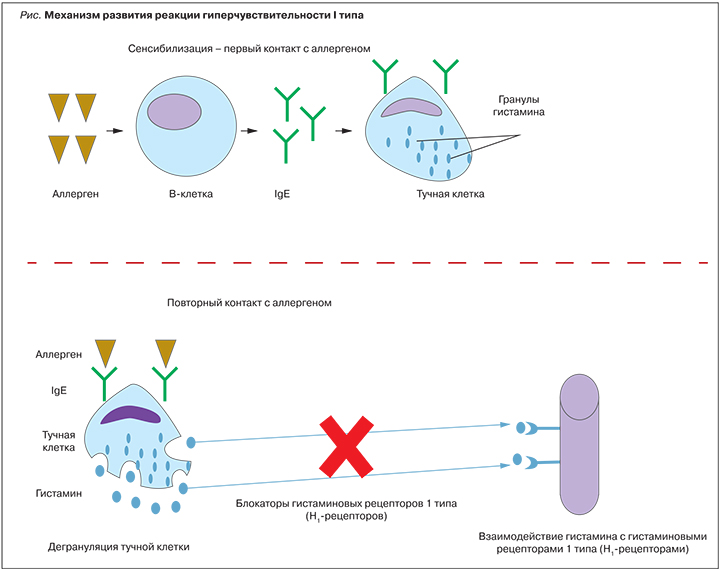
Аллергические заболевания представляют собой группу заболеваний, в основе развития которых лежит повышенная чувствительность иммунной системы к аллергенам [1]. Неуклонно растущая распространенность аллергопатологии вызывает настороженность врачей во всем мире. Предполагается, что ее увеличение связано с влиянием различных факторов: ухудшением экологической обстановки, появлением новых веществ и др. [1, 2]. Аллергопатология объединяет в себе широкий спектр заболеваний, таких как аллергический ринит, аллергический конъюнктивит, атопический дерматит, пищевая аллергия, лекарственная аллергия, крапивница [1]. Несмотря на то что формально это одна группа патологических состояний, в основе развития разных нозологий могут лежать разные механизмы (типы аллергических реакций), что будет определять различный подход к подбору терапии. Применение блокаторов гистаминовых рецепторов 1 типа (H1-блокаторов) патогенетически обосновано в терапии тех аллергических заболеваний, в основе которых лежит реакция гиперчувствительности 1 типа (рис.). На первом этапе происходит сенсибилизация, т.е. у предрасположенного субъекта в ответ на первый контакт с аллергеном происходит запуск синтеза IgE-антител и их связывание с мембраной тучных клеток. На втором этапе у сенсибилизированных субъектов при повторном контакте с аллергеном возникает мощный выброс медиаторов из гранул тучных клеток, основным из которых является гистамин [1, 3]. Далее гистамин взаимодействует с Н1-рецепторами [4], принадлежащими к суперсемейству рецепторов, связанных с G-белком. Рецепторы из этого семейства можно рассматривать как «клеточные переключатели», которые находятся в равновесии между неактивным («выключенным») и активным («включенным») состоянием. Гистамин, взаимодействуя с определенными доменами Н1-рецепторов, переводит их в активное состояние, запуская целый каскад реакций, обусловливающих появление основных симптомов аллергии: бронхоспазма, зуда, боли, расширения сосудов, увеличения проницаемости малых сосудов и транссудации жидкости в околососудистое пространство. Несмотря на свое название, антигистаминные препараты (H1-блокаторы) не являются собственно антагонистами H1-рецепторов и не противодействуют связыванию гистамина. Свое действие они осуществляют путем связывания с другими доменами рецепторов, тем самым переводя их в неактивное состояние. То есть антигистаминные препараты оказывают на рецепторы действие, противоположное гистамину, и по своей сути являются обратными агонистами [5, 6]. Типичными клиническими примерами нозологий, в основе которых лежит данный вид аллергических реакций, могут служить аллергический ринит, аллергическая астма, крапивница и анафилактический шок [3].
