В настоящее время на фоне чрезвычайно высокой распространенности артериальной гипертензии (АГ) и абдоминального ожирения (АО) среди населения прослеживается устойчивая тенденция к увеличению доли лиц молодого возраста в структуре АГ и АО. Так, распространенность АГ среди молодых людей до 30 лет варьирует от 3,4 до 40,7% [1]. При этом даже редкие эпизоды повышения артериального давления (АД) могут привести к сердечно-сосудистым осложнениям (ССО) в любом возрасте [2]. Особенностью, затрудняющей диагностику АГ на ранних стадиях у молодых людей, часто является транзиторный характер повышения АД, низкая приверженность данного контингента к выполнению врачебных рекомендаций по диагностике и лечению заболевания, включая модификацию факторов риска [3]. Вместе с тем установлено, что АО в настоящее время является одним из наиболее значимых факторов риска АГ у лиц до 45 лет. По данным Всемирной организации здравоохранения (ВОЗ), 39% взрослых старше 18 лет имеют избыточную массу тела и 13% – ожирение [4]. В Российской Федерации 24,1% населения имеют ожирение, и по этому показателю наша страна находится на 8 месте в мире [5]. К сожалению, хорошо организованных эпидемиологических исследований распространенности ожирения в Российской Федерации до недавнего времени не проводилось с 1985 г. [6, 7]. Сочетание АГ и АО вместе с нарушениями углеводного обмена и дислипидемией составляют основу понятия метаболический синдром (МС). Патогенетические звенья МС в виде инсулинорезистентности (ИР) периферических тканей, гиперинсулинемии, увеличения массы висцерального жира при определенной генетической предрасположенности начинают формироваться уже с этапа внутриутробного развития [8]. При развитии манифестных клинических проявлений МС в ближайшие 10 лет в 5 раз возрастает риск развития сахарного диабета (СД) 2 типа и в 2 раза – риск сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний (ССЗ). Параллельно растет частота острых тромботических событий. Суммарный риск сердечно-сосудистой смерти при МС в 2 раза выше по сравнению с людьми, не имеющими МС, независимо от наличия сердечно-сосудистых катастроф в анамнезе [9]. Остаются недостаточно изученными независимый и взаимосвязанный спектр врожденных и приобретенных факторов риска АГ и АО, а также самостоятельный и комплексный вклад этих компонентов МС в поражение органов-мишеней (ПОМ) и формирование протромботического статуса, дисбаланса адипокинов у молодых пациентов.
Цель исследования – изучение взаимосвязи между показателями гемостаза, содержанием адипокинов, полиморфизмами генов ренин-ангиотензиновой системы и поражением органов-мишеней у молодых пациентов с артериальной гипертензией и абдоминальным ожирением.
Материал и методы
Тип исследования: поперечный срез (cross-sectional study).
Исследуемая популяция: пациенты амбулаторного и стационарного звена МБУЗ «Городская клиническая больница № 11» г. Челябинска, обратившиеся за период 2013–2016 гг.
Критерии включения: наличие абдоминального ожирения и/или впервые диагностированной артериальной гипертензии, молодой возраст (18–44 лет), информированное согласие пациентов на участие в исследовании.
Критерии исключения: симптоматические артериальные гипертензии, ассоциированные клинические состояния (III стадия гипертонической болезни), сахарный диабет 1 и 2 типа, системные заболевания соединительной ткани, беременность и период лактации.
Всего обследован 251 человек. Больные были разделены на 4 группы: группа 1 – пациенты с изолированной АГ (35 человек; 17 мужчин; средний возраст 33,1±8,7 года), группа 2 – пациенты с изолированным АО (76 больных; 39 мужчин; средний возраст 31,9±8,9 года), группа 3 – больные с сочетанием АГ и АО (60 человек; 30 мужчин; средний возраст 36,5±6,9 года), группа 4 – контрольная (80 человек; 38 мужчин; средний возраст 30,3±7,8 года). В контрольную группу вошли практически здоровые волонтеры из медицинского персонала и амбулаторных пациентов, не имеющие АГ и АО.
Диагнозы АГ и АО устанавливались согласно Национальным рекомендациям Российского кардиологического общества (2010) и Российского медицинского общества по артериальной гипертонии (2013).
