ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Пищевые волокна (ПВ) – это сумма полисахаридов и лигнина, которые не перевариваются эндогенными секретами желудочно-кишечного тракта человека; именно такое определение дали этой группе веществ в своей работе Trowell H.C. и Burkitt D.P. в 1987 г. [1]. Согласно более современной дефиниции, к ПВ относят съедобные части растений или аналогичные углеводы, устойчивые к перевариванию и абсорбции в тонком кишечнике человека и полностью либо частично ферментируемые в толстом кишечнике [2].
На сегодняшний день применение ПВ является популярным и востребованным предметом клинических исследований в связи с их доказанными положительными эффектами в отношении профилактики некоторых заболеваний и улучшения течения уже имеющихся. Введение в рацион ПВ одобрено многими авторитетными организациями, в том числе Американской ассоциацией кардиологов (AHA) и Комиссией по надзору за продовольствием и лекарственными средствами (FDA) [2]. Рекомендации американской диетологической ассоциации (ADA) заключаются в назначении как минимум 14 г ПВ на каждые 1000 потребляемых килокалорий в день [3]. По данным Европейской организации безопасности пищевых продуктов (EFSA), адекватная доза ПВ в рационе составляет 25 г/сут [4]. В соответствии с рекомендациями ПВ предлагается получать из овощей, фруктов, цельнозерновых круп. При этом предпочтительно выбирать продукты с высоким содержанием ПВ, но низкой гликемической нагрузкой [3]. AHA также рекомендует переход на диету, богатую ПВ, для предотвращения развития сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, например «средиземноморскую диету» или диету DASH (диетологический подход к лечению артериальной гипертензии) [5].
ПВ могут опосредованно влиять на все органы и системы организма, включая сердечно-сосудистую систему. В рекомендациях Российского кардиологического общества по диагностике и коррекции нарушений липидного обмена подчеркивается важность планирования питания с содержанием ПВ не менее 45–50% рациона с целью профилактики и лечения атеросклероза [6]. Не менее важное свойство ПВ – их способность регулировать массу тела и углеводный обмен как у здоровых людей, так и у пациентов, страдающих метаболическими нарушениями.
Вместе с тем на сегодняшний день в клинической практике рекомендации по внедрению ПВ в рацион остаются нереализованными в полной мере ввиду плохой переносимости большим количеством пациентов продуктов, богатых этими веществами. Кроме того, данные всемирно известных организаций расходятся относительно количества и источников ПВ, необходимых для ежедневного приема. В России четкие указания на этот счет также отсутствуют.
Виды пищевых волокон
По химическому составу ПВ классифицируют на лигнин (фенилпропановый полимер ароматических спиртов), крахмал и некрахмальные полисахариды. Последние можно разделить на целлюлозу и нецеллюлозные полисахариды. К нецеллюлозным полисахаридам относятся гемицеллюлоза, пектиновые вещества, камеди, слизи, запасные полисахариды, подобные инулину и гуару (рис. 1) [2, 7].
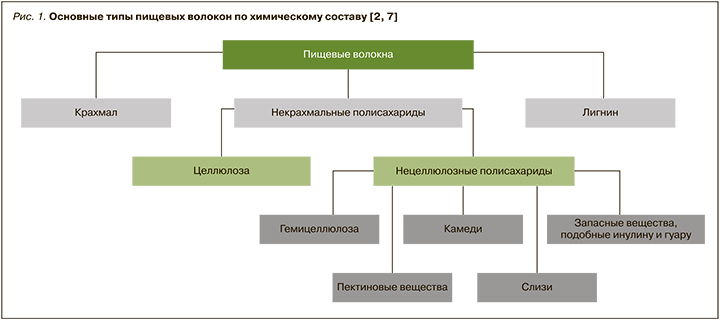
Также ПВ можно классифицировать на следующие группы:
- водорастворимые (пектины, камеди, слизи, дериваты целлюлозы);
- водонерастворимые (целлюлоза, лигнин).
По степени микробной ферментации в толстой кишке выделяют:
- почти полностью ферментируемые ПВ (пектин, камеди, слизи, гемицеллюлоза);
- частично ферментируемые ПВ (целлюлоза);
- неферментируемые ПВ (лигнин) [8].
ВЛИЯНИЕ ПИЩЕВЫХ ВОЛОКОН НА МЕТАБОЛИЗМ КИШЕЧНОЙ МИКРОБИОТЫ
Данные о влиянии ПВ на состав кишечной микробиоты приводятся во многих актуальных исследованиях. Их употребление ассоциировано с ускорением насыщения, снижением массы тела, снижением инсулинорезистентности, улучшением липидного профиля, а также с изменением качественных и количественных характеристик кишечной микробиоты [9].
