Известно, что сахарный диабет (СД) 2 типа увеличивает риск сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний (ССЗ) и сердечно-сосудистой смерти [1, 2]. При этом он часто сочетается с другими независимыми факторами кардиоваскулярного риска. Так, популяционное исследование с использованием ретроспективного анализа медицинских данных пациентов с СД 2 типа в возрасте старше 14 лет показало, что к наиболее частым факторам сердечно-сосудистого риска при этом заболевании относятся артериальная гипертензия (59,3%), дислипидемия (41,4%) и ожирение (18,5%) [3]. Результаты анализа медицинских карт 102 394 пациентов с СД 2 типа в Великобритании подтвердили высокую распространенность артериальной гипертензии (АГ) у больных СД 2 типа (42,8% мужчин и 45,8% женщин) [4]. В свою очередь, в исследовании Steno-2 было убедительно продемонстрировано, что воздействие на несколько факторов сердечно-сосудистого риска позволяет вдвое снизить вероятность развития ССЗ и смертности, а также увеличить продолжительность жизни до 8 лет [5].
В связи с этим основой персонифицированного подхода при лечении СД 2 типа служит многофакторный метаболический контроль, который, помимо управления гликемией, включает снижение риска ассоциированных с СД макро- и микрососудистых осложнений, а также контроль других факторов сердечно-сосудистого риска путем достижения целевых уровней артериального давления (АД), холестерина липопротеидов низкой плотности (ЛПНП) и контроля массы тела [6]. Кроме того, учитывая необходимость постоянного приема сахароснижающих препаратов (ССП) и активной вовлеченности пациентов в процесс управления СД, большое значение при выборе подходов и отдельных препаратов уделяется удобству терапии и улучшению приверженности пациентов назначенному лечению.
Для улучшения качества медицинской помощи пациентам с хроническими заболеваниями, в том числе СД 2 типа, необходимы следующие меры оптимизации системы оказания медицинской помощи [7]:
- • переход от реактивной к проактивной системе оказания медицинской помощи;
- • обучение и высокая степень вовлеченности пациента в процесс оказания медицинской помощи;
- • поддержка принятия решений;
- • разработка и внедрение клинических информационных систем с использованием реестров, которые могут обеспечить поддержку в принятии решений как в стране, отдельных регионах, так и при ведении конкретного пациента;
- • использование общественных и политических ресурсов для поддержки здорового образа жизни и предупреждения социально значимых неинфекционных заболеваний и их неблагоприятных исходов;
- • создание системы здравоохранения, ориентированной на качество оказания медицинской помощи.
Проведенное в США 5-летнее исследование эффективности модели медицинской помощи больным с хроническими заболеваниями (Chronic Care Model) с участием 53 436 пациентов с СД 2 типа на уровне оказания первичной медицинской помощи показало, что использование этой модели снижает совокупную частоту связанных с диабетом осложнений и смертность от всех причин. Так, риск ССЗ снизился на 56,6%, микрососудистых осложнений – на 11,9%, а смертности – на 66,1% [8]. То же исследование позволило установить, что в группе Chronic Care Model были ниже затраты на медицинские услуги [8].
ФАРМАКОТЕРАПЕВТИЧЕСКИЕ ИННОВАЦИИ В ЛЕЧЕНИИ САХАРНОГО ДИАБЕТА 2 ТИПА
Последние два десятилетия ознаменовались бурным ростом числа ССП и появлением новых классов антидиабетических препаратов с принципиально новыми механизмами действия: ингибиторов дипептилпептидазы 4 (иДПП-4), агонистов рецепторов глюкагоноподобного пептида 1 (аГПП-1), ингибиторов натрий-глюкозного котранспортера 2 (иНГЛТ- 2). Данные завершенных крупномасштабных рандомизированных контролируемых исследований (РКИ) по оценке кардиоваскулярного риска новых противодиабетических препаратов убедительно продемонстрировали, что иНГЛТ-2 снижают смертность от MACE (major adverse cardiovascular events – основные неблагоприятные кардиоваскулярные события, включающие сердечно-сосудистую смерть, нефатальный инфаркт миокарда, нефатальный инсульт) и от всех причин в большей степени, чем аГПП-1 [9]. В то время как ингибиторы дипептидилпептидазы-4 (иДПП-4) не показали сердечно-сосудистых преимуществ по сравнению с плацебо и уступали иНГЛТ-2 и аГПП-1 в отношении смертности [9]. Более того, выводы РКИ о способности иНГЛТ-2 улучшать сердечно-сосудистый прогноз и почечные исходы у пациентов с СД 2 типа подтверждены данными реальной клинической практики.
Результаты этих исследований привели к пересмотру рекомендаций по лечению СД 2 типа и профилактике ССЗ у пациентов с этим заболеванием. В настоящее время как международные, так и отечественные клинические рекомендации предлагают при выборе терапии у отдельных категорий пациентов с СД 2 типа (с установленным атеросклеротическим ССЗ, сердечной недостаточностью, хронической болезнью почек), наряду с метформином, отдавать предпочтение аГПП-1 и иНГЛТ-2 [6, 7, 10]. Важное отличие обновленных клинических рекомендаций – фокус на раннее применение иНГЛТ-2 или аГПП-1 при лечении СД 2 типа с целью предупреждения неблагоприятных сердечно-сосудистых и почечных исходов у пациентов с атеросклеротическими ССЗ, высоким и очень высоким кардиоваскулярным риском, сердечной недостаточностью и хронической болезнью почек (ХБП) независимо от достижения гликемического контроля (HbA1c <7%) на фоне терапии метформином.
Как иНГЛТ-2, так и аГПП-1 обладают выраженным сахароснижающим эффектом, способствуя значимому улучшению гликемического контроля, благоприятно влияют на массу тела и АД, а также не ассоциируются с повышенным риском гипогликемий. ИНГЛТ-2 и отдельные аГПП-1 (дулаглутид, лираглутид, семаглутид) продемонстрировали в масштабных РКИ сердечно-сосудистую эффективность и безопасность у пациентов с СД 2 типа [9], подтвержденную данными реальной практики [11–13]. Оба класса проявляют кардио- и нефропротективные свойства не только за счет прямого гипогликемического действия, но и благодаря многочисленным прямым и непрямым плейотропным метаболическим и гемодинамическим эффектам [14]. Некоторые уникальные эффекты, связанные с применением иНГЛТ-2, такие как уменьшение объема висцерального жира и эпикардиального жира, повышение чувствительности тканей к инсулину и улучшение функции β-клеток, рассчитанное с использованием гомеостатической модели HOMA-β, могут помочь в преодолении ряда нерешенных проблем при лечении СД.
