ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Гиперсекреция трахеобронхиального секрета в дыхательных путях является характерной особенностью острых и хронических легочных заболеваний, таких как острый и хронический бронхит, хроническая обструктивная болезнь легких (ХОБЛ), муковисцидоз, бронхоэктатическая болезнь и бронхиальная астма. Регулярный кашель с экспекторацией мокроты (продуктивный кашель) вместе с нарушениями мукоцилиарного клиренса (МЦК) являются значимыми при клинической оценке тяжести легочного заболевания и аргументом в пользу назначения муколитических и мукоактивных препаратов. Основной механизм действия современных муколитических средств состоит в воздействии на характер секрета (снижение вязкости), объем и характер мобилизации мокроты через их взаимодействие с эпителием бронхов и бронхиол [1].
Современная классификация мукоактивных препаратов проста и базируется на их основном действии. Принято выделять экспекторанты (отхаркивающие), муколитики, мукокинетики и мукорегуляторы. Такие средства, как экспекторанты, усиливают секрецию муцинов и повышают их гидратацию (гвайфенезин, гипертонический раствор). Муколитики существенно уменьшают вязкость слизи (N-ацетилцистеин, карбоцистеин, дорназа альфа). Мукокинетики активно изменяют активность движения ресничек, что повышает мобилизацию секрета и облегчает кашель (амброксол, β2-адреноагонисты, сурфактант) [2].
В настоящее время пристальное внимание обращено к яркому представителю вазициноидов амброксолу – единственному метаболиту бромгексина, обладающему выраженным стимулирующим влиянием на МЦК. Отмечается существенное нарастание числа рандомизированных клинических исследований, изучающих его эффективность при респираторных заболеваниях с гиперсекрецией секрета при ХОБЛ [3], обострениях хронического бронхита [4–8], у пациентов с муковисцидозом [9, 10], при терапии новорожденных с болезнью гиалиновых мембран (респираторный дистресс-синдром новорожденных) [11, 12], у пациентов с бронхиальной астмой [13], при антиоксидантной терапии [14], для предупреждения бронхолегочных осложнений после торакальных вмешательств [15], при острых заболеваниях верхних дыхательных путей [16], легочных альвеолярных протеинозах [17]. В экспериментальных работах на животных изучается возможность использования амброксола для уменьшения фиброзирования легочной ткани [18].
ХИМИЧЕСКАЯ ФОРМУЛА И СВОЙСТВА МОЛЕКУЛЫ
Амброксол представляет собой производное бензиламинов – транс-4-[(2-амино-3,5-дибромбензил) амино] циклогексанола гидрохлорид. По своей химической формуле амброксола гидрохлорид представляет собой активный N-десметил-метаболит бромгексина – синтетического производного алкалоида вазицина – вещества, получаемого путем экстракции из травы Adhatoda vasica (Адатода сосудистая), которая последние девять столетий известна в аюрведической медицине арабских и европейских стран как противовоспалительное, обезболивающее, отхаркивающее, диуретическое, противоастматическое и абортивное средство, обладающее к тому же антисептическими, инсектицидными, успокоительными и противоспазматическими свойствами. Амброксол отличается от бромгексина отсутствием метильной группы и наличием гидроксильной группы в пара-транспозиции циклогексильного кольца (рис. 1).
ПЕРВИЧНАЯ ФАРМАКОЛОГИЯ АМБРОКСОЛА
Механизмы действия амброксола были тщательно исследованы в многочисленных фармакологических и клинических исследованиях на животных. Они разнообразны и включают мукокинетическое действие [19], мукоцилиарную активность [19], стимуляцию продукции сурфактанта [20, 21], противовоспалительное и антиоксидантное действие [22], а также локальные обезболивающие (анестетические) свойства [23, 24]. Рассмотрим подробнее некоторые их них.
Мукокинетическое действие
В исследованиях на животных (анестезированные кролики и морские свинки) амброксол достоверно и дозозависимо повышал бронхиальную секрецию [25]. Кроме того, он достоверно увеличивался объем жидкости в респираторном тракте животных (кролики) в течение 9 ч после назначения препарата [26]. Когда амброксол вводился интратрахеально (хорьки и собаки), дозозависимо повышалась секреция гликопротеинов муцинов [27]. Очевидно, что амброксол оказывает выраженный мукокинетический дозозависимый эффект. Наилучшим способом введения амброксола для прямого интратрахеального действия следует признать ингаляционный путь доставки (небулайзерная терапия).
