АКТУАЛЬНОСТЬ
Фибрилляция предсердий (ФП) остается наиболее распространенным нарушением ритма сердца у взрослых, требующим лечения. Она ассоциирована с высокой заболеваемостью и смертностью, что приводит к значительной нагрузке на пациентов, общественное здоровье и экономику здравоохранения. В настоящее время ФП выявляют у 2–4% взрослого населения, при этом ожидается рост ее распространенности более чем в два раза из-за увеличения продолжительности жизни, а также более активного поиска недиагностированной ФП [1].
К наиболее тяжелым осложнениям ФП относятся ишемический инсульт (ИИ) и системные эмболии (СЭ), обусловленные тромбообразованием в ушке или полости левого предсердия. У больных неклапанной формой ФП риск ИИ повышается примерно в 6 раз, а при митральном стенозе – почти в 17 [2, 3]. В структуре тромбоэмболических осложнений у пациентов с ФП на ИИ приходится более 90%. При этом среди различных типов ИИ кардиоэмболический ассоциирован с наихудшим прогнозом, обусловленным высокой смертностью и развитием стойкой инвалидности [4].
Единственной группой лекарственных препаратов, позволяющих снизить риск развития ИИ и системных тромбоэмболий, являются антикоагулянты [5]. Согласно современным клиническим рекомендациям, основой стратификации тромбоэмболического риска у пациентов с ФП служит шкала CHA2DS2-VASc. Антикоагулянтная терапия показана мужчинам, имеющим ≥2 баллов, и женщинам с ≥3 баллами по этой шкале. При наличии только одного дополнительного фактора риска развития тромбоэмболических осложнений следует рассмотреть назначение антикоагулянтов с учетом индивидуальных характеристик, предпочтений пациента и риска развития кровотечений, если же таких факторов риска нет, то антитромботическая терапия не показана [1, 4].
Первым пероральным антикоагулянтом, вошедшим в клиническую практику, стал варфарин, который ингибирует VKORC1 субъединицу эпоксид-редуктазного комплекса и тем самым нарушает синтез витамин-K-зависимых факторов свертывания крови, к которым относятся факторы II, VII, IX и X, а также антикоагулянтные белки C и S. Практическое применение нашли и некоторые другие антагонисты витамина К (АВК) – производные кумарина (аценокумарол) и индандиона (фенилин). Проведенные исследования показали, что применение варфарина у больных ФП снижает относительный риск (ОР) развития инсультов на 64%, а общую смертность – на 26% [6]. Несмотря на доказанную эффективность в предупреждении ИИ и СЭ у пациентов с ФП, применение АВК имеет ряд существенных недостатков. К их числу следует отнести наличие индивидуальной чувствительности, узкий терапевтический диапазон, большое количество межлекарственных взаимодействий, медленное развитие эффекта при инициации терапии и его длительное угасание после ее отмены, а также высокую частоту геморрагических осложнений. Узкий терапевтический диапазон и риск передозировки требуют регулярного лабораторного контроля коагулограммы с оценкой уровня международного нормализованного отношения (МНО) и коррекции дозировки применяемого АВК. Все это сделало актуальным разработку новых лекарственных препаратов, имеющих более стабильный и предсказуемый антикоагулянтный эффект, а также меньший риск геморрагических осложнений.
Начиная с 2010 г., в Европе, США и России были зарегистрированы и одобрены к применению у пациентов с ФП четыре новых (прямых) оральных антикоагулянта (ПОАК), являющихся селективными ингибиторами Xa фактора свертывания (ривароксабан, апиксабан и эдоксабан) или прямым ингибитором тромбина (дабигатрана этексилат). Действующие отечественные и международные рекомендациями отдают предпочтение ПОАК перед АВК для профилактики инсульта у пациентов с ФП, которым показана антикоагулянтная терапия, за исключением больных с механическими протезами клапанов сердца, митральным стенозом средней и тяжелой степени тяжести, антифосфолипидным синдромом, тяжелой хронической болезнью почек (ХБП), а также в период беременности и лактации [1, 4].
ПРЯМЫЕ ОРАЛЬНЫЕ АНТИКОАГУЛЯНТЫ У ПАЦИЕНТОВ С ФИБРИЛЛЯЦИЕЙ ПРЕДСЕРДИЙ В ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯХ РЕАЛЬНОЙ ПРАКТИКИ
Несмотря на то что все ПОАК в рамках многоцентровых клинических исследований продемонстрировали как минимум не меньшую эффективность и лучший профиль безопасности по сравнению с варфарином [7–10], выбор препарата среди ПОАК часто вызывает затруднение у практикующих врачей. Рандомизированные исследования по сравнению эффективности и безопасности ПОАК между собой вплоть до настоящего времени отсутствуют.