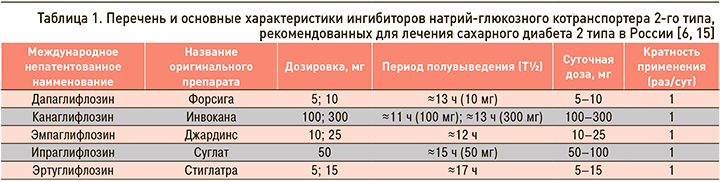
Для лечения СД 2 типа в настоящее время в России одобрены 5 иНГЛТ-2 – дапаглифлозин, канаглифлозин, эмпаглифлозин, а также зарегистрированные в 2019 г. ипраглифлозин и эртуглифлозин. Кроме того, проводятся предрегистрационные клинические исследования еще нескольких представителей этого класса препаратов. Основные характеристики зарегистрированных в России иНГЛТ-2 представлены в таблице 1.
ОБЩИЕ ПОДХОДЫ К ЛЕКАРСТВЕННОЙ ТЕРАПИИ САХАРНОГО ДИАБЕТА 2 ТИПА
Даже при адекватном контроле факторов кардиоваскулярного риска вероятность развития ССЗ у пациентов с СД 2 типа на 21% выше по сравнению с лицами того же возраста без диабета. Поэтому достижение адекватного контроля углеводного обмена по-прежнему остается ведущей задачей лечения этого заболевания. При этом рекомендуется выбор индивидуальных целей гликемического контроля в зависимости от возраста пациента, ожидаемой продолжительности жизни, функциональной зависимости, наличия атеросклеротических ССЗ и риска тяжелой гипогликемии (уровень убедительности рекомендаций С). Для большинства взрослых пациентов с СД 2 типа адекватным считается целевой уровень HbA1с менее 7,0% [6, 7].
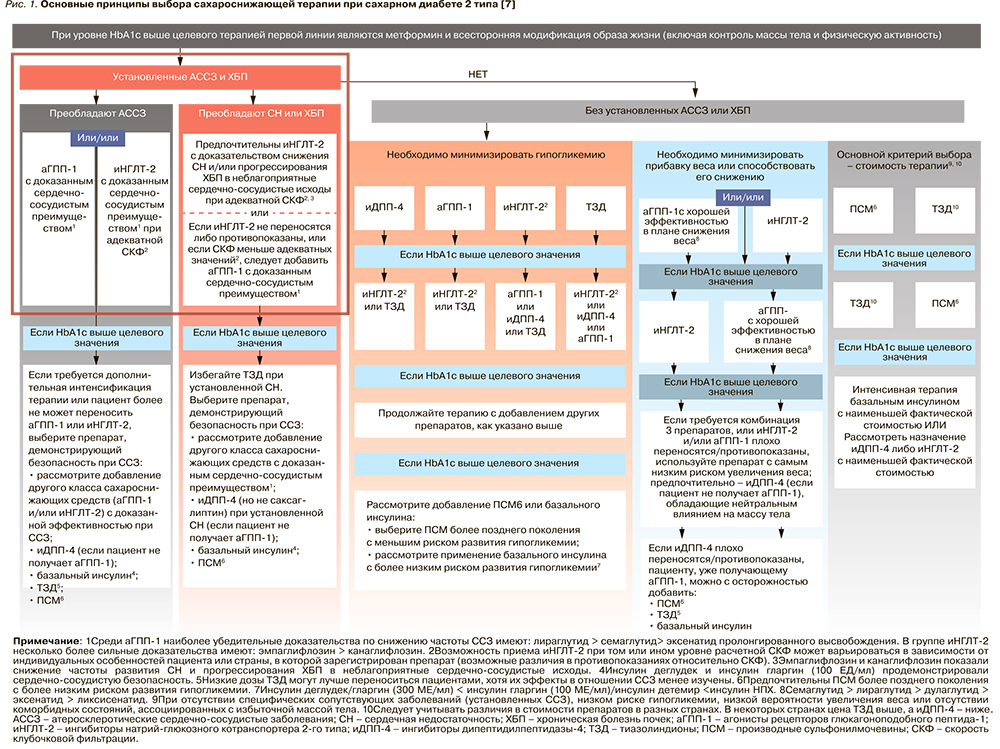
На рисунке 1 и в таблице 2 приведены основные подходы к фармакотерапии СД 2 типа и свойства основных классов препаратов, которые следует учитывать при выборе и коррекции сахароснижающей терапии у этой группы пациентов [6, 7].
Несмотря на то что, согласно российским и международным клиническим рекомендациям по лечению СД 2 типа, предпочтительным препаратом в начале лечения по-прежнему остается метформин (уровень убедительности рекомендаций А), некоторые другие классы ССП имеют доказанные преимущества при применении у ряда пациентов уже на старте терапии. Так, у больных с СД 2 типа и атерослеротическими ССЗ и/или ХБП для снижения сердечно-сосудистого риска и улучшения прогноза на ранних этапах лечения может быть рассмотрена возможность применения комбинированной терапии с использованием иНГЛТ-2 или аГПП-1 (уровень убедительности рекомендаций А). У больных со множественными факторами кардиоваскулярного риска также рекомендуется включать в состав комбинированной сахароснижающей терапии иНГЛТ-2 или аГПП-1 (уровень убедительности рекомендаций В). А у больных с ХСН или высоким риском ХСН рекомендуется использовать иНГЛТ-2 (уровень убедительности рекомендаций А).
Также важно своевременно интенсифицировать терапию СД 2 типа у пациентов, не достигших индивидуальных целей лечения. Согласно принятым рекомендациям, следует регулярно (каждые 3 мес) оценивать эффективность проводимой терапии и при необходимости своевременно корректировать ее с учетом конкретных факторов, влияющих на выбор лечения.