Мукоцилиарная активность
В исследованиях на изолированных бронхолегочных препаратах (крысы, хомячки, кошки) амброксол усиливал цилиарную активность [28]. Достоверное усиление частоты цилиарных сокращений под действием амброксола установлено в клетках трахеи морских свинок [19]. В исследовании in situ дозозависимый эффект усиления клиренса слизи отмечен у амброксола при его топическом назначении [29]. Очевидно, что высокая мукоцилиарная активность присуща амброксолу, особенно при его топическом интрабронхиальном назначении.
Стимуляция сурфактанта
 В ряду мукоактивных средств амброксол обладает уникальными свойствами благодаря своей химической формуле. Он способен активировать сурфактантную систему легких. Хорошо известно, что сурфактант (поверхностно-активное вещество) может блокировать прилипание слизи к стенкам бронхиального дерева. Это способствует усилению транспорта слизи [30].
В ряду мукоактивных средств амброксол обладает уникальными свойствами благодаря своей химической формуле. Он способен активировать сурфактантную систему легких. Хорошо известно, что сурфактант (поверхностно-активное вещество) может блокировать прилипание слизи к стенкам бронхиального дерева. Это способствует усилению транспорта слизи [30].
Амброксол, единственный среди муколитиков, активно стимулирует продукцию сурфактанта пневмоцитами (альвеолоцитами) II типа и клетками Клара [31]. Подтверждением тому является увеличение числа меченых предшественников альвеолярного фосфатидилхолина в пластинчатом теле альвеолоцитов II типа (высокие поверхностно-активные свойства сурфактанта объясняются присутствием в нем дипальмитоилфосфатидилхолина). Регуляция уровня сурфактанта, возможно, является основным механизмом защиты от вирусов гриппа А [32]. У лабораторных животных, леченных амброксолом в дозах 100 и 200 мг/кг перорально в течение 3 и 6 дней, наблюдался выраженный объемный рост альвеолоцитов II типа с достоверным увеличением процентного соотношения пластинчатых тел к общей площади альвеолярной ткани [33]. Лечение амброксолом (200 мг/(кг×сут) перорально) сопровождалось увеличением числа включений (инкорпораций) 3H-пальмитиновой кислоты в альвеолярную ткань, что приводило к повышению синтеза легочного сурфактанта [34, 35]. Стимуляция сурфактанта отмечена в исследованиях на недоношенных и новорожденных особях. Терапия беременных крольчих амброксолом (50 мг/кг внутривенно) на 24‒26 день беременности приводила к улучшению легочной функции недоношенных плодов [36]. Интересно, что у преждевременно извлеченных недоношенных плодов, получавших внутриутробно амброксол, обнаруживалось достоверное увеличение числа зрелых альвеол [37]. Назначение амброксола [4 мг/(кг×сут)] беременным животным на 21‒24 день гестации сопровождалось улучшением созревания легочной ткани у 25-дневных преждевременно извлеченных недоношенных кроликов [38].
Действие амброксола на сурфактант изучалось у взрослых животных с острым респираторным дистресс-синдромом (ОРДС). У взрослых мини-пигов (карликовых свиней) ОРДС вызывался аспирацией соляной кислоты. Терапия амброксолом приводила к выживанию всех леченых особей, в то время как в контрольной группе все животные погибли в течение 12 ч [39]. Очевидно, что активация сурфактантной системы легких амброксолом способствует нормализации мукоцилиарного транспорта. Усиление выработки сурфактанта альвеолоцитами II типа под действием амброксола является главным защитным механизмом, способным противодействовать вирусной инфекции и острому поражению легочной ткани (ОРДС). Наилучшим способом доставки амброксола является ингаляционный путь для прямого внутрибронхиального действия.
Антиоксидантная и противовоспалительная активность
Способность амброксола поглощать свободные радикалы была изучена и документирована в серии исследований [40‒44]. Они демонстрируют способность амброксола к защите легочной системы от оксидативного стресса и свободных радикалов, образующихся при вдыхании табачного дыма, ингаляции токсических веществ, а также активности нейтрофилов и альвеолярных макрофагов [45]. Так, назначение амброксола защищало сердце мыши от перекисного окисления липидов, индуцированного назначением цитостатиков (доксорубицин) [46].