Всем пациентам определяли концентрацию глюкозы, общего холестерина (ОХС), холестерина липопротеидов низкой плотности (Хс-ЛПНП), холестерина липопротеидов высокой плотности (Хс-ЛПВП), триглицеридов, уровень иммунореактивного инсулина (ИРИ) крови с расчетом индекса HOMA-IR [HOMA-IR = глюкоза натощак (ммоль/л) × инсулин натощак (мкЕд/мл)/22,5), концентрацию лептина (набор Diagnostics Biochem Canada Inc, Канада) и адипонектина (АssayPro, США; анализатор Analette Biochem, HTI, США)]. Лабораторное исследование системы гемостаза включало определение клоттинговых тестов (АЧТВ, протромбиновое время, тромбиновое время, фибриноген), D-димера, активности антитромбина III, ингибитора пути тканевого фактора (TFPI) (АssayPro, США; анализатор Analette Biochem, HTI, США) [10]. Молекулярно-генетическое тестирование выполнялось методом полимеразной цепной реакции (ПЦР) с использованием набора реактивов («Литех», Москва) на ПЦР-анализаторе «Терцик» («ДНК-технология», Россия). Анализу подвергалась геномная ДНК, выделенная из лейкоцитов цельной крови, стабилизированной ЭДТА, с помощью реагента «ДНК-экспресс-кровь». Исследовались аллельные полиморфизмы генов, кодирующих различные компоненты РАС: I/D – гена ангиотензинпревращающего фермента (ACE), T174M и M235T – гена ангиотензиногена (AGT), A1166C – гена рецептора 1-го типа ангиотензина II (AGTR1).
Критерием диагностики гипертрофии левого желудочка принималось значение индекса массы миокарда левого желудочка (ИММЛЖ) более 95 г/ м2 у женщин и более 115 г/м2 у мужчин [11]. Пороговую величину толщины комплекса интима-медиа (ТКИМ) принимали до 40 лет 0,7 мм, от 40 до 44 лет – 0,8 мм [12]. Расчет скорости клубочковой фильтрации проводился по формуле CKD-Epi (Chronic Kidney Desease Epidemiology Collaboration).
Статистическая обработка данных осуществлялась с помощью пакета MedCalc (Version 15.6, 2015). Данные в тексте представлены в виде средней арифметической и ее среднеквадратичного отклонения (M±SD) – при параметрическом распределении; медианы и интерквартильного размаха (Ме (Q25–Q75)) – при непараметрическом распределении. Применялись критерии Стьюдента, Манна–Уитни, Краскелла–Уоллиса, дисперсионный анализ и хи-квадрат Пирсона (χ2) в зависимости от типа данных и с учетом характера распределения. Для всех видов анализа статистически достоверными считались значения p <0,05.
Результаты и обсуждение
Общая характеристика факторов риска сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, показатели углеводного и липидного обмена в сравниваемых группах представлены в табл. 1. Обращает на себя внимание высокая частота модифицируемых факторов сердечно-сосудистого риска в исследуемых группах пациентов молодого возраста: курение, дислипидемии и гипергликемии натощак, особенно при сочетании АГ и АО.
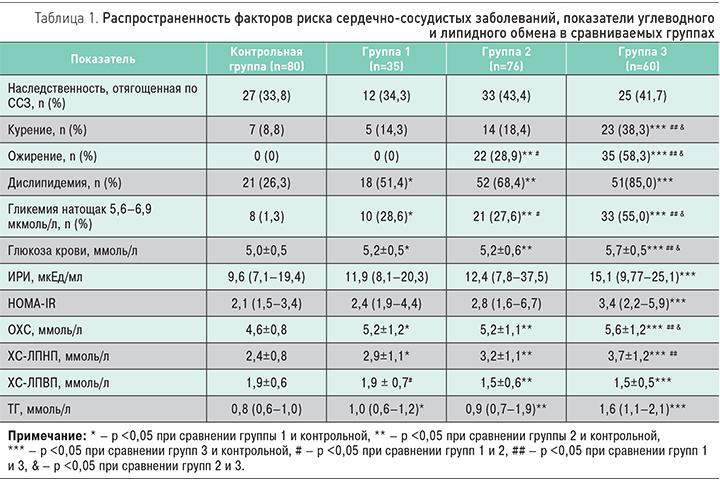
У пациентов трех групп оказались выше уровни глюкозы, общего холестерина, ХС-ЛПНП и ТГ по сравнению с контрольной группой, при этом наиболее высокие показатели отмечены в группе 3. Среди пациентов группы 3 выявлены наиболее высокие значения ИРИ и индекса HOMA-IR, отражающие ИР и гиперинсулинемию. Значимых различий по изучаемым показателям в группе 1 и 2 (с изолированными АГ и АО) получено не было.