ВЛИЯНИЕ ИНГИБИТОРОВ НАТРИЙ-ГЛЮКОЗНОГО КОТРАНСПОРТЕРА 2-ГО ТИПА НА ГЛИКЕМИЧЕСКИЙ КОНТРОЛЬ
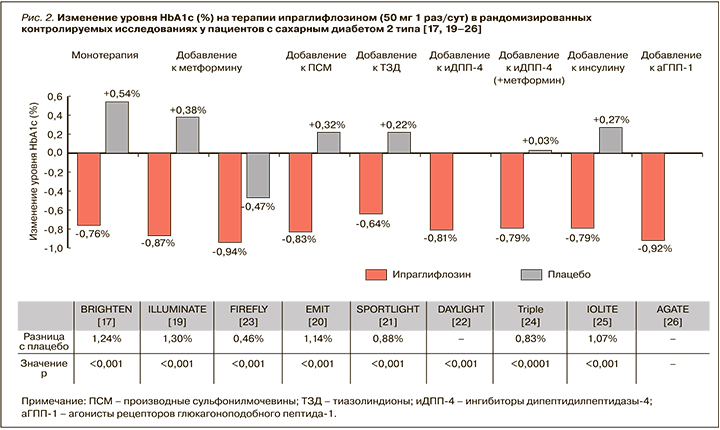
Результаты опубликованных рандомизированных исследований ипраглифлозина при СД 2 типа и метаанализов продемонстрировали быстрое улучшение гликемического контроля со значимым снижением уровней HbA1с и глюкозы плазмы натощак при приеме этого иНГЛТ-2 [16–26].
Так, в международном исследовании Fonseca V.A. et al. монотерапия ипраглифлозином по 50 мг 1 раз/ сут уже через 12 нед приводила к статистически значимому и значительному снижению HbA1c: расчетная средняя разница между группами ипраглифлозина и плацебо составила -1,00% (-1,11; -0,89) [16].
В исследовании Kashiwagi A. et al. более длительная монотерапия ипраглифлозином у больных СД 2 типа также сопровождалась значимым улучшением гликемического контроля: через 16 нед после начала применения препарата в дозе 50 мг 1 раз/сут уровень HbA1c снизился от исходного в среднем на 0,8% (стандартизованная средняя разница с плацебо составила -1,24% (-1,63; -0,91); р <0,001), уровень глюкозы плазмы натощак снизился в среднем на 2,33 ммоль/л от исходного (стандартизованная средняя разница с плацебо -2,54 ммоль/л; р <0,001). 16,1% пациентов в группе ипраглифлозина (против 3,0% в группе плацебо) к концу 16-недельного периода лечения достигли HbA1c <7,0% [17]. При этом у лиц с более выраженной декомпенсацией углеводного обмена (HbA1c ≥8,4%) снижение HbA1c было более выраженным и достигало 1,5% в сравнении с плацебо (р <0,001).
В целом, согласно данным опубликованного метаанализа, монотерапия ипраглифлозином в дозах 50 и 100 мг приводит к снижению уровня HbA1c на 1,20 и 1,48% соответственно [18].
Клинические исследования у пациентов, получавших ранее фармакотерапию по поводу СД 2 типа, но не достигших на ее фоне целей гликемического контроля, также продемонстрировали, что добавление ипраглифлозина к другим ССП способствует значимому улучшению параметров гликемии. Так, при добавлении ипраглифлозина по 50 мг к метформину отмечалось значимое снижение уровня HbA1c: через 26 нед этот показатель снизился в среднем на 1,30% (р <0,001), а уровень глюкозы плазмы натощак – на 1,23 ммоль/л [19]. В свою очередь, при добавлении ипраглифлозина к препаратам сульфонилмочевины (ПСМ) уровень HbA1c относительно исходной величины снизился в среднем на 0,84% (1,14% в сравнении с плацебо; р <0,001), глюкозы плазмы натощак – на 2,3 ммоль/л (р <0,001) [20]. При этом продолжение приема ипраглифлозина позволяло удерживать достигнутый результат. Через 52 нед после добавления ипраглифлозина к метформину среднее снижение HbA1c составило 1,01%, а ГПН – 1,67 ммоль/л от исходного [19].
Прием ипраглифлозина по 50 мг 1 раз/сут в комбинации с метформином у российских больных СД 2 типа также способствовал значимому улучшению гликемического контроля. Уже через 12 нед после добавления к терапии ипраглифлозина уровень HbA1с снизился с 8,4 до 7,4% (-1,0%; р <0,05), глюкозы плазмы натощак – с 9,5 до 8,5 ммоль/л (-1,0 ммоль/л; р <0,05). 35% пациентов достигли уровня HbA1с <7,0% [27]. Отмеченное улучшение параметров гликемии сохранялось до окончания наблюдения (через 24 нед), а повышение дозы ипраглифлозина до 100 мг 1 раз/сут способствовало достижению целевого уровня HbA1с <7,0% еще у 13% пациентов [27].
Данные о влиянии ипраглифлозина (при монотерапии или добавлении к ранее проводимой терапии) на снижение уровня HbA1c обобщены на рисунке 2 [17, 19–26].
Важно, что сочетание иНГЛТ-2 с инсулинотерапией у больных СД 2 типа не только способствует улучшению гликемического контроля, но и уменьшает вариабельность гликемии, а также снижает потребность в инсулине [25].
УПРАВЛЕНИЕ СЕРДЕЧНО-СОСУДИСТЫМИ РИСКАМИ
Поскольку ведущими причинами заболеваемости и смертности пациентов с СД 2 типа являются атеросклеротические ССЗ (ишемическая болезнь сердца, цереброваскулярная болезнь или заболевания периферических артерий) и сердечная недостаточность, современные руководства по лечению СД 2 типа рекомендуют придерживаться стратегии многофакторного воздействия и, помимо адекватного контроля углеводного обмена, проводить регулярную оценку кардиоваскулярного риска, а также лечение любых модифицируемых факторов риска, которые включают ожирение/избыточный вес, артериальную гипертонию, дислипидемию, курение, ишемическую болезнь сердца ИБС в семейном анамнезе, ХБП и альбуминурию [6, 7]. Ценность иНГЛТ-2 состоит в том, что, наряду со значимым улучшением гликемического контроля, они оказывают многочисленные положительные негликемические эффекты, способствуя как раз уменьшению массы тела и уровня АД, коррекции дислипидемии, снижению сердечно-сосудистого риска, уменьшению альбуминурии.
