализ этих исследований показал, что сочетание «витамин С + цинк» было значительно более эффективно в плане снижения выраженности ринореи в течение 5 дней терапии по сравнению с плацебо (рис. 6). При этом тяжесть ринореи становилась достоверно ниже к 5-м сут исследования (р=0,05). В отличие от таблеток сульфата цинка сочетание «витамин С + цинк» хорошо переносилось пациентами [49].
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Ионы цинка и витамин С интенсивно накапливаются в лимфоцитах и необходимы для поддержки иммунитета. Доказательные исследования подтверждают целесообразность использования препаратов цинка и витамина С для снижения длительности ОРЗ, в т.ч. для сокращения времени регистрации отдельных симптомов.
В России зарегистрирована биологически активная добавка (БАД)1 – комбинация цинка с витамином C в виде шипучих таблеток «Цинк 10 + С» (Верваг Фарма, Германия) для приготовления раствора для питья. Одна таблетка содержит 120 мг витамина С (200% рекомендуемого суточного потребления – РСП) и 10 мг цинка (67% РСП). При помещении таблетки в воду (200 мл, т.е. 1 стакан) в растворе образуется органическая соль с высокой биодоступностью цинка и отличными органолептическими и фармакокинетическими характеристиками (до 100%) растворимости в воде – цитрат цинка. Водный раствор «Цинк 10 + С» характеризуется хорошими органолептическими свойствами, не вызывает тошноты и рвоты. «Цинк 10 + С» способствует укреплению иммунной системы и может применяться для профилактики по 1 табл./сут в виде раствора для питья.
В острый период ОРЗ целесообразно использовать цинк в дозах 70–90 мг/сут, а витамин С – в дозах 1–2 г/сут. Эффективность именно этих доз витамина С и цинка подтверждается как приводимыми выше результатами мета-анализов, так и многолетним клиническим опытом профилактики и лечения ОРЗ у детей, подростков и взрослых.
Авторы располагают собственным ограниченным клиническим опытом применения «Цинк 10 + С» в острый период ОРЗ в повышенных дозировках (до 5–7 табл./сут). Такой режим приема БАД способствует значительному сокращению сроков разрешения симптомов ОРЗ. Он может сочетаться со стандартными методами лечения ОРЗ и гриппа. Следует подчеркнуть, что суточные дозы цинка и витамина С при интенсивном применении «Цинк 10 + С» сопоставимы с использовавшимися в многочисленных клинических исследованиях по лечению и профилактике ОРЗ [30, 31, 44, 45]. Тем не менее изучение эффективности и переносимости рассмотренного режима применения «Цинк 10 + С» у различных категорий пациентов (дети, подростки, взрослые, пожилые больные, страдающие хроническими заболеваниями органов дыхания) должно быть продолжено в масштабных рандомизированных клинических исследованиях.