При анализе показателей гемостаза (табл. 2) у пациентов группы 3 были выявлены наиболее высокие уровни фибриногена и D-димера в сочетании с замедлением фибринолиза, повышением концентрации PAI-1 и увеличение уровня TFPI в сравнении с контрольной группой. Необходимо отметить, что повышение TFPI и PAI-1 нами обнаружено также в группе 1 по сравнению с контрольной группой. Параллельно у пациентов в трех группах выявлен дисбаланс адипокинов – повышение концентрации лептина и снижение адипонектина относительно контрольной группы. Так, в группе с АГ в сочетании с АО концентрация лептина оказалась в 3 раза выше, а в группе с изолированным АО – в 4 раза выше по сравнению с контрольной группой. Во всех трех группах концентрация адипонектина была достоверно ниже, чем в контрольной группе (табл. 2).
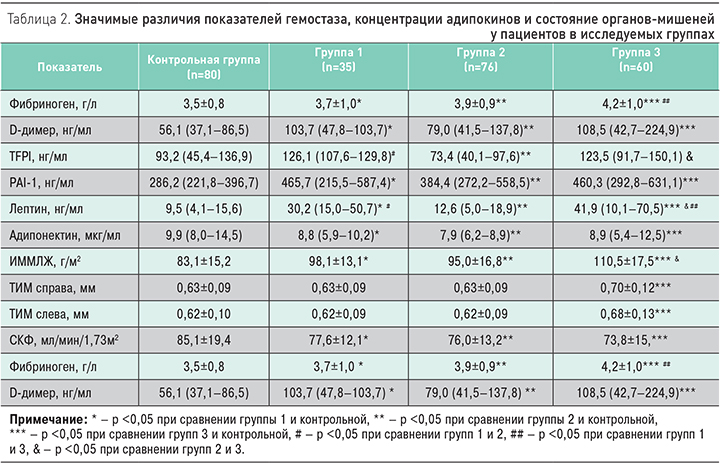
Исследование полиморфизмов генов ренин-ангиотензиновой системы было выполнено у 30 пациентов в группе 1, 40 пациентов в группе 2, 40 пациентов в группе 3 и у 75 пациентов в контрольной группе (табл. 3). У пациентов в группе 1 чаще выявлялось носительство «мутантного» С-аллеля (ОШ 11,3; 95% ДИ 3,6–35,9; р <0,001) полиморфизма A1166С гена рецептора 1-го типа ангиотензина II и «мутантный» СС-генотип по сравнению с группой 2 и контрольной группой (ОШ 3,07; 95% ДИ 1,27–7,40; р=0,01). В группе 3 чаще выявлялось носительство «мутантного» Т-аллеля полиморфизма M235T гена ангиотензиногена (ОШ 4,6; 95% ДИ 1,9–11,1; р <0,001) и генотип M/T гена ангиотензиногена (ОШ 3,1; 95% ДИ 1,4-6,9; р=0,005) в сравнении с контрольной группой, а также носительство «мутантного» M-аллеля полиморфизма T174M гена ангиотензиногена (ОШ 3,1; 95% ДИ 1,4–6,8; р=0,006) и генотип T/M гена ангиотензиногена (ОШ 2,9; 95% ДИ 1,3–6,5; р=0,008) в сравнении с контрольной группой. Различий в распределении частот аллелей и генотипов полиморфизма I/D гена ACE в сравниваемых группах выявлено не было.