Появление Н1-блокаторов I поколения в 40-х гг. ХХ в. обозначил серьезный прорыв в фармакотерапии аллергических заболеваний, однако их применение сопровождалось большим количеством побочных явлений. Главным недостатком этих препаратов считается их способность преодолевать гематоэнцефалический барьер (ГЭБ) [4, 5, 6, 7, 8]. Гистамин является важным нейромедиатором в мозге человека, влияющим на циркадный ритм сна и бодрствования, память, контроль аппетита, контроль температуры тела [9]. Неудивительно, что антигистаминные препараты, проникающие через ГЭБ, влияют на все эти процессы. Н1-блокаторы первого поколения даже в рекомендованных производителем дозах часто вызывают сонливость в дневное время, седативный эффект, усталость, а также снижение концентрации внимания и памяти, негативно влияют на способность управлять транспортным средством [7, 8, 9]. Кроме того, антигистаминные препараты 1 поколения обладают низкой селективностью и могут взаимодействовать с различными рецепторами из суперсемейства рецепторов, связанных с G-белком [5, 6], вызывая антихолинергическое, антимускариновое, анти-альфа-адренергическое и антисеротониновое действие, что и объясняет широкий спектр их побочных эффектов [5, 6, 8]. Например, с блокадой М-холинорецепторов связаны такие нежелательные явления, как сухость слизистых оболочек, расстройство мочеиспускания и нарушение зрения [7]. Поэтому на сегодняшний день мировым сообществом рекомендуется избегать назначения антигистаминных препаратов 1 поколения для лечения аллергических заболеваний, за исключением случаев, требующих парентерального введения этого класса лекарственных средств [2, 7, 8]. Единственным преимуществом Н1-блокаторов первого поколения может считаться доступность лекарственных форм для внутримышечного и внутривенного введения, которые способны оказать быстрое действие [7].
Значительный прогресс в разработке антигистаминных препаратов произошел в 1980-х гг. с появлением H1-блокаторов 2 поколения [5, 6], которые не проходят через ГЭБ и поэтому обладают минимальным седативным эффектом (или вовсе лишены его). Кроме того, эти препараты высокоселективны по отношению к рецепторам гистамина 1 типа, что также существенно сокращает количество их побочных эффектов [5, 6, 7, 8]. К существенным преимуществам антигистаминных препаратов 2 поколения можно также отнести быстрое начало и более продолжительное терапевтическое действие за счет длительного связывания с рецепторами. Это позволяет назначать их 1 раз в сутки, что способствует существенному повышению приверженности к терапии [6, 7].
В настоящее время на фармрынке представлено много различных антигистаминных препаратов 2 поколения. К наиболее эффективным и безопасным среди них относится ЭСПА-БАСТИН® производства «Эспарма ГмбХ» – немецкой компании с безупречной репутацией. ЭСПА-БАСТИН® выпускается в виде таблеток, покрытых пленочной оболочкой, по 10 и 20 мг [10]. Действующим веществом препарата служит эбастин. После приема внутрь препарат быстро всасывается и почти полностью метаболизируется в печени, превращаясь в активный метаболит карэбастин [4]. Эффект препарата ЭСПА-БАСТИН® начинает проявляться уже в течение 1 ч от момента его приема [10, 11, 12] и сохраняется 48 ч [10]. Максимальная концентрация лекарства достигается через 4–6 ч после приема, что позволяет принимать препарат 1 раз в сутки [4, 10, 11, 12]. После отмены препарата через 5 дней применения его действие сохраняется еще на протяжении 72 ч [4, 13]. Период полувыведения карэбастина составляет от 15 до 19 ч, 66% вещества выводится в виде конъюгатов через почки [4].
Благодаря современному фармакокинетическому профилю, эбастин имеет ряд существенных преимуществ.
