ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Заболевания органов дыхания относятся к наиболее распространенным проблемам профессиональной патологии; главным образом это относится к бронхиальной астме (БА) и хронической обструктивной болезни легких (ХОБЛ).
В последнее время все больше внимания уделяется взаимодействию метаболических нарушений и бронхообструктивных заболеваний. В механизме развития патологии лежат гипоксия и окислительный стресс, электролитные сдвиги, системное воспаление, дисбаланс в обмене липидов и другие причины, приводящие к системной интоксикации организма [1]. В связи с этим диетотерапия пациентов с заболеваниями бронхолегочной системы на фоне профессиональных вредных условий труда должна быть направлена на снижение интоксикации и повышение защитных сил организма, улучшение регенерации эпителия дыхательных путей, уменьшение экссудации в бронхах [1].
Функциональные нарушения легочной функции, характерные для БА, возникающая тяжелая симптоматика не только способствуют нарушению качества жизни астматиков, но и увеличивают риск сопутствующего развития ХОБЛ [2]. Этиологическими факторами указанных бронхолегочных заболеваний выступают как генетические нарушения, так и факторы окружающей среды. Отметим, что, несмотря на значимую роль наследственных факторов, увеличение распространенности БА и ХОБЛ (особенно профессионального генеза), начиная со второй половины XX в., в основном было обусловлено факторами окружающей среды, такими как курение, загрязнение воздуха, изменение образа жизни и диеты [3].
В последние несколько лет были опубликованы многочисленные работы, указывающие на то, что при течении БА наблюдается снижение уровня микронутриентов [4–6]. В ряде обзоров сообщалось о защитной связи между потреблением фруктов, овощей, бобовых, злаков и БА [7–9]. Эти взаимосвязи могут быть частично объяснены дополнительным поступлением в организм антиоксидантов, витаминов, микроэлементов, а также пищевых волокон. Пищевые волокна потенциально могут уменьшать воспаление дыхательных путей, способствуя выработке противовоспалительных цитокинов, улучшая контроль уровня глюкозы и модулируя иммунологический ответ со стороны микробиома и слизистой оболочки кишечника [10]. Показано, что среди взрослых с тяжелой БА наблюдалось снижение потребления клетчатки, что тесно связано с усилением эозинофильного воспаления дыхательных путей [11].
Исследования последних лет свидетельствуют, что окислительный стресс играет особо важную роль в патогенезе бронхолегочной патологии, оказывая отрицательное влияние не только на ткани легких, но и других органов, в частности скелетные мышцы и печень. В связи с этим витамины, способные оказывать противовоспалительное и антиоксидантное действие (А, С и Е), очевидно, играют важную защитную роль при прогрессировании БА и ХОБЛ. Так, обнаружено, что индекс массы тела (ИМТ) у пациентов с ХОБЛ в значительной степени коррелирует с окислительным стрессом, при этом низкие значения этого параметра ассоциированы со сниженным уровнем глутатиона и повышенным перекисным окислением липидов [12], а повышенный окислительный стресс во время обострений заболевания связан с уменьшением концентрации витаминов А и Е в сыворотке крови. Исследованиями показано, что витамин Е при приеме в дозе 400 МЕ/сут в течение 12 нед снижает перекисное окисление липидов при ХОБЛ [13], а дополнительное потребление витамина А приводит к улучшению объема форсированного выдоха за 1-ю секунду (ОФВ1, +23%) и форсированной жизненной емкости легких (ФЖЕЛ, +25%) [14].
Ранее проведенными исследованиями было установлено, что развитие и течение ХОБЛ, мышечных дистрофий в определенной мере ассоциировано с уровнем ряда микроэлементов в организме пациентов. Фенотипическими исследованиями показано, что у лиц генетически высоким уровнем железа имеется положительная корреляция с саркопенией, тогда как концентрации кальция в сыворотке крови, напротив, отрицательно коррелируют с этим состоянием, развивающимся у пациентов с ХОБЛ [15]. Вместе с тем существует и противоположная точка зрения на этот счет. Так, одно из недавних исследований показало, что у пациентов с дефицитом железа и тяжелой формой ХОБЛ уровень ферритина в сыворотке крови был низким, и такое снижение в значительной мере коррелировало с уменьшением пройденного расстояния, измеренного с помощью стандартного теста 6-минутной ходьбы; это свидетельствует о снижении мышечной функции у данной группы пациентов [16].