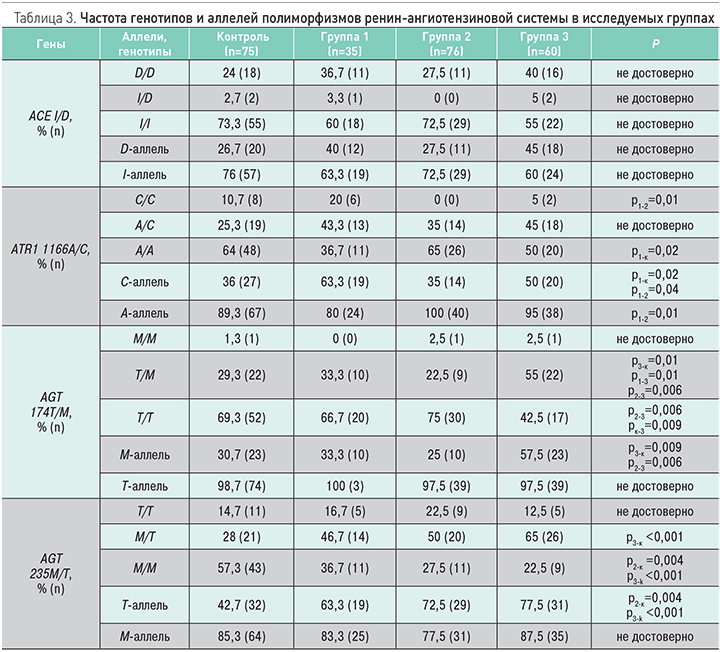
При оценке состояния органов-мишеней только в группах 1 и 3 выявлялась гипертрофия левого желудочка, причем достоверно чаще, чем в группе 2 и контрольной группе. Во всех трех группах ИММЛЖ был выше по сравнению с контрольной группой (см. табл. 2). Толщина комплекса интима-медиа на сонных артериях оказалась достоверно выше в группе 3 по сравнению с другими группами, в том числе с изолированной АГ. Скорость клубочковой фильтрации оказалась ниже во всех трех группах по сравнению с контрольной, причем в группе 3 СКФ <60 мл/мин/ м2 была выявлена у каждого 5-го пациента (20%). В соответствии с полученными данными, II стадия АГ диагностирована у 6 пациентов в группе 1 (17,1%) и у 12 пациентов в группе 2 (20%).
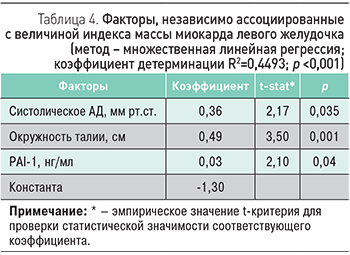 Для оценки ассоциации изучаемых факторов с величиной индекса массы миокарда левого желудочка нами проведен множественный регрессионный анализ. Детерминантами, независимо связанными с величиной ИММЛЖ, оказались величина систолического артериального давления и характеристики метаболических нарушений – окружность талии и концентрация PAI-1 (табл. 4).
Для оценки ассоциации изучаемых факторов с величиной индекса массы миокарда левого желудочка нами проведен множественный регрессионный анализ. Детерминантами, независимо связанными с величиной ИММЛЖ, оказались величина систолического артериального давления и характеристики метаболических нарушений – окружность талии и концентрация PAI-1 (табл. 4).
В нашем исследовании обращает на себя внимание высокая распространенность модифицируемых факторов сердечно-сосудистого риска среди обследованных групп: курения, дислипидемии, ожирения и нарушения толерантности к глюкозе. Одновременно у пациентов всех сравниваемых групп обнаружена большая частота сочетания трех и более факторов риска ССЗ: в группе с изолированным АО – у каждого третьего пациента, в группе с АГ в сочетании с АО – у 2/3 пациентов. Сочетание АО и АГ с другими факторами риска развития ССЗ формирует кластер, который называется «метаболический синдром». В нашем исследовании МС диагностирован в 81,7% случаев у пациентов при наличии АГ в сочетании с АО. В то же время у лиц с АО без АГ данный синдром определялся только у 42,1% пациентов.