Во-первых, прием пищи не оказывает влияния на клинические эффекты препарата.
Во-вторых, высокий профиль безопасности позволяет использовать препарат в том числе у пациентов, отягощенных сопутствующей патологией (например, с болезнями печени и почек), а также у лиц пожилого возраста и подростков старше 12 лет [10, 14, 15]. Так, у пожилых пациентов фармакокинетические показатели существенно не изменяются [14]. При почечной и печеночной недостаточности, несмотря на то что период полувыведения несколько возрастает, концентрация препарата не превышает терапевтических значений. Поэтому больным с нарушенной функцией почек, а также с легкой и умеренной печеночной недостаточностью (классы А, В по классификации Чайлд–Пью) коррекция дозы не требуется [4, 15]. Однако максимально разрешенная доза препарата Эспа-Бастин® пациентам с почечной недостаточностью (класс C по Чайлд–Пью) составляет 10 мг 1 раз/сут [10, 15].
Немаловажную роль играет возможность приема препарата ЭСПА-БАСТИН® совместно с этанолом, этанолсодержащими средствами и препаратами седативного действия, такими как диазепам. Были изучены возможные последствия сочетанного назначения эбастина с лекарственными средствами, в метаболизме которых участвуют те же энзимы, а именно с эритромицином и кетоконазолом. По результатам проведенных исследований не было выявлено значительных клинических последствий приема таких лекарственных комбинаций [4].
Согласно инструкции по применению, ЭСПА-БАСТИН® зарегистрирован для использования при аллергическом рините и крапивнице различной этиологии [10]. На сегодня накоплен огромный мировой опыт по применению эбастина для лечения этих заболеваний. Свою эффективность действующее вещество препарата подтвердило в многочисленных клинических исследованиях, проведенных в соответствии со стандартами GCP и GMP. В большинстве своем это были двойные слепые и плацебо-контролируемые или активно контролируемые исследования [16–28].
ПРИМЕНЕНИЕ ЭБАСТИНА ПРИ АЛЛЕРГИЧЕСКОМ РИНИТЕ
Аллергический ринит (АР) клинически определяется симптомами гиперчувствительности носа, которые вызваны иммунологически опосредованным (чаще всего IgE-зависимым) воспалением после воздействия аллергена. Симптомы АР включают ринорею, нарушение носового дыхания, зуд в носу, чихание и обычно сохраняются на протяжении всей жизни (если не проводилась аллерген-специфическая терапия – АСИТ). AР – одно из самых распространенных заболеваний в мире, которое представляет собой серьезную медико-экономическую проблему. По различным оценкам, распространенность АР составляет от 2 до 25% у детей и от 1 до >40% у взрослых. По сравнению с другими заболеваниями АР может показаться несерьезным, поскольку не связан с инвалидизацией и повышенной смертностью. Тем не менее его симптомы связаны со значительным снижением качества жизни, сна, уровня энергии и способности фокусировать внимание. Кроме того, неадекватная коррекция симптомов АР служит предпосылкой для развития бронхиальной астмы, а также ухудшает ее течение [1, 2, 4, 7].
Блокаторы гистаминовых рецепторов 1 типа на протяжении многих лет успешно применяются для лечения АР. Согласно большинству международных и отечественных рекомендаций, предпочтение следует отдавать препаратам 2 поколения, к которым относится ЭСПА-БАСТИН® [1, 2, 7, 8]. Все проведенные исследования эбастина в контексте сезонного АР подтвердили эффективность препарата в сравнении с плацебо [16–22]. Кроме того, в двух из этих исследований дополнительно были проведены испытания для сравнения эффективности различных доз эбастина. В результате были получены несколько противоречивые результаты. Одно из этих исследований (n=101) не выявило существенных различий эффективности между дозами эбастина 10 и 20 мг при приеме 1 раз/ сут [16]. В то же время в другом исследовании (n=343) наблюдалось значительное превосходство эффективности эбастина в дозировке 20 мг [19]. При сравнении с другими антигистаминными препаратами 2 поколения (лоратадином в дозе 10 мг и цетиризином в дозе 10 мг) эбастин в дозе 10 мг продемонстировал схожую эффективность, а в дозе 20 мг значительно превзошел эти препараты [19].