Противовоспалительные свойства амброксола исследованы при оценке воспалительных эффектов нейтрофилов, макрофагов и тучных клеток.
Доказано, что амброксол способен:
- подавлять продукцию супероксид-аниона и хлорноватистой кислоты (HOCl);
- сдерживать экзоцитоз эластазы и первичных миелопероксидаз позитивных гранул;
- нарушать продукцию HOCl путем уменьшения доступа к миелопероксидазе;
- непосредственно поглощать HOCl и защищать α1-антитрипсин от нейтрофильно индуцированной инактивации;
- восстанавливать мощность антипротеазных комплексов;
- инактивировать эластазы [47].
Амброксол достоверно снижает индуцированный липополисахаридом синтез цитокинов в альвеолярных макрофагах крыс и липополисахарид-индуцированную продукцию оксида азота [48, 49].
Амброксол достоверно уменьшает уровень гистамина и высвобождение фактора роста тучных клеток и моноцитов легких, кожи и кишечника. Указанные реакции ответственны за развитие острой фазы реакции гиперчувствительности немедленного типа с высвобождением гистамина, который приводит к сокращению гладких мышц, вазодилатации и усилению сосудистой проницаемости. Доказано, что амброксол уменьшает бронхиальную констрикцию путем подавления выброса гистамина и лейкотриенов [50‒52].
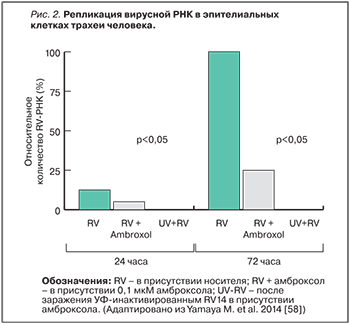
Противовоспалительные свойства амброксола были дополнительно изучены в острой модели повреждения легких. Амброксол уменьшал липополисахарид-индуцированное легочное кровотечение, отек, экссудацию и нейтрофильную инфильтрацию. При терапии амброксолом достоверно уменьшались концентрация белка, фактора некроза опухоли α, интерлейкина-6 и трансформирующего ростового фактора β1 в бронхоальвеолярной лаважной жидкости [53, 54]. Нужно отметить, что в серии исследований амброксола установлен его защитный эффект в отношении легочной ткани [55‒56]. При гриппозной инфекции амброксол подавлял размножение (мультиплицирование) вируса в жидких средах дыхательных путей, что достоверно повышало выживаемость мышей, инфицированных вирусом гриппа А [57]. Интерес представляет влияние амброксола на 14-й тип риновирусной инфекции RV14 (основной в группе риновирусов) в первичной культуре эпителиальных клеток трахеи человека. Амброксол уменьшал титры RV14 и концентрации цитокинов (интерлейкинов-1β, 6 и 8), снижал экспрессию ICAM-1 и количество кислых эндосом, уменьшал активацию фактора транскрипции ядерного фактора κВ (NF-κB) в ядре [58] (рис. 2).
Таким образом, антиоксидантные свойства амброксола как вещества, поглощающего свободные радикалы, не вызывают сомнений. Противовоспалительное действие амброксола связано с активным подавлением высвобождения гистамина и уменьшением синтеза лейкотриенов в ткани легкого, что обеспечивает защитную функцию при остром поражении легкого (ОРДС) или вирусной инфекции дыхательных путей.
Местный (локальный) обезболивающий (анестезирующий) эффект
Несмотря на то что местное анестезирующее свойство амброксола было описано впервые в 1977 г., его основной молекулярный механизм действия был мало понятен. В настоящее время имеются неопровержимые доказательства того, что амброксол является мощным ингибитором нейронного вольтаж-зависимого натриевого канала, с чем и связывают его локальное анестезирующее действие [59]. Очевидно, что этот эффект амброксола, связанный с ингибированием нейронного натриевого канала, способен обеспечить подавление кашля и болевого компонента (першение в горле) при острых респираторных инфекциях дыхательных путей.