Проведенные экспериментальные и клинические исследования показали роль компонентов жировой ткани в реализации метаболических нарушений в организме. Механизмом повышения АД на фоне АО является инсулин-опосредованная стимуляция симпатической нервной системы. Гиперинсулинемия ассоциируется также с нарушением сосудодвигательной функции, в том числе за счет β-адренергической стимуляции и вазоконстрикции с последующим снижением кровотока. В нашем исследовании наиболее высокие значения ИРИ и индекса HOMA-IR выявлены именно в группе сочетания АГ с АО.
Гиперлептинемия является другим потенциально возможным механизмом развития АГ при АО, в том числе за счет стимуляции симпатической нервной системы. В нашем исследовании концентрация лептина была максимально высокой у пациентов с АО, особенно в сочетании с АГ. В то же время среди пациентов с АГ без АО уровень лептина не отличался от такового в контрольной группе.
В возникновении сердечно-сосудистых (инсульты, инфаркты) и венозных тромбоэмболических осложнений при МС особое значение придают изменениям в системе гемостаза. Считается, что протромботическое состояние гемостаза может быть патогенетически связано с провоспалительными изменениями. В нашем исследовании одновременно с признаками активации внутрисосудистого свертывания (повышение D-димера) обнаруживалось повышение концентрации TFPI и PAI-1, особенно среди пациентов с АГ в сочетании с АО. Повышение концентрации TFPI нами отмечено также среди пациентов с АГ с наличием и отсутствием АО, что, возможно, свидетельствует о компенсаторной активации эндотелия в условиях активации коагуляции.
Важно отметить, что экспрессия гена ангиотензиногена в абдоминальном жире выше, чем в висцеральном и нежировой ткани. Высокие уровни ангиотензина II (АТ II) и рецептора 1 типа АТ II могут способствовать развитию АГ у больных с резистентностью к инсулину. В нашем исследовании среди пациентов с АГ в сочетании с АО или при его отсутствии чаще выявлялось носительство генетических полиморфизмов РАС. Так, при наличии «мутантного» С-аллеля полиморфного маркера A1166С гена рецептора 1-го типа ангиотензина II шанс иметь АГ увеличивался в 11 раз. Наличие «мутантного» Т-аллеля полиморфного маркера M235T гена ангиотензиногена или «мутантного» M-аллеля полиморфного маркера T174M гена ангиотензиногена в 4,6 и 3,1 раз соответственно увеличивало шанс иметь АГ в сочетании с АО.
Признаки поражения органов-мишеней отмечаются у пациентов с ожирением с раннего возраста. Эндотелиальная дисфункция, повышенная артериальная жесткость и увеличение толщины комплекса интима-медиа при АГ было изучено в ряде исследований во взаимосвязи с гиперинсулинемией, гипергликемией, гиперлептинемией, гипоадипонектинемией и активацией ренин-ангиотензиновой системой. В нашем исследовании II стадия АГ диагностирована у 17,1% пациентов с АГ и у 20% с АГ в сочетании с АО.
Таким образом, нарушения липидного и углеводного обмена, наряду с дисбалансом адипокинов и отдельных компонентов ренин-ангиотензиновой системы, могут служить патофизиологической основой для ремоделирования сердца и сосудов с последующей активацией металлопротеиназ.
Нами была разработана регрессионная модель, которая позволяет оценить независимую ассоциацию изучаемых клинико-лабораторных и генетических факторов с величиной индекса массы миокарда левого желудочка. Такими факторами оказались величина систолического АД, окружность талии и концентрация ингибитора активатора плазминогена 1 типа.
Заключение
Таким образом, выявленные особенности распределения факторов риска сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, инсулинорезистентность и лептинорезистентность в сочетании с протромботическим состоянием гемостаза и большей частотой носительства определенных генотипов полиморфизмов T174M и M235T гена ангиотензиногена и полиморфизма A1166C гена рецептора 1-го типа ангиотензина II у пациентов с АГ с наличием/отсутствием АО позволяет расширить представления о патогенетических механизмах развития МС в молодом возрасте. Полученные данные, в свою очередь, могут являться основой для разработки оптимальных патогенетических подходов к лечению больных АГ, связанной с ожирением, и оценки новых экспериментальных результатов.