Немаловажную роль при заболеваниях бронхолегочной системы выполняет и цинк, поскольку он замедляет окислительные процессы в организме, а также ингибирует ароматазу и 5α-редуктазу, необходимые для метаболизма гормонов, в частности тестостерона [17]. Установлено, что использование антиоксидантных добавок, содержащих глюконат цинка и селен, в сочетании с факторами легочной реабилитации пациентов улучшает силу четырехглавой мышцы и увеличивает долю волокон I типа у пациентов с ХОБЛ [18].
Гипомагниемия считается предиктором тяжести заболевания у пациентов с ХОБЛ, а магний может уменьшать системное воспаление и уровни провоспалительных цитокинов [19]. Установлено, что концентрация ионизированного магния в нейтрофильных лейкоцитах у больных ХОБЛ достоверно ниже, чем у здоровых некурящих лиц. Наряду с этим у пациентов с ХОБЛ отмечается значительно более высокое соотношение концентраций Ca2+/Mg2+ в плазме и нейтрофилах [20]. В одном из рандомизированных контролируемых исследований было продемонстрировано, что потребление сывороточных напитков, обогащенных магнием и витамином С, пациентами с ХОБЛ средней и тяжелой степени сопровождается повышением безжировой массы тела, индекса безжировой массы тела и мышечной силы [21, 22]. Кроме того, имеются данные о том, что концентрация магния в сыворотке положительно коррелирует с мышечной силой [23].
Таким образом, для пациентов, страдающих БА, ХОБЛ и другими заболеваниями бронхолегочной системы, большое значение имеет присутствие в рационе фруктов, овощей, пищевых волокон, а также таких минеральных веществ, как калий, магний, фосфор, цинк, селен, кальций и, вполне вероятно, ряда других, менее изученных микроэлементов. Микроэлементный дефицит, обусловленный низким поступлением их с рационом питания, неблагоприятно сказывается на функции дыхательной мускулатуры, развитии и течении большинства бронхолегочных заболеваний.
Целью настоящего исследования стало изучение эффективности, безопасности и переносимости специализированного пищевого продукта диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ» в комплексной терапии пациентов с патологией бронхолегочной системы, а также оптимизации путей коррекции микронутриентной недостаточности.
МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДЫ
Для изучения клинической эффективности, безопасности и переносимости применения у пациентов с бронхолегочной патологией использовался специализированный пищевой продукт диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ», в составе которого содержатся фрукты, ягоды, овощи, овес, витамины С, Е, РР (ниацин), А, В2, В6, микроэлементы цинк, селен, марганец, экстракты зеленого чая, расторопши, лопуха, одуванчика, куркума, янтарная кислота, L-цистин, лимонная кислота, кофеин. Основание для исследования этого напитка стали ранее полученные данные о его антиоксидантной, противовоспалительной, иммунотропной активности при интоксикации, обусловленной различными заболеваниями и экологически неблагоприятными факторами окружающей среды (SARS-CoV-2, злокачественные новообразования, профессиональные интоксикации) [23–27].
Изучалась эффективность 15-дневного приема продукта (по 1 разу в день во время или после еды). Для проведения исследования были сформированы две группы пациентов с бронхолегочной патологией (БА и ХОБЛ), рандомизированных по полу и возрасту, а также степени тяжести и давности заболевания.
В основную группу вошли 20 пациентов с бронхолегочной патологией обоего пола в возрасте от 55 до 76 лет. Среди них 17 человек страдают профессиональной БА, 3 человека – ХОБЛ. В анамнезе у 5 больных основной группы имелся установленный диагноз COVID-19 (время с момента установления диагноза – от 3 до 18 мес; 4 человека перенесли новую коронавирусную инфекцию средней степени тяжести, 1 – легкую форму). У 7 человек был выявлен гастрит, у 4 отмечались жалобы на различные дискомфортные ощущения в области живота: боль, тошноту, диарею, потерю аппетита.
Контрольную группу составили 18 пациентов с бронхолегочными заболеваниями, которые находились на стандартной терапии без включения в рацион питания диетического лечебного продукта для детоксикации.
Все обследованные пациенты получали стандартную терапию согласно установленному диагнозу.