КЛИНИЧЕСКАЯ ФАРМАКОКИНЕТИКА И МЕТАБОЛИЗМ
Существует многообразие лекарственных форм амброксола: внутривенные и внутримышечные растворы, сиропы, гранулы, таблетки, капсулы, суппозитории и медленно высвобождающиеся оральные препараты. После внутривенной инфузии амброксола его общий плазматический клиренс составит 660 мл/мин, в то время как почечный клиренс 53 мл/мин, не превышая 8% от общего [60].
 Объемное распределение амброксола высокое (около 560 л, с более чем 17-кратным преоладанием в легких по сравнению с плазмой крови), в силу чего период его полувыведения признается длительным (10 ч). Абсолютная биодоступность после перорального приема составит 79%, а устойчивый дозозависимый эффект сохраняется в диапазоне от 30 до 500 мг для таблетированных форм. Абсорбция (поглощение) быстрое, Tmax 1,6 ч. Связывание с белками плазмы составляет 90% [61].
Объемное распределение амброксола высокое (около 560 л, с более чем 17-кратным преоладанием в легких по сравнению с плазмой крови), в силу чего период его полувыведения признается длительным (10 ч). Абсолютная биодоступность после перорального приема составит 79%, а устойчивый дозозависимый эффект сохраняется в диапазоне от 30 до 500 мг для таблетированных форм. Абсорбция (поглощение) быстрое, Tmax 1,6 ч. Связывание с белками плазмы составляет 90% [61].
Амброксол в основном выводится из организма посредством биотрансформации, в которой первая фаза представлена метаболитами 3,5-дибромантраниловой кислоты, а вторая – разнообразными глюкуронидами. Как было показано, цитохром P450 3A4 ответственен за оксидативный метаболизм амброксола. Однако никаких существенных взаимодействий «лекарство‒лекарство» при назначении амброксола установлено не было [62].
Таким образом, разнообразные формы амброксола обладают длительными клиническими эффектами с большим «терапевтическим окном» дозировок. Отмечено быстрое, устойчивое распределение амброксола в плазме с преимущественным накоплением в ткани легкого. Лекарственных взаимодействий амброксола с другими лекарственными средствами в границах терапевтических дозировок не установлено.
КЛИНИЧЕСКИЕ ДОКАЗАТЕЛЬСТВА ЭФФЕКТИВНОСТИ АМБРОКСОЛА
Анализ клинических данных о применении мукоактивных субстанций в терапии неинфекционных заболеваний человека сопряжен с рядом существенных трудностей. Во-первых, подавляющее число исследований выполнено более 40 лет назад, когда руководство по «надлежащей клинической практике» (GCP) не являлось общепринятым. Во-вторых, исследование механизмов легочных заболеваний, ассоциированных с кашлем и продукцией мокроты, находилось тогда в «зачаточном» состоянии. Зачастую отсутствовали согласительные документы по диагностике и лечению хронических респираторных заболеваний, например бронхита, ХОБЛ, эмфиземы, бронхиальной астмы [63].
Клиническая оценка влияния хронического кашля с продукцией мокроты на заболеваемость и смертность пациентов с легочной патологией исследовалась в середине 90-х гг. ХХ в. Установлено, что у пациентов с гиперсекрецией мокроты 54% случаев смертей вызывалось инфекцией нижних дыхательных путей в сравнении с 28% у пациентов без гиперсекреции мокроты. Хроническая гиперсекреция мокроты стала признаваться достоверным предиктором смерти больных ХОБЛ, ассоциированной с инфекцией нижних дыхательных путей (относительный риск 3,5), в отличие от аналогичных смертей без такой инфекции (относительный риск 0,9) [64].
Это позволило изменить взгляд на дальнейшие исследования мукоактивных препаратов. Первичными конечными точками клинических исследований стали:
- влияние препарата на смертность;
- влияние препарата на обострения болезни;
- влияние препарата на состояние здоровья и качество жизни.
Из базы данных клинических исследований амброксола нами были отобраны 92 исследования, отвечающие требованиям GCP и применимые для правильной оценки клинической эффективности при лечении острых и хронических заболеваний нижних дыхательных путей у взрослых и детей.
Эффекты лечения амброксолом взрослых
Все исследования нами подразделялись на кратковременные (<2 нед) и долгосрочные (>4 нед). Учитывая требование рандомизации, ослепления, наличия групп плацебо или активного контроля, только 3 из 24 краткосрочных и 7 из 12 долгосрочных исследований были включены в анализ. Несмотря на положительные результаты, остальные 68 исследований не рассматривались по причине плохого дизайна (открытое, не контролируемое, небольшое число пациентов, малопонятные разовые дозы).