В последние годы опубликованы результаты целого ряда исследований реальной клинической практики (в том числе регистров, анализов баз данных страховых компаний и электронных медицинских архивов), а также их метаанализов, посвященных сравнению результатов применения различных ПОАК. Основные характеристики и результаты этих исследований представлены в таблице.
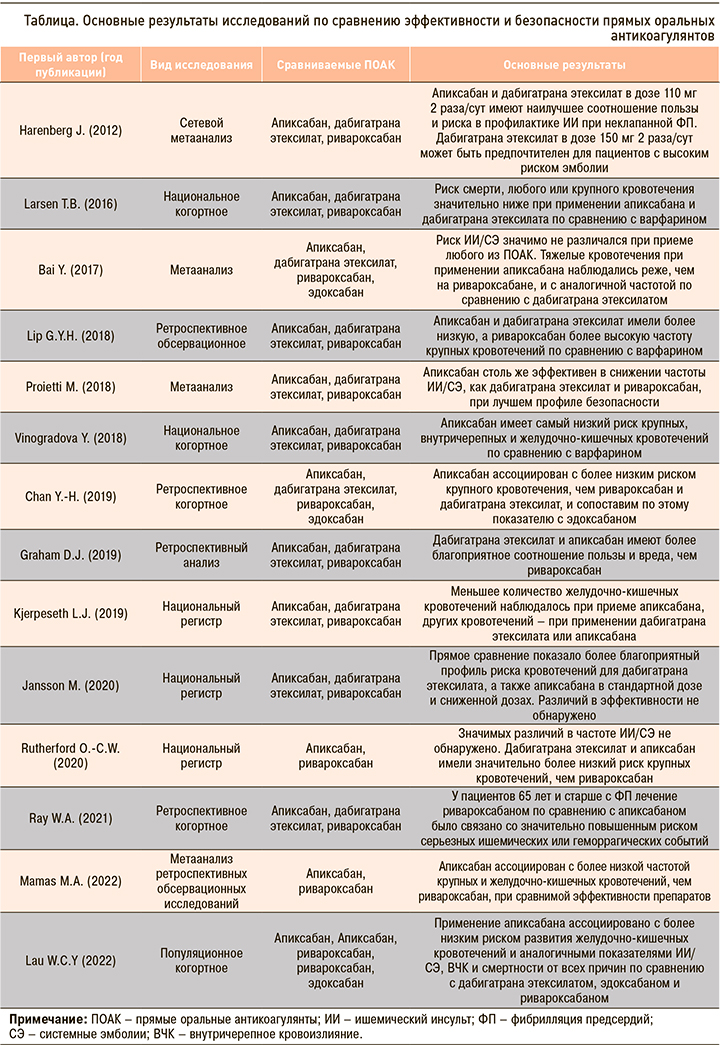
Harenberg J. et al. (2012) провели сетевой метаанализ регистрационных исследований, в которых дабигатрана этексилат, ривароксабан и апиксабан сравнивались с варфарином у пациентов с ФП. Наибольшую эффективность в снижении риска ИИ/СЭ показал дабигатрана этексилат в дозе 150 мг 2 раза/ сут, превзошедший в этом отношении дабигатрана этексилат 110 мг 2 раза/сут (р=0,0364) и ривароксабан (р=0,0388). Апиксабан обладал эквивалентной эффективностью с ривароксабаном и дабигатрана этексилатом (в любой дозе) и большей безопасностью (меньшая частота крупных кровотечений), чем дабигатран (150 мг 2 раза/сут, р=0,036) или ривароксабан (р=0,0002). Внутримозговое кровоизлияние происходило с одинаковой частотой при приеме всех препаратов, за исключением ривароксабана (более высокий риск, чем у дабигатрана этексилата в дозе 110 мг 2 раза/сут, р=0,007). Инфаркт миокарда случался реже при применении апиксабана и ривароксабана по сравнению с любой дозой дабигатрана этексилат (все р <0,05) [11].