ВЛИЯНИЕ ИНГИБИТОРОВ НАТРИЙ-ГЛЮКОЗНОГО КОТРАНСПОРТЕРА 2-ГО ТИПА НА МАССУ ТЕЛА И ВИСЦЕРАЛЬНЫЙ ЖИР
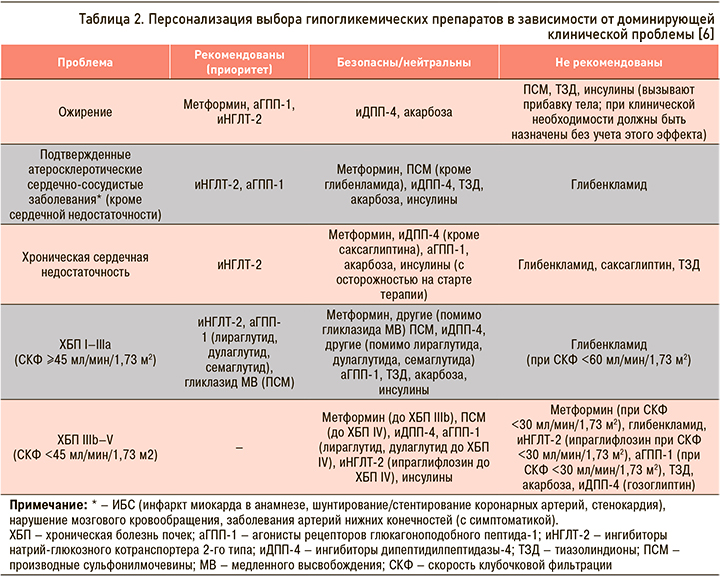
Ожирение – это не только избыточный объем жировой ткани, но и сложный комплекс гемодинамических и метаболических нарушений. В связи с этим контроль за массой тела у пациентов с СД 2 типа должен быть направлен не просто на снижение веса, но и на достижение благоприятных метаболических эффектов: улучшение контроля гликемии и показателей липидного обмена, снижение уровня АД. Снижение массы тела на 5–10 % за 3–6 мес терапии и удержание результата в течение года позволяет снизить риски для здоровья, улучшить течение заболеваний, ассоциированных с ожирением, и качество жизни пациентов [28]. При этом даже умеренное (на 3–5% от исходной) устойчивое снижение массы тела у пациентов с СД 2 типа приводит к повышению чувствительности к инсулину, улучшению гликемического контроля и уменьшению потребности в ССП. При выборе ССП для лечения СД 2 типа у пациентов с избыточным весом или ожирением необходимо учитывать влияние препаратов на вес (уровень убедительности рекомендаций B). По возможности следует избегать назначения лекарственных средств, связанных с риском увеличения веса, особенно у пациентов с коморбидными состояниями (например, сердечной недостаточностью, артериальной гипертензией, неалкогольной жировой болезнью печени и др.). У больных с избыточной массой тела или ожирением (ИМТ ≥27 кг/м2) при выборе сахароснижающей терапии предпочтение отдается препаратам, способствующим снижению веса [6].
ИНГЛТ-2 уменьшают реабсорбцию глюкозы и вызывают фармакологическую глюкозурию, сопровождающуюся снижением потребляемых калорий и уменьшением массы тела в среднем от ≈1 до 4 кг [29]. Так, монотерапия ипраглифлозином сопровождалась снижением массы тела в среднем на 2,33 кг (р <0,001) [17], а добавление этого препарата к метформину приводило к уменьшению веса в среднем на 2,33 и 3,16 кг от исходных значений через 24 и 52 нед соответственно [19].
При лечении ипраглифлозином в российской популяции пациентов с СД 2 типа также отмечалось снижение массы тела: через 24 нед после его добавления к метформину вес в среднем уменьшился на 2,01 кг (р <0,001) [27].
Использование ипраглифлозина в комбинации с другими ССП (в том числе пиоглитазоном, ПСМ и инсулином) при лечении СД 2 типа ослабляет их негативное влияние на массу тела. В зависимости от вида сопутствующей сахароснижающей терапии терапия ипраглифлозином сопровождалась снижением веса в среднем от 1,1 до 2,7 кг (р <0,001; рис. 3) [17–25].
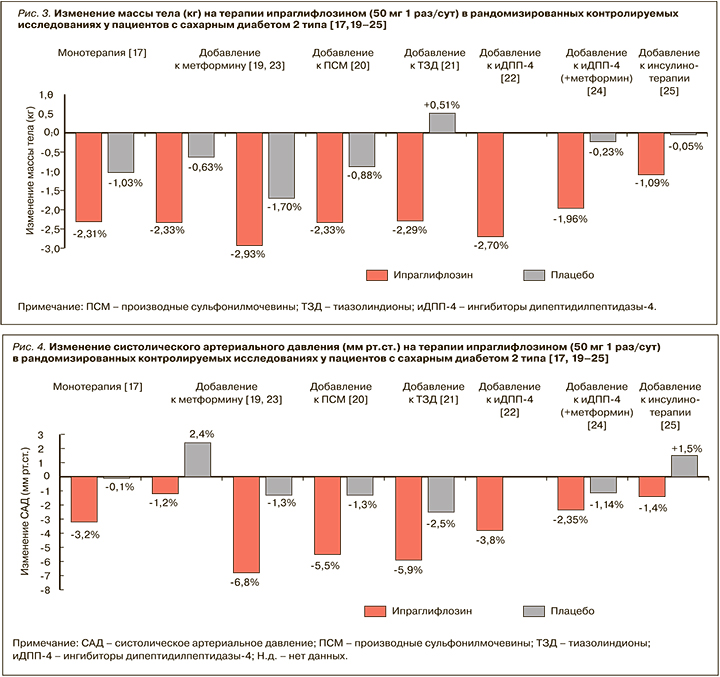
Удержание достигнутого снижения массы тела на фоне длительной терапии ипраглифлозином в течение всего периода лечения. По данным проспективного исследования STELLA-LONG TERM, через 3 года после начала применения этого иНГЛТ-2 у пациентов с СД 2 типа среднее снижение веса от исходного составило 2,32 кг [30].