Критерии включения в исследования:
- мужчины и женщины в возрасте старше 45 лет, имеющие профессиональное заболевание бронхолегочной системы;
- наличие подписанного информированного согласия на участие в исследовании.
Критерии невключения:
- для женщин – беременность и кормление грудью;
- наличие алкогольной зависимости (в анамнезе или на момент включения в исследование)
- наркотическая зависимость (в анамнезе или на момент включения в исследование), в том числе связанная с применением наркотических анальгетиков в рамках терапии основного заболевания, наличие которой может оказать отрицательное влияние на безопасность пациента или соблюдение им требований протокола исследования;
- участие пациента в каких-либо других научных или клинических исследованиях лекарственных средств на момент визита с целью скрининга и отбора в исследование и параллельно с текущим исследованием либо участие в таких испытаниях в предшествующие 3 мес до начала первого лечебного периода данного исследования;
- неспособность понять предоставленную информацию об исследовании, нежелание соблюдать требования протокола исследования.
Критерии исключения из исследования:
- тяжелые побочные явления при применении специализированного пищевого продукта диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания;
- отказ пациента от продолжения участия в исследовании;
- индивидуальная непереносимость ингредиентов изучаемого продукта;
- нарушение протокола пациентом или исследователем;
- решение исследователя в интересах пациента;
- выявление хотя бы одного из критериев исключения;
- административные проблемы.
Участники исследования были проинформированы об ингредиентном составе предлагаемых продуктов. От каждого участника было получено информированное согласие на выполнение оценки эффективности специализированного пищевого продукта диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания для детоксикации. Также все пациенты дали добровольное информированное согласие на участие в исследовании.
Проведение исследования было одобрено локальным этическим комитетом ФГБНУ «Научно-исследовательский институт медицины труда им. академика Н.Ф. Измерова». При применении специализированного пищевого продукта диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ» в течение 15 дней всем обследованным дважды (до начала исследований и через 15 дней) выполнялось обследование, включающее общий клинический, биохимический анализ крови (общий холестерин, глюкоза, аспартатаминотрасфераза, аланинаминотрансфераза, гамма-глютамилтранспептидаза, общий билирубин, прямой билирубин). Также все участники исследования прошли обследование у терапевта с целью выявления жалоб со стороны бронхолегочной системы и желудочно-кишечного тракта (ЖКТ). Для оценки эффективности специализированного пищевого продукта диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания, качества жизни больных до и после его применения использовалась разработанная анкета «качества жизни», содержащая вопросы об общем состоянии обследованного, состоянии бронхолегочной системы (кашель, приступы удушья), ЖКТ (боли и дискомфорт в ЖКТ). Органолептические свойства исследуемого продукта оценивались по 5 параметрам (внешний вид, запах, цвет, вкус, консистенция) и 5-балльной системе.
Оценка динамики показателей клинического анализа крови (уровней гемоглобина, лейкоцитов, эритроцитов, тромбоцитов, показателей лейкоцитарной формулы) выполнялась на автоматическом анализаторе Sysmex XN-1000. Определение динамики биохимических показателей (глюкозы, общего холестерина, липопротеидов низкой плотности, липопротеидов высокой плотности, триглицеридов, общего белка, аспартатаминотрасферазы, аланинаминотрансферазы, гамма-глютамилтранспептидазы, общего билирубина, прямого билирубина, мочевины, креатинина, С-реактивного белка) проводилась на автоматическом биохимическом анализаторе Konelab PRIME 30i (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Всем обследованным были рассчитаны лейкоцитарные индексы интоксикации: лейкоцитарный индекс интоксикации по Кальф–Калифу (ЛИИ), лейкоцитарный индекс интоксикации по Островскому (ЛИИост), индекс Кребса и индекс, характеризующий системное воспаление (PLR – platelet to lymphocyte ratio).
Формула Кальф–Калифа служит достаточно быстрым и легким методом определения ЛИИ в крови у человека:
ЛИИ = (4Мн + ЗЮ + 2П + С) × (Пл + 1) / (Мон + Л) × (Э+ 1), где Мн – миелоциты; Ю – юные формы; П – палочкоядерные нейтрофилы; С –сегментоядерные нейтрофилы; Мон – моноциты; Л – лимфоциты; Э – эозинофилы; Пл – плазматические клетки.