В анализ трех Датских национальных баз данных были включены 61 678 пациентов с неклапанной ФП, не принимавших ранее антикоагулянты. Больные были распределены на группы в зависимости от проводившейся антикоагулянтной терапии: группа варфарина (n=35 436), дабигатрана этексилата 150 мг (n=12 701), ривароксабана 20 мг (n=7192) и апиксабана 5 мг (n=6349). При оценке частоты развития ИИ значимых различий между всеми ПОАК и варфарином выявлено не было, однако ежегодный риск смерти был значительно ниже в группах апиксабана (5,2%; ОР 0,65; 95% доверительный интервал (ДИ): 0,56–0,75) и дабигатрана (2,7%; ОР 0,63; 95% ДИ: 0,48–0,82) по сравнению с варфарином (8,5%), но не с ривароксабаном (7,7%). Частота всех кровотечений за год у апиксабана (3,3%) и дабигатрана этексилата (2,4%) была значимо ниже, чем у варфарина (5,0%) и ривароксабана (5,3%) [12].
Bai Y. et al. (2017) выполнили метаанализ 30 исследований для оценки эффективности и безопасности апиксабана в сравнении с варфарином, ривароксабаном, дабигатрана этексилата или эдоксабаном у пациентов с ФП. Риск ИИ/СЭ при приеме апиксабана был аналогичен ривароксабану, дабигатрана этексилату и эдоксабану, однако крупные кровотечения на фоне терапии апиксабаном в исследованиях реальной клинической практики происходили реже, чем на дабигатрана этексилате (ОР 0,45; 95% ДИ: 0,38–0,53), и с той же частотой, что на дабигатране (ОР 1,44; 95% ДИ: 0,33–6,30) [13].
Proietti М. et al. (2018) был проведен систематический обзор и метаанализ 16 наблюдательных исследований из реальной практики, сравнивавших апиксабан с другими доступными пероральными антикоагулянтами. Апиксабан оказался столь же эффективен, как дабигатрана этексилат и ривароксабан, в снижении частоты ИИ/СЭ, и имел значимо меньший риск крупных кровотечений по сравнению с варфарином, дабигатрана этексилатом и ривароксабаном (снижение ОР на 38, 35 и 46% соответственно). Риск внутричерепного кровоизлияния (ВЧК) также был значительно ниже для апиксабана, чем для варфарина и ривароксабана (46 и 54% соответственно), но не для дабигатрана этексилата. Вероятность желудочно-кишечного кровотечения (ЖКК) была меньше при использовании апиксабана по сравнению со всеми остальными пероральными антикоагулянтами (р <0,00001 для всех сравнений) [14].
Lip G.Y.H. et al. (2018) провели ретроспективное обсервационное исследование пациентов с неклапанной ФП, принимавших апиксабан, дабигатрана этексилат, ривароксабан или варфарин, которое включило анализ баз данных медицинских центров США. Апиксабан (ОР 0,61; 95% ДИ: 0,54–0,69), дабигатрана этексилат (ОР 0,80; 95% ДИ: 0,68–0,94) и ривароксабан (ОР 0,75; 95% ДИ: 0,69–0,82) имели более низкие показатели ИИ/СЭ по сравнению с варфарином. При приеме апиксабана (ОР 0,58; 95% ДИ: 0,54–0,62) и дабигатрана этексилата (ОР 0,73; 95% ДИ: 0,66–0,81) отмечалась более низкая, а при применении ривароксабана (ОР 1,07; 95% ДИ: 1,02–1,13) более высокая частота крупных кровотечений относительно варфарина [15].
В анализ двух баз данных первичной медицинской помощи Великобритании вошли пациенты, принимавшие варфарин (n=132 231), ривароксабан (n=37 863), апиксабан (n=18 223) или дабигатрана этексилат (n=7744); среди них 103 270 больных получали антикоагулянты по поводу ФП. У пациентов с этим заболеванием прием апиксабана по сравнению с варфарином был связан со снижением риска крупных кровотечений (ОР 0,66; 95% ДИ: 0,54–0,79) и внутричерепного кровотечения (ОР 0,40; 95% ДИ: 0,25–0,64), а использование дабигатрана этексилата было ассоциирован со снижением риска только внутричерепного кровотечения (ОР 0,45; 95% ДИ: 0,26–0,77). Авторы пришли к выводу, что апиксабан является самым безопасным антикоагулянтным препаратом, имеющим наименьший риск крупных ВЧК и ЖКК по сравнению с варфарином [16].