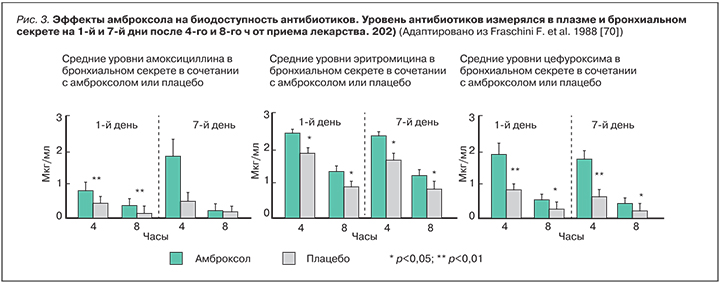
Кратковременные исследования (<2 нед). Первичные конечные точки кратковременных исследований нацелены на изменение респираторных симптомов, количества/качества слизи, продуктивности кашля, откашливания слизи, показателей проходимости воздуха по бронхиальному дереву (объем форсированного выдоха за 1 с [ОФВ1]), пиковая скорость выдоха [ПСВ]). Три исследования отмечают выраженную клиническую эффективность амброксола в улучшении респираторных симптомов, облегчении откашливания, уменьшении образования слизи [65], снижении объема и вязкости мокроты [4], уменьшение числа пациентов, не отвечающих на терапию [66]. Функция внешнего дыхания (ФВД) оценивалась во всех выбранных исследованиях, и, как ожидалось, амброксол не оказывал влияни на показатель ОФВ1, ни на ПСВ [4, 65–67]. В исследовании Germouty и Jirou-Najou (1987), в котором амброксол назначался вместе с антибиотиком и приводилось сравнение клинической эффективности комбинации в сравнении с плацебо, установлено, что он повышает концентрацию антибиотика в легочной ткани и слизи, что является уникальным свойством этого мукоактивного вещества [67]. В двойном плацебо-контролируемом исследовании Fraschini (1988) 60 больным ХОБЛ с гнойной мокротой, разделенных на 3 группы, назначался амоксицилин, эритромицин или цефуроксим (все по 1500 мг/сут) вместе с амброксолом (90 мг/сут) в течение 7 дней. Уровень антибиотиков измерялся в плазме и бронхиальном секрете на 1-й и 7-й дни после 4-го и 8-го ч от приема лекарства. В сравнении с плацебо комбинация с амброксолом достоверно повышала уровень антибиотика в бронхиальном секрете (p <0,05), но не в плазме [68] (рис. 3).
Эффекты краткосрочного влияния амброксола на легочный МЦК изучался в группе пациентов с ХОБЛ с нарушениями МЦК. У больных ХОБЛ с выраженным нарушением МЦК амброксол достоверно улучшал клиренс, хотя общие изменения оставались умеренными [4]. Однако в исследованиях по изучению индекса проникновения (т.е. насколько глубоко в дыхательных путях распространяются меченные радиоактивные частицы вещества) амброксол достоверно его увеличивал в каждом наблюдении. Полученные результаты позволяют предполагать, что амброксол уменьшает обструкцию мелких воздухоносных путей (бронхиолы и бронхи) за счет усиления клиренса мокроты. Такое же влияние на индекс проникновения наблюдался также у бромгексина в отличие от других муколитиков (гуайфенесин, 2-меркаптоэтана сульфонат, N-ацетилцистеин, которые никогда не обнаруживали подобных эффектов [69].
Долгосрочные исследования (>4 нед). Пять отобранных исследований являлись рандомизированными, двойными слепыми, плацебо-контролируемыми [5, 70–73]. В 5 из 7 исследований длительность терапии амброксолом превышала 6 мес, и первичными конечными точками в 4 из них являлись частота обострений ХОБЛ и число дней нетрудоспособности [71]. Вторичные конечные точки исследования оценивали объем мокроты, физическое состояние, симптомы заболевания (кашель и продукцию мокроты), а также показатели ФВД. Доза амброксола составляла 75 мг/сут в исследованиях продолжительностью ≥6 мес и 120 мг/сут в 2 исследованиях продолжительностью в 4 нед [73].