Величина индекса в норме составляет 1,0–1,4. ЛИИ более 1,5 свидетельствует о легкой, свыше 5 – о тяжелой степени интоксикации.
Лейкоцитарный индекс интоксикации по Островскому рассчитывается по формуле:
ЛИИост. = (Нейтр+ Пл) / (М + Л + Э), где Нейтр – нейтрофилы.
Все значения выражены в процентах; нормальное значение ЛИИост. 1,6.
Индекс Кребса (ИК) – отношение всей суммы процентного содержания нейтрофилов к такому же количеству лимфоцитов (отношение клеток неспецифической и специфической защиты). ИК объективно отражает степень интоксикации. В норме этот коэффициент составляет 1,8±0,46. При воспалительном процессе с легкой эндогенной интоксикацией (ЭИ) он равен 2,8±0,4, при средней степени тяжести ЭИ – 4,86±0,97, при тяжелой – более 5,76±1,19. Увеличение коэффициента до 4,0 и более свидетельствует о нарастании тяжелой интоксикации.
Отношение тромбоцитов к лимфоцитам (PLR) – новый воспалительный параметр, который недавно привлек внимание исследователей в связи с тем, что может выступать в качестве индикатора воспаления при широком спектре заболеваний.
Критериями эффективности исследуемого продукта служили результаты сравнительного анализа выбранных параметров, а также отсутствие нежелательных явлений на фоне его применения в период наблюдения и приятные органолептические свойства.
Статистическая оценка полученных данных проводилась на основании расчета парного критерия Стьюдента. Уровень значимости был принят за 5%. Результаты оценки представлены в виде М±m, где М – среднее значение, m – стандартное отклонение, в некоторых случаях – как М (от min до max), где min и max – соответственно минимальные и максимальные изменения значений, полученные для обследуемой группы.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
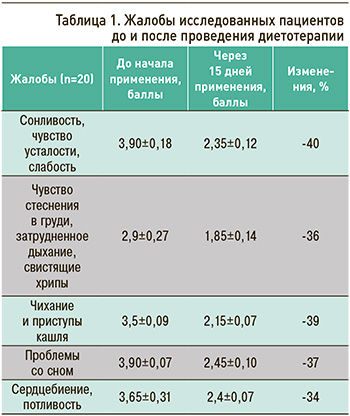
До начала применения специализированного пищевого продукта диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания у обследованных выявлялись жалобы на сонливость, чувство усталости, слабость, чувство стеснения в груди, затрудненное дыхание, свистящие хрипы, чихание и приступы кашля, проблемы со сном, сердцебиение, потливость. Включение в состав рациона исследуемого продукта в течение 15 дней значительно улучшило все анализируемые показатели (от 36 до 40% положительных изменений). Данные результатов анкетирования пациентов представлены в таблице 1.
Анализ общего клинического анализа крови у основной группы пациентов, получавших специализированный пищевой продукт «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ», показал отсутствие достоверных изменений эритроцитарных показателей, что служит одним из показателей отсутствия развития аллергических реакций. При исследовании лейкоцитарной формулы после 15-дневного применения исследуемого продукта было установлено достоверное повышение абсолютного содержания моноцитов (р=0,012) и лимфоцитов (р=0,023), при этом все показатели не выходили за пределы референсных значений.
Анализ лейкоцитарных показателей интоксикации продемонстрировал, что практически все расчетные лейкоцитарные индексы (табл. 2) значительно снизились – более чем на 30,29–41,68%, что значительно превысило аналогичные результаты в контрольной группе. Это свидетельствует о тенденции к снижению интоксикационных явлений на фоне приема исследуемого продукта.