Важно, что снижение массы тела на ипраглифлозине не зависит от гликемического контроля и обусловлено преимущественно уменьшением жировой массы, а не мышечной массы или внутрисосудистого объема [31]. Исследования с использованием компьютерной томографии продемонстрировали, что уменьшение жировой массы происходит преимущественно за счет уменьшения объема висцерального жира [32]. Это важно, поскольку абдоминальный тип ожирения с преимущественным накоплением жира в висцеральных депо и сопутствующая ему инсулинорезистентность предрасполагают к прогрессированию атерогенной дислипидемии и увеличению сердечно-сосудистого риска.
ВЛИЯНИЕ ИНГИБИТОРОВ НАТРИЙ-ГЛЮКОЗНОГО КОТРАНСПОРТЕРА 2-ГО ТИПА НА АРТЕРИАЛЬНОЕ ДАВЛЕНИЕ
Учитывая, что артериальная гипертензия (АГ) выступает одним из значимых факторов кардиоваскулярного риска, при каждом плановом посещении врача пациенту с СД 2 типа рекомендуется измерять АД. При повышенном АД (≥140/90 мм рт.ст.) необходимо провести дополнительное обследование на наличие АГ. У больных с СД 2 типа и АГ целевые показатели АД также должны быть индивидуализированы с учетом существующих рекомендаций по снижению сердечно-сосудистого риска, сопутствующих заболеваний и проводимой терапии, потенциальных побочных эффектов антигипертензивных препаратов, возможного лекарственного взаимодействия и предпочтений пациента (уровень убедительности рекомендаций В).
При выборе ССП для лечения СД 2 при подтвержденной АГ также необходимо учитывать их влияние на АД и другие факторы кардиоваскулярного риска.
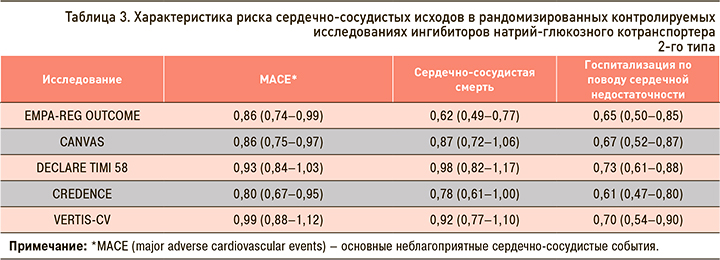
В клинических исследованиях у пациентов с СД 2 типа применение иНГЛТ-2 ассоциировалось со снижением систолического (на 1,66–6,9 мм рт.ст.) и диастолического АД (на 0,88–3,5 мм рт.ст.) [29]. Это, по-видимому, связано с умеренным диуретическим, осмоуретическим и натрийуретическим эффектами иНГЛТ-2, которые ведут к уменьшению внутрисосудистого объема и, как следствие, снижению пост- и преднагрузки [9, 33, 34]. Однако более долгосрочное влияние иНГЛТ-2 на АД может быть связано со снижением массы тела, а также с ингибированием ренин-ангиотензиновой системы и уменьшением инсулинорезистентности, которая является общим патогенетическим механизмом для СД 2 типа, висцерального ожирения и АГ [9, 33, 35].
В клинических исследованиях с участием больных СД 2 типа прием ипраглифлозина способствовал снижению систолического АД в среднем на 4,4 мм рт.ст., ДАД – на 2,7 мм рт.ст. (рис. 4) [19–25, 36].
ИНГИБИТОРЫ НАТРИЙ-ГЛЮКОЗНОГО КОТРАНСПОРТЕРА 2-ГО ТИПА И РЕГУЛЯЦИЯ ЛИПИДНОГО ОБМЕНА
Если гипергликемия повышает риск микрососудистых осложнений, то дислипидемия служит основным фактором риска макрососудистых осложнений при СД 2 типа. Повышенный уровень холестерина липопротеидов низкой плотности (ХС ЛПНП) – основная предпосылка к развитию атеросклероза и атеросклеротических ССЗ. Таким образом, управление уровнем ХС ЛПНП является основной целью терапии диабетической дислипидемии [10, 38].
Вместе с тем, несмотря на достижение целевого уровня ХС ЛПНП у ряда пациентов, сохраняется высокий остаточный риск сердечно-сосудистых осложнений. К наиболее частым причинам остаточного риска относятся высокий уровень триглицеридов (ТГ) и низкая концентрация холестерина липопротеидов высокой плотности (ХС ЛПВП) в плазме крови. Наличие инсулинорезистентности при СД 2 типа располагает к развитию характерной для этого заболевания дислипидемии в виде сочетания повышенного уровня ТГ, переносимых частицами липопротеидов очень низкой плотности (ЛПОНП), низкого содержания ХС ЛПВП, увеличения мелких плотных частиц ЛПНП без существенного повышения уровня ХС ЛПНП [37]; это может вводить в заблуждение при оценке кардиоваскулярного риска у пациентов с СД 2 типа и выборе стратегии коррекции дислипидемии. Другая особенность нарушений липидного обмена при СД2 – раннее развитие атеросклероза, потенциально предшествующего диагностике СД 2 типа на несколько лет [37].
В соответствии с современными рекомендациями всем пациентам с СД 2 типа и установленными ССЗ для медикаментозного лечения дислипидемии показано назначение статинов в максимально переносимых дозах (уровень убедительности рекомендаций А) [38]. В многочисленных исследованиях показано, что при применении с целью первичной и вторичной профилактики эта группа препаратов значительно снижает заболеваемость и смертность от ССЗ (во всех возрастных группах, не зависимо от пола), замедляет прогрессирование атеросклеротической бляшки и даже ее регрессию.