В исследовании АМЕТИСТ (2004) назначение больших доз амброксола (120 мг/сут) пациентам с ХОБЛ, не использующим ингаляционные глюкокортикостероиды, приводило к максимальному снижению числа обострений, дней нетрудоспособности и числа госпитализаций [7]. Отмечено, что обострения заболевания (в особенности связанные с госпитализацией) значительно удорожают стоимость лечения больных ХОБЛ [74].
Установлено, что терапия амброксолом не изменяла показателей ФВД. Амброксол не оказывал влияния на симптомы заболевания, определяемые по результатам анкетирования качества жизни больных ХОБЛ. Несмотря на хороший дизайн исследования (критерии включения/исключения, статистические методы), размер выборки и длительность наблюдения не полностью соответствовали требованиям полной оценки опросника QoL [75]. Слабое влияния амброксола на респираторные симптомы объясняется малой продолжительностью муколитической терапии, поскольку в большинстве исследований влияния пролонгированных бронходилататоров, ингаляционных стероидов на пациентов с ХОБЛ предусматривается продолжительность терапии не менее 1 года.
Клиническая безопасность амброксола
В форме лекарства амброксол появился на рынке с 1973 г. Безопасность применения амброксола основывается на его применении более чем у 15 000 пациентов более чем в 100 исследованиях, на общей группе в 4,789,563 пациенто-лет, о чем официально сообщалось в Periodic Safety Update Report. К редко встречаемым реакциям на применение амброксола можно отнести кожные высыпания, тошноту и рвоту, боли в животе, диспепсию, анафилактические реакции. Частота встречаемости нежелательных реакций не превышала таковую для других мукоактивных препаратов. Амброксол может быть в целом расценен как высоко безопасная мукоактивная субстанция, он хорошо переносится взрослыми и детьми [76].
СОВРЕМЕННАЯ ДОКТРИНА МУКОЛИТИЧЕСКОЙ ТЕРАПИИ
В ходе многолетней врачебной практики амброксол признается субстанцией, активно влияющей на базовые механизмы физиологической продукции и транспорта бронхиальной слизи. Он обладает выраженным муколитическим и секретомоторным действием, восстанавливает физиологические механизмы очистки дыхательных путей, способствует предотвращению «прилипания» вязкого секрета, снижает сопротивление дыхательных путей и способствует бронхоальвеолярной аэрации. Благодаря своим уникальным механизмам действия амброксол в состоянии восстановить и улучшить защиту легких от инфекции (естественные защитные силы). Он оказывает противовоспалительный и антиоксидантный эффекты, полезные с точки зрения уравновешивания воспалительных реакций, облегчения симптомов кашля и простуды [76].
Анализ клинических свойств амброксола указывает на необходимость его использования в схемах лекарственной терапии у пациентов с бронхолегочными заболеваниями и гиперсекрецией слизи. Таким образом, очерчивается основная группа пациентов, у которых муколитическая терапия способна уменьшить число обострений заболевания и создает условия для постоянного поддержания «бронхиальной гигиены». В силу этого показаниями к применению амброксола являются:
- E84.0 Кистозный фиброз с легочными проявлениями.
- J01 Острый синусит.
- J02 Острый фарингит.
- J04 Острый ларингит и трахеит.
- J04.1 Острый трахеит.
- J18 Пневмония без уточнения возбудителя.
- J20 Острый бронхит.
- J20-J22 Другие острые респираторные инфекции нижних дыхательных путей.
- J22 Острая респираторная инфекция нижних дыхательных путей неуточненная.
- J31 Хронический ринит, назофарингит и фарингит.
- J32 Хронический синусит.
- J37 Хронический ларингит и ларинготрахеит.
- J40 Бронхит, не уточненный как острый или хронический.
- J40-J47 Хронические болезни нижних дыхательных путей.
- J42 Хронический бронхит неуточненный.
- J44 Другая хроническая обструктивная легочная болезнь.
- J45 Астма.
- J47 Бронхоэктатическая болезнь [бронхоэктаз].
- P22 Дыхательное расстройство у новорожденного [дистресс].
- R05 Кашель.
- R09.3 Мокрота.
- Z100 КЛАСС XXII Хирургическая практика.