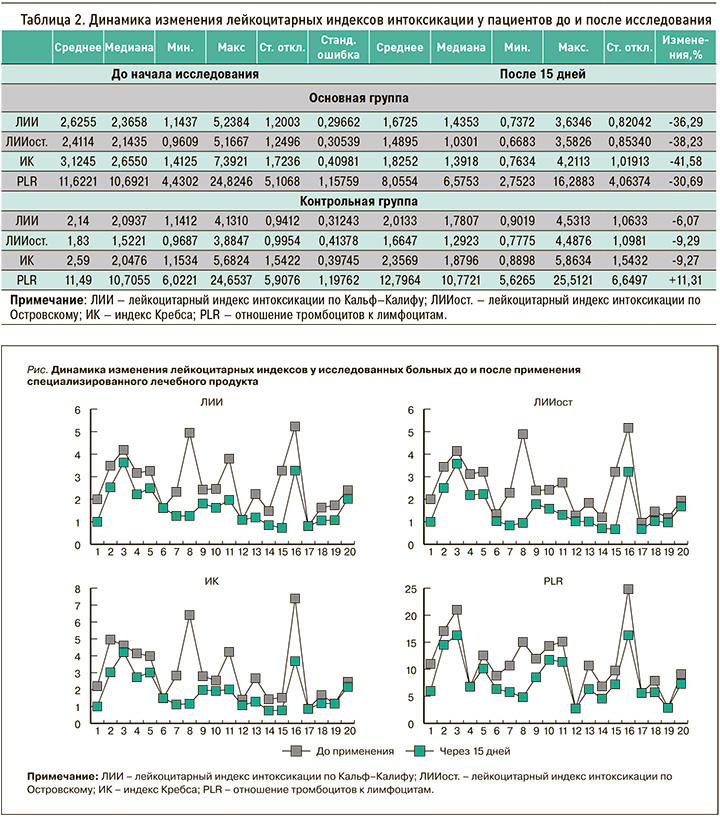
При индивидуальном анализе индексов интоксикации (рис.) у некоторых пациентов были выявлены значительные снижения их значений: для ЛИИ – до 75,9%, ЛИИост. – до 80,6%, ИК – до 81,9%, PLR – до 67,8%. Полученные результаты указывают на выраженную противовоспалительную и, очевидно, иммунотропную активность продукта диетического питания, обусловленную наличием в нем растительных компонентов с доказанными противовоспалительными и иммуномодулирующими свойствами. Об этих эффектах говорит и статистически значимое снижение активности маркера воспаления – С-реактивного белка (на 22,41%) – по сравнению с данными контрольной группы (8,42%; табл. 3).
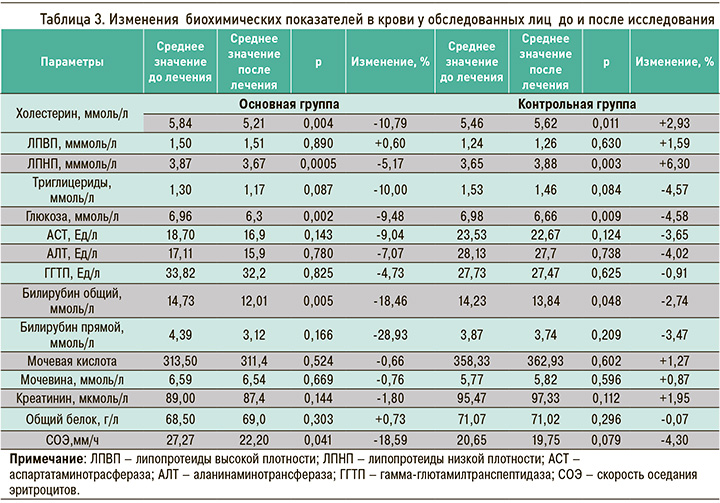
Под влиянием диетотерапии с включением специализированного пищевого продукта для детоксикации в состав комплексной терапии лиц с профессиональной бронхолегочной патологией была отмечена достоверная положительная динамика уровня холестерина и липопротеидов низкой плотности (ЛПНП) в сыворотке, отражающих состояние липидного обмена пациентов. Сравнительный анализ изменения биохимических параметров крови показал (см. табл. 3), что дополнительное включение в рацион питания диетического продукта для интоксикации после короткого 15-дневного курса терапии в стационаре сопровождалось достоверным снижением концентрации холестерина (на 10,79%), триглицеридов (10%), общего и прямого билирубина (18,46 и 28,93% соответственно) и аспартатаминотрасферазы (9,04%). Указанные изменения были статистически достоверны и по сравнению с данными контрольной группы пациентов. Также наблюдалось достоверное снижение уровня глюкозы (на 9,48%) в сыворотке (р=0,002) к 15-му дню применения лечебно-профилактического напитка (см. табл. 3). Это, очевидно, связано с тем, что лечебный напиток для детоксикации содержит метаболики и пищевые волокна из овса, ягод, фруктов и овощей, бета-глюканы из овса, улучшающие обмен веществ и способствующие снижению липидо- и глюкозотоксичности. Большинство остальных компонентов биохимического анализа крови показало тенденцию к снижению, что свидетельствует об активном влиянии диетического продукта на метаболические процессы в печени, обеспечивающие активацию ее антитоксической функции.