При лечении других нарушений липидного спектра (включая гипертриглицеридемии) также показано назначение статинов [38]. При этом врач должен учитывать и корректировать другие модифицируемые факторы риска (ожирение, метаболический синдром, СД, хронические заболевания печени и почек гипотиреоз), а также факт приема лекарственных средств, повышающих уровень ТГ. Пациентам с атеросклеротическими ССЗ или другими факторами риска, которые получают статины и контролируют уровень ХС ЛПНП, при отсутствии достижения целевого уровня ТГ (а именно сохранении концентрации ТГ в пределах 1,5–5,6 ммоль/л, несмотря на терапию статинами) показано добавление фибратов и омега-3-полиненасыщенных жирных кислот (уровень убедительности рекомендаций В).
Современные ССП – иДПП-4, аГПП-1, иНГЛТ-2 – характеризуются сердечно-сосудистой безопасностью, а последние 2 класса препаратов имеют целый ряд доказанных специфических преимуществ, обусловленных в том числе их противовоспалительными и антиатерогенными свойствами.
Данные о влиянии иНГЛТ2 на липиды крови противоречивы. Метаанализ результатов РКИ канаглифлозина, дапаглифлозина и эмпаглифлозина показал, что в целом их применение при СД 2 типа ассоциировано с незначительным повышением холестерина не-ЛПВП, ЛПНП и ЛПВП относительно плацебо [39]. Однако доступные результаты исследований сердечно-сосудистых исходов не позволяют сделать окончательные выводы о клиническом значении подобных эффектов иНГЛТ-2 в отношении липидов крови. Вместе с тем объединенный анализ клинических исследований ипраглифлозина у больных СД 2 типа позволил заключить, что его применение ассоциируется со значимым снижением уровня ТГ и повышением уровня ЛПВП без увеличения уровня общего ХС и ХС ЛПНП [40]. Кроме того, в отдельном исследовании у пациентов с СД 2 типа (из которых боле 85% получали гиполипидемические препараты) было установлено, что добавление ипраглифлозина к сахароснижающей терапии связано со статистически значимым снижением ХС ЛПНП (-0,37 против 14,4 мг/дл; р=0,038), мелких плотных ЛПНП (-1,28 против 2,81 мг/дл; р=0,012) и уменьшением отношения ЛПНП/мелких плотных ЛНП (-3,20 против 4,58%; р=0,040) в сравнении с контрольной группой [41]. Таким образом, ипраглифлозин может иметь потенциал для снижения уровня наиболее атерогенных мелких плотных ЛПНП у пациентов с СД 2 типа.
ВЛИЯНИЕ ИНГИБИТОРОВ НАТРИЙ-ГЛЮКОЗНОГО КОТРАНСПОРТЕРА 2-ГО ТИПА НА СЕРДЕЧНО-СОСУДИСТЫЕ ОСЛОЖНЕНИЯ
Метаанализы РКИ подтвердили сердечно-сосудистую безопасность иНГЛТ-2 при лечении пациентов с СД 2 типа независимо от наличия и степени выраженности нарушений функции почек [42–44]. Помимо значимого и последовательного снижения риска госпитализации по поводу сердечной недостаточности во всех исследованиях иНГЛТ-2 (независимо от наличия атеросклеротических ССЗ и нарушений функции почек, пола и этнической принадлежности), результаты специально спланированных испытаний показали, что эмпаглифлозин ассоциируется со сниженным риском смерти от ССЗ, а канаглифлозин и дапаглифлозин – со сниженным риском развития МАСЕ (табл. 3) [44]. Эти данные стали основанием для изменения клинических рекомендаций как по лечению СД 2 типа, так и контролю кардиоваскулярных рисков у пациентов с этим заболеванием [6, 7, 10, 45].
Положительные результаты применения иНГЛТ- 2 в отношении сердечно-сосудистых исходов у больных с СД 2 типа были подтверждены реальной клинической практикой. Анализ национальных баз медицинских данных, проведенный в рамках многоцентровых исследований CVD-REAL и CVD-REAL 2, свидетельствует, что использование иНГЛТ-2 при лечении СД 2 типа существенно снижает риски неблагоприятных сердечно-сосудистых исходов (общую смертность, госпитализации по поводу сердечной недостаточности, инфаркта миокарда, инсульта); вследствие этого представляются обоснованным приоритетное назначение иНГЛТ-2 для лечения СД2 отдельным категориям пациентов (с хронической сердечной недостаточностью, атеросклеротическими ССЗ или высоким риском их развития, с ХБП) независимо от достижения целей гликемического контроля [11, 12].
Специально спланированные долгосрочные исследования влияния ипраглифлозина на сердечно-сосудистые исходы не проводились, поскольку, по данным метаанализа рандомизированных контролируемых исследований II и III фазы у пациентов с СД 2 типа, было показано, что терапия этим препаратом не приводит к неприемлемому повышению кардиоваскулярного риска относительно плацебо (отношение рисков 0,41; 95% доверительный интервал 0,15–1,10) [46]. Опубликованные данные 3-летнего исследования безопасности и эффективности ипраглифлозина в клинической практике подтвердили отсутствие увеличения частоты сердечно-сосудистых исходов при его длительном применении [30].
На рисунке 5 суммированы современные представления о кардиопротекторных механизмах действия иНГЛТ-2 [47].