Chan Y.-H. et al. (2019) сравнили эффективность и безопасность ПОАК и варфарина в азиатской популяции, проанализировав данные Тайваньского национального ретроспективного когортного исследования. Пациенты с ФП были разделены на группы, принимавших эдоксабан (n=4577), апиксабан (n=9952), ривароксабан (n=33 022), дабигатрана этексилат (n=22 371) и варфарин (n=19 761). Все ПОАК имели более низкий риск ИИ/СЭ и крупных кровотечений, чем варфарин. Применение апиксабана было ассоциировано с более низким риском крупного кровотечения, чем прием ривароксабана и дабигатрана этексилата, и сопоставимо по этому показателю с эдоксабаном [17].
В ретроспективное когортное исследование Graham D.J. et al. (2019) вошли пациенты с неклапанной ФП, зарегистрированные в системе Medicare (США), которые начали принимать варфарин (n=183 318) или стандартные дозы дабигатрана этексилата (n=86 198), ривароксабана (n=106 389) или апиксабана (n=73 039). Частота тромбоэмболического инсульта была сопоставима у всех ПОАК, однако прием ривароксабана был ассоциирован с повышенным риском ВЧК (по сравнению с дабигатрана этексилатом: ОР 1,71; 95% ДИ: 1,35–2,17), крупного экстракраниального кровотечения (по сравнению с дабигатраном: ОР 1,32; 95% ДИ: 1,21–1,45; по сравнению с апиксабаном: ОР 2,70; 95% ДИ 2,38–3,05) и смерти (в сравнении с дабигатраном: ОР 1,12; 95% ДИ: 1,01–1,24; в сравнении с апиксабаном: ОР 1,23; 95% ДИ: 1,09–1,38). Использование дабигатрана этексилата, с одной стороны, ассоциировалось со снижением риска ВЧК (ОР 0,70; 95% ДИ: 0,53–0,94), но с другой – с повышением вероятности крупного экстракраниального кровотечения (ОР 2,04; 95% ДИ: 1,78–2,32) по сравнению с апиксабаном [18].
По данным Норвежского национального регистра в течение 1 года наблюдения все ПОАК были столь же эффективны в профилактике ИИ/СЭ, как и варфарин. Пациенты, принимавшие ПОАК, имели меньшее количество ВЧК, а также меньшее количество ЖКК при приеме апиксабана и других кровотечений при использовании дабигатрана этексилата и апиксабана [19].
В другом Норвежском регистре было выполнено прямое попарное сравнение показателей эффективности и безопасности апиксабана, дабигатрана этексилата и ривароксабана между собой (n=52 476). Значения отношения шансов (ОШ) развития ИИ/СЭ составили 0,88 (95% ДИ: 0,76– 1,02) для дабигатрана этексилата и ривароксабана, 0,88 (95% ДИ 0,75–1,02) для дабигатрана этексилата и апиксабана и 1,00 (95% ДИ 0,89–1,14) для апиксабана против ривароксабана. В отношении риска крупного кровотечения ОШ равнялось 0,75 (95% ДИ 0,64–0,88) для дабигатрана этексилата по сравнению с ривароксабаном, 1,03 (95% ДИ 0,85–1,24) для дабигатрана этексилата относительно апиксабана и 0,79 (95% ДИ 0,68–0,91) для апиксабана в сопоставлении с ривароксабаном [20].
При изучении Шведского регистра качества антикоагулянтов, в который были включены 25 843 пациента с неклапанной ФП, было проведено прямое сравнение эффективности апиксабана, дабигатрана этексилата и ривароксабана в стандартной и сниженной дозировках. Пациенты, получавшие стандартную дозу апиксабана или дабигатрана этексилата, имели более низкий риск крупных кровотечений, чем пациенты, применявшие ривароксабан (ОР 0,69; 95% ДИ: 0,54–0,88 и ОР 0,64; 95% ДИ: 0,48–0,87 соответственно). Что касается сниженных доз препаратов, то у пациентов на апиксабане риск крупных кровотечений был ниже, чем у пациентов на дабигатрана этексилате (ОР 0,62; 95% ДИ: 0,44–0,88) или ривароксабане (ОР 0,45; 95% ДИ: 0,33–0,61). У пациентов, получавших сниженную дозировку дабигатрана этексилата, отмечалась самая низкая смертность от всех причин. Различий в показателях эффективности между изученными ПОАК обнаружено не было [21].