ПВ служат субстратом пищи и энергии для бактерий. Добавление ПВ в рацион питания способствует увеличению разнообразия микробиоты кишечника [10]. Один из механизмов влияния ПВ на кишечную микробиоту состоит в модуляции образования короткоцепочечных жирных кислот (КЦЖК), основными из которых являются ацетат, пропионат и бутират. Особенности активности кишечной микробиоты определяют количество и соотношение синтезируемых КЦЖК, однако и свойства КЦЖК обладают модулирующим эффектом на состав кишечной микробиоты. Наиболее «влиятельная» КЦЖК в этом плане бутират: он выступает энергетическим источником для колоноцитов, способствующим их пролиферации и дифференцировке. КЦЖК также регулируют абсорбцию некоторых микроэлементов, в частности кальция и магния, участвуют в регуляции баланса натрия и воды. Влияние КЦЖК на микрофлору кишечника связано с их способностью изменять рН в кишечнике, что стимулирует рост микроорганизмов одних видов и угнетает активность других. Например, при адекватном синтезе КЦЖК поддерживается жизнедеятельность бифидо- и лактобактерий и подавляется деятельность условно-патогенных бактерий, которые продуцируют оксид азота (NO), участвующий в окислительном стрессе, а также другие метаболиты, неблагоприятно воздействующие не только на микробиоту, но и на организм в целом [11].
Было отмечено, что при обогащении рациона питания продуктами, содержащими ПВ, уменьшалась относительная концентрация уксусной кислоты, в то время как концентрация масляной кислоты, наоборот, увеличивалась. Зарегистрированные изменения метаболизма кишечной микробиоты сопровождались снижением массы тела и уменьшением частоты жалоб на метеоризм и флатуленцию, дискомфорт в животе, запор, урчание в животе при пальпации [12].
В исследовании А.А. Курмангулова с соавт. антропометрических и метаболических параметров у пациентов с метаболическим синдромом было выявлено, что включение в суточный рацион ПВ в количестве не менее 35 г/сут приводило к улучшению функциональной активности кишечной микробиоты, которое проявлялось статистически значимым увеличением рН кала, снижением содержания солей жирных кислот, йодофильных микроорганизмов, а также увеличением общего пула и изменением профиля КЦЖК [13].
ВЛИЯНИЕ ПИЩЕВЫХ ВОЛОКОН НА УГЛЕВОДНЫЙ ОБМЕН
Некоторые исследователи называют снижение употребления населением ПВ одним из патогенетических механизмов развития нарушений углеводного обмена [2]. ПВ могут регулировать гликемию путем снижения скорости всасывания глюкозы в кишечнике, изменения транзита пищи в желудке и тонкой кишке, а также через управление стимуляции гликолиза и изменение инкреции инсулина и интестинальных гормонов [8]. Наряду с этим ПВ поддерживают чувство насыщения, что способствует профилактике ожирения и положительно влияет на углеводный обмен [14]. Не менее важной является способность ПВ модулировать состав, функции кишечной микробиоты и соотношение ее метаболитов.
В метаанализе имеющихся исследований о влиянии различных ПВ на профилактику сахарного диабета 2-го типа (СД 2), выполненном Yao B. et al., был сделан вывод о том, что ежедневный прием ПВ снижает риск развития этого заболевания. Питание испытуемых было обогащено за счет ПВ, содержащихся во фруктах, крупах, нерастворимых ПВ, а также общих ПВ во всех продуктах питания. Участники исследований были разделены на группы по половому, возрастному и национальному признаку. В исследуемых группах относительный риск (ОР, RR) развития СД 2 составлял 0,98 (95% доверительный интервал (ДИ): 0,90–1,06), 0,97 (95% ДИ: 0,87–1,07), 0,89 (95% ДИ: 0,80–0,99), 0,76 (95% ДИ: 0,65–0,88) и 0,66 (95% ДИ: 0,53–0,82) при ежедневном приеме 15, 20, 25, 30 и 35 г ПВ соответственно. Авторы выявили линейную зависимость риска развития СД 2 от количества употребляемых ежедневно ПВ, кроме того, была обнаружена связь этого риска с характером применяемых ПВ. Наибольшей эффективностью в профилактике СД 2 обладали нерастворимые ПВ (ОР 0,75; 95% ДИ: 0,63–0,89), почти настолько же эффективными оказались ПВ из круп (ОР 0,77; 95% ДИ: 0,69–0,85). В группе участников, получавших смесь ПВ ОР развития СД 2, оказался равен 0,81 (95% ДИ: 0,73–0,90), а самое высокое значение этого показателя было в группе, применявшей ПВ из фруктов – 0,94 (95% ДИ: 0,88–0,99) [15].