Таким образом, продемонстрирована обоснованность применения специализированного пищевого продукта диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ» в комплексной терапии больных с заболеваниями органов дыхания.
Органолептические свойства специализированного пищевого продукта диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ» были высоко оценены всеми обследованными. Участники отмечали его хорошие органолептические свойства, приятный внешний вид, консистенцию, характерную для данного типа продуктов. Незначительные расхождения в оценках были связаны, по-видимому, с индивидуальными предпочтениями пациентов. Все пациенты принимали продукт с удовольствием, отмечали его хорошие вкусовые качества. При изучении мотивации к дальнейшему употреблению специализированного пищевого продукта диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ» все обследованные высказали желание и в последующем использовать этот продукт.
За время проведенного исследования в течение 15 дней на фоне приема специализированного пищевого продукта диетического питания для детоксикации у пациентов не наблюдалось признаков аллергических реакций или других нежелательных эффектов.
Подытоживая проведенные исследования клинической эффективности, переносимости и безопасности применения специализированного пищевого продукта диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ», можно констатировать, что он обладает детоксикационными, антиоксидантными, гепатопротекторными, общеукрепляющими, противовоспалительными свойствами, оказывает профилактическое и оздоравливающее действие на организм.
ВЫВОДЫ
1. Специализированный пищевой продукт диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ» обладает хорошими органолептическими свойствами и не вызывает явлений непереносимости и аллергических реакций.
2. Применение специализированного лечебного продукта для детоксикации в составе комплексной терапии больных с заболеваниями органов дыхания улучшает качество жизни, что проявляется снижением частоты приступов удушья, чихания и кашля, а также улучшением настроения и повышением жизненной энергии, снижением чувства усталости, нормализацией сна.
3. Снижение показателей С-реактивного белка более чем на 22% и скорости оседания эритроцитов на 18,59% свидетельствует об уменьшении воспаления при употреблении продукта «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ». При исследовании лейкоцитарной формулы у исследованных пациентов выявлено достоверное повышение абсолютного содержания моноцитов (р=0,012) и лимфоцитов (р=0,023), при этом все показатели не выходили за пределы референсных значений.
4. При применении продукта «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ» установлено достоверное снижение маркеров интоксикации: ЛИИ на 36,3%, ЛИИост. – на 38,23%, ИК – на 41,6%, индекса PLR – на 30,7%. Это обусловлено тем, что исследуемый продукт оказывает выраженное детоксикационное действие и снижает эндогенную интоксикацию организма у больных с бронхолегочной патологией.
5. У пациентов с профессиональной бронхолегочной патологией на фоне приема специализированного пищевого продукта диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ» было отмечено достоверное снижение уровня холестерина на 10,8%, ЛПНП на 5,2%, триглицеридов на 10% и глюкозы на 9,5%, что обеспечивается содержанием в продукте метаболически-активных компонентов и пищевых волокон из ягод, фруктов и овощей, а также бета-глюканов из овса, улучшающих обмен веществ и способствующих снижению липидо- и глюкозотоксичности.
6. При использовании специализированного пищевого продукта диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического питания «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ» не было обнаружено достоверных изменений основных ферментов печени у пациентов, хотя и отмечалась тенденция к их снижению. Это было связано с коротким сроком применения продукта (15 дней).
7. «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ» улучшает антитоксическую функцию печени, что подтверждено достоверным снижением уровня билирубина у больных.
8. Специализированный лечебный продукт «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ» рекомендуется для включения в комплексную терапию больных с заболеваниями органов дыхания, в том числе гериатрических пациентов, для снижения интоксикации организма и повышения эффективности применяемой терапии.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Исследованиями показано, что специализированный пищевой продукт диетического лечебного и диетического профилактического действия «Напиток для детоксикации ЛЕОВИТ» обладает выраженными противовоспалительным, детоксикационным и общеукрепляющийм действием, хорошо переносится и безопасен. Учитывая длительность процессов восстановления жизненно важных параметров организма при заболеваниях бронхолегочной системы, продукт рекомендуется к применению курсом от 15 дней и более, в том числе и у возрастных пациентов в гериатрической практике.