Средние суточные дозы амброксола
Даже допуская вариации дозировок амброксола, разумным считается диапазон от 1,2 до 6 мг/кг массы тела. Внутри данного диапазона амброксол не имеет значимых побочных эффектов. Необходимо помнить, что максимальную суточную дозу необходимо разделить на 2‒3 приема, связав их с приемами пищи. От вечернего/ночного приема лекарства рекомендовано воздержаться из-за снижения активности реснитчатого эпителия в период сна. Надо признать, что такая рекомендация не имеет жесткого характера.
Способ доставки амброксола
Установлено, что чем выше концентрация и «прямота» действия (отсутствие дополнительного метаболизма), тем выраженнее эффекты амброксола. Рекомендуется инициировать терапию амброксолом с ингаляционного пути введения посредством небулайзера непосредственно в трахеобронхиальный отдел дыхательной системы. Преимущества неоспоримы:
- очевидная возможность широкого варьирования дозы;
- местные анестезирующие эффекты амброксола (прекращается першение и уменьшается кашель);
- высокая локальная концентрация препарата.
Кроме того, мелкая дисперсия и значительная респирабильная фракция обеспечивают проникновение лекарства в дистальные отделы бронхов, позволяя реализовывать прямое муколитическое, секретомоторное, противовоспалительное и антиоксидантное действие. Изменение агрегатного состояния раствора при небулизации вызывает его охлаждение, поэтому для правильной ингаляционной терапии амброксол необходимо согреть до 26-29 оС (чтобы не вызвать рефлекторного кашля и бронхоспазма). Продолжительность ингаляционной терапии должна составлять 7 дней, несмотря на то что первые эффекты возможны уже через 1,5‒3 ч от ее начала. На практике активная фаза муколитической терапии никогда не бывает меньше 7 дней, да и простудные проявления проходят обычно к 7 дню. Именно в эти семь дней существует высокая необходимость обеспечения эффективного муколитического и секретомоторного действия для поддержания адекватного МЦК.
Амброксол разумно использовать для противовоспалительной и антиоксидантной терапии пациентов с хроническими заболеваниями легких (например, ХОБЛ). В таком случае назначают прием таблетированных форм препарата (для взрослых). Действие амброксола по защите легочной ткани начинается на 2 нед терапии, в связи с чем рекомендуется длительная схема применения пролонгированных форм амброксола в среднесуточной дозе 75‒120 мг/сут, длительностью от 1 до 12 мес. Безопасность и эффективность такой терапии доказана в исследовании АМЕТИСТ [7]. Длительная терапия амброксолом также необходима при остром поражении легких, когда воздействие на сурфактантную систему является первоочередной задачей. В таких случаях целесообразна как внутривенная, так и ингаляционная доставка препарата в течение 6‒8 мес. Рекомендуются средние суточные терапевтические дозы, исходя из веса тела пациента. Сочетание внутривенного и ингаляционного путей доставки амброксола у пациентов с пневмонией повышает потенциал антибиотикотерапии, поскольку происходит усиление накопления лекарства в пораженном легком. Очевидно, что длительность такого лечения должна превышать одну неделю. В этом случае можно ожидать развития антиоксидантных и противовоспалительных эффектов амброксола. Применение указанной схемы в течение одного месяца формирует устойчивую «барьерную защиту» у лиц, перенесших пневмонию. У таких пациентов отмечено уменьшение риска последующих рецидивов вирусных инфекций и вероятности простудных явлений.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Разнообразные лекарственные формы амброксола хорошо изучены при различных формах острых и хронических воспалительных заболеваний верхних и нижних дыхательных путей. Новое прочтение свойств амброксола с позиции «медицины, основанной на доказательствах», открывает новую страницу современной доктрины муколитической терапии. Многофункциональная концепция муколитической терапии амброксолом основана на знании особенностей фармакокинетики и метаболизма препарата, установленных в ходе научных исследований. Руководствуясь почти полувековым опытом использования различных лекарственных форм амброксола, разумно применять в широкой терапевтической практике различные схемы терапии этим препаратом. Современные схемы муколитической терапии позволяют практикующему врачу добиваться уменьшения числа обострений и госпитализаций пациентов с хроническими легочными заболеваниями, а значит, существенно влияют на прогноз и течение хронического заболевания с гиперсекрецией слизи и нарушениями физиологического механизма мукоцилиарного транспорта бронхиального секрета.