Также эбастин подтвердил свою эффективность в сравнении с плацебо у пациентов, страдающих круглогодичным ринитом [23–25]. В одном исследовании обе дозировки эбастина – 10 и 20 мг – показали свою эффективность в сравнении с плацебо через 1 нед от начала исследования, но в долгосрочном плане более эффективным оказался эбастин в дозе 20 мг [23]. Davies et al в своем мультицентровом рандомизированном сравнительном двойном слепом исследовании продемонстрировали более высокую эффективность эбастина в дозах 10 мг и 20 мг при сравнении с лоратадином в дозе 10 мг при круглогодичном АР после 4 нед терапии [24]. В другом исследовании эбастин в дозе 10 мг и цетиризин в дозе 10 мг продемонстрировали схожую эффективность в отношении круглогодичного ринита спустя 4 нед от начала терапии [25].
ДРУГИЕ ОБЛАСТИ ПРИМЕНЕНИЯ ЭБАСТИНА
ЭСПА-БАСТИН® зарегистрирован также для лечения крапивницы [10]. Крапивницей называют этиологически гетерогенную группу заболеваний и состояний, объединенных основным симптомом и первичным кожным элементом – волдырем.
H1-блокаторы 2 поколения (в том числе ЭСПА-БАСТИН®) рассматриваются мировым сообществом как препараты первой линии для лечения крапивницы. Наибольшие сложности связаны с терапией хронической рецидивирующей формы заболевания, при которой отмечаются упорные симптомы с выраженным изнуряющим кожным зудом, существенно снижающим качество жизни больных [7, 8]. Эффективность эбастина в отношении терапии хронической идиопатической крапивницы была исследована в рандомизированных двойных слепых плацебо-контролируемых исследованиях. Было показано, что эбастин в дозе 10 мг при приеме 1 раз/сут значительно превосходит по эффективности плацебо. Эффективность эбастина стала очевидной с 1-й недели лечения: уже на этом сроке было отмечено снижение тяжести зуда, уменьшение количества и размера уртикариев [26, 27].
Небольшие исследования подтверждают эффективность эбастина в отношении холодовой и демографической крапивницы [28, 29]. Кроме того, небольшие исследования показали обнадеживающие результаты при использовании эбастина у пациентов с бронхиальной астмой, простудой, а также повышенной чувствительностью к укусам комаров [30–33].
В небольшом двойном слепом плацебо-контролируемом перекрестном исследовании был оценен эффект эбастина у 28 пациентов, чувствительных к укусам комаров. Препарат в дозе 20 мг продемонстрировал свою эффективность в плане купирования таких немедленных симптомов, вызванных укусами комаров, как зуд и размер поражения после укуса. Что касается отсроченных симптомов, то эбастин значительно уменьшил зуд, но не влиял на размер поражения [32].
М. Robert et al. в двойном слепом контролируемом исследовании установили положительное влияние на клиническое течение простуды однократного приема 10 мг эбастина в сочетании с 120 мг псевдоэфедрина [33].
АСПЕКТЫ БЕЗОПАСНОСТИ
Переходя к вопросу о переносимости эбастина, следует отметить, что в исследованиях как при АР, так и крапивнице различной этиологии он продемонстрировал высокий профиль безопасности, в том числе у пожилых пациентов и подростков старше 12 лет. В целом частота развития побочных эффектов препарата была не выше, чем при приеме плацебо [17, 18, 20–24]. В сравнительных исследованиях по частоте нежелательных явлений эбастин был сопоставим с лоратадином [20, 22, 24] и цетиризином [19]. Большинство зарегистрированных нежелательных явлений были легкими или средней степени тяжести. На основании данных о более чем 3000 пациентах, получавших лечение эбастином по 10 или 20 мг, наиболее распространенным побочным эффектом препарата у взрослых и подростков в возрасте более 12 лет были головная боль (7,9%), сонливость (3%) и сухость во рту (2,1%) [4].