Ray W.A. et al. (2021) в ретроспективном когортном исследовании сравнили частоту серьезных ишемических и геморрагических событий у пациентов с ФП 65 лет и старше, получавших ривароксабан (n=227 572) или апиксабан (n=353 879) в стандартной или сниженной дозе. В группе ривароксабана был повышен риск как серьезных ишемических (8,6 против 7,6 на 1000 человеко-лет; ОР 1,12; 95% ДИ: 1,04–1,20), так и геморрагических событий (7,5 против 5,9 на 1000 человеко-лет; ОР 1,26; 95% ДИ: 1,16–1,36), в том числе, фатальных экстракраниальных кровотечений (1,4 против 1,0 на 1000 человеко-лет; ОР, 1,41; 95% ДИ: 1,18–1,70). Пациенты, применявшие ривароксабан, характеризовались повышенным риском нефатального экстракраниального кровотечения (39,7 против 18,5 на 1000 человеко-лет; ОР 2,07; 95% ДИ: 1,99–2,15), фатального ишемического/ геморрагического события (4,5 против 3,3 на 1000 человеко-лет; ОР 1,34; 95% ДИ: 1,21–1,48) и общей смертности (44,2 против 41,0 на 1000 человеко- лет; ОР 1,06; 95% ДИ: 1,02–1,09). Риск серьезного ишемического или геморрагического события был выше как у тех, кто получал уменьшенную дозу (27,4 против 21,0 на 1000 человеко-лет; ОР 1,28; 95% ДИ: 1,16–1,40), так и стандартную дозу (13,2 против 11,4 на 1000 человеко-лет; ОР 1,13; 95% ДИ: 1,06–1,21) ривароксабана [22].
Mamas M.A. et al. (2022) провели метаанализ 10 ретроспективных исследований данных реальной практики, посвященный сравнению эффектов апиксабана и ривароксабана у пациентов с неклапанной формой ФП. Скорректированное ОШ составило 0,88 (95% ДИ: 0,81–0,95), что указывает на значительно меньший риск ИИ/СЭ при приеме апиксабана. Терапия аписксабаном также была сопряжена с меньшей угрозой крупного кровотечения (ОР 0,62; 95% ДИ: 0,56–0,69) и ЖКК (ОР 0,57; 95% ДИ: 0,50–0,64) [23].
Совсем недавно были представлены результаты международного популяционного когортного исследования, в котором были проанализированы сведения из пяти стандартизированных электронных баз данных, охватывающих 221 млн пациентов из Франции, Германии, Великобритании и США. В окончательный анализ вошли данные 527 226 пациентов, начавших прием ПОАК (апиксабан, n=281 320; дабигатрана этексилат, n=61 008; эдоксабан, n=12 722; ривароксабан, n=172 176). Применение апиксабана ассоциировалось с более низким риском развития ЖКК, чем дабигатрана этексилата (ОР 0,81; 95% ДИ: 0,70–0,94), эдоксабана (ОР 0,77; 95% ДИ: 0,66–0,91) или ривароксабана (ОР 0,72; 95% ДИ: 0,66–0,79). Значимых различий по другим показателям эффективности и безопасности между изученными ПОАК не наблюдалось. Более низкий риск ЖКК при применении апиксабана относительно ривароксабана был отмечен среди больных, получавших как стандартную (ОР 0,72; 95% ДИ: 0,64–0,82), так и сниженную дозу (ОР 0,68; 95% ДИ: 0,61–0,77) препаратов, а также у пациентов с хронической болезнью почек (ОР 0,68; 95% ДИ: 0,59–0,77) [24].
Следует отметить, что большинство представленных исследований носят ретроспективный характер, а сравнение эффективности и безопасности ПОАК чаще проводилось не напрямую, а по отношению к варфарину. Тем не менее общий объем выборки и количество работ позволяет предположить высокую эффективность и, вероятно, лучший профиль безопасности (прежде всего наименьший риск развития ЖКК) апиксабана по сравнению с другими ПОАК. Однако результаты исследований реальной клинической практики, несомненно, должны быть подтверждены в последующих проспективных рандомизированных исследованиях.