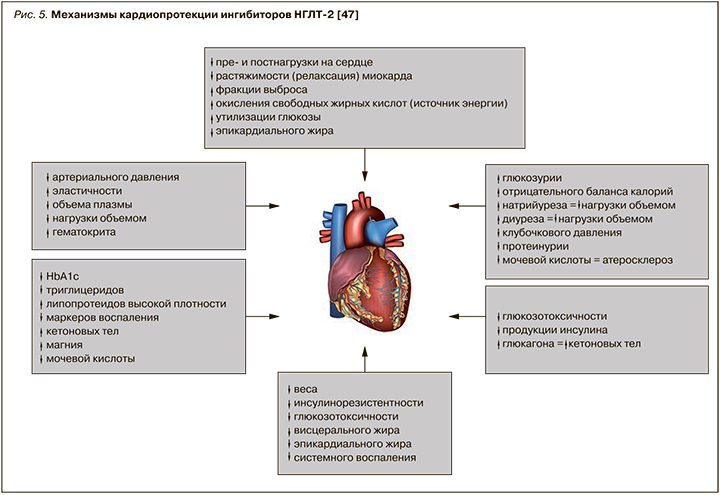
Продемонстрированные преимущества иНГЛТ-2 перед другими ССП делают этот класс препаратов предпочтительным при лечении пациентов СД 2 типа, так как его представители позволяют не только улучшать гликемический контроль, но и, что крайне существенно, влиять на долгосрочный прогноз у пациентов. Поэтому в настоящее время иНГЛТ-2 рассматриваются как препараты выбора при лечении СД 2 типа для снижения сердечно-сосудистого риска у пациентов с ССЗ, а также с очень высоким или высоким кардиоваскулярным риском (уровень убедительности рекомендаций А) [6, 7, 10, 38].
ВЛИЯНИЕ ИНГИБИТОРОВ НАТРИЙ-ГЛЮКОЗНОГО КОТРАНСПОРТЕРА 2-ГО ТИПА НА ФУНКЦИЮ ПОЧЕК И НЕФРОПРОТЕКТИВНЫЕ ЭФФЕКТЫ
Для пациентов с ХБП характерны прогрессирующие протеинурия (альбуминурия) и снижение функции почек, а также снижение количества фильтруемой почками глюкозы. Вследствие этого иНГЛТ-2 имели ограниченное применение или были противопоказаны пациентам со сниженной расчетной скоростью клубочковой фильтрации в связи с возможностью ослабления сахароснижающей эффективности по мере прогрессирования нарушений фильтрационной способности почек. Однако более поздние клинические исследования, а также экспериментальные модели на животных показали, что прием иНГЛТ-2 связан с улучшением как суррогатных, так и истинных почечных исходов.
Вследствие снижения тубулотоксичности глюкозы и образования конечных продуктов гликирования и активных форм кислорода применение иНГЛТ-2 приводит к уменьшению тубулярной гипертрофии. Кроме того, в настоящее время активно обсуждаются потенциальные прямые почечные эффекты фармакологического ингибирования НГЛТ-2. В эксперименте на мышах продемонстрировано, что прием иНГЛТ-2 связан с замедлением прогрессирования диабетической нефропатии, снижением выраженности процессов воспаления, фиброза и тубулярного некроза [48].
Предполагается, что снижение доставки натрия к области macula densa приводит к подавлению канальцево-клубочковой обратной связи и способствует афферентной вазодилатации, усилению почечного кровотока и гиперфильтрации, которая является фактором риска развития диабетической нефропатии. ИНГЛТ-2 снижают реабсорбцию натрия в проксимальном канальце и увеличивают его концентрацию в толстой части петли Генле и в области macula densa. Такой механизм действия сопровождается ответной активацией обратной канальцево-клубочковой связи, сужением афферентных (приносящих) артериол клубочков и расширением выносящих (или эфферентных) артериол, что, в свою очередь, влечет за собой уменьшение гиперфильтрации, снижение гидростатического давления в почечных клубочках, снижение активности локальной ренин-ангиотензин-альдостероновой системы [49]. Все это может предотвращать ухудшение функции почек и быть причиной незначительного, транзиторного снижения СКФ (примерно на 5 мл/мин) в начале лечения.
Кроме того, использование иНГЛТ-2 вызывает снижение выраженности протеинурии – одного из основных маркеров диабетической нефропатии. Так, в клинических исследованиях ипраглифлозина у пациентов с СД 2 типа отмечалось значительное снижение альбуминурии. Данный эффект проявляется практически сразу после начала лечения и сохраняется длительное время (до 2 лет) [50].
Позитивное влияние иНГЛТ-2 при их длительном применении приводит к значимому снижению частоты истинных почечных исходов, таких как устойчивое снижение расчетной СКФ на ≥40%, развитие терминальной почечной недостаточности, требующей заместительной почечной терапии (диализа, трансплантации), или смерть по причине ХБП [43].
ПРОФИЛЬ БЕЗОПАСНОСТИ И ПЕРЕНОСИМОСТЬ ИНГИБИТОРОВ НАТРИЙ-ГЛЮКОЗНОГО КОТРАНСПОРТЕРА 2-ГО ТИПА
Профиль безопасности ингибиторов НГЛТ-2 хорошо изучен, и появление новых данных существенно не изменило представлений о потенциальном риске развития отдельных побочных эффектов при приеме отдельных препаратов этого класса.
Поскольку действие иНГЛТ-2 определяется уровнем глюкозы, при ее концентрации в крови менее 5,0 ммоль/л экскреция глюкозы почками практически отсутствует. Кроме того, эффективность иНГЛТ-2 не зависит от уровня инсулина в крови и чувствительности к нему тканей. При этом сами иНГЛТ-2 снижают уровень инсулина в крови, повышают синтез глюкагона и не нарушают нормальную продукцию эндогенной глюкозы в ответ на гипогликемию. В результате препараты этого класса характеризуются низким риском гипогликемии по сравнению с другими ССП (относительный риск 0,60; 95% доверительный интервал 0,45–0,81) [51].
В целом частота гипогликемии при лечении иНГЛТ-2 зависит от сопутствующей терапии СД 2 типа. К примеру, монотерапия иНГЛТ-2, а также их применение в комбинации с большинством других ССП (за исключением ПСМ и препаратов инсулина) ассоциируется с низким риском гипогликемии. При приеме иНГЛТ-2 в сочетании с ПСМ частота гипогликемии может увеличиваться [51]. Для снижения риска гипогликемии при использовании иНГЛТ-2 в комбинации с инсулиновыми препаратами или с средствами, повышающими секрецию инсулина (например, с теми же ПСМ), может потребоваться снижение дозы последних.