В другом исследовании, где сравнивались диета, обогащенная ПВ, и диета с повышенным содержанием белка, было обнаружено, что чувствительность тканей к инсулину оказалась в среднем на 25% больше в группе пациентов, употребляющих ПВ. Авторы исследования связывают полученные результаты с тем, что у группы, придерживающейся высокобелковой диеты, был обнаружен повышенный синтез фактора инициации трансляции сериновой киназы-6-1 в жировой ткани, которая способствует инсулинорезистентности, индуцированной аминокислотами. Было отмечено, что употребление ПВ снижает всасывание белка [16].
В своем исследовании Parker E.D. et al. пришли к заключению, что увеличение потребления цельнозерновой пшеницы снижает вероятность развития СД 2 пропорционально количеству употребляемых ПВ [17]. Аналогичные результаты были опубликованы в метаанализе de Munter J.S. et al.: исследователи точно так же установили, что риск развития СД 2 имеет обратную зависимость с употреблением ПВ. В этом метаанализе подчеркивается, что более значимый эффект наблюдался при приеме отрубей, чем зародышей зерновых [18]. Диета с повышенным содержанием ПВ способствовала улучшению гликемического контроля: уровень гликолизированного гемоглобина (HbA1c) составил менее 7% у 89% пациентов, соблюдавших диету, и лишь у 50% в контрольной группе. В этом же исследовании был измерен индекс активности продукции КЦЖК. Он оказался в значительной степени выше в группе пациентов, соблюдавших диету с повышенным содержанием ПВ [19].
Положительное влияние ПВ на поддержание оптимальной массы тела стало выводом масштабного анализа CARDIA. В нем были проанализированы результаты 27 исследований с участием 2909 лиц молодого возраста (от 18 до 30 лет), не имеющих хронических заболеваний. Прием ПВ способствовал не только снижению энергетической ценности рациона на 10%, но и уменьшению уровня постпрандиальной гликемии, инсулинемии, холестеринемии и триглицеридемии. При более длительном наблюдении у исследуемых также было зафиксировано снижение синтеза атерогенных липопротеинов и оптимизация массы тела [20].
Lutsey P.L. et al. оценивали взаимосвязь между употреблением цельнозерновой пшеницы и СД 2, инсулинорезистентностью, ожирением и субклиническими кардиоваскулярными заболеваниями. В исследовании приняли участие 5496 человек. Ассоциация применения указанного источника ПВ с субклинически протекающими сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями обнаружена не была, однако была выявлена обратная зависимость между употреблением цельнозерновой пшеницы и риском развития СД 2, инсулинорезистентностью и ожирением [21].
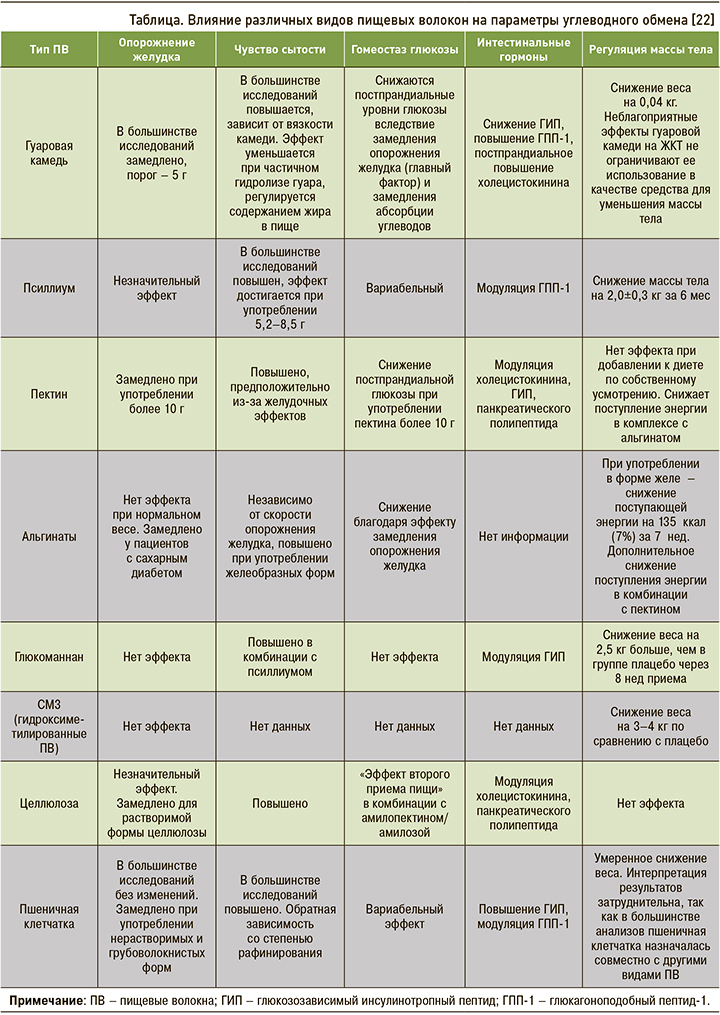
Аспекты влияния различных видов ПВ на параметры углеводного обмена обобщенно отражены в таблице.