ПРИМЕНЕНИЕ ПРЯМЫХ ОРАЛЬНЫХ АНТИКОАГУЛЯНТОВ У ПОЖИЛЫХ И ОСЛАБЛЕННЫХ ПАЦИЕНТОВ С ФИБРИЛЛЯЦИЕЙ ПРЕДСЕРДИЙ
Частота ФП прогрессивно увеличивается с возрастом, который выступает независимым фактором риска нежелательных явлений у пациентов с этим заболеванием. Пожилые пациенты реже получают антикоагулянты, несмотря на достаточное количество данных в пользу их приема у этой группы пациентов [1]. Больные ФП с отягощенной коморбидной патологией (прежде всего это касается ослабленных (хрупких) пациентов, пожилого и старческого возраста) имеют более высокий риск инсульта и поэтому особенно нуждаются в эффективной протекции, которая в не меньшей мере должна быть безопасна с учетом высокой вероятности кровотечений в этой популяции. Пациенты в возрасте ≥75 лет обычно мало представлены в рандомизированных клинических исследованиях, однако они составляли почти 40% всей популяции в регистрационных исследованиях ПОАК [25]. Результаты этих исследований убедительно показывают, что ПОАК имеют лучший показатель соотношения пользы и риска по сравнению с варфарином у больных пожилого и старческого возраста. При этом следует помнить, что возраст пациента 80 лет и старше является критерием снижения дозы ПОАК в случае назначения апиксабана или дабигатрана этексилата [26, 27].
Количество исследований, посвященных сравнению различных ПОАК у пожилых и ослабленных пациентов с ФП, ограниченно. Так, Martinez B.K. et al. (2018) выявили, что прием ривароксабана, в отличие от апиксабана и дабигатрана этексилата, связан со снижением риска СЭ относительно варфарина у ослабленных пациентов с неклапанной ФП. При этом ни один из ПОАК не продемонстрировал существенной разницы в частоте крупных кровотечений по сравнению с варфарином [28].
В японском крупномасштабном многоцентровом проспективном обсервационном исследовании было выполнено сравнение эффективности и безопасности стандартной и сниженной дозы апиксабана у пациентов с ФП в возрасте 75 лет и старше. Частота ИИ/СЭ и кровотечений, требующих госпитализации, была одинаковой в обеих группах, однако случаи общей и сердечно-сосудистой смерти наблюдались значительно чаще у пациентов, принимавших сниженную дозу препарата, что, по-видимому, было обусловлено более высоким исходным риском в этой группе [29]. Эти результаты согласуются с полученными ранее данными о том, что назначение сниженной дозы ПОАК менее эффективно для профилактики нежелательных явлений ФП [1].
По данным Lau W.C.Y. et al. (2022), применение апиксабана у пациентов с ФП 80 лет и старше ассоциировалось с более низким риском развития ЖКК, чем прием дабигатрана этексилата, эдоксабана или ривароксабана, при сопоставимой частоте ИИ/СЭ и кровотечений других локализаций [24].
Таким образом, старческая астения, сопутствующие заболевания и высокий риск падений не перевешивают пользу от назначения ПОАК с учетом небольшого абсолютного риска развития кровотечения у пожилых пациентов на антикоагулянтной терапии [1]. Вместе с тем вопрос выбора предпочтительного ПОАК у таких больных остается открытым.
ПРИМЕНЕНИЕ ПРЯМЫХ ОРАЛЬНЫХ АНТИКОАГУЛЯНТОВ У ПАЦИЕНТОВ С ОЖИРЕНИЕМ И ФИБРИЛЛЯЦИЕЙ ПРЕДСЕРДИЙ
Некоторые международные рекомендации предостерегают от назначения ПОАК пациентам с чрезвычайно высокой (>120 кг) или низкой (≤60 кг) массой тела из-за недостаточного опыта их применения в этих группах населения [30]. Однако в последние несколько лет были опубликованы результаты нескольких исследований, посвященных именно этому вопросу.
Так, в post hoc-анализе исследования ARISTOTLE был оценен эффект рандомизированного лечения (апиксабан против варфарина), стратифицированный по массе тела пациентов. Лечебный эффект апиксабана по сравнению с варфарином в отношении исходов (частоты ИИ/СЭ, смерти от всех причин или инфаркта миокарда) был одинаковым по всему спектру веса (≤60, >60–120, >120 кг). Апиксабан имел лучший профиль безопасности (меньшую частоту крупных кровотечений), чем варфарин, во всех весовых категориях, в том числе у пациентов высоким весом [31].