Механизм сахароснижающего действия иНГЛТ- 2 – фармакологически индуцированная глюкозурия, и связанные и ней натрийурез и осмодиурез лежат в основе развития полиурии и дегидратации. Также в клинических исследованиях и наблюдательных программах наиболее часто сообщается о повышенном риске инфекций мочевыводящих путей и грибковых генитальных инфекций (в основном баланит и вульвовагинит) [52]. Некоторые исследования показали, что прием иНГЛТ-2 может быть также связан повышенным риском инфекций мочевыводящих путей (ИМП). Однако выполненные метаанализы с участием большой популяции и без этнических ограничений показали, что иНГЛТ-2, за исключением высоких доз дапаглифлозина (10 мг/сут), по-видимому, не увеличивают риск ИМП у пациентов с СД 2 типа [53, 54]. Тяжелые ИМП (пиелонефрит и уросепсис) являются крайне редкими побочными эффектами иНГЛТ-2, причем четкой взаимосвязи между развитием этих инфекций и приемом иНГЛТ-2 не установлено (относительный риск 0,89; 95% доверительный интервал 0,67–1,19) [52].
Четкой взаимосвязи между терапией иНГЛТ-2 и такими серьезными нежелательными явлениями, как острое повреждение почек, венозная тромбоэмболия и острый панкреатит, также не выявлено (относительный риск 1,04; 95% доверительный интервал 0,93–1,16) [52].
К редким, но грозным побочным эффектам терапии иНГЛТ-2 относятся диабетический эугликемический кетоацидоз и ампутации нижних конечностей [52]. Анализ безопасности иНГЛТ- 2, выполненный FDA, и метаанализ медицинских баз данных подтвердили повышенный риск ампутаций нижних конечностей у больных СД 2 типа, принимавших канаглифлозин, но не другие иНГЛТ- 2 [55, 56]. Хотя из одобренных для лечения СД 2 иНГЛТ- 2 только канаглифлозин, по данным отдельных клинических исследований, был связан с более высоким риском ампутаций нижних конечностей и переломов костей относительно плацебо, остается неясным, связан ли такой риск со всеми иНГЛТ-2 или только с отдельными препаратами. Также неизвестен и точный механизм увеличения вероятности ампутации нижних конечностей на фоне приема канаглифлозина. Возможно, это обусловлено индуцированным иНГЛТ-2 уменьшением объема циркулирующей крови, приводящим к нарушению кровообращения в дистальных отделах периферических артерий. Принимая во внимание тот факт, что иНГЛТ-2 показаны для лечения СД 2 типа, который как раз является основным фактором риска ампутаций нижних конечностей, пациенты, которым планируется назначение препаратов этого класса, а также уже их принимающие должны проходить обследование с целью выявления нарушений и контроля за адекватностью кровообращения в сосудах нижних конечностей и следить за достаточным потреблением жидкости.
Прием иНГЛТ-2 может приводить к повышению секреции глюкагона, активации липолиза и подавлению синтеза жира в адипоцитах, что сопровождается повышением синтеза кетоновых тел в печени и угнетением их окисления. Согласно результатам опубликованного метаанализа, в целом лечение иНГЛТ редко связано с кетоацидозом: относительный риск у пациентов, имевших и не имевших предшествующего опыта сахароснижающей терапии, составил 0,65 (95% доверительный интервал 0,25–1,71) и 0,66 (95% доверительный интервал 0,16–2,71) соответственно [53]. Однако, по данным отдельных клинических исследований, а также ретроспективного анализа электронных баз контроля за безопасностью терапии, у некоторых больных прием иНГЛТ-2 может приводить к развитию кетоацидоза даже при не очень высоком уровне глюкозы крови (10–15 ммоль/л). Факторами риска развития кетоацидоза при приеме иНГЛТ-2 служат состояния, характеризующиеся выраженным или прогрессирующим дефицитом инсулина (например, СД 1 типа, тяжелые инфекции и интоксикации, необоснованное снижение дозы инсулина и др.). Для оценки сохранности инсулиносекреторной способности β-клеток поджелудочной железы у пациентов с длительным анамнезом СД и высокой потребностью в инсулине может быть рекомендовано определение уровня С-пептида в крови.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
ИНГЛТ-2 – современные ССП с уникальным инсулинонезависимым механизмом действия, эффект которых не зависит от выраженности инсулинорезистентности и функции β-клеток. Тонкие механизмы поддержания баланса электролитов, воды и энергии в проксимальном почечном канальце, регулируемые НГЛТ-2, модулируют не только уровень глюкозы в крови и объем плазмы, но и многие метаболические процессы. Поэтому наряду с улучшением гликемического контроля, массы тела и АД представители этого класса препаратов проявляют благоприятные сердечно-сосудистые и ренопротекторные эффекты.
Более глубокое понимание механизмов действия иНГЛТ-2 в почках и их влияния на организм в целом привело к улучшению терапевтических подходов, пересмотру клинических рекомендаций по лечению СД 2 типа, расширению возможностей многофакторного управления диабетом. Однако клинические исследования – только первый шаг в алгоритме принятия решений о выборе фармакотерапии у каждого отдельного пациента. Знания, полученные в ходе исследований, должны быть реализованы в клинической практике. Современные клинические рекомендации по лечению СД 2 типа (Российская ассоциация эндокринологов, 2019) ввиду доказанных преимуществ рассматривают иНГЛТ-2 как предпочтительные препараты для лечения СД 2 типа у пациентов с установленными ССЗ или высоким и очень высоким кардиоваскулярным риском, сердечной недостаточностью и ХБП (как правило, в комбинации с метформином) [6]. Однако для улучшения прогноза как у отдельного пациента с СД 2 типа, так и в целом у данной популяции больных при принятии решений о выборе терапии каждый раз необходимо преодоление инертности. Более широкое внедрение иНГЛТ-2 в клиническую практику не просто раздвигает горизонты фармакотерапии СД 2 типа с учетом особенностей конкретного пациента, гетерогенности патогенеза заболевания, индивидуальных рисков, переносимости, ответа на лечение, но и имеет доказанные преимущества в отношении сердечно-сосудистых осложнений и смертности у пациентов с СД 2 типа. Очевидно, что при более раннем включении в терапию иНГЛТ-2 можно ожидать наибольшего эффекта в плане защиты сердечно-сосудистой системы и почек и предупреждения развития сердечной недостаточности, ХБП и микрососудистых осложнений.