ПИЩЕВЫЕ ВОЛОКНА И ОЖИРЕНИЕ
Исследование Lairon D. с участием 2532 мужчин и 3429 женщин продемонстрировало влияние разных типов ПВ на снижение индекса массы тела (ИМТ), индекса «талия–бедра», улучшение липидного профиля, уменьшение артериального давления (АД). С меньшей эффективностью был связан прием растворимых ПВ. ПВ, получаемые из круп, приводили к снижению ИМТ, АД и уровня гомоцистеина. Прием ПВ из овощей ассоциировался с уменьшением АД и уровня гомоцистеина, ПВ из фруктов – со снижением индекса «талия–бедра» и АД. ПВ из высушенных фруктов и орехов способствовали снижению ИМТ, индекса «талия–бедра», уровня глюкозы и аполипопротеина B натощак. При употреблении ПВ из бобовых значимых изменений оцениваемых параметров обнаружено не было [23].
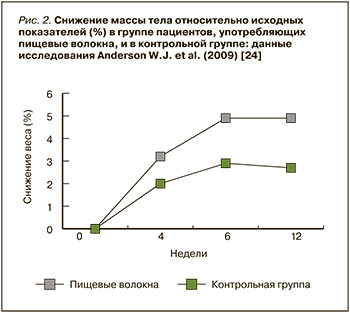
В исследовании Anderson W.J. et al., в котором оценивались эффекты преимущественно нерастворимых ПВ на 423 участниках в сравнении с 391 добровольцем (контроль), снижение массы тела было более значительным именно в основной группе. Так, через 4 нед в контрольной группе масса тела в среднем снизилась на 1,7 кг, тогда как в группе пациентов, получавших ПВ, – на 3,0 кг. К 8-й неделе аналогичные показатели снижения веса в группах исследования равнялись 2,4 и 4,9 кг, к 12-й неделе – 2,7 и 4,9 кг соответственно. Относительно исходной массы тела ее снижение в контроле и группе участников, получающих ПВ, через 4 нед составило 2,0 и 3,2%, через 8 нед – 2,9 и 4,9%, через 12 нед – 2,7 и 4,9% соответственно (рис. 2) [24].
Влияние ПВ на снижение массы тела также было показано в исследовании Liu S. et al. с участием 74 091 женщины среднего возраста, употребляющих ПВ на протяжении 12 лет. У женщин, применяющих наибольшее количество ПВ по сравнению с остальными, наблюдалась прибавка массы тела в среднем на 2,65 кг, в то время как в группе женщин с наименьшим (относительно других групп) употреблением ПВ прибавка вес в среднем увеличился на 5,1 кг за все время наблюдения. Исследователи подчеркивают, что наиболее эффективными оказались ПВ из цельнозерновых злаков, а также делают вывод о том, что среди цельнозерновых следует выделять особую группу очищенных цельнозерновых злаков, демонстрирующих наибольшую эффективность [25].
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Полезные свойства ПВ в отношении массы тела и углеводного обмена продемонстрированы в большом количестве исследований и на данный момент не вызывают сомнений. На сегодняшний день, помимо давно известных механизмов метаболического действия ПВ посредством управления пассажем пищи, изучается их опосредованное влияние на обмен веществ через кишечную микробиоту и ее метаболиты.
Несмотря на то что ПВ рассматриваются как натуральные продукты, которые, в отличие от лекарственных препаратов, имеют минимальное количество потенциальных побочных эффектов, известно, что они в недостаточном количестве потребляются населением. Это объясняется частично плохой переносимостью некоторых пищевых продуктов, богатых ПВ: их не употребляют в пищу в связи с выраженным газообразованием и флатуленцией. Также низкое потребление ПВ можно объяснить недостаточной информированностью населения об их положительных эффектах и отсутствием указания на прием конкретных дозировок ПВ в клинических рекомендациях. Один из путей решения этой проблемы видится в углубленном исследовании свойств ПВ и их влияния на кишечную микробиоту и ее метаболизм.