С учетом того что лечение как АР, так и крапивницы может требовать длительного приема антигистаминных препаратов, важнейшей характеристикой Н1-блокаторов 2 поколения служат показатели долгосрочной безопасности [2, 8]. Согласно имеющимся данным, эбастин хорошо переносится при продолжительном использовании: это было подтверждено в 4-месячном сравнительном исследовании применения препарата при АР [18] и в 3-месячном исследовании его приема при крапивнице [27].
Принимая во внимание, что прием некоторых антигистаминных препаратов (например, терфенадина) ассоциирован с удлинением интервала QT и развитием желудочковой тахикардии по типу пируэт (torsade de pointes), было пристально изучено влияние эбастина на сердечно-сосудистую систему [4, 5, 6]. Не было выявлено отрицательного клинического эффекта терапевтических доз эбастина (10 и 20 мг) на интервал QT как у здоровых добровольцев, так и у пациентов (в том числе пожилых) [34, 35]. Более того, не отмечено клинически значимого действия эбастина на интервал QT и ритм сердечных сокращений при 7-дневном курсе приема препарата даже в дозе, в 10 раз превышающей терапевтическую (100 мг), и при однократном приеме препарата в дозировке, в 50 раз превышающей рекомендованную (500 мг) [36, 37].
Эбастин в терапевтических дозах не обладает седативным эффектом и не вызывает клинически значимого действия на когнитивные и психомоторные функции, включая способность управлять транспортным средством [4].
Таким образом, ЭСПА-БАСТИН® – антигистаминный препарат 2 поколения, отвечающий всем требованиям, которые предъявляются к современным представителям этой категории лекарственных средств. На сегодня препарат зарегистрирован для лечения АР и крапивницы различной этиологии, но, помимо этого, имеются многообещающие данные о положительном влиянии его действующего вещества (эбастина) на течение таких заболеваний, как бронхиальная астма, простуда и др. Эффективность и безопасность эбастина доказаны в многочисленных исследованиях, проведенных в соответствии с актуальными требованиями доказательной медицины, и подтверждены реальной клинической практикой на протяжении трех десятилетий во всем мире. Благодаря высокому профилю безопасности препарат можно использовать у подростков старше 12 лет и у пожилых людей.
К несомненным преимуществам препарата можно отнести удобство приема препарата – всего 1 раз/сут. Кроме того, ЭСПА-БАСТИН® выпускается в виде таблеток по 10 и 20 мг, что позволяет обеспечить персонифицированный подход к выбору дозировки. В пользу препарата говорит высокая скорость наступления клинического эффекта – уже через 1 ч после приема, и его длительное сохранение терапевтического действия – 48 ч. Более того, после 5 дней терапии эффект эбастина длится до 72 ч.
Благодаря фармокакокинетическим особенностям эбастина ЭСПА-БАСТИН® обладает рядом важных качеств, значительно увеличивающих приверженность пациентов к терапии. Во-первых, прием пищи не влияет на клинические эффекты препарата, во-вторых, возможен сочетанный его прием с этанолом и этанолсодержащими препаратами. Еще большим достоинством препарата следует признать высокий профиль безопасности. ЭСПА-БАСТИН® не проникает через ГЭБ и поэтому не обладает седативным эффектом и не влияет на способность управлять транспортным средством. Также он не влияет на ритм сердечных сокращений. Благодаря этому возможен длительный прием препарата ЭСПА-БАСТИН®.