O’Kane C.P. et al. (2022) изучили эффективность и безопасность апиксабана и ривароксабана у пациентов с неклапанной ФП и индексом массы тела (ИМТ) ≥50 кг/м2 в рамках ретроспективного когортного исследования. Частота исходов (ИИ, СЭ и кровотечений) сравнивалась относительно когорты пациентов с ИМТ от 18 до 30 кг/м2. После 1619 пациенто-лет наблюдения у 595 пациентов частота ИИ была практически одинаковой в обеих группах: 1,3 на 100 пациенто-лет в группе с ИМТ ≥50 кг/м2 по сравнению с 2,0 на 100 пациенто-лет в группе с ИМТ <30 кг/м2 в группе (ОР 0,65; 95% ДИ: 0,38–1,82, р=0,544). Частота крупных кровотечений и клинически значимых незначительных кровотечений также достоверно не различалась между двумя группами [32].
Это исследование вносит вклад в растущую доказательную базу того, что ПОАК эффективны и безопасны у пациентов выраженным ожирением. Тем не менее полученные результаты пока должны быть интерпретированы с осторожностью и подтверждены дополнительными исследованиями.
ПРЯМЫЕ ОРАЛЬНЫЕ АНТИКОАГУЛЯНТЫ У ПАЦИЕНТОВ С ФИБРИЛЛЯЦИЕЙ ПРЕДСЕРДИЙ И НАРУШЕННОЙ ФУНКЦИЕЙ ПОЧЕК
Выбор перорального антикоагулянта и подбор его дозы у пациента со сниженной функцией почек зачастую представляет серьезную дилемму для лечащих врачей. У больных с легкой и умеренной почечной дисфункцией (клиренс креатинина 30–49 мл/мин) безопасность и эффективность ПОАК по сравнению с варфарином соответствует таковой у пациентов без ХБП. Критерии снижения дозировок ПОАК в зависимости от состояния функции почек следующие:
- для ривароксабана доза 15 мг 1 раз/сут должна быть назначена при значении клиренса креатинина 15–49 мл/мин;
- для апиксабана дозу 2,5 мг 2 раза/сут назначают при наличии 2 из 3 критериев: возрасте ≥80 лет, массе тела ≤60 кг или уровне креатинина сыворотки крови ≥133 мкмоль/л;
- для эдоксабана снижение дозировки до 30 мг/ сут показано при уровне клиренсе креатинина 15–50 мл/мин [26, 33, 34];
- для дабигатрана этексилата непосредственно состояние функции почек не является критерием снижения дозы препарата, однако дозировка 110 мг 2 раза/ сут может быть назначена по усмотрению врача пациентам с клиренсом креатинина 30–49 мл/ мин при наличии высокого риска кровотечений. Пациентам с клиренсом креатинина менее 30 мл/мин назначение дабигатрана противопоказано [27].
Наиболее сложным и малоизученным остается вопрос применения антикоагулянтов у пациентов с ФП и терминальной стадией ХБП, учитывая крайне высокий риск развития кровотечений в этом случае. Следует иметь в виду, что в рамках регистрационных исследований ПОАК не изучались у больных с клиренсом креатинина <30 мл/мин (в случае апиксабана <25 мл/мин), а доказательная база оральных антикоагулянтов у пациентов, находящихся на гемодиализе или других видах почечной заместительной терапии, недостаточна и противоречива [1].
Решение о необходимости назначения антикоагулянтной терапии и выборе антикоагулянта у больных с ХБП и клиренсом креатинина <15 мл/мин и/или находящихся на гемодиализе или других видах почечной заместительной терапии должно приниматься мультидисциплинарной командой специалистов с учетом всех особенностей пациента [1, 4].
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Несмотря на не до конца решенные некоторые вопросы, не вызывает сомнений вытекающая из принципов доказательной медицины обоснованность обновленных клинических рекомендаций Европейского общества кардиологов (2020) и Минздрава России (2020), подчеркивающих значимые преимущества ПОАК перед АВК как в эффективности, так и в безопасности их применения у различных групп больных ФП с целью снижения риска ИИ, СЭ и сердечно-сосудистой смерти. Имеющиеся данные подтверждают высокую эффективность и профиль безопасности апиксабана у пациентов с ФП и различными сопутствующими состояниями. Тем не менее выбор ПОАК должен осуществляться непосредственно лечащим врачом с учетом всех данных анамнеза, сопутствующей патологии, функции почек пациента, а также возможных побочных эффектов и противопоказаний к препаратам этого класса.


